Abstract
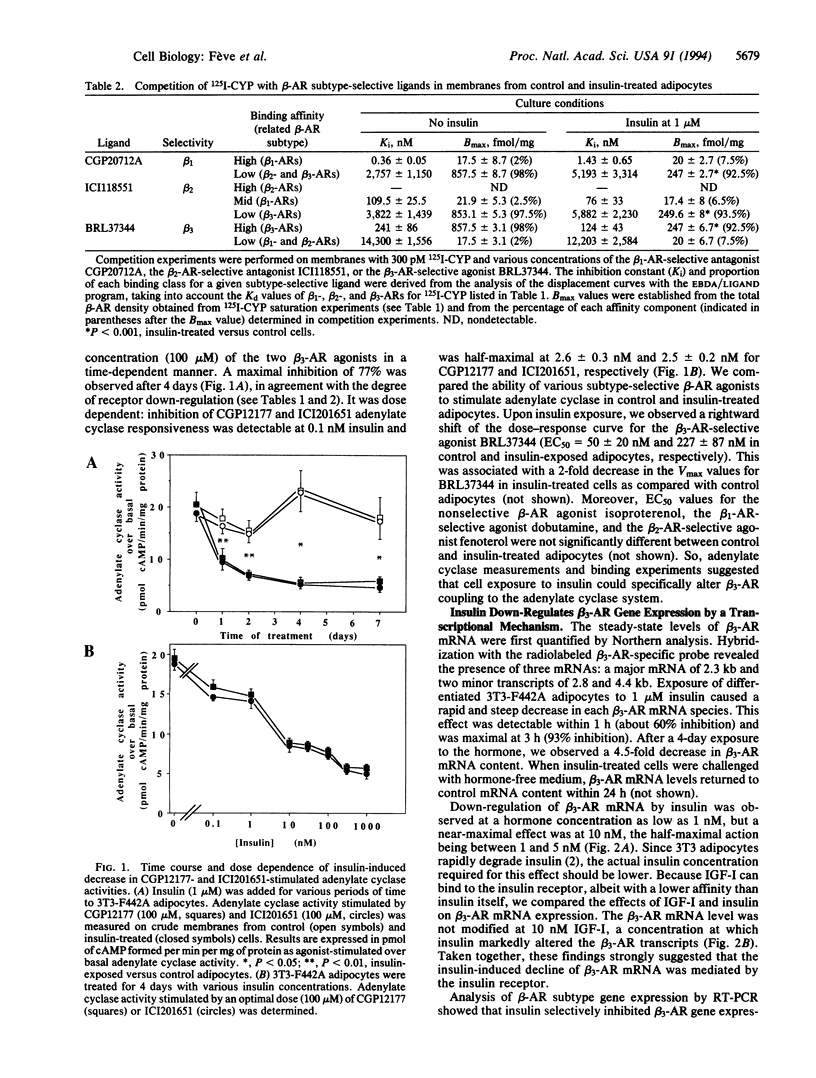
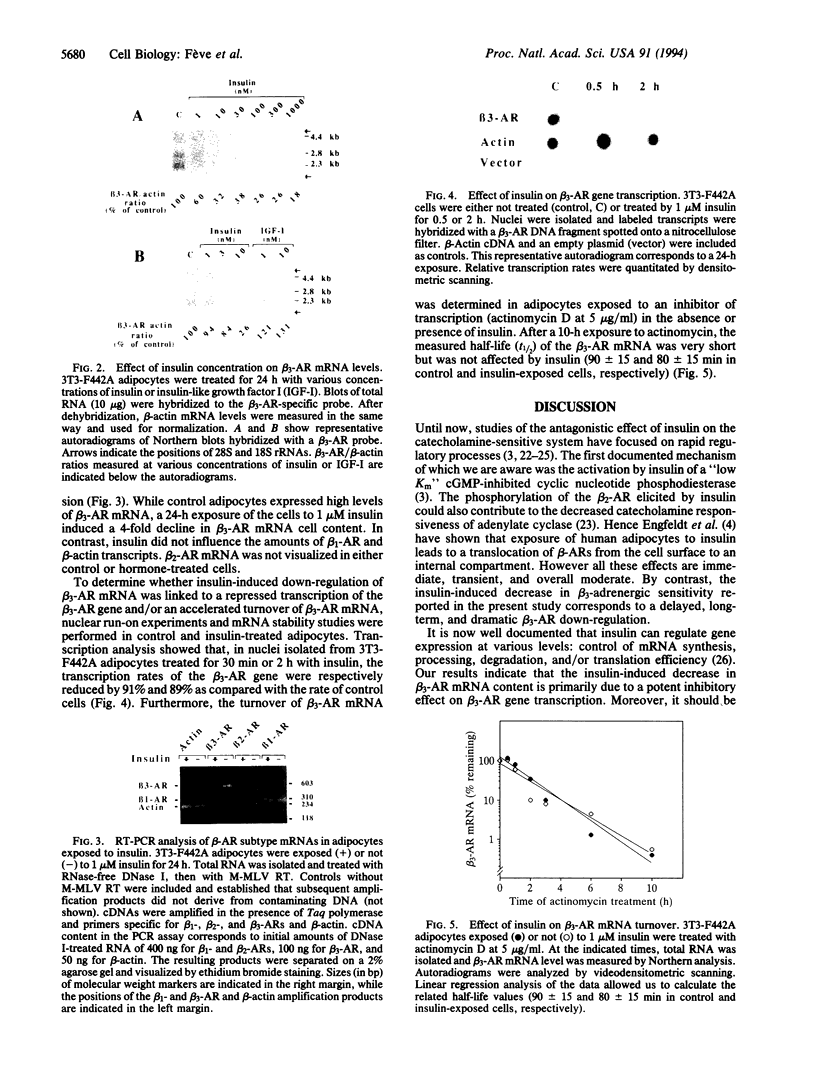
Modulation of the three beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes (beta-ARs) by insulin was investigated in mouse 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Saturation and competition experiments measuring binding of 125I-labeled (-)-cyanopindolol to adipocyte membranes demonstrated that cell exposure to insulin for 4 days caused a 3.5-fold decrease in the density of the major beta-AR component of the adipocyte, the beta 3-AR, while beta 1-AR sites remained unchanged and beta 2-ARs were undetectable. This correlated with a lower potency of the beta 3-AR-selective agonists CGP12177, ICI201651, and BRL37344 in stimulating adenylate cyclase. Northern blotting analysis indicated that insulin induced a rapid and sharp decrease in beta 3-AR mRNA levels. This effect was detectable at low insulin concentrations (EC50 = 3 nM) and was not observed in the presence of insulin-like growth factor I, suggesting an insulin receptor-mediated phenomenon. Reverse transcriptase-PCR analysis showed that, in contrast to its dramatic down-regulatory effect on beta 3-AR mRNA, insulin did not modify the levels of beta 1- and beta 2-AR transcripts. As assessed by nuclear run-on assays, insulin inhibited the beta 3-AR gene transcription rate by 90% within 30 min. mRNA turnover experiments showed that the half-life of beta 3-AR mRNA was short (90 min) and remained unaffected by insulin. These findings demonstrate the genetic control of a beta-AR subtype expression by insulin and reveal a mechanism for the regulation by this hormone of cAMP-dependent biological processes in adipocytes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antras J., Lasnier F., Pairault J. Adipsin gene expression in 3T3-F442A adipocytes is posttranscriptionally down-regulated by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1157–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antras J., Lasnier F., Pairault J. Beta-adrenergic-cyclic AMP signalling pathway modulates cell function at the transcriptional level in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;82(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90030-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Haupt D. M., Stumpo D. J. Insulin activation of protein kinase C: a reassessment. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10946–10952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Camoin L., Maigret B., Strosberg A. D. Structural and conformational features determining selective signal transduction in the beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;44(6):1094–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigny O., Ricquier D., Blondel O., Mayers R. M., Briscoe M. G., Holloway B. R. Beta 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation restores message and expression of brown-fat mitochondrial uncoupling protein in adult dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10774–10777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson D. E., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleotide sequence and hormonal regulation of mouse glycerophosphate dehydrogenase mRNA during adipocyte and muscle cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1804–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt P., Hellmér J., Wahrenberg H., Arner P. Effects of insulin on adrenoceptor binding and the rate of catecholamine-induced lipolysis in isolated human fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15553–15560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Baude B., Krief S., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J., Emorine L. J. Inhibition by dexamethasone of beta 3-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Evidence for a transcriptional mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15909–15915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Lasnier F., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Differential regulation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor protein and mRNA levels by glucocorticoids during 3T3-F442A adipose differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16343–16349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Spontaneous heritable changes leading to increased adipose conversion in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Port J. D., Gelman M. S., Malbon C. C. Cross-talk between tyrosine kinase and G-protein-linked receptors. Phosphorylation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):26017–26022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himms-Hagen J. Brown adipose tissue thermogenesis: interdisciplinary studies. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2890–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Flores-Riveros J. R., McLenithan J. C., Janicot M., Lane M. D. Transcriptional repression of the mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter (GLUT4) gene by cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krief S., Lönnqvist F., Raimbault S., Baude B., Van Spronsen A., Arner P., Strosberg A. D., Ricquier D., Emorine L. J. Tissue distribution of beta 3-adrenergic receptor mRNA in man. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):344–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI116191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny L., Dib K., Haye B., Corrèze C., Jacquemin C., Lambert B. The effect of glycosyl inositol-phosphate on cAMP production in isolated rat fat-cells is transduced by a pertussis toxin sensitive G-protein. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80951-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias C., Blin N., Elalouf J. M., Mattei M. G., Strosberg A. D., Emorine L. J. Molecular characterization of the mouse beta 3-adrenergic receptor: relationship with the atypical receptor of adipocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3721–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada M. T., Haskell K. M., Ecker D. J., Stadel J. M., Crooke S. T. Genetic regulation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors in 3T3-L1 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2600053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Granner D. K. Regulation of gene expression by insulin. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):609–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2780609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olansky L., Pohl S. L. beta-Adrenergic desensitization by chronic insulin exposure in 3T3-L1 cultured adipocytes. Metabolism. 1984 Jan;33(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pairault J., Lasnier F., Laudat M. H. Développement de la stimulation de l'adénylate cyclase par l'isoprotérénol et la corticotropine-bêta (1-24) au cours de la conversion adipocytaire des cellules 3T3-F442A en culture. Effets dissociés de l'insuline et induction des bêta-récepteurs lors de la différenciation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):351–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulauskis J. D., Sul H. S. Hormonal regulation of mouse fatty acid synthase gene transcription in liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):574–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynolds M. V., Awald P. D., Gordon D. F., Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Rule D. C., Wood W. M., Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase gene expression in rat adipocytes is regulated by isoproterenol and insulin through different mechanisms. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1416–1422. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehnmark S., Néchad M., Herron D., Cannon B., Nedergaard J. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic induction of the expression of the uncoupling protein thermogenin in brown adipocytes differentiated in culture. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16464–16471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Bouillaud F., Toumelin P., Mory G., Bazin R., Arch J., Pénicaud L. Expression of uncoupling protein mRNA in thermogenic or weakly thermogenic brown adipose tissue. Evidence for a rapid beta-adrenoreceptor-mediated and transcriptionally regulated step during activation of thermogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13905–13910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Lai E., Rosen O. M. Acquisition of increased hormone sensitivity during in vitro adipocyte development. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3554–3557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafrir E. Animal models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992 Oct;8(3):179–208. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Manganiello V. C. Role of hormone-sensitive low Km cAMP phosphodiesterase in regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and lipolysis in rat adipocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman B. M., Green H. Cyclic AMP-mediated control of lipogenic enzyme synthesis during adipose differentiation of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J., Atkinson R. L., Pohl S. L. Insulin-induced insulin resistance of lipolysis in human adipocytes in organ culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Oct;51(4):921–924. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-4-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand A. L., Lupien J., Bukowiecki L. J. Interactions of cold exposure and starvation on glucose tolerance and insulin response. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):E575–E581. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.6.E575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila M. C., Milligan G., Standaert M. L., Farese R. V. Insulin activates glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis) through a phospholipid-derived mediator. Apparent involvement of Gi alpha and activation of a phospholipase C. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8735–8740. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]