Abstract
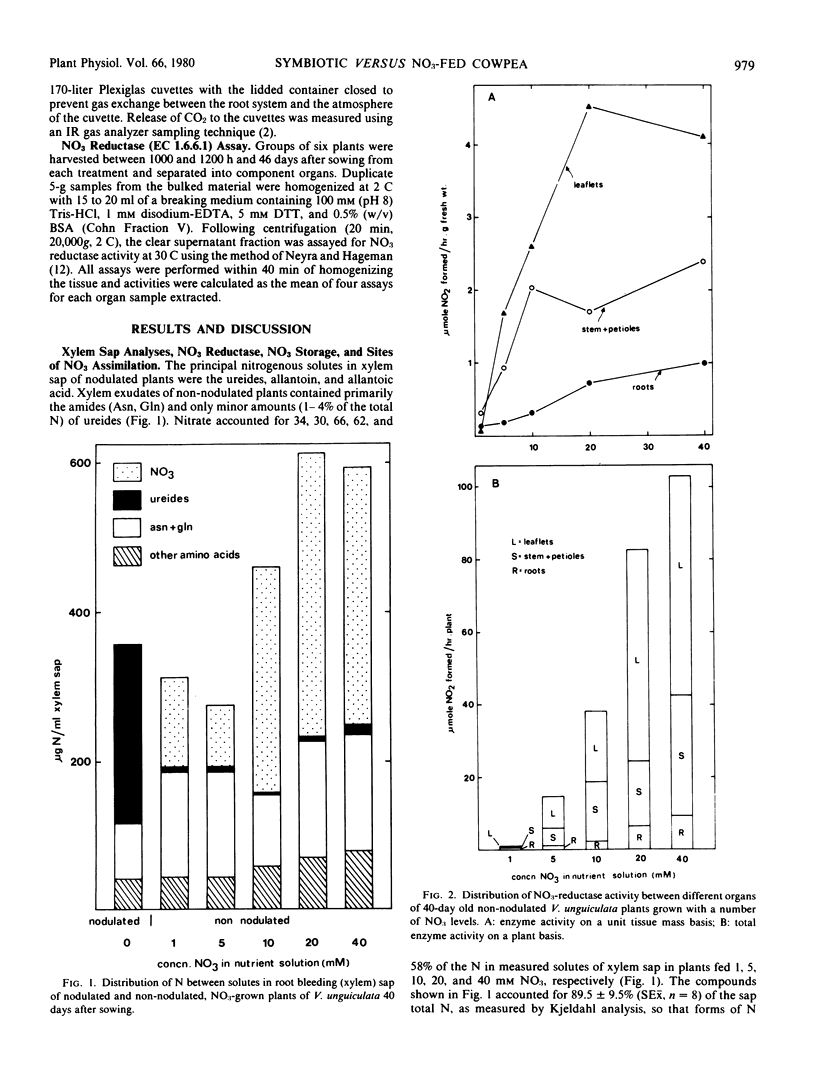
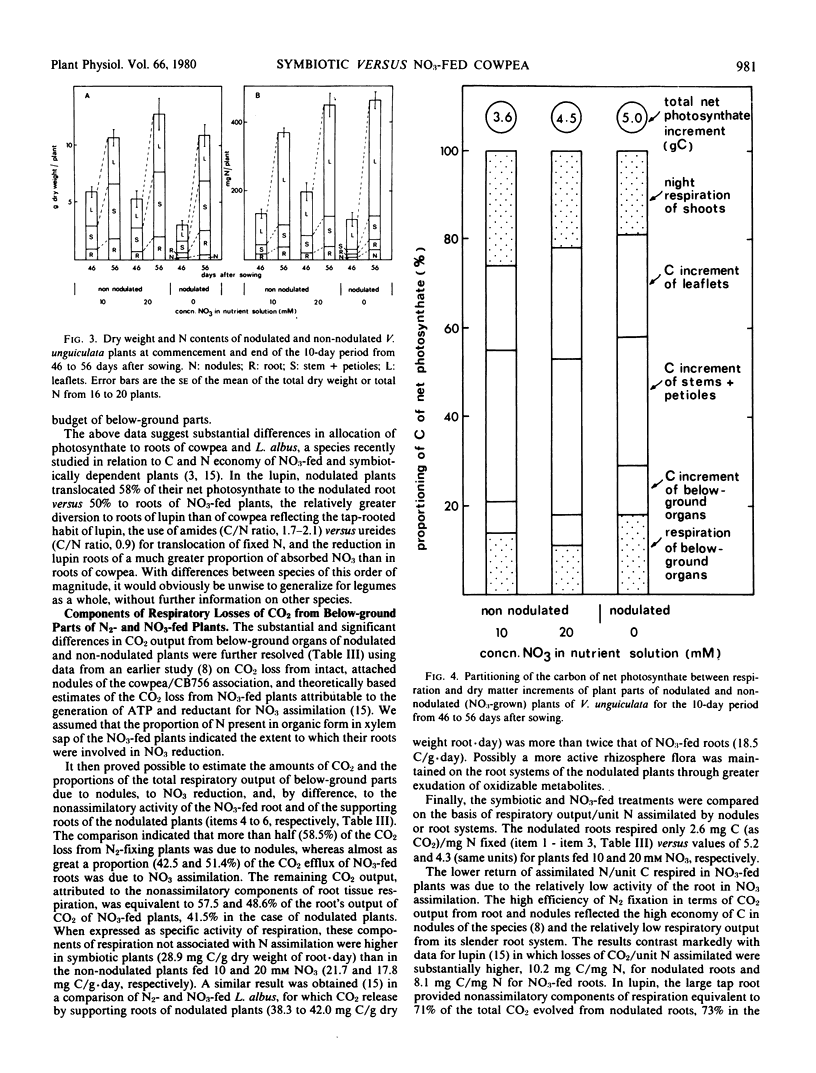
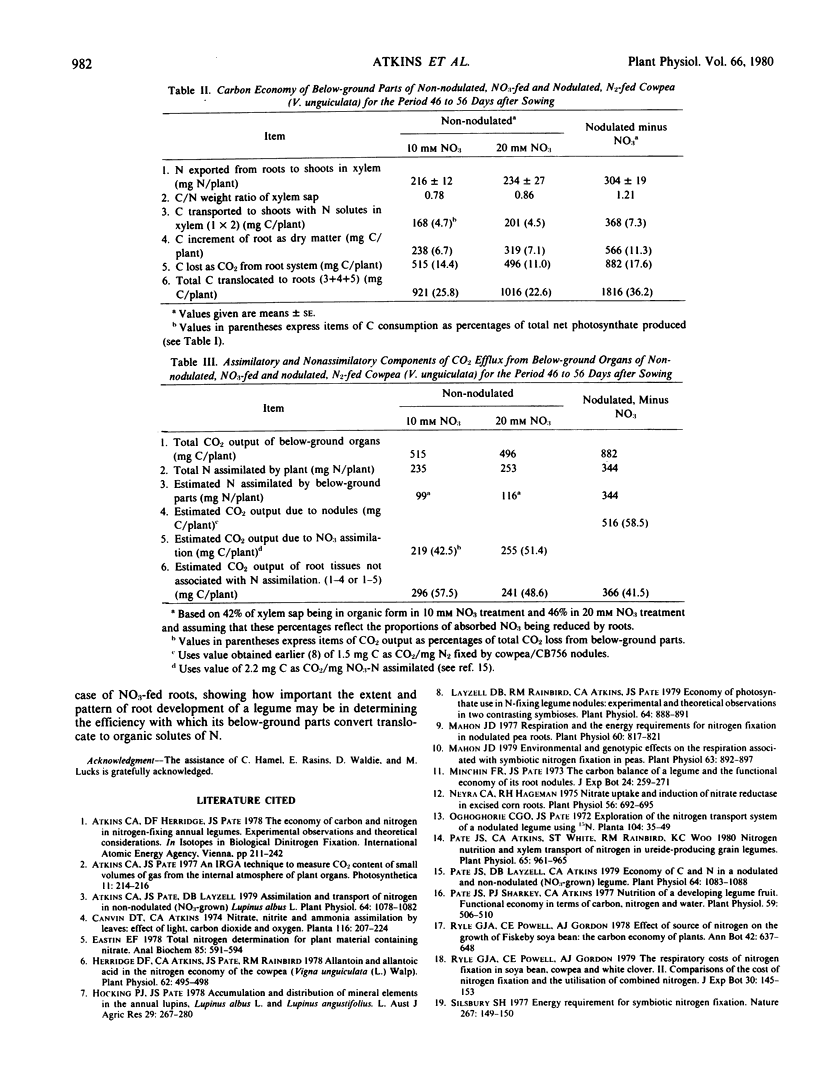
The response of non-nodulated cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. cv Caloona) to a wide range of NO3 levels in the rooting medium was studied 40 days after sowing by in vitro assays of plant organs for NO3 reductase (EC 1.6.6.1) and analyses of root bleeding (xylem) sap for nitrogenous solutes. Plants fed 1, 5, 10, 20, and 40 millimolar NO3 showed, respectively, 64, 92, 94, and 91% of their total reductase activity in shoots and 34, 30, 66, 62, and 58% of the total N of their xylem sap as NO3. These data, and the absence in the plants of significant pools of stored NO3, indicated that shoots were major organs of NO3 assimilation, especially at levels of NO3 (10 to 40 millimolar) that maintained plant growth at near maximum rates. Partitioning and utilization of C and N were studied in nodulated, minus NO3 plants and non-nodulated plants fed 10 or 20 millimolar NO3, the levels of NO3 which gave rates of growth and N assimilation closest to those of the symbiotic plants. The conversion of the C of net photosynthate to dry matter was similar in nodulated plants (67%) and NO3-grown plants (64%), but greater proportions of photosynthate were translocated to below ground parts of nodulated plants (37%) than of NO3-fed plants (23 to 26%). Greater photosynthate consumption by nodulated roots was associated with proportionately greater root growth and respiration and 2-fold greater export of C in xylem than in the NO3-fed plants. Theoretical considerations suggest that the elevated CO2 output of nodulated roots was due not only to CO2 loss associated with nodule function, but also to a much greater nonassimilatory component of respiration in the supporting root of the nodulated plant compared to roots of the NO3-fed plants. Data are compared with previously published information from other legumes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Layzell D. B. Assimilation and Transport of Nitrogen in Nonnodulated (NO(3)-grown) Lupinus albus L. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1078–1082. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastin E. F. Total nitrogen determining for plant material containing nitrate. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):591–594. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herridge D. F., Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Rainbird R. M. Allantoin and Allantoic Acid in the Nitrogen Economy of the Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.). Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):495–498. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzell D. B., Rainbird R. M., Atkins C. A., Pate J. S. Economy of Photosynthate Use in Nitrogen-fixing Legume Nodules: Observations on Two Contrasting Symbioses. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):888–891. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon J. D. Environmental and genotypic effects on the respiration associated with symbiotic nitrogen fixation in peas. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):892–897. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahon J. D. Respiration and the energy requirement for nitrogen fixation in nodulated pea roots. Plant Physiol. 1977 Dec;60(6):817–821. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyra C. A., Hageman R. H. Nitrate uptake and induction of nitrate reductase in excised corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):692–695. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Atkins C. A., White S. T., Rainbird R. M., Woo K. C. Nitrogen Nutrition and Xylem Transport of Nitrogen in Ureide-producing Grain Legumes. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):961–965. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Layzell D. B., Atkins C. A. Economy of Carbon and Nitrogen in a Nodulated and Nonnodulated (NO(3)-grown) Legume. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1083–1088. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. S., Sharkey P. J., Atkins C. A. Nutrition of a developing legume fruit: functional economy in terms of carbon, nitrogen, water. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):506–510. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silsbury J. H. Energy requirement for symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):149–150. doi: 10.1038/267149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Degradation of allantoin by Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



