Abstract
The mechanism of 3-O-methyl-d-glucose transport through the plasmalemma has been investigated in protoplasts isolated from the mesophyll of Pisum sativum L. var. Dan.
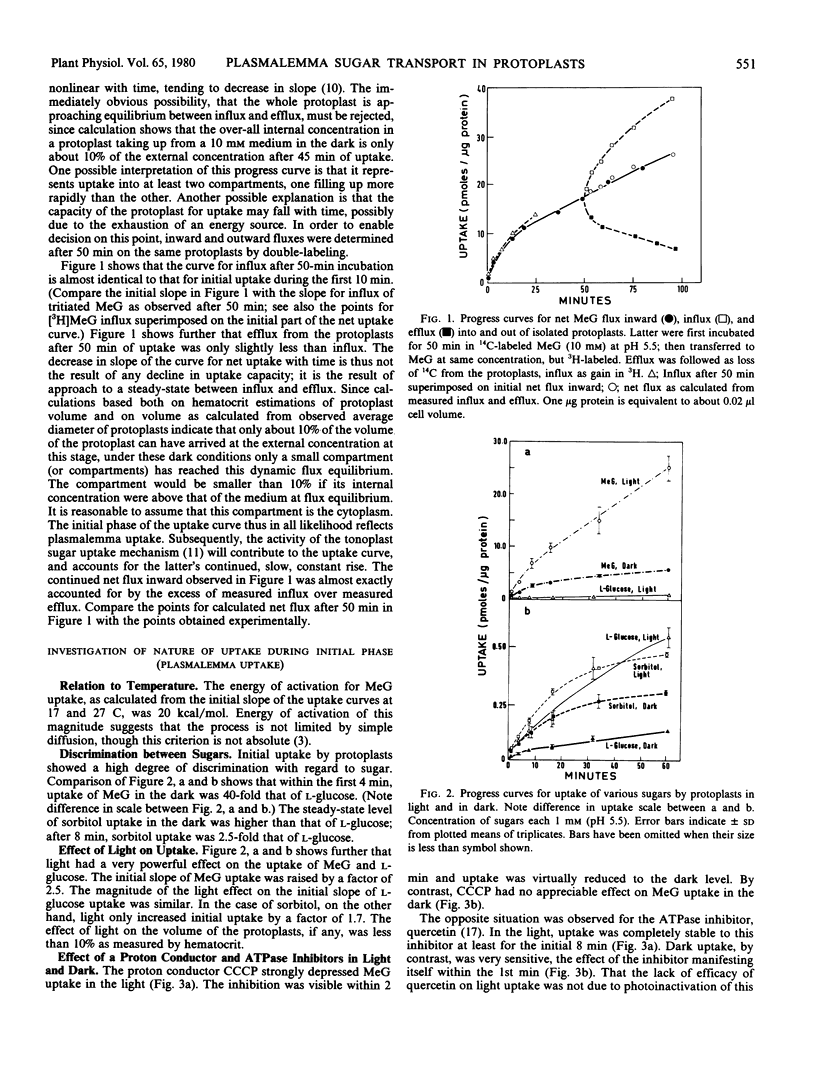
Analysis of the fluxes after 50 minutes of uptake showed that the gradual decrease in slope of the net uptake curve with time was not due to any decline in uptake capacity; it represented the approach to flux equilibrium of a small compartment of the protoplast, probably the cytoplasm.
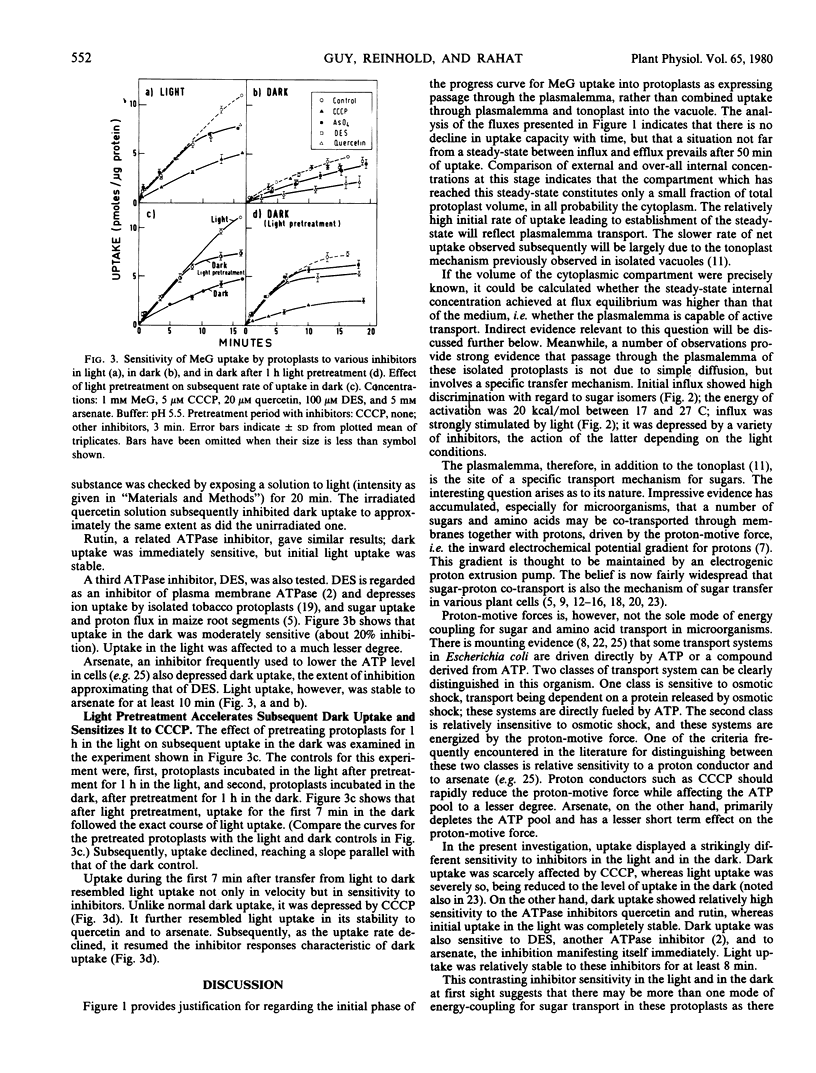
The energy of activation for initial flux into this compartment was 20 kilocalories per mole between 17 and 27 C. Very high discrimination was shown with regard to sugar isomers. Light strongly promoted flux (by a factor of 2.5 in the case of methyl glucose). Initial flux showed sharply contrasting inhibitor sensitivity in the light and the dark. Light uptake was sensitive to the proton conductor carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP), but stable for at least the first 10 minutes to the ATPase inhibitors quercetin, rutin, and diethylstilbestrol, as well as to arsenate. Dark uptake, on the other hand, was stable to CCCP but was immediately depressed by quercetin, rutin, diethylstilbestrol, and arsenate.
Protoplasts which received a light pretreatment before incubation in the dark took up methyl glucose at the accelerated light rate for the first 7 minutes. Moreover, the light pretreatment sensitized subsequent initial dark uptake to CCCP, and conferred on it the stability to ATPase inhibitors and arsenate characteristic of light uptake. After about 7 minutes the characteristic inhibitor responses of dark uptake were resumed.
It is proposed that more than one mode of energy-coupling for sugar transport may operate in these protoplasts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L., Reinhold L. Loss of membrane transport ability in leaf cells and release of protein as a result of osmotic shock. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):620–625. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini G., Koch A. L. Effect of uncouplers on "downhill" beta-galactoside transport in energy-depleted cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):187–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.187-195.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Boos W., Schwartz M., Szmelcman S. Energy-coupling of the transport system of Escherichia coli dependent on maltose-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):187–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaquinta R. Phloem Loading of Sucrose: pH Dependence and Selectivity. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):750–755. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy M., Reinhold L. Membrane transport of sugars and amino acids in isolated protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):593–596. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy M., Reinhold L., Michaeli D. Direct evidence for a sugar transport mechanism in isolated vacuoles. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jul;64(1):61–64. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komor E., Tanner W. The hexose-proton symport system of Chlorella vulgaris. Specificity, stoichiometry and energetics of sugar-induced proton uptake. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 2;44(1):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettler I. J., Leonard R. T. Ion transport in isolated protoplasts from tobacco suspension cells: I. General characteristics. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):183–190. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold L., Eshhar Z. Transport of 3-o-Methylglucose Into and Out of Storage Cells of Daucus carota. Plant Physiol. 1968 Jul;43(7):1023–1030. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.7.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


