Abstract
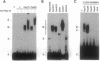
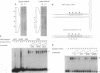
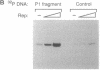
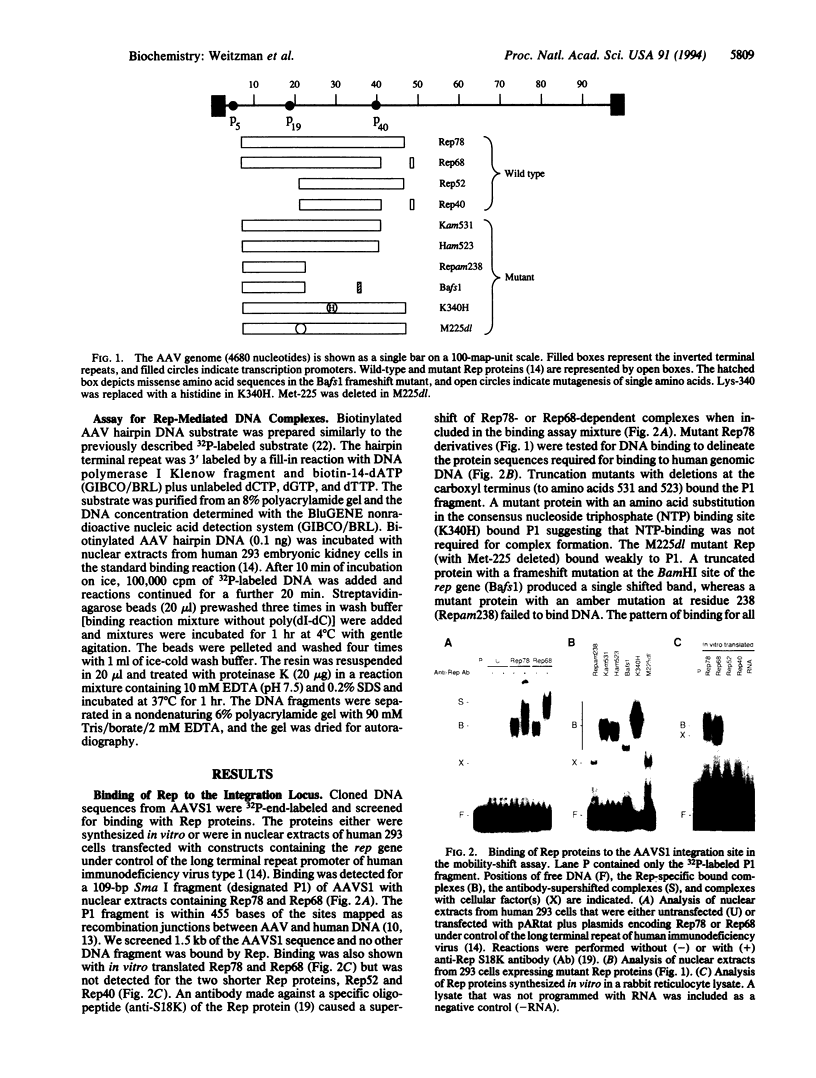
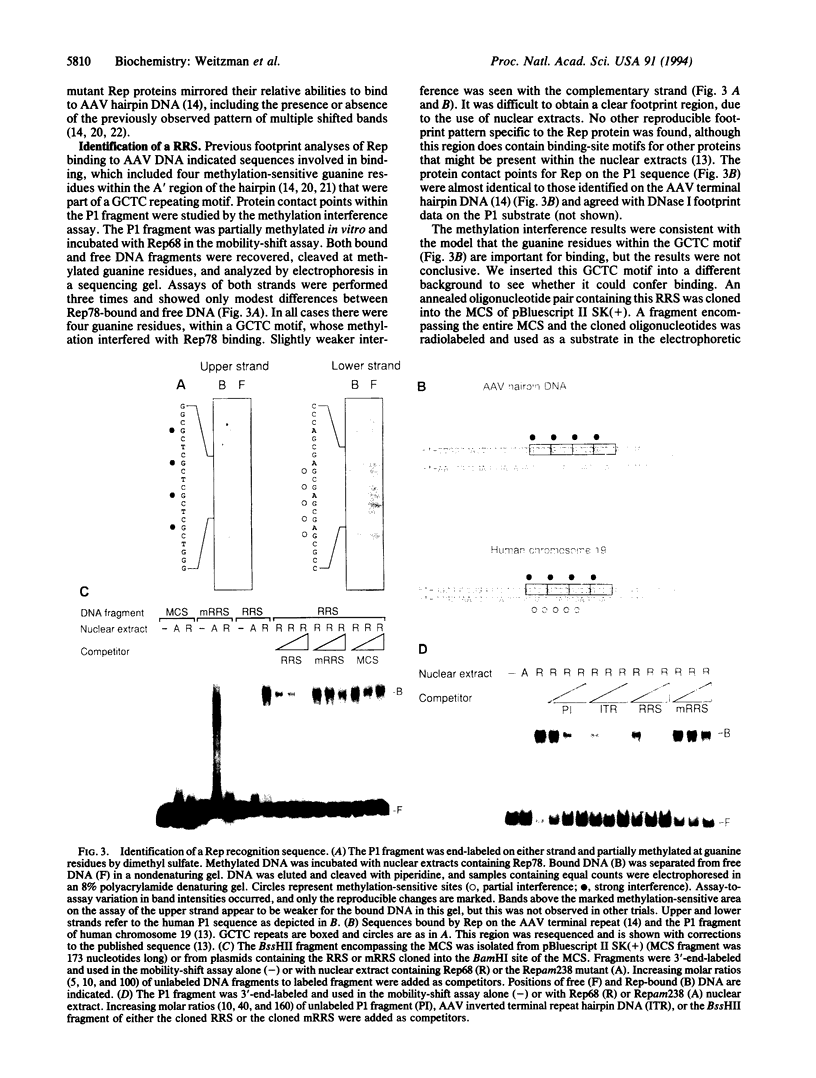
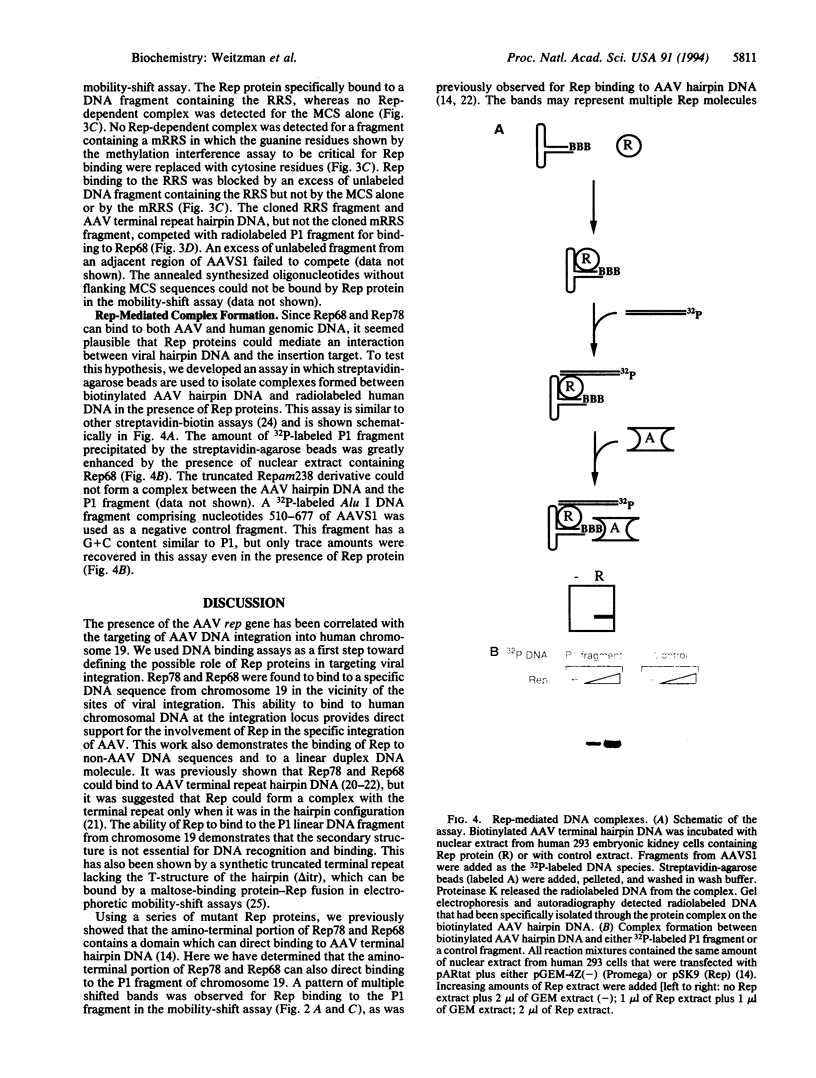
AAV is unique among eukaryotic viruses in the ability of its DNA to integrate preferentially into a specific region of the human genome. Understanding AAV integration may aid in developing gene therapy systems with predictable integration sites. Using a gel mobility-shift assay, we have identified a DNA sequence within the AAV integration locus on human chromosome 19 which is specifically bound by the AAV Rep78 and Rep68 proteins. This Rep recognition sequence is a GCTC repeating motif very similar to sequences within the inverted terminal repeats of the AAV genome which are also bound by Rep78 and Rep68. Cloned oligonucleotides containing the recognition sequence can direct specific binding by Rep proteins. Binding assays with mutant Rep proteins show that the amino-terminal portion of Rep78 and Rep68 can direct binding to either the AAV terminal repeat hairpin DNA or chromosome 19. This human genomic DNA can be complexed with AAV DNA by Rep proteins as demonstrated by a dual-label (32P/biotin) assay. These results suggest a role for Rep in targeting viral integration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashktorab H., Srivastava A. Identification of nuclear proteins that specifically interact with adeno-associated virus type 2 inverted terminal repeat hairpin DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3034–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3034-3039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Pinkerton T. C., Thomas G. F., Hoggan M. D. Detection of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-specific nucleotide sequences in DNA isolated from latently infected Detroit 6 cells. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):556–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Johnson P. R., Wong K. K., Jr Dual-target inhibition of HIV-1 in vitro by means of an adeno-associated virus antisense vector. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1485–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.1359646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Replication of a human parvovirus nonsense mutant in mammalian cells containing an inducible amber suppressor. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiorini J. A., Weitzman M. D., Owens R. A., Urcelay E., Safer B., Kotin R. M. Biologically active Rep proteins of adeno-associated virus type 2 produced as fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.797-804.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotte T. R., Afione S. A., Solow R., Drumm M. L., Markakis D., Guggino W. B., Zeitlin P. L., Carter B. J. Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator from a novel adeno-associated virus promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3781–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotte T. R., Solow R., Owens R. A., Afione S., Zeitlin P. L., Carter B. J. Gene expression from adeno-associated virus vectors in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Sep;7(3):349–356. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Origin and termination of adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Factors that bind to adeno-associated virus terminal repeats. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3095–3104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3095-3104.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90526-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessberger R., Berg P. Repair of deletions and double-strand gaps by homologous recombination in a mammalian in vitro system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):445–457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Berns K. I. Organization of adeno-associated virus DNA in latently infected Detroit 6 cells. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):460–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Linden R. M., Berns K. I. Characterization of a preferred site on human chromosome 19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5071–5078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Menninger J. C., Ward D. C., Berns K. I. Mapping and direct visualization of a region-specific viral DNA integration site on chromosome 19q13-qter. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Siniscalco M., Samulski R. J., Zhu X. D., Hunter L., Laughlin C. A., McLaughlin S., Muzyczka N., Rocchi M., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Cardellichio C. B., Coon H. C. Latent infection of KB cells with adeno-associated virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):515–524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.515-524.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKown R. L., Orle K. A., Chen T., Craig N. L. Sequence requirements of Escherichia coli attTn7, a specific site of transposon Tn7 insertion. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):352–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.352-358.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Trempe J. P., Carter B. J. Identification of the trans-acting Rep proteins of adeno-associated virus by antibodies to a synthetic oligopeptide. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):823–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.823-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro-Cacho C. A., Samulski R. J., Kaplan D. Gene transfer in human lymphocytes using a vector based on adeno-associated virus. J Immunother (1991) 1992 May;11(4):231–237. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. A., Trempe J. P., Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Adeno-associated virus rep proteins produced in insect and mammalian expression systems: wild-type and dominant-negative mutant proteins bind to the viral replication origin. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):14–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90817-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. A., Weitzman M. D., Kyöstiö S. R., Carter B. J. Identification of a DNA-binding domain in the amino terminus of adeno-associated virus Rep proteins. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.997-1005.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Zhu X., Xiao X., Brook J. D., Housman D. E., Epstein N., Hunter L. A. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3941–3950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. O., Im D. S., Ni T., Xiao X., Samulski R. J., Muzyczka N. Features of the adeno-associated virus origin involved in substrate recognition by the viral Rep protein. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6096–6104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6096-6104.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Lusby E. W., Berns K. I. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the adeno-associated virus 2 genome. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.555-564.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. E., Liu J. M., Xiao X., Young N. S., Nienhuis A. W., Samulski R. J. Regulated high level expression of a human gamma-globin gene introduced into erythroid cells by an adeno-associated virus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7257–7261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]