Abstract
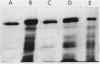
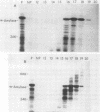
The poly(A)-containing mRNA from barley aleurone layers pretreated with gibberellic acid has been purified by phenol-chloroform extraction and repeated oligo[d(pT)]-cellulose chromatography. This RNA has been translated in both the wheat germ and reticulocyte lysate in vitro translation systems with greater than 50% of the synthesized protein being α-amylase. The mRNA for α-amylase has been further purified by dimethylsulfoxide-formamide-sucrose density gradient centrifugation and by gel electrophoresis. By these methods, its molecular weight has been determined to be 580,000.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruening G., Beachy R. N., Scalla R., Zaitlin M. In vitro and in vivo translation of the ribonucleic acids of a cowpea strain of tobacco mosaic virus. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrispeels M. J., Varner J. E. Gibberellic Acid-enhanced synthesis and release of alpha-amylase and ribonuclease by isolated barley and aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):398–406. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. T. Response of barley aleurone layers to abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):175–178. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. T., Varner J. E. Hormonal control of messenger ribonucleic acid metabolism in barley aleurone layers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4783–4786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V. Interactions between Gibberellic Acid, Ethylene, and Abscisic Acid in Control of Amylase Synthesis in Barley Aleurone Layers. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):198–202. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Zwar J. A. Gibberellic acid causes increased synthesis of RNA which contains poly(A) in barley aleurone tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3290–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Decaleya R., Rappaport L. Synthesis of a possible precursor of alpha-amylase in wheat aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):195–200. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taiz L., Honigman W. A. Production of cell wall hydrolyzing enzymes by barley aleurone layers in response to gibberellic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):380–386. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]