Abstract
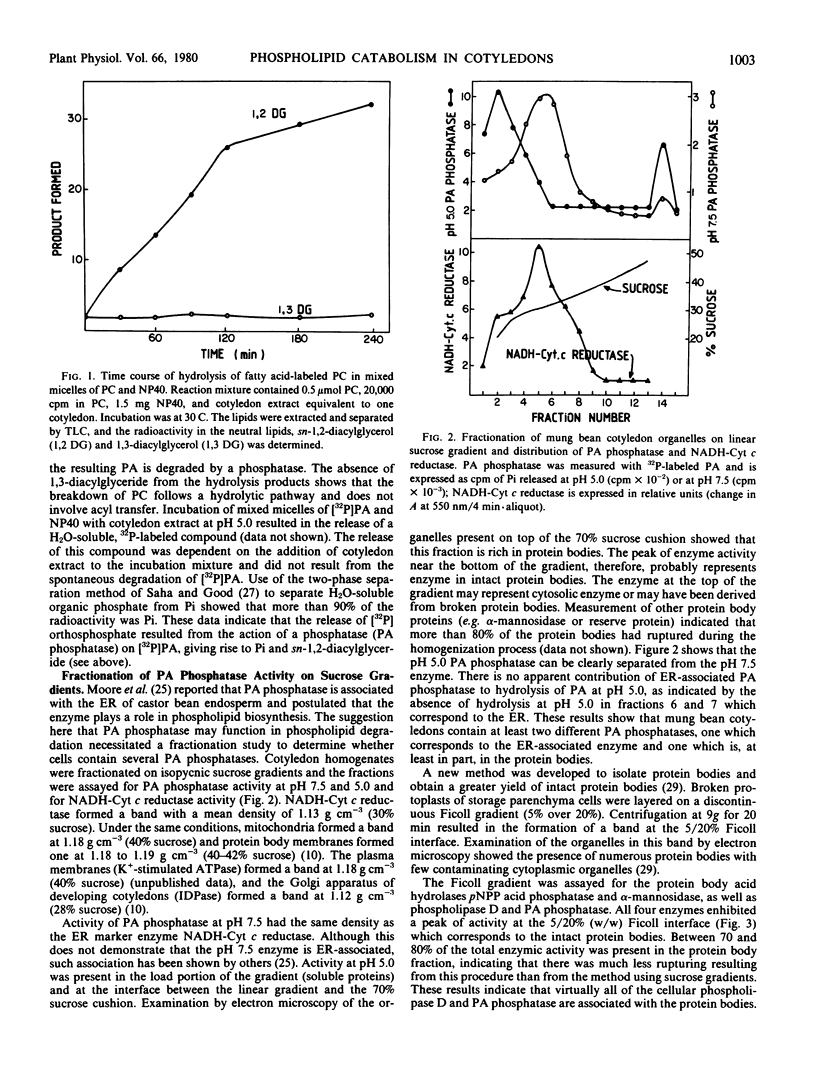
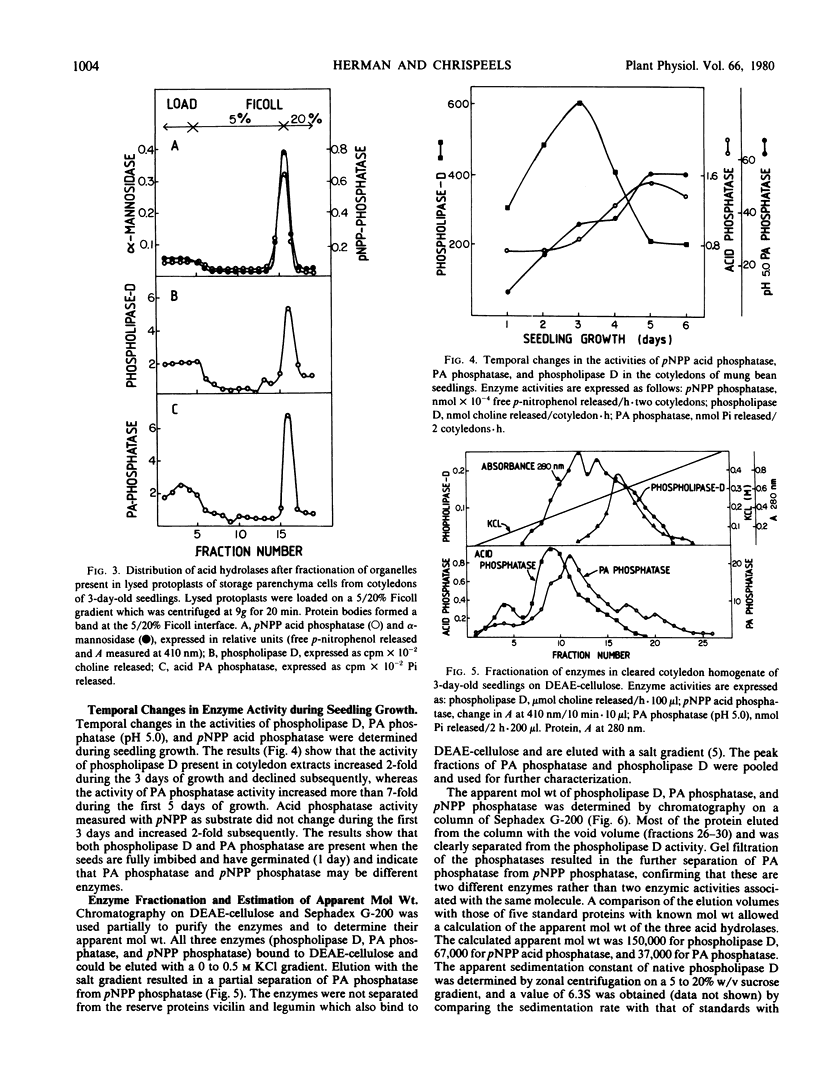
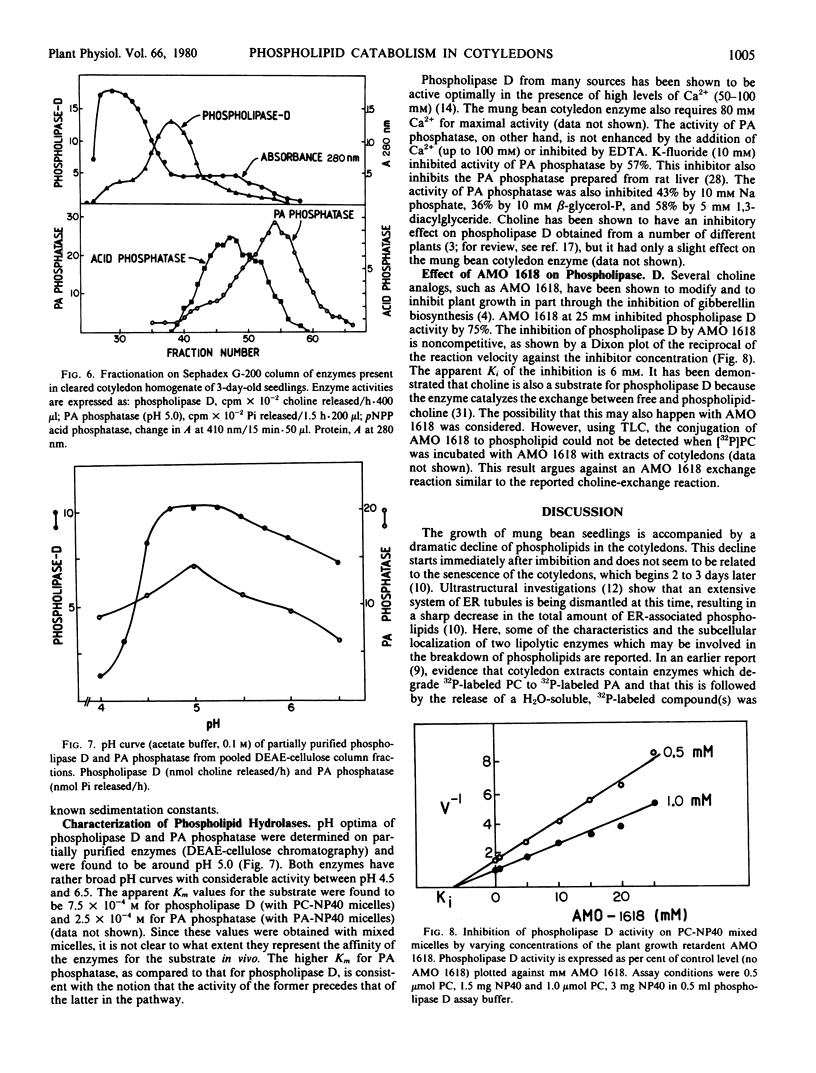
Mixed micelles of 32P-labeled phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidic acid (PA) and the nonionic detergent octylphenol polyethylene oxide (NP-40 Nonidet) were used to assay the activities of phospholipase D and PA phosphatase in crude extracts of mung bean (Vigna radiata) cotyledons. Together these enzymes degrade phosphatidylcholine to free choline, inorganic phosphate, and sn-1,2-diacylglycerol. Both enzymes have pH optima around 5.0. The enzymes are present in fully imbibed cotyledons and increase in activity during seedling growth. Fractionation of cotyledon extracts on sucrose gradients showed that the cells contain two PA phosphatases. One enzyme with a pH optimum of 7.5 has the same distribution on sucrose gradient as the endoplasmic reticulum marker enzyme NADH-cytochrome c reductase. The other, PA phosphatase, with a pH optimum of 5.0, was present in a protein body-rich fraction and in the load portion of the gradient. Fractionation of broken protoplasts on Ficoll gradients (a method which allows for the isolation of a high proportion of intact protein bodies) indicates that most of the cellular phospholipase D and PA phosphatase (pH 5.0) are associated with the protein bodies. Using column chromatography (DEAE-cellulose and Sephadex G-200), PA phosphatase (pH 5.0) was found to be a different enzyme from the major acid phosphatase in the cotyledons. Apparent molecular weights of phospholipase D and PA phosphatase were 150,000 and 37,000, respectively. The activity of phospholipase D was not affected by free choline, but was markedly inhibited by the choline analog and plant growth retardant isopropyl 4′-(trimethylammonium chloride-5′-methylphenyl piperidine-1-carboxylate (AMO 1618). The finding that these acid hydrolases are located in the protein bodies supports the conclusion that protein bodies form the general lytic compartment in the storage parenchyma cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allgyer T. T., Wells M. A. Phospholipase D from savoy cabbage: purification and preliminary kinetic characterization. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5348–5353. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N. Some properties of purified phospholipase D and especially the effect of amphipathic substances. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):76–86. doi: 10.1042/bj1020076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. T., Upper C. D., West C. A. An enzymic site of inhibition of gibberellin biosynthesis by Amo 1618 and other plant growth retardants. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):948–952. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson M. C., Chrispeels M. J. Isolation and Characterization of Glucosamine-containing Storage Glycoproteins from the Cotyledons of Phaseolus aureus. Plant Physiol. 1973 Aug;52(2):98–104. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliard T. The enzymic deacylation of phospholipids and galactolipids in plants. Purification and properties of a lipolytic acyl-hydrolase from potato tubers. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):379–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1210379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R. E., Mudd J. B. Identification of an acyl donor in steryl ester biosynthesis by enzyme preparations from spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):348–353. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Chrispeels M. J. Endoplasmic Reticulum of Mung Bean Cotyledons: ACCUMULATION DURING SEED MATURATION AND CATABOLISM DURING SEEDLING GROWTH. Plant Physiol. 1980 Apr;65(4):600–604. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.4.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. Rapid degradation and limited synthesis of phospholipids in the cotyledons of mung bean seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jul;64(1):38–42. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris N., Chrispeels M. J. Histochemical and biochemical observations on storage protein metabolism and protein body autolysis in cotyledons of germinating mung beans. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):292–299. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasson E. P., Laties G. G. Separation and characterization of potato lipid acylhydrolases. Plant Physiol. 1976 Feb;57(2):142–147. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Aladjem E., Shapiro B. Phospholipase D in peanut seeds. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Dec;50(9):1395–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Arad R. Properties of the phospholipase D from peanut seeds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 14;210(2):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M. Phospholipase D. Adv Lipid Res. 1978;16:267–326. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024916-9.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Hirayama O. Purification and properties of a lipolytic acyl-hydrolase from potato leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 27;573(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman R. E., Smith M., Cook K. Intermediary metabolism of phospholipids in brain tissue. II. Phosphatidic acid phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3513–3517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKersie B. D., Lepock J. R., Kruuv J., Thompson J. E. The effects of cotyledon senescence on the composition and physical properties of membrane lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90325-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. S., Lord J. M., Kagawa T., Beevers H. Enzymes of phospholipid metabolism in the endoplasmic reticulum of castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):50–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarles R. H., Dawson R. M. The distribution of phospholipase D in developing and mature plants. Biochem J. 1969 May;112(5):787–794. doi: 10.1042/bj1120787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha S., Good N. E. Products of the photophosphorylation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5017–5021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Hübscher G. Metabolism of phospholipids. X. Partial purification and properties of a soluble phosphatidate phosphohydrolase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):397–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



