Abstract
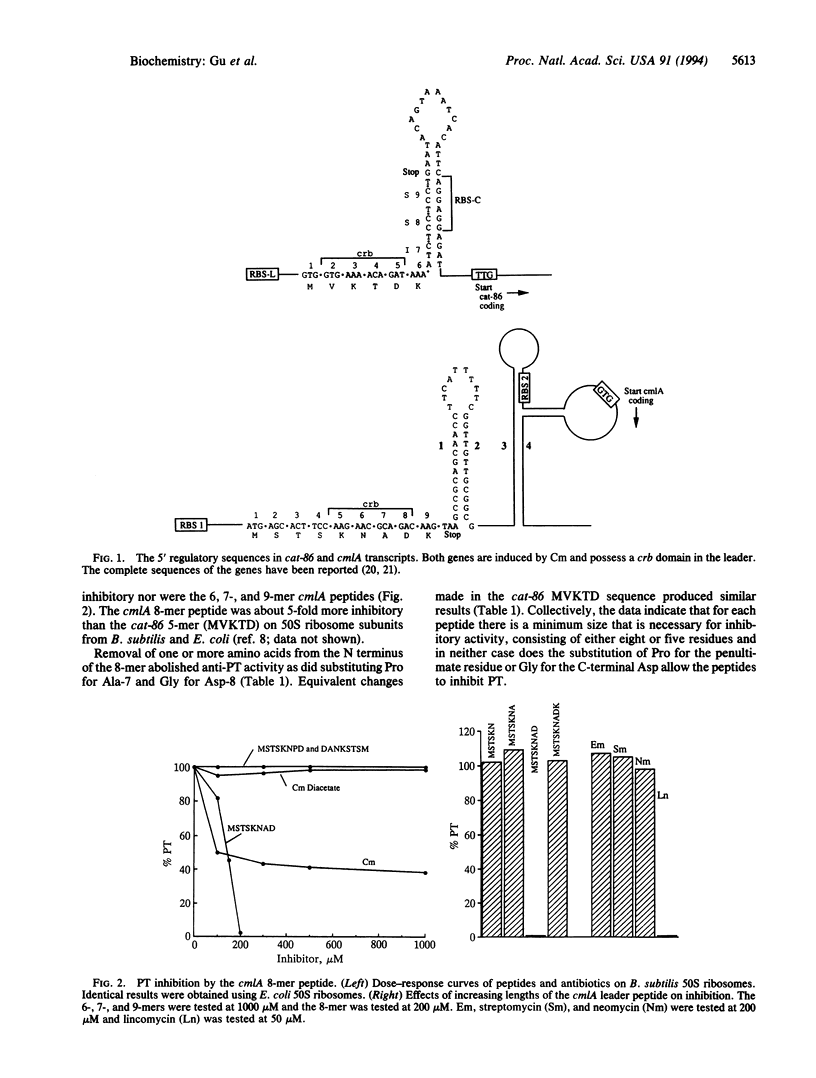
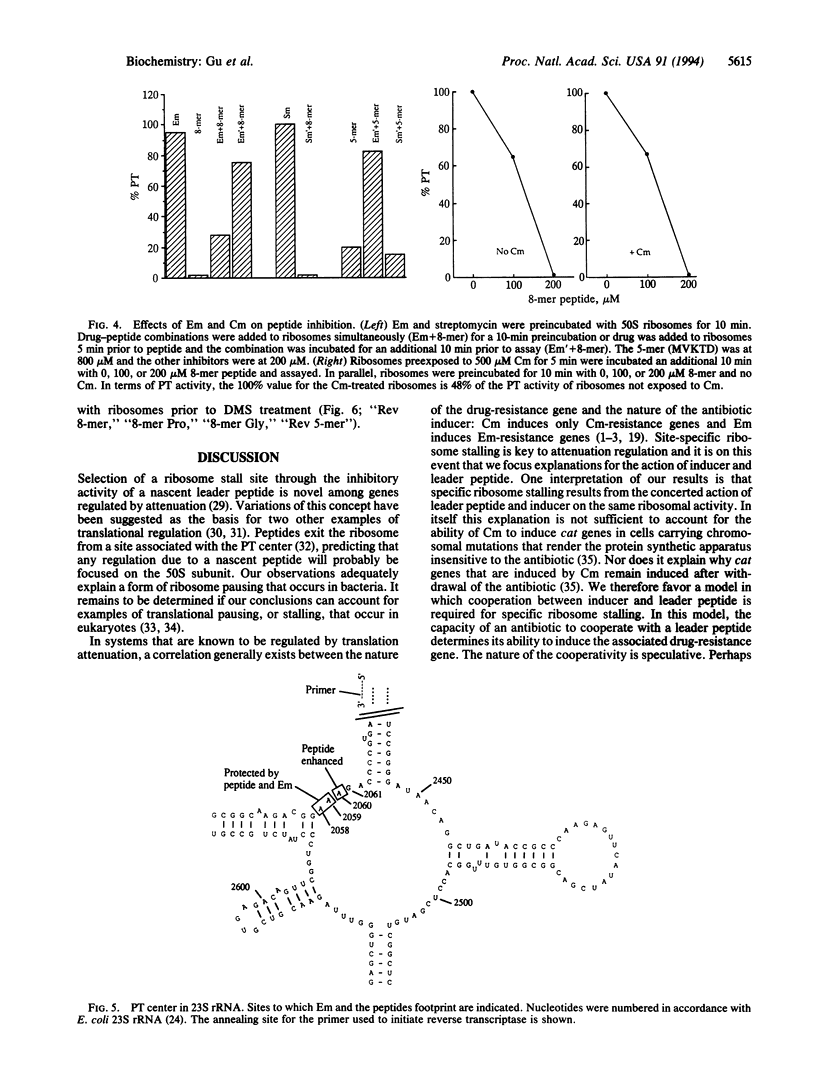
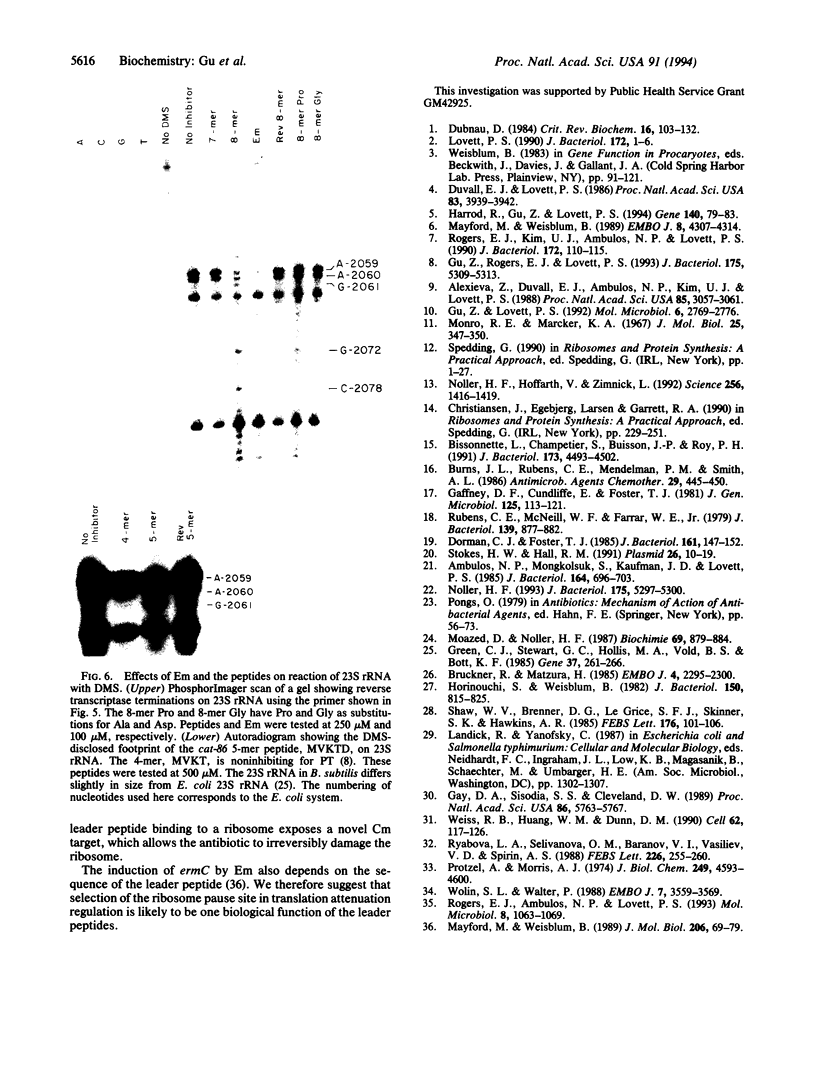
The chloramphenicol (Cm)-inducible cmlA gene of Tn1696 specifies nonenzymatic resistance to Cm and is regulated by attenuation. The first eight codons of the leader specify a peptide that inhibits peptidyl transferase in vitro. Functionally similar, but less inhibitory, peptides are encoded by the leaders of Cm-inducible cat genes. However, the cat and cmlA coding sequences are unrelated and specify proteins of unrelated function. The inhibition of peptidyl transferase by the leader peptides is additive with that of Cm. Erythromycin competes with the inhibitory action of the peptides, and erythromycin and the peptides footprint to overlapping sites at the peptidyl transferase center of 23S rRNA. It is proposed that translation of the cmlA and cat leaders transiently pauses upon synthesis of the inhibitor peptides. The predicted site of pausing is identical to the leader site where long-term occupancy by a ribosome (ribosome stalling) will activate downstream gene expression. We therefore propose the inducer, Cm, converts a peptide-paused ribosome to the stalled state. We discuss the idea that cooperativity between leader peptide and inducer is necessary for ribosome stalling and may link the activation of a specific drug-resistance gene with a particular antibiotic.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexieva Z., Duvall E. J., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Kim U. J., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol induction of cat-86 requires ribosome stalling at a specific site in the leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3057–3061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambulos N. P., Jr, Mongkolsuk S., Kaufman J. D., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol-induced translation of cat-86 mRNA requires two cis-acting regulatory regions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette L., Champetier S., Buisson J. P., Roy P. H. Characterization of the nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance (cmlA) gene of the In4 integron of Tn1696: similarity of the product to transmembrane transport proteins. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4493–4502. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4493-4502.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brückner R., Matzura H. Regulation of the inducible chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of the Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pUB112. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2295–2300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03929.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Rubens C. E., Mendelman P. M., Smith A. L. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a gene encoding nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):445–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman C. J., Foster T. J. Posttranscriptional regulation of the inducible nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance determinant of IncP plasmid R26. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):147–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.147-152.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Translational attenuation: the regulation of bacterial resistance to the macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(2):103–132. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvall E. J., Lovett P. S. Chloramphenicol induces translation of the mRNA for a chloramphenicol-resistance gene in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney D. F., Cundliffe E., Foster T. J. Chloramphenicol resistance that does not involve chloramphenicol acetyltransferase encoded by plasmids from gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):113–121. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Sisodia S. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulatory control of beta-tubulin mRNA stability is linked to translation elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Stewart G. C., Hollis M. A., Vold B. S., Bott K. F. Nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis ribosomal RNA operon, rrnB. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Lovett P. S. Perturbing highly conserved spatial relationships in the regulatory domain that controls inducible cat translation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(19):2769–2776. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Rogers E. J., Lovett P. S. Peptidyl transferase inhibition by the nascent leader peptide of an inducible cat gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5309–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5309-5313.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrod R., Gu Z., Lovett P. S. Analysis of the secondary structure that negatively regulates inducible cat translation by use of chemical probing and mutagenesis. Gene. 1994 Mar 11;140(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90734-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett P. S. Translational attenuation as the regulator of inducible cat genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.1-6.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. Conformational alterations in the ermC transcript in vivo during induction. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4307–4314. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Weisblum B. ermC leader peptide. Amino acid sequence critical for induction by translational attenuation. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalysed reaction of puromycin with a formylmethionine-containing oligonucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Hoffarth V., Zimniak L. Unusual resistance of peptidyl transferase to protein extraction procedures. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1416–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1604315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Peptidyl transferase: protein, ribonucleoprotein, or RNA? J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5297–5300. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5297-5300.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protzel A., Morris A. J. Gel chromatographic analysis of nascent globin chains. Evidence of nonuniform size distribution. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4594–4600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers E. J., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Gu Z., Lovett P. S. Parallel induction strategies for cat-86: separating chloramphenicol induction from protein synthesis inhibition. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1063–1069. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers E. J., Kim U. J., Ambulos N. P., Jr, Lovett P. S. Four codons in the cat-86 leader define a chloramphenicol-sensitive ribosome stall sequence. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.110-115.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., McNeill W. F., Farrar W. E., Jr Transposable plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid sequence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa which mediates resistance to gentamicin and four other antimicrobial agents. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):877–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.877-882.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryabova L. A., Selivanova O. M., Baranov V. I., Vasiliev V. D., Spirin A. S. Does the channel for nascent peptide exist inside the ribosome? Immune electron microscopy study. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Brenner D. G., LeGrice S. F., Skinner S. E., Hawkins A. R. Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene of staphylococcal plasmid pC221. Nucleotide sequence analysis and expression studies. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Hall R. M. Sequence analysis of the inducible chloramphenicol resistance determinant in the Tn1696 integron suggests regulation by translational attenuation. Plasmid. 1991 Jul;26(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(91)90032-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. B., Huang W. M., Dunn D. M. A nascent peptide is required for ribosomal bypass of the coding gap in bacteriophage T4 gene 60. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90245-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]