Abstract
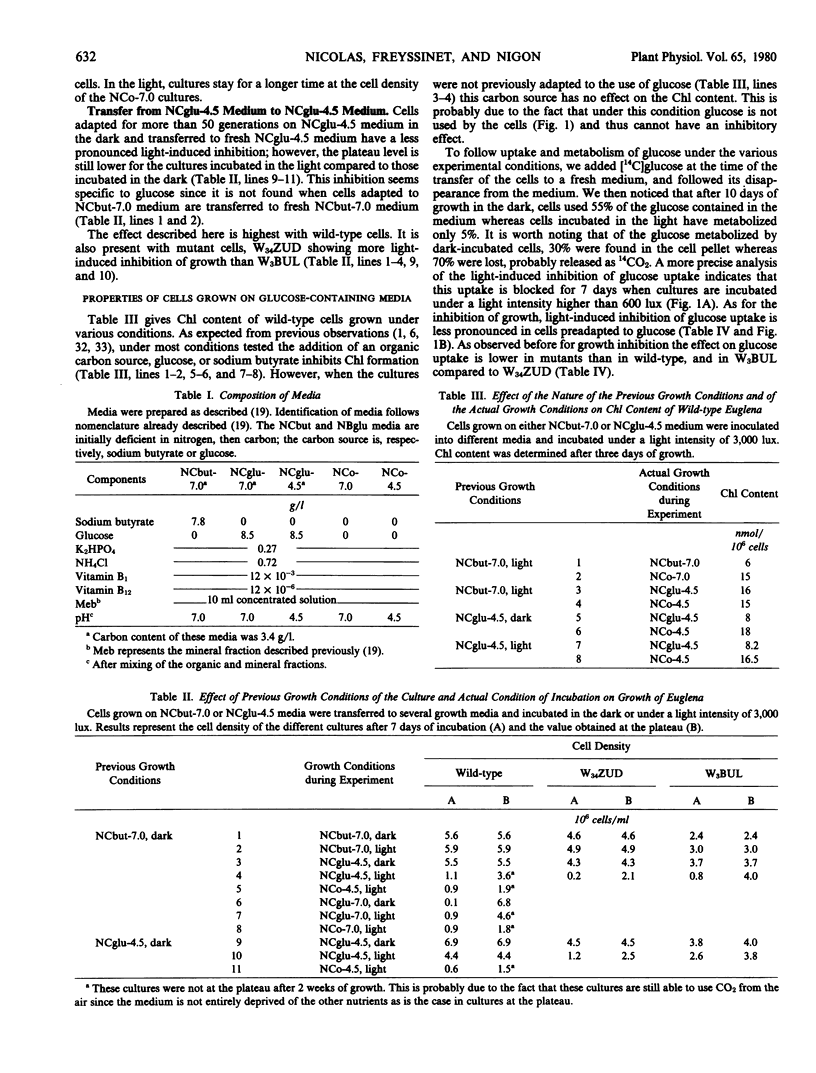
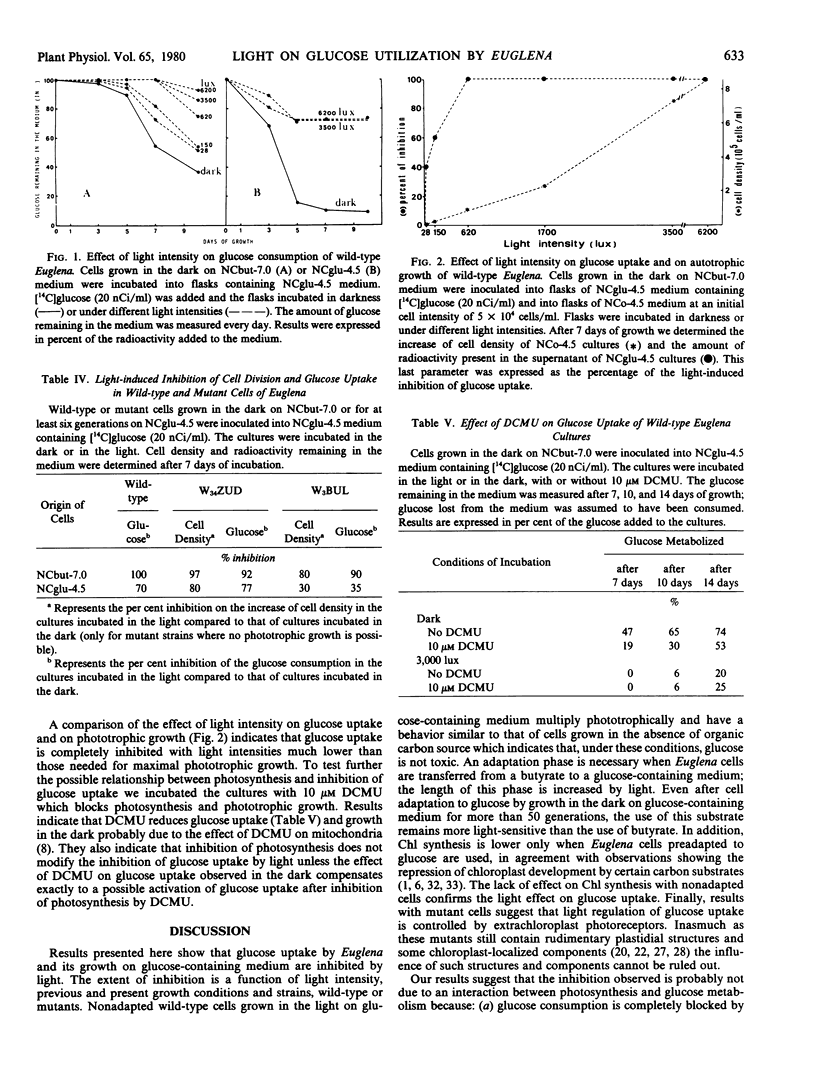
The effect of light on glucose consumption by wild-type Euglena gracilis Z. and mutant cells has been studied. When dark- or light-grown wild-type cells are transferred from a medium containing sodium butyrate as the only carbon source to a glucose-containing medium, glucose consumption is blocked for 6 to 7 days when cultures are incubated under a light intensity of at least 600 lux. During this time cells multiply at the same rate as controls kept on media devoid of any utilizable organic carbon source. This light-induced inhibition of glucose consumption and of growth on glucose-containing medium is not related to photosynthesis since: (a) glucose consumption is inhibited by light intensities much lower than those required for high phototrophic growth; (b) the inhibition of photosynthesis by 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1, 1-dimethylurea does not overcome the inhibition of glucose consumption; and (c) nonphototrophic-growing mutants also show light-induced inhibition of glucose consumption and of growth on glucose-containing medium. This inhibition of growth by light might be explained by modification in the permeability of the cellular membrane.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY S. N. Utilization of glucose by Astasia longa. J Protozool. 1962 Nov;9:395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehler R. A., Danforth W. F. Glucose utilization by Euglena gracilis var. bacillaris: short-term metabolic studies. J Protozool. 1968 Feb;15(1):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow D. E. Acetate repression of chlorophyll synthesis in Euglena gracilis. Nature. 1967 Mar 18;213(5081):1127–1128. doi: 10.1038/2131127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Schiff J. A. Events surrounding the early development of Euglena chloroplasts. Photoregulation of the transcription of chloroplastic and cytoplasmic ribosomal RNAs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colson A. M., The Van L., Convent B., Briquet M., Goffeau A. Mitochondrial heredity of resistance to 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea, an inhibitor of cytochrome b oxidation, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. R., Heinrich B. Glucose vs. acetate metabolism in Euglena. J Protozool. 1965 Nov;12(4):581–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1965.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. R., Kaiser H., Jr Factors affecting pH-dependent photo-inhibition of division in Euglena gracilis. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Dec;82(3):489–495. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Merrett M. J. The Effect of Light on the Synthesis of Mitochondrial Enzymes in Division-synchronized Euglena Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1974 Apr;53(4):575–580. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.4.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer M. R., Smillie R. M. A light-induced beta-1,3-glucan breakdown associated with the differentiation of chloroplasts in Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 1;216(2):392–401. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN M., SCHIFF J. A., EPSTEIN H. T. STUDIES OF CHLOROPLAST DEVELOPMENT IN EUGLENA. XII. TWO TYPES OF SATELLITE DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Apr;11:769–774. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. M., Dorsky D., Schiff J. A. Events Surrounding the Early Development of Euglena Chloroplasts: VI. Action Spectra for the Formation of Chlorophyll, Lag Elimination in Chlorophyll Synthesis, and Appearance of TPN-dependent Triose Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Alkaline DNase Activities. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):318–323. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. B., Jr Effects of different substrates on glucose uptake and hexokinase activity in Euglena gracilis. J Protozool. 1971 Aug;18(3):543–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann P. H., Salvador G. F., Nigon V. Occurrence of plastidial rRNAs and plastidial structures in bleached mutants of Euglena gracilis. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMILLIE R. M., EVANS W. R., LYMAN H. METABOLIC EVENTS DURING THE FORMATION OF A PHOTOSYNTHETIC FROM A NONPHOTOSYNTHETIC CELL. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1964 Mar;16:89–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzbach S. D., Schiff J. A., Goldstein N. H. Events surrounding the early development of euglena chloroplasts: v. Control of paramylum degradation. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):313–317. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwelitz F. D., Cisneros P. L., Jagielo J. A. The effect of glucose on the biochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of developing Euglena chloroplasts. J Protozool. 1978 Aug;25(3 Pt 2):398–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


