Abstract
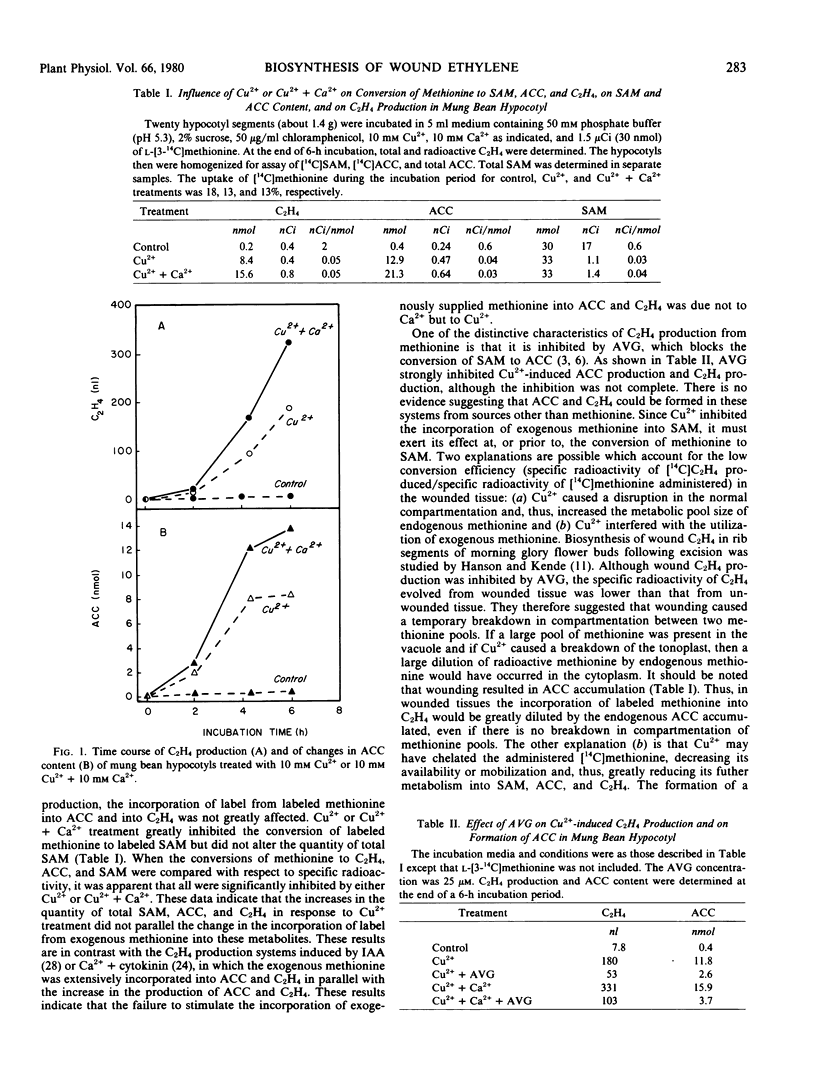
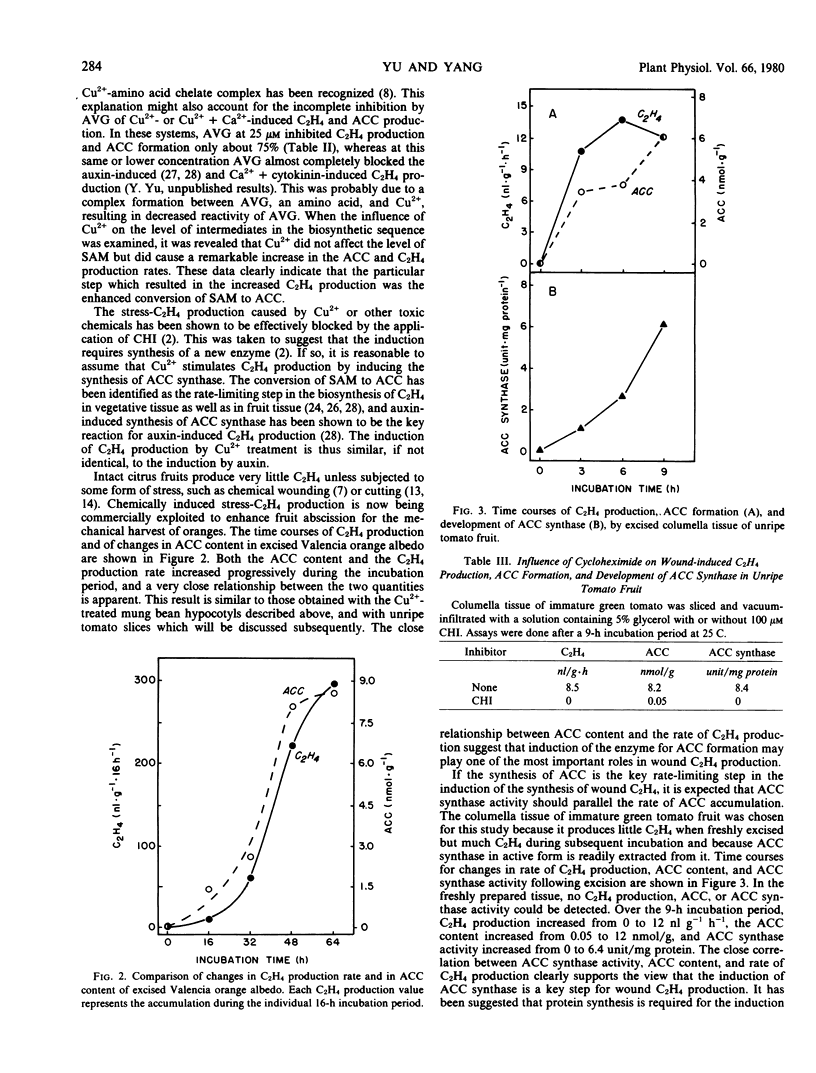
Untreated mung bean hypocotyls produced very little C2H4 but, upon treatment with 10 millimolar Cu2+ or 10 millimolar Cu2+ + 10 millimolar Ca2+, C2H4 production increased 20- and 40-fold, respectively, within 6 hours. This increase in C2H4 production was preceded and paralleled by an increase in 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid (ACC) content, but the level of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) was unaffected, suggesting that the conversion of SAM to ACC is a key reaction in the production of wound-induced C2H4. This view was further supported by the observation that application of aminoethoxyvinylglycine, a known inhibitor of the conversion of SAM to ACC, eliminated the increases in ACC formation and in C2H4 production. A significant increase in C2H4 production was observed in the albedo tissue of orange in response to excision, and it was paralleled by an increase in ACC content. In columella tissue of unripe green tomato fruit, massive increases in the C2H4 production rate (from 0 to 12 nanoliters per gram per hour), in ACC content (from 0.05 to 12 nmoles per gram), and in ACC synthase activity (from 0 to 6.4 units per milligram protein) occurred during the 9-hour incubation period following excision. Infiltration with 0.1 millimolar cycloheximide, an inhibitor of protein synthesis, completely blocked wound-induced C2H4 production, ACC formation, and development of ACC synthase activity. These data indicate that wounding induces the synthesis of ACC synthase, which is the rate-controlling enzyme in the pathway of C2H4 biosynthesis and, thereby, causes accumulation of ACC and increase in C2H4 production.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles A. L. Biochemical Pathway of Stress-induced Ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1972 Oct;50(4):496–498. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.4.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. O., Yang S. F. Ethylene biosynthesis: Identification of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the conversion of methionine to ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):170–174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adato I., Gazit S. Water-deficit Stress, Ethylene Production, and Ripening in Avocado Fruits. Plant Physiol. 1974 Jan;53(1):45–46. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. C., Rasmussen G. K., Rogers B. J., Reece P. C., Henry W. H. Control of abscission in agricultural crops and its physiological basis. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1560–1576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer R. I., Peale A. L. Measurement of S-adenosyl-L-methionine levels by SP Sephadex chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1978 Dec;91(2):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeschl J. D., Rappaport L., Pratt H. K. Ethylene as a factor regulating the growth of pea epicotyls subjected to physical stress. Plant Physiol. 1966 May;41(5):877–884. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.5.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Kende H. Biosynthesis of wound ethylene in morning-glory flower tissue. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):538–541. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyodo H. Ethylene Production by Albedo Tissue of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) Fruit. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jan;59(1):111–113. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau O. L., Yang S. F. Stimulation of ethylene production in the mung bean hypocotyls by cupric ion, calcium ion, and kinetin. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):88–92. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizada M. C., Yang S. F. A simple and sensitive assay for 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):140–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlasson W. B., Pratt H. K. Effects of Wounding on Respiration and Ethylene Production by Cantaloupe Fruit Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1964 Jan;39(1):128–132. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael B. L., Jordan W. R., Powell R. D. An effect of water stress on ethylene production by intact cotton petioles. Plant Physiol. 1972 Apr;49(4):658–660. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.4.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltveit M. E., Dilley D. R. Rapidly Induced Wound Ethylene from Excised Segments of Etiolated Pisum sativum L., cv. Alaska: I. Characterization of the Response. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):447–450. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenk F., Zydek C. R., Ehninger D. J., Dainko J. L. The production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine and S-adenosyl-L-ethionine by yeast. Enzymologia. 1965 Nov 6;29(3):283–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Adams D. O., Yang S. F. 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylate synthase, a key enzyme in ethylene biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Nov;198(1):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Adams D. O., Yang S. F. Regulation of Auxin-induced Ethylene Production in Mung Bean Hypocotyls: Role of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):589–590. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Yang S. F. Auxin-induced Ethylene Production and Its Inhibition by Aminoethyoxyvinylglycine and Cobalt Ion. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1074–1077. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



