Abstract
Aims
To evaluate patterns of multiorgan dysfunction and neurologic outcome in children with respiratory and cardiac arrest after drowning.
Methods
Single center retrospective chart review of children aged 0 to 21 years admitted between January 2001 and January 2012 to the pediatric intensive care unit at Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh with a diagnosis of drowning/submersion/immersion. Organ dysfunction scores were calculated for first 24 hours of admission as defined by the Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction Score-1 (PELOD-1) and Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (P-MODS). Neurologic outcome at hospital discharge was assigned Pediatric Cerebral and Overall Performance Category Scale scores.
Results
We identified 60 cases of pediatric drowning in which 21 children experienced cardiorespiratory arrest (CA) and 39 had respiratory arrest (RA). All children with CA had multiorgan failure and 81% had a poor neurologic outcome at hospital discharge while 49% of children with RA had multiorgan failure and none had an unfavorable neurological outcome (p<0.001). The most common organ failures in both CA and RA groups within the first 24 hours of admission were respiratory, followed by neurologic, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hematological, and least commonly, renal.
Conclusion
Patterns of organ failure differ in children with CA and RA due to drowning. The contribution of multiorgan failure to poor outcome and evaluation of the impact of augmenting cerebral resuscitation with MOF-targeting therapies after drowning deserves to be explored.
Keywords: drowning, children, multiorgan failure, organ dysfunction, arrest, neurologic outcome
INTRODUCTION
Drowning is the leading cause of unintentional injury-related death and disability worldwide between the ages of 1 and 4 years and the third leading cause in the United States between the ages of 1 and 21 years1. Drowning occurs from primary respiratory impairment due to submersion in a liquid medium2–4, and is followed by breath-holding and involuntary laryngospasm that leads to hypercapnia, hypoxemia, and if prolonged, respiratory (RA) and or cardiorespiratory arrest (CA)2,5,6. Systemic hypoxemia and/or ischemia during RA or CA, respectively, increase the risk of hepatic, renal, and neurologic organ injury and reversible or irreversible impairment of function2,5,7.
Duration of submersion under water and need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) after extraction are associated with outcome in pediatric drowning. Children who progress to CA and have generalized edema present on early brain computed tomography uniformly have poor outcomes8. Children with RA are still at increased risk of disability and death9. Reports on neurologic outcome and mortality after drowning-related RA are lacking but mortality in all-cause acute respiratory failure is 22 – 40% in children10,11.
Typpo and colleagues have reported on multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) on Day 1 of pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) admission and found an incidence of 18%, with 30 – 35% of those having an unfavorable neurologic outcome12. Post-resuscitation MODS is not well described after pediatric drowning specifically. Our primary objective was to explore the severity and patterns of MODS in the first 24 hours in children with CA and RA after drowning.
METHODS
This is a single center retrospective chart review of children aged 0 to 21 years admitted between January 2001 and January 2012 to the PICU at Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh with a diagnosis of drowning, submersion, or immersion per International Classification of Diseases, volume 9 (ICD-9) codes (994.1, E830, E830.1 – 830.9, E832, E910, E910.1 – 910.4, E910.8, E910.9, E954, E965, E984, E979.8). The Institutional Review Board of University of Pittsburgh approved the study and informed consent was waived.
Data collected included patient and incident characteristics and resuscitation, post-resuscitation details during the Emergency Medical Services, Emergency Department, and PICU care periods for the first 24 hours after admission. Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction Score-1 (PELOD-1) and Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (P-MODS) were calculated for the first 24 hours of hospitalization13,14. In addition, we used the first 24-hour scores since the largest data set reporting on organ dysfunction in PICU patients by Typpo and colleagues12 utilized scores on day 1. Both scoring systems assign a score based on the severity of organ dysfunction. Normal function for each organ system as defined by the PELOD-1 score is as follows: Neurologic system - Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 12 – 15 and reactive pupils; Cardiovascular system - age-dependent values for heart rate and systolic blood pressure; Renal system - age appropriate creatinine values; Respiratory system -PaO2/FiO2 > 69.8 mmHg and PaCO2 ≤ 87.8 mmHg and no need for mechanical ventilation; Haematological system - white blood cell (WBC) count ≥ 4.5 * 109/L and a platelet (PLT) count ≥ 35 * 109/L; and Hepatic system - aspartate transaminase (AST) < 950 iU/L and an international randomized ration (INR) < 1.4. In the event of missing data, normal function was assumed as described by Graciano and colleagues13. Normal function for each organ system as defined by the P-MODS system is as follows: Cardiovascular system- Lactic acid < 1 mmol/L; Respiratory system- PaO2/FiO2 > 150 mmHg; Hepatic system- Bilirubin < 0.5 mg/dL; Hematological system- Fibrinogen > 150 mg/dL; and Renal system- Blood Urea Nitrogen < 20 mg/dL. MODS was defined as two or more organ dysfunctions15.
Neurologic outcome at hospital discharge was assigned Pediatric Cerebral and Overall Performance Category Scale scores (PCPC/POPC) using clinical notes. Favorable neurologic outcome was defined as a PCPC/POPC less than or equal to 3 or no change in the baseline score. Unfavorable neurologic outcome represented patients with severe neurologic impairment with PCPC/POPC > 3. To compare organ dysfunction in both neurologic outcome groups, we used P-MODS as the MODS score since it lacks a neurologic component.
Drowning victims were categorized into two groups: CA and RA. CA was defined as need for CPR by healthcare personnel (Emergency Medical Services or Emergency Department) whereas RA was defined as apnea or cyanosis with palpable pulse and therefore lack of need for CPR.
Non-parametric numeric data are presented as median [interquartile range] or total number of patients (percentages), while parametric data are presented as mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM). Fisher exact tests for categorical variables were performed for outcome groups. The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare organ dysfunction scores and neurologic outcome. Spearman’s rank correlation was used to test the relationship between duration of CPR and organ dysfunction in children with CA after drowning. All p- values were two-tailed and values less than 0.05 were considered significant. Data analysis was performed using SigmaStat 3.5 (Systat Software, Inc.).
RESULTS
Patients and Drowning Characteristics
We identified 60 children who met study criteria over the study period with a median age of 2.4 years and 60% were males (Table 1). Fifty-seven events occurred in the summer months (May – October). Forty-one (68%) of the events were unwitnessed and the median reported submersion time was 2 minutes (range of 0 to 30 minutes). Median CPR duration in children with CA was 2 minutes and ranged from 1 to 90 minutes. Thirty-nine (65%) children were in RA and 21 (35%) were in CA at the drowning location. Most 41 (68%) children were intubated and the initial recorded temperature on hospital arrival was 35.7 C [24 to 39.3 C]. All but 2 children were transferred by Emergency Medical Services to a referring hospital emergency department; the remaining 2 children presented to a referring hospital with family members. Children were subsequently transferred to Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh emergency department prior to PICU admission or were directly admitted to the PICU where 15/21 of children in CA group remained pulseless. Six of those 15 pulseless children died, 7 were discharged to a rehabilitation facility and 2 discharged home. Overall, 17/60 patients had severe neurological impairment and 8/60 children died. All of the children who had severe neurological impairment and those who died had suffered a CA (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient, Drowning, and Outcome Characteristics
| Overall | RA (n= 39) | CA (n= 21) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 2.4 (0.1–16.6) | 2.9 (0.4–16.6) | 1.9 (0.1–15.1) |
|
| |||
| Gender, male | 36 (60) | 23 (59) | 13 (62) |
|
| |||
| Ethnicity | |||
| Caucasian | 50 (85) | 33 (85) | 17 (81) |
| Black | 8 (14) | 4 (10) | 4(19) |
| Other/Missing | 2 (1) | 2 (5) | 0 (0) |
|
| |||
| Location | |||
| Home swimming pool | 30 (50) | 21 (54) | 9 (43) |
| Bathtub | 12 (20) | 6 (15) | 6 (28) |
| Public pool | 9 (15) | 7 (18) | 2 (10) |
| Other | 9 (15) | 5 (13) | 4 (19) |
|
| |||
| PICU LOS, days | 4 (1 – 60) | 2 (1 – 11) | 12 (1 – 60) |
|
| |||
| Hospital LOS, days | 5 (1 – 103) | 3 (1 – 15) | 21 (1 – 103) |
|
| |||
| Duration of Resuscitation, min | N/A | N/A | 30 (2 – 90) |
|
| |||
| Disposition of survivors | |||
| Home | 41 (68) | 39 (100) | 2 (10) |
| Rehabilitation facility | 11 (18) | 0 (0) | 11 (52) |
|
| |||
| Unfavorable Neurologic Outcome | 17 (28) | 0 (0) | 17 (81) |
|
| |||
| Mortality at Hospital Discharge | 8 (14) | 0 (0) | 8 (38) |
Data is expressed in median (range) or n (%)). RA: Respiratory arrest, CA: Cardiac arrest, PICU: Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, LOS: Length of Stay, min: minutes.
Frequency, Patterns, and Clinical Impact of Organ Failure
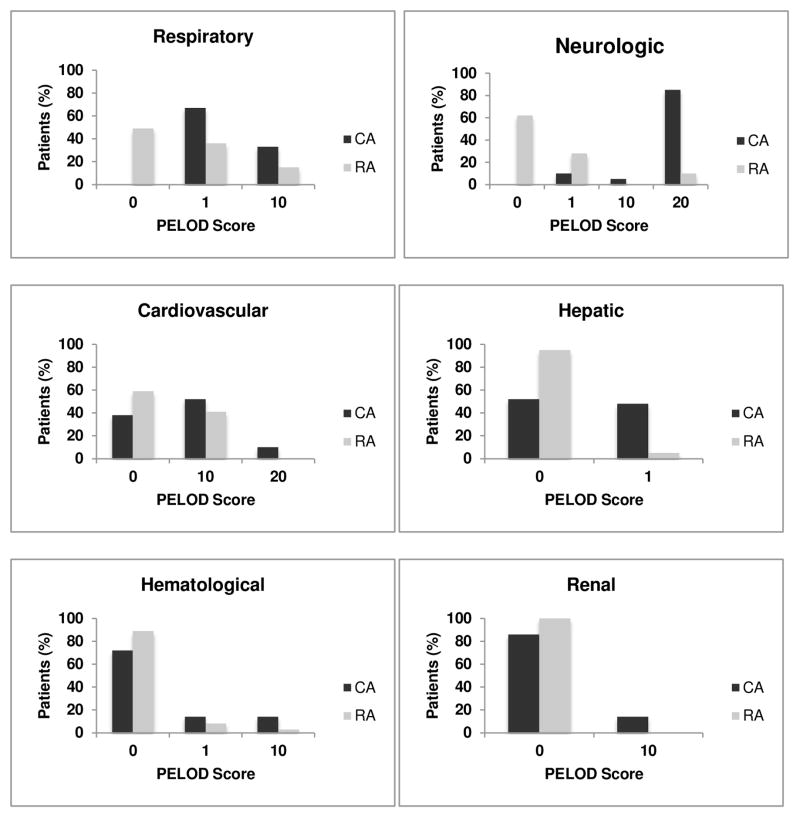
Forty (66%) children had MODS, 7 (12%) had a single organ dysfunction, and 13 (22%) had no organ failure. Of the children with MODS, 21/40 (52%) had CA and 19/40 (48%) had RA. 100% of children in CA group vs. 49% of children in RA group had MODS. Children with CA had higher PELOD-1 and P-MODS scores than children with RA (CA vs. RA; PELOD-1: 32 ± 3.2 vs. 9 ± 1.5; P-MODS: 6 ± 3 vs. 1 ± 2. p < 0.01) (Table 2). In addition, children with CA had more severe organ dysfunction in each organ system affected (Figure 1).
Table 2. Organ dysfunction scores by arrest type.
Patients who suffered a cardiorespiratory arrest had more organ dysfunction and more severe multiorgan failure in the first 24 hrs after admission.
| CA N= 21 |
RA N= 39 |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of organ dysfunctions | 3.5 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | < 0.001 |
| PELOD | 32 ± 3 | 9 ± 1.5 | < 0.001 |
| P-MODS | 6 ± 3 | 1 ± 2 | < 0.01 |
Data expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. CA= cardiorespiratory arrest, RA= respiratory arrest.
Figure 1. Organ dysfunction by arrest group.
Overall, most common organ failure within first 24 hours of PICU admission was respiratory, followed by neurologic, cardiovascular, hepatic and renal systems in both the CA and RA groups.
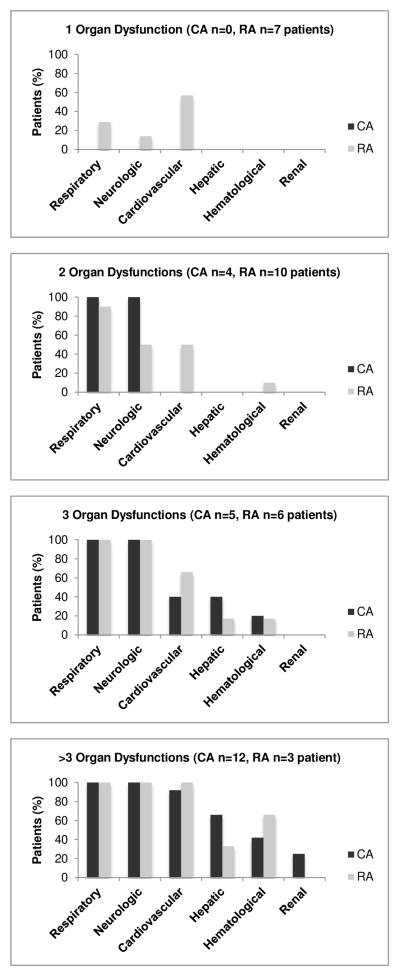
In both CA and RA patients, the respiratory system was most frequently affected, followed by neurologic, cardiovascular, hepatic, hematologic, and lastly the renal system. The only exception to this pattern was noted in patients with RA and single organ dysfunction, where the most commonly affected system was cardiovascular followed by respiratory then neurologic. More children with CA had neurologic, respiratory, hepatic, and renal system dysfunction (all p<0.05); whereas there were no differences between groups in occurrence of cardiovascular and hematologic system dysfunction (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Patterns of organ dysfunction.
Figures below show patterns of organ dysfunction in patients with 1, 2, 3 and > 3 organ failures as defined by PELOD-1 score > 0 for each organ. No CA patient had less than 2 organ dysfunctions and the cardiovascular system was the most common organ failure in patients with RA. CA: Cardiac arrest, RA: Respiratory arrest, PELOD: Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction Score
The duration of mechanical ventilation was longer in the CA vs. RA group (21.4 ± 5.3 days vs. 3.8 ± 0.6 days, p < 0.05). Nineteen of the 39 RA patients had an arterial blood gas performed in the first 24 hours of ICU admission while all of the CA children had an arterial blood gas done. Of the children with an arterial blood gas, the worst PaO2/FiO2 was not different by group (151 ± 69 vs. 179 ± 58, CA vs. RA group respectively, p = 0.35). Three children received inhaled nitric oxide for poor oxygenation, all in the CA group. Initial non-sedated GCS score was lower in the CA vs. RA group (4 ± 1 vs. 12 ± 1, p < 0.001). Nearly all (35/40) children with MODS had neurologic failure (non-sedated GCS <12) compared to 2/20 in the non-MODS group (p < 0.01). Eighteen of 21 children in the CA vs. 7/39 in the RA group required inotropic or vasopressor support. One child required veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the CA group. In children with CA, longer CPR durations showed a trend for increased number of organ dysfunction (p=0.09) (Table 3). Highest blood AST levels in the first 24 hrs of admission for the CA group averaged 456 ± 210 iU/L vs. 83 ± 22 iU/L for the RA group (p < 0.001); whereas INR for the CA group was 1.4 ± 0.2 vs. 1.1 ± 0.05 for the RA group (p < 0.001). There were no differences in lowest white blood cell or platelet counts or creatinine values between CA or RA groups. Lastly, one child in the CA group required continuous renal replacement therapy and subsequently intermittent hemodialysis.
Table 3. CPR duration and number of organ dysfunctions.
This table depicts the percentage of patients with a certain number of organ dysfunctions according to CPR duration. Total number of patients = 21
| Number of Organ Dysfunctions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| CPR Duration | ≤ 10 min | 1 (16.7) | 3 (50) | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0) |
| 11 – 30 min | 3 (37.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (37.5) | 2 (25) | |
| > 30 min | 0 (0) | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | 0 (0) | |
N (%). p = 0.093. CPR: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Neurologic outcome
Twenty-eight percent of all children had an unfavorable neurologic outcome or severe neurologic impairment. Eighty percent of children with CA had an unfavorable neurologic outcome in comparison to none of the RA children. CPR duration for CA children with unfavorable neurologic outcome was 37.9 ± 6.3 minutes vs. 6 ± 2 minutes in the favorable outcome group (p < 0.01). In addition, children with unfavorable neurologic outcome had a higher number of organ failures than the favorable outcome group (3.6 ± 0.2 vs. 1.6 ± 0.2, p < 0.001), the latter was also reflected in the P-MODS scores where the unfavorable outcome group P-MODS score was 6 ± 0.8 vs. 2 ±0.3 for the favorable outcome group.
DISCUSSION
To our knowledge, this is the first study to describe and compare early (first 24 hours of PICU admission) patterns of organ dysfunction in children with CA or RA due to drowning. Multiorgan dysfunction and unfavorable neurologic outcome were more common and more severe after CA in comparison to children with RA. The most common organ system failures in both groups were the respiratory, neurologic and cardiovascular systems. Although having RA did not preclude development of early MODS, favorable neurologic outcomes were frequently attained.
The hallmark of MODS is the development of progressive physiologic dysfunction in 2 or more organ systems after alterations in systemic homeostasis16,17. Risk factors are diverse and include infection, non-infectious inflammatory conditions, traumatic or burn injury, ischemia, toxin exposure, and immune system activation17. Whether these divergent stimuli produce phenotypic organ injury by a single common pathway is unknown. In the pediatric literature, MODS is reported to occur in approximately 10 –56% of all PICU admissions and has an associated mortality of 10 – 54%15,18–23. Typpo and colleagues explored MODS incidence in a general pediatric population that included children with traumatic and non-traumatic diagnoses using the International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria on day 1 of PICU admission. They reported an 18% rate of MODS with a corresponding mortality rate of 10%. The incidence of MODS in our study was significantly higher at 56%, with a similar mortality rate of 14% and all patients who died had at least 3 organ failures. Similar to our findings in pediatric drowning, respiratory dysfunction was the most frequently reported organ dysfunction. Different from our findings, cardiovascular dysfunction was the next most common organ dysfunction followed by neurologic dysfunction12. Interestingly, 30 – 35% of the patients in the Typpo study with MODS had an unfavorable neurologic outcome in contrast to our specific drowning population in which 50% of children with MODS had unfavorable neurologic outcome12. This difference may be partly attributable to differences in pathophysiology that lead to organ dysfunction unique to drowning vs. MODS of all causes including the large number of children suffering asphyxial CA in our study. Thus drowning represents a unique physiological phenotype in contrast to other causes of MODS, suggesting that resuscitation and post-resuscitation therapeutic strategies should be targeted to phenotype24,25.
As stated previously, pediatric drowning literature has focused on individual organ dysfunctions3,7,24,26,27. Lung injury, frequently reported in the drowning literature, is characterized by abnormal surfactant function and increased capillary endothelial permeability7. This injury leads to increased intrapulmonary shunting, ventilation/perfusion mismatch, atelectasis, and poor lung compliance, which cause further hypoxemia and hypercarbia. When severe enough, this process may lead to ARDS. Next, the most significant consequence of drowning and the most frequent cause of death is hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. The degree of neurologic injury is related to the duration of cardiac arrest and CPR, the effectiveness of initial CPR, and secondary cerebral injuries after resuscitation7,28,29. Drowning patients frequently have ventilation and oxygenation derangements for hours to days post-resuscitation. Recent studies that may impact treatment for some drowning patients have shown that hyperoxia and hypoxia are associated with increased mortality in CA patients29, and hypocapnia and hypercapnia post-CA are independently associated with poor neurologic outcome30. In addition, arterial hypotension, seen in up to 40% of patients in this study, after return of spontaneous circulation is also a predictor of in-hospital death and poor outcome after CA31. These studies suggest that treating and preventing secondary organ insults in the post-resuscitation period may affect neurological outcome. Problematically, there are no prospective studies demonstrating the best physiologic targets and management approach for oxygenation, ventilation, and blood pressure in pediatric patients who drown with or without CA, but an approach similar to post-CA resuscitation should be considered until more data are available32.
Lastly, in our patient population, renal dysfunction occurred in only 3/60 (5%) children, all with CA. Renal dysfunction incidence has been reported to be between 2 –40% in the pediatric population including those without MODS. There are differences in the frequency of kidney dysfunction by disease presentation. A study by Ackan-Arikan and colleagues found that the frequency of acute kidney injury was lower in children with CA (66%) than in children with sepsis or septic shock (87%); the frequency of other organ dysfunctions was not reported 12,33. This difference may be related to inherent differences in vulnerability of the kidney to hypoxia/ischemia in CA vs. inflammation and coagulation dysregulation with or without hypoxia/ischemia in sepsis and septic shock34.
Our data show that despite the occurrence of MODS after RA, children with drowning often have favorable outcomes with supportive ICU care. Research on the outcomes of RA is scarce, but Schindler and colleagues compared outcomes after all-cause out-of-hospital pediatric RA and CA9. Forty-three percent (9/21) of RA patients survived to discharge and while a considerable 30% (3/9) of survivors had an unfavorable neurologic outcome. None of the 8% (6/80) of CA survivors in their series had a favorable outcome and only 9/80 children in the CA group had drowned, and none survived9. However, the majority of RA patients in the Schindler study had a traumatic etiology, making our results less comparable as children with traumatic CA generally have poor outcomes35.
The limitations of our study include the retrospective nature of the review and collection of organ dysfunction data was limited to the first day after PICU admission. In addition, P-MODS and PELOD-1 scores were not reported as part of the patient’s chart and were calculated based on available laboratory data and health care professional notes. Pre-drowning and hospital discharge PCPC and POPC scores were assigned retrospectively after review of medical records. Assessment of outcomes was limited to hospital discharge although full recovery and rehabilitation after drowning may take years. Detailed neuropsychological outcome testing was not performed which would be particularly important to assess in the RA patients where favorable outcome was achieved. Recent literature by Suominen and colleagues36 suggests that discharge examination is not a reliable indicator of the pediatric drowning victim neurologic outcome and there is a need for proper neurological and neurophysiological assessments to determine the severity of the neurologic insult. In addition, the study of MODS in the pediatric population is the lack of use of a uniform scoring system in all published studies, thus making data interpretation and comparisons challenging. Finally, our study did not investigate the effects of different therapeutic approaches on outcomes in children with MODS after pediatric drowning.
CONCLUSIONS
Drowning with CA conferred the greatest risk for early MODS and resulted in a worse neurologic outcome than children with RA, but MODS in children with RA did not result in unfavorable outcome. Prospective research is needed to discern whether or not specific therapies targeting extra-cerebral facets of MODS, particularly, respiratory, and cardiovascular targets in the resuscitation and post-resuscitation periods may confer added benefit to current brain-oriented therapy to improve outcomes after pediatric drowning, especially in the setting of CA.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors are supported by a variety of federal grants (PMK: NS070003; JAC: GM108618; MJB: NS081041; ELF: K23NS065132).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST STATEMENT:
HM: Nothing to disclose
PMK: NS070003
JAC: GM108618
MJB: NS081041
ELF: K23NS065132
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.CDC. Drowning 2005–2009. MMWR. 2012;61:344–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Layon AJ, Modell JH. Drowning: Update 2009. Anesthesiology. 2009;110:1390–401. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181a4c3b8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Szpilman D, Bierens JJ, Handley AJ, Orlowski JP. Drowning. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;366:2102–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1013317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Beeck EF, Branche CM, Szpilman D, Modell JH, Bierens JJ. A new definition of drowning: towards documentation and prevention of a global public health problem. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2005;83:853–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hasibeder WR. Drowning. Current opinion in anaesthesiology. 2003;16:139–45. doi: 10.1097/00001503-200304000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Miller R. Anesthesia. 5. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Meyer RJ, Theodorou AA, Berg RA. Childhood drowning. Pediatrics in review / American Academy of Pediatrics. 2006;27:163–8. doi: 10.1542/pir.27-5-163. quiz 9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Quan L, Wentz KR, Gore EJ, Copass MK. Outcome and predictors of outcome in pediatric submersion victims receiving prehospital care in King County, Washington. Pediatrics. 1990;86:586–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schindler MB, Bohn D, Cox PN, et al. Outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac or respiratory arrest in children. The New England journal of medicine. 1996;335:1473–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199611143352001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Timmons OD, Havens PL, Fackler JC. Predicting death in pediatric patients with acute respiratory failure. Pediatric Critical Care Study Group. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. Chest. 1995;108:789–97. doi: 10.1378/chest.108.3.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Flori HR, Glidden DV, Rutherford GW, Matthay MA. Pediatric acute lung injury: prospective evaluation of risk factors associated with mortality. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2005;171:995–1001. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200404-544OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Typpo KV, Petersen NJ, Hallman DM, Markovitz BP, Mariscalco MM. Day 1 multiple organ dysfunction syndrome is associated with poor functional outcome and mortality in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatric critical care medicine : a journal of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the World Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care Societies. 2009;10:562–70. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181a64be1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Graciano AL, Balko JA, Rahn DS, Ahmad N, Giroir BP. The Pediatric Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (P-MODS): development and validation of an objective scale to measure the severity of multiple organ dysfunction in critically ill children. Critical care medicine. 2005;33:1484–91. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000170943.23633.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Leteurtre S, Martinot A, Duhamel A, et al. Validation of the paediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD) score: prospective, observational, multicentre study. Lancet. 2003;362:192–7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13908-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tantalean JA, Leon RJ, Santos AA, Sanchez E. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in children. Pediatric critical care medicine : a journal of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the World Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care Societies. 2003;4:181–5. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000059421.13161.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Critical care medicine. 1992;20:864–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Marshall JC, Cook DJ, Christou NV, Bernard GR, Sprung CL, Sibbald WJ. Multiple organ dysfunction score: a reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Critical care medicine. 1995;23:1638–52. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199510000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wilkinson JD, Pollack MM, Ruttimann UE, Glass NL, Yeh TS. Outcome of pediatric patients with multiple organ system failure. Critical care medicine. 1986;14:271–4. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198604000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Despond O, Proulx F, Carcillo JA, Lacroix J. Pediatric sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Current opinion in pediatrics. 2001;13:247–53. doi: 10.1097/00008480-200106000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Proulx F, Fayon M, Farrell CA, Lacroix J, Gauthier M. Epidemiology of sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in children. Chest. 1996;109:1033–7. doi: 10.1378/chest.109.4.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Proulx F, Gauthier M, Nadeau D, Lacroix J, Farrell CA. Timing and predictors of death in pediatric patients with multiple organ system failure. Critical care medicine. 1994;22:1025–31. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199406000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leclerc F, Leteurtre S, Duhamel A, et al. Cumulative influence of organ dysfunctions and septic state on mortality of critically ill children. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2005;171:348–53. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200405-630OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Khilnani P, Sarma D, Zimmerman J. Epidemiology and peculiarities of pediatric multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in New Delhi, India. Intensive care medicine. 2006;32:1856–62. doi: 10.1007/s00134-006-0373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Topjian AA, Berg RA, Bierens JJ, et al. Brain resuscitation in the drowning victim. Neurocritical care. 2012;17:441–67. doi: 10.1007/s12028-012-9747-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kochanek PM, Callaway CW. Targeting therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal resuscitation and beyond: it is time to phenotype. Resuscitation. 2014;85:458–9. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Seong EY, Rhee H, Lee N, et al. A case of severe acute kidney injury by near-drowning. Journal of Korean medical science. 2012;27:218–20. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Modell JH, Davis JH. Electrolyte changes in human drowning victims. Anesthesiology. 1969;30:414–20. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196904000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ferguson LP, Durward A, Tibby SM. Relationship between arterial partial oxygen pressure after resuscitation from cardiac arrest and mortality in children. Circulation. 2012;126:335–42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.085100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kilgannon JH, Jones AE, Shapiro NI, et al. Association between arterial hyperoxia following resuscitation from cardiac arrest and in-hospital mortality. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 2010;303:2165–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Roberts BW, Kilgannon JH, Chansky ME, Mittal N, Wooden J, Trzeciak S. Association between postresuscitation partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide and neurological outcome in patients with post-cardiac arrest syndrome. Circulation. 2013;127:2107–13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trzeciak S, Jones AE, Kilgannon JH, et al. Significance of arterial hypotension after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Critical care medicine. 2009;37:2895–903. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0b013e3181b01d8c. quiz 904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nolan JP, Neumar RW, Adrie C, et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication: A scientific statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation; the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Stroke (Part 1) International emergency nursing. 2009;17:203–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2009.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL. Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney international. 2007;71:1028–35. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Safar P. Resuscitation in Hemorrhagic Shock, Coma, and Cardiac Arrest. In: Cowley RA, Trump BF, editors. Pathophysiology of Shock, Anoxia, and Ischemia. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1982. pp. 411–38. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Matos RI, Watson RS, Nadkarni VM, et al. Duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and illness category impact survival and neurologic outcomes for inhospital pediatric cardiac arrests. Circulation. 2013;127:442–51. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.125625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Suominen PK, Vahatalo R. Neurologic long term outcome after drowning in children. Scandinavian journal of trauma, resuscitation and emergency medicine. 2012;20:55. doi: 10.1186/1757-7241-20-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.