Abstract
Objective
Neonatal male circumcision (NMC) is not routinely practiced in Zambia, but it promising long-term HIV prevention strategy. We studied the feasibility and safety of three different NMC methods
Patients and Methods
We enrolled healthy newborns in a controlled trial of the Mogen, Gomco, and Plastibell devices. Doctors, nurses, and clinical officers were trained to perform Mogen, Gomco, and Plastibell techniques. Each provider performed at least 10 circumcisions using each device. Neonates were reviewed at one week and six weeks post circumcision for adverse events.
Results
Between October 2009 and March 2011, 17 providers (5 physicians, 9 nurse-midwives, and 3 clinical officers) without prior NMC experience were trained, and 640 circumcisions performed. The median infant birth weight was 3.2kg (IQR 2.9–3.5 kg) and median age at the time of procedure was 11 days (IQR:7–18 days); 149 babies (23.3%) were HIV-exposed. The overall adverse event rate was 4.9% (n=31/630), and the moderate-severe AE rate was 4.1% (n=26/630). Write in what this was. Rates did not significantly differ by method. Most providers (65%) preferred the Mogen clamp over the Gomco and Plastibell.
Conclusions
Doctors, nurses, and clinical officers can be trained to safely provide NMC in a programmatic setting. The three studied techniques had comparable safety profiles. Mogen clamp was the preferred device for most providers.
Introduction
As early as 2001, ecological studies first suggested that countries with widespread coverage of male circumcision, such as those in West Africa, had lower burdens of HIV infection. (1–4) Subsequently, three large randomized trials in sub-Saharan Africa have conclusively shown that male circumcision (MC) reduces HIV acquisition among heterosexual men by up to 60%.(5–7) Based on these findings, the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNAIDS recommended MC scale up as one component of a comprehensive HIV prevention strategy for settings of low MC prevalence and high HIV prevalence.(8) While adolescents and young adults are the primary targets for most prevention-oriented MC programs, to maximize long-term HIV prevention benefits, circumcision programs have also begun targeting male infants.
Neonatal male circumcision (NMC) (or circumcision within the first couple of months of life) is generally regarded as a cheaper, simpler and safer procedure compared to circumcision of older boys and men (9, 10). In industrialized-country settings, the procedure is commonly performed using one of three specialized devices (Mogen Clamp, Plastibell, or Gomco) designed to achieve hemostasis without sutures. Complication rates among the three devices are similar (11), and choice among the devices is usually determined by provider preference (12–14). The WHO recommends all three of these methods in addition to the dorsal slit method for neonatal circumcision (15).
Although neonatal male circumcision is rarely practiced in Zambia, the Ministry of Health of Zambia has ambitious plans to reach 80% of all male infants with NMC by 2020 (16). We conducted a neonatal male circumcision study to determine the acceptability, feasibility, and safety of neonatal circumcision. The goal was to advise the Zambian Ministry of Health on the best method for national scale up. In this manuscript, we report on device preference among different types of providers as well as safety.
Patients and Methods
Study Setting
We conducted a prospective trial of neonatal male circumcision in 3 Lusaka sites: the University Teaching Hospital (UTH), and two public-sector primary health care clinics. Neonatal vitamin K is not routinely used in our setting and was not administered to participants in our trial.
Recruitment and Training of NMC Providers
Prior to participant enrollment, we developed an NMC training package consisting of didactic lectures, practice on models of neonatal genitalia, and clinical practice. Nine physicians from the UTH were trained to serve as NMC supervisors for provider trainees enrolling in the study. During the study, these supervisors evaluated the competence of the trainees at set intervals, examined infants at review visits, and assessed adverse events.
Provider trainees, including physicians, clinical officers, nurse midwives, and registered nurses. After completing informed consent to participate in the study of NMC provider training, providers were trained in groups consisting of 2-to-4 trainees depending on the availability of trainees. The individual methods were taught sequentially and in blocks. If a supervisor determined that a trainee was not competent in a given method after 10 procedures, then the provider would perform that particular method until competency and before moving on to another method. To ensure variation in the sequence of the three methods among trainees (assuming sequence could influence their competence and preferences among methods), the order of NMC methods for each provider was pre-determined by an independent statistician. (Table 1) Providers were blinded to the sequence. Blinding the postoperative evaluations was not possible since the Plastibell technique involves a small plastic bell remaining on the penis for up to a week and the other two techniques did not
Table 1.
Characteristics of infants enrolled in a comparison of three methods for neonatal circumcision, Lusaka, Zambia
| Mogen (n=216) | Gomco (n=206) | Plastibell (n=218) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| N | Value | N | Value | N | value | P value | |
| Age at procedure median (IQR) | 215 | 11.0 (7.0, 21.0) | 206 | 11.0 (7.0, 16.0) | 218 | 11.0 (7.0, 18.0) | 0.446 |
| ≤ 48 hours | 23 | 10.7% | 26 | 12.6% | 19 | 8.7% | 0.475 |
| 3–14 days | 107 | 49.8% | 112 | 54.4% | 121 | 55.5% | |
| 15–28 days | 85 | 39.5% | 68 | 33.0% | 78 | 35.8% | |
| Birth Weight, median kg (IQR) | 212 | 3.2 (2.9, 3.5) | 204 | 3.1 (2.8, 3.5) | 214 | 3.2 (2.9, 3.5) | 0.069 |
| ≥ 3500 | 53 | 25.0% | 53 | 26.0% | 63 | 29.4% | |
| 2500–3499 | 151 | 71.2% | 134 | 65.7% | 145 | 67.8% | |
| 1500–2499 | 8 | 3.8% | 17 | 8.3% | 6 | 2.8% | |
| Procedure Weight, median, kg (IQR) | 210 | 3.5 (3.2, 4.0) | 202 | 3.5 (3.2, 4.0) | 216 | 3.6 (3.2, 4.0) | 0.653 |
| ≥ 4500 | 29 | 13.8% | 18 | 8.9% | 21 | 9.7% | 0.552 |
| 3500–4999 | 101 | 48.1% | 105 | 52.0% | 110 | 50.9% | |
| 1500–3499 | 80 | 38.1% | 79 | 39.1% | 85 | 39.4% | |
| HIV Exposed | |||||||
| Yes | 45 | 20.8% | 45 | 21.8% | 59 | 27.1% | 0.497 |
| No | 164 | 75.9% | 156 | 75.7% | 155 | 71.1% | |
| Unknown | 7 | 3.2% | 5 | 2.4% | 4 | 1.8% | |
| Mode of delivery | |||||||
| Vaginal | 175 | 81.8% | 167 | 81.5% | 182 | 85.0% | 0.557 |
| Cesarean | 39 | 18.2% | 38 | 18.5% | 32 | 15.0% | |
NMC Provider Trainee Evaluations
The supervisors evaluated trainees using standard competency checklists (tailored to the procedure type being evaluated) after every five procedures. The trainees completed pre-and post-training questionnaires, to assess their knowledge, attitudes and previous experience with male circumcision, as well as their NMC method preferences (post-training only).
Informed Consent and Eligibility Screening
Parents of newborn boys were recruited for the study by peer educators in the post-natal wards of the three NMC sites and other public clinics. One or both parents (if available) or legal guardians of eligible infants completed an informed consent process prior to their infant’s circumcision. All healthy male infants of gestational age >37 weeks at birth, aged 0–28 days, and between 2,500 grams and 5,000 grams were considered eligible to be in the study. Infants with urethral or penile shaft abnormality, local infection, any current illness, or family history of bleeding disorder were excluded. Testing of mothers and infants for HIV was not offered in the study. However all pregnant mothers are routinely tested for HIV under the Ministry of Health policy guidelines.
NMC Method Selection
Participating infants received a dorsal nerve block using 0.8ml of 1% lignocaine for local anesthesia, and were given up to one ml of an oral glucose solution, administered using a pacifier for analgesia during the procedure. Infants were then circumcised using one of the three NMC methods being trained (Mogen, Gomco, or Plastibell). The method performed on a given infant was determined based on which method was being practiced by the attending provider trainee at the time of the procedure, as previously described. For each circumcision performed, information such as provider, location, type of procedure used, procedure start and end time, and individual infant characteristics as well as parental characteristics were recorded on standard clinic forms.
Infant Follow Up
Study staff performed a detailed physical exam on all infants at one week and six weeks following the procedure using standardized follow-up forms to guide their examinations. At infants’ six weeks visits, parents completed a satisfaction survey during which they were asked to rate their level of satisfaction with the procedure outcome using a scale between 0 and 100, where 0 = not at all satisfied, and 100 = completely satisfied. Study participants who missed their scheduled visits were followed up at home.
Evaluation of Adverse Events
Any observed complication was referred to study staff and recorded on an adverse events form. We categorized adverse events as mild, moderate, or severe based on criteria previously defined by the WHO(17). Mild bleeding episodes were defined as requiring pressure to control, moderate events required placement of a suture, and severe events were those requiring transfusion. We defined mild infections as requiring local cleaning, a moderate one as needing application of topical antibiotic ointment, and severe ones as requiring systemic antibiotics. A surgical revision was always classified as a severe cosmetic adverse event.
Data Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize provider characteristics, parental and infant characteristics. Differences in provider, parent and infant characteristics between the three neonatal male circumcision methods were compared using the nonparametic Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and the Pearson Chi-square test for categorical variables. Providers ranked the three methods according to preference and ease of use, and the method with the highest rank was tallied. Mean parent satisfaction scores and procedure times were compared across the three circumcision methods, first using a one–way ANOVA model. Pairwise differences were evaluated using the Tukey’s HSD test to control for multiple comparisons.
The classification of the adverse event status for each participant was conducted in two ways. First, participants with missing follow up data were treated as missing at random and removed from the denominator of all calculations. A separate sensitivity analysis classifying these missing patients as having an adverse event provided a conservative estimate of the upper bound for the percentage of adverse events. Adverse events were also tabulated by infant characteristics (such as HIV exposure status, age at procedure, birth and procedure weight) and provider characteristics, including provider type. Although the study was not powered to detect any specific differences in adverse events between the three circumcision methods, a safety analysis was performed for the descriptive comparison of the methods. Data was summarized in terms of percentage of infants experiencing an adverse event at each follow-up visit. Separate comparisons between categorizations of adverse events and between each circumcision method were made using Fisher’s exact test. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.1.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina).
Sample Size
Our sample size was predetermined and based on convenience. Our goal was to train 15–20 providers, who would perform at least 10 circumcisions in each of three methods, for a total of approximately 600 circumcisions (200 per method). Enrollment of infants ended once all healthcare providers had completed at least 30 procedures and reached competency. Some providers completed more than 30 procedures; all procedures were included in the analysis.
The study protocol and informed consent documents underwent continuing ethical review from the relevant Institutional Review Boards at the University of Zambia, the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT01115335.)
Results
Provider characteristics
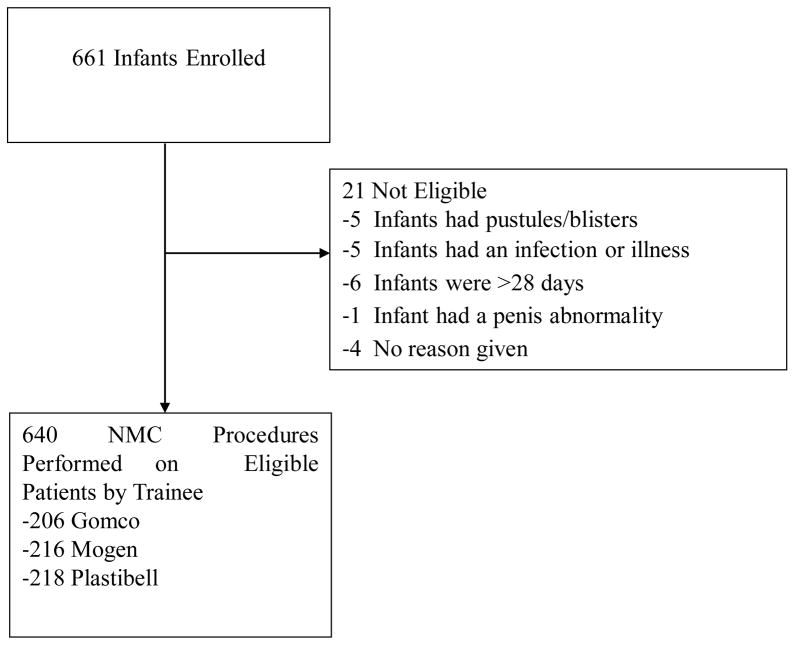
Between October 27, 2009 and March 24, 2011, we enrolled 17 providers into our study, each of whom performed at least 30 circumcisions (10 of each method). 661 infants were enrolled and 21 (3.2%) were excluded due to ineligibility after enrolling. Infants were excluded from the study if they were older than 28 days, had an infection or illness at the time of the procedure, or if they had pustules or blisters on their body. These infants did not undergo circumcision. (Figure 1) The total number of circumcisions performed was 640. Six of the 17 providers (35%) were male, 5 were doctors, 3 were clinical officers, and 9 were nurses or midwives. Of the doctors, 1 was a surgeon. None of the providers had previous experience performing neonatal circumcision, but 5 had experience with adult circumcision. 6 providers were trained in Plastibell first, 6 providers performed Mogen first, and 5 providers were trained in Gomco methods first.
Figure 1.
Diagram of infants enrolled into the neonatal circumcision study
Infant and parent characteristics
635/640 (99%) had a one week follow up visit and 630/640 (98%) were seen at six weeks post-procedure. The median age of the infants at time of circumcision was 11 days (IQR 7–18 days). Approximately 11% were less than 48 hours at the time of the procedure. The median birthweight was 3.2 kg (IQR: 2.9–3.5 kg) and the median weight at the time of the procedure was 3.6 kg (IQR: 3.2–4.0 kg). 23.3% (149/624) were HIV exposed, and 17.2% were delivered by cesarean section. None of these infant characteristics differed by circumcision method. (Table 1) Parental characteristics are described in Table 3. The median age of infant’s mothers was 28 years (IQR:24–32 years) and 34 years (IQR: 30–38 years) for the fathers. The majority of mothers reported being married (92.6%). 70% had a household income greater than $200 US Dollars/month. More than half of all fathers (51.0%) were circumcised. Overall 10.7% of mothers were Muslim and 11.3% of fathers were Muslim. Infants circumcised by the Mogen group were more likely to have a Muslim mother (p=0.001), and have a Muslim father (p<0.001).
Table 3.
Moderate and severe adverse events by circumcision method*
| Mogen (n=212) | Gomco (n=203) | Plastibell (n=215) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| N | Value | N | Value | N | Value | P value | |
| Bleeding | |||||||
| Yes | 2 | 0.9% | 6 | 3.0% | 3 | 1.4% | 0.298 |
| No | 210 | 99.1% | 197 | 97.0% | 212 | 98.6% | |
| Infection | |||||||
| Yes | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.5% | 3 | 1.4% | 0.226 |
| No | 212 | 100.0% | 202 | 99.5% | 212 | 98.6% | |
| Cosmetic | |||||||
| Yes | 8 | 3.8% | 2 | 1.0% | 1 | 0.5% | 0.036 |
| No | 204 | 96.2% | 201 | 99.0% | 214 | 99.5% | |
| Hospitalizations^ | |||||||
| Yes | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 1.0% | 3 | 1.4% | 0.291 |
| No | 212 | 100.0% | 201 | 99.0% | 212 | 98.6% | |
| Any Moderate/Severe | |||||||
| Adverse Event | 10 | 4.7% | 9 | 4.4% | 7 | 3.3% | 0.746 |
| Yes | 202 | 95.3% | 194 | 95.6% | 208 | 96.7% | |
| No | |||||||
In infants with a six week follow up visit
Hospitalizations include infants with a bleeding, infection or cosmetic complication
Parental Preferences
For the 613 mothers and 64 fathers who completed a satisfaction survey, mean satisfaction score for mothers and fathers was 96.4 (SD 7.5) and 95.9 (SD 8.2), respectively, based on a scale from 0 (very dissatisfied) to 100 (very satisfied). Parental satisfaction scores did not differ significantly by method and no pair-wise differences between any two methods was found.
Provider Preferences and procedures
11/17 providers (65%) preferred the Mogen clamp to the Gomco or the Plastibell. (Table 3) The majority of providers (15/17, 88%) also found that the Mogen clamp was the easiest to perform. (Table 3) The mean duration of the procedures differed significantly by method and was 11.5 minutes (SD: +/− 6.7) for the Mogen clamp, 13.9 minutes for the Gomco (SD=+/−6.3), and 11.9 minutes for the Plastibell (SD: +/−4.0)(p<0.001). Tukey-adjusted pairwise comparisons indicated that the duration of the Gomco procedure was 2.4 minutes longer (95%CI: 1.1–3.8 minutes) compared to the Mogen and 2.0 minutes longer (95%CI:0.7–3.4 minutes) compared to the Plastibell procedures. The mean number of procedures to competency was 10.3 (SD:+/−3.3) for Gomco, 10.3 (SD:+/−3.7) for Plastibell and 8.9 (SD:+/−2.9) for the Mogen clamp. All providers were competent in each circumcision method by fifteen procedures. In general, nurses took longer to train than the other providers but this was not statistically significant.
Adverse events
Treating participants with missing follow-up data as missing at random, the overall adverse event rate was 31/630 (4.9%, 95% CI: 3.4%–6.9%). When patients missing a follow-up visit were classified as having an adverse event, the overall adverse event rate was 41/640 (6.4%, 95% CI: 4.6% − 8.6%). The 31 documented adverse events included 5 (16%) which were mild adverse events, 10 (32%) which were moderate events, and 16 (52%) which were severe events. All of the mild events were bleeding events requiring pressure to stop. The ten moderate complications included bleeding needing either Surgicel or a suture to attenuate. The sixteen severe complications included 11 cosmetic issues requiring revisions, one retained Plastibell that required removal in the theatre, three infections requiring intravenous antibiotics and hospitalization, and one transfusion for bleeding in a patient who was delayed on the way to the tertiary hospital. The overall adverse event rate did not differ by method (p=0.609). There were more cosmetic complications with the Mogen clamp compared to the other methods. (Table 4)
Discussion
In this prospective study, one of the largest to date of neonatal circumcision in Africa (18), and the only operational study of its kind, we show that neonatal circumcision can be provided by a variety of health care providers with relatively low complication rates (4.9%). We also found that most providers preferred the Mogen clamp over the Gomco and Plastibell techniques. We observed that providers were more likely to remove insufficient skin with the Mogen clamp, prompting surgical revision. However, this was not statistically significant given the small sample size of our study and the infrequent occurrence of these events.
Our complication rates were relatively low, but higher than rates of other studies from the United States. Between 1963 and 1972, Gee and colleagues retrospectively analyzed almost 6,000 infants who had been circumcised in the United States; approximately half of the infants had been circumcised with the Gomco method and half with the Plastibell method. The overall complication rate was 0.2% with no significant difference between the two different methods(12). Another study of NMC from Israel also report very low complication rates at 0.003% with almost all related to hemorrhage, cosmetic, and penile trauma which is consistent with our causes of morbidity. (14). A few studies in Africa have reported complication rates as high as 20% (19). Our complication rates may be slightly higher than those observed in other studies, given that we classified any post-procedure bleeding as an adverse event – even if it was mild. We also categorized any surgical revision for redundant foreskin as a severe adverse event, whereas other studies have typically excluded cosmetic events. In addition, since our study involved newly trained providers (as opposed to providers who had performed hundreds of procedures) we think it is safe to assume that our complication rates represent the upper limit of what could be expected in real practice. As providers perform more circumcisions and become more skilled, complication rates are likely to decline further. (9)
A recognized weakness of our study is that we did not perform individual infant randomization, but rather chose to assign the providers to different orders of the procedures. Individual randomization would have interfered with analysis of the provider training, as skill development is most easily achieved through repetition of the same technique a number of times in a short time frame. One result of our study design was imbalance between allocations groups. For example, more infants of Asian descent were included in the Mogen method group compared to the other methods, a result of patient clustering. We believe that this can be attributed to similar groups of mothers being brought to the clinic together on a given day by one woman from the community.
In our study, all types of providers preferred the Mogen clamp. This method has many benefits: one size can be used for all clients, the instrument consists of only one piece (versus the Gomco clamp which contains several pieces which much fit together); and it can be sterilized for re-use which may reduce on cost. Our safety outcomes were not significantly different between physicians and nurses although we had relatively few complications. Given the limited number of physicians (the physician patient ratio is 1:14,000 and WHO recommendation is 1:5,000), this method will lend itself to easier scale up using mid level providers. In general, we found that it did take longer for nurses to achieve competency compared to the other types of trainees.
Conclusion
As Southern African countries turn their attention to scaling up early infant circumcision services for future prevention of male HIV acquisition, strategic decisions must be made regarding which method(s) to employ and which types of providers to train. We recommend that countries adopt and focus on a single NMC method, to ensure standardization in provider proficiency, to streamline training and procurement, and to minimize complications. Finally, given that the relatively high complication rates for NMC – particularly when compared to industrialized country settings – carefully monitoring of adverse events is urgently needed and systems to ensure ongoing clinical mentorship and training should be implemented.
Table 2.
Characteristics of parents enrolled in a neonatal circumcision study in Lusaka, Zambia
| Mogen (n=216) | Gomco (n=206) | Plastibell (n=218) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||
| N | Value | N | Value | N | value | P value | |
| Maternal | |||||||
| Age, median (range) | 215 | 28.0 (23.0, 31.0) | 206 | 28.0 (24.0, 33.0) | 216 | 28.0(24.0, 34.0) | 0.064 |
| ≤25 | 80 | 37.2% | 67 | 32.5% | 70 | 32.4% | 0.319 |
| 26–35 | 118 | 54.9% | 113 | 54.9% | 116 | 53.7% | |
| >35 | 17 | 7.9% | 26 | 12.6% | 30 | 13.9% | |
| Religion | |||||||
| Muslim | 34 | 15.8% | 23 | 11.2% | 11 | 5.1% | 0.001 |
| Christian | 181 | 84.2% | 183 | 88.8% | 205 | 94.9% | |
| Education | |||||||
| Primary | 29 | 13.5% | 34 | 16.5% | 45 | 20.8% | 0.046 |
| Secondary | 131 | 60.9% | 117 | 56.8% | 135 | 62.5% | |
| Post-secondary | 55 | 25.6% | 55 | 26.7% | 36 | 16.7% | |
| Marital Status | |||||||
| Married | 198 | 92.1% | 189 | 92.2% | 200 | 93.5% | 0.836 |
| Not Married | 17 | 7.9% | 16 | 7.8% | 14 | 6.5% | |
| Household Income | |||||||
| ≤$50/month | 9 | 4.2% | 6 | 2.9% | 2 | 0.9% | 0.210 |
| $50–$250/month | 54 | 25.1% | 53 | 25.9% | 66 | 30.6% | |
| >$250/month | 152 | 70.7% | 146 | 71.2% | 148 | 68.5% | |
| Father Age | 197 | 33.0 (30.0, 37.0) | 190 | 34.0 (30.0, 37.0) | 198 | 34.0 (30.0, 38.0) | 0.856 |
| ≤25 | 15 | 7.6% | 14 | 7.4% | 13 | 6.6% | 0.784 |
| 26–35 | 114 | 57.9% | 100 | 52.6% | 115 | 58.1% | |
| 36+ | 68 | 34.5% | 76 | 40.0% | 70 | 35.4% | |
| Father circumcised | |||||||
| Yes | 115 | 54.2% | 109 | 52.9% | 99 | 46.0% | 0.191 |
| No | 97 | 45.8% | 97 | 47.1% | 116 | 54.0% | |
| Religion | |||||||
| Muslim | 37 | 17.2% | 23 | 11.2% | 12 | 5.6% | <.001 |
| Christian | 178 | 82.8% | 183 | 88.8% | 203 | 94.4% | |
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge all the patients who participated in the study as well as the dedicated providers. We would also like to acknowledge Richard Levine for initial help in training.
Funding: Funding was provided by the Centers for Disease Prevention & Control (CDC). We have not entered into an agreement with the funder that may have limited our ability to complete the research as planned. We had full control of all primary data and the funder did not assist in (1) study design; (2) the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; (3) the writing of the report; or (4) the decision to submit the paper for publication. All authors contributed substantially to the manuscript.
References
- 1.Nagelkerke NJ, Moses S, de Vlas SJ, Bailey RC. Modelling the public health impact of male circumcision for HIV prevention in high prevalence areas in Africa. BMC Infect Dis. 2007;7:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-7-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moses S, Plummer FA, Bradley JE, Ndinya-Achola JO, Nagelkerke NJ, Ronald AR. The association between lack of male circumcision and risk for HIV infection: a review of the epidemiological data. Sex Transm Dis. 1994 Jul-Aug;21(4):201–10. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199407000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drain PK, Halperin DT, Hughes JP, Klausner JD, Bailey RC. Male circumcision, religion, and infectious diseases: an ecologic analysis of 118 developing countries. BMC Infect Dis. 2006;6:172. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Halperin DT, Bailey RC. Male circumcision and HIV infection: 10 years and counting. Lancet. 1999 Nov 20;354(9192):1813–5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)03421-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bailey RC, Moses S, Parker CB, Agot K, Maclean I, Krieger JN, et al. Male circumcision for HIV prevention in young men in Kisumu, Kenya: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007 Feb 24;369(9562):643–56. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gray RH, Kigozi G, Serwadda D, Makumbi F, Watya S, Nalugoda F, et al. Male circumcision for HIV prevention in men in Rakai, Uganda: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2007 Feb 24;369(9562):657–66. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Auvert B, Taljaard D, Lagarde E, Sobngwi-Tambekou J, Sitta R, Puren A. Randomized, controlled intervention trial of male circumcision for reduction of HIV infection risk: the ANRS 1265 Trial. PLoS Med. 2005 Nov;2(11):e298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Consultation WUT. Male circumcision for HIV prevention: Research implications for policy and programming. Reproductive Health Matters. 2007;15(29):11–4. doi: 10.1016/S0968-8080(07)29307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weiss HA, Dickson KE, Agot K, Hankins CA. Male circumcision for HIV prevention: current research and programmatic issues. AIDS. Oct;24(Suppl 4):S61–9. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000390708.66136.f4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Binagwaho A, Pegurri E, Muita J, Bertozzi S. Male circumcision at different ages in Rwanda: a cost-effectiveness study. PLoS Med. Jan;7(1):e1000211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Weiss HA, Quigley MA, Hayes RJ. Male circumcision and risk of HIV infection in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS. 2000 Oct 20;14(15):2361–70. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200010200-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gee WF, Ansell JS. Neonatal circumcision: a ten-year overview: with comparison of the Gomco clamp and the Plastibell device. Pediatrics. 1976 Dec;58(6):824–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Canadian Pediatric Society FaNC. Neonatal circumcision revisited. Can Med Assoc J. 1996;154:769–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weiss HA, Larke N, Halperin D, Schenker I. Complications of circumcision in male neonates, infants and children: a systematic review. BMC Urol. 10:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-10-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.World Health Organization, UNAIDS, JHPIEGO. Manual for Male circumcision under local anesthesia. 2007 [Google Scholar]
- 16.Government of Zambia, Ministry of Health. National Male Circumcision Strategy and Implementation Plan 2010 – 2020. 2009:6. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Manual for Early Infant Male Circumcision under local anesthesia. Geneva: World Health Organization, JPHIEGO; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Banieghbal B. Optimal time for neonatal circumcision: an observation-based study. J Pediatr Urol. 2009 Oct;5(5):359–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Okeke Linus I, Asinobi Adanze A, Ikuerowo Odunayo S. Epidemiology of complications of male circumcision in Ibadan, Nigeria. BMC Urology. 2006;6:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-6-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]