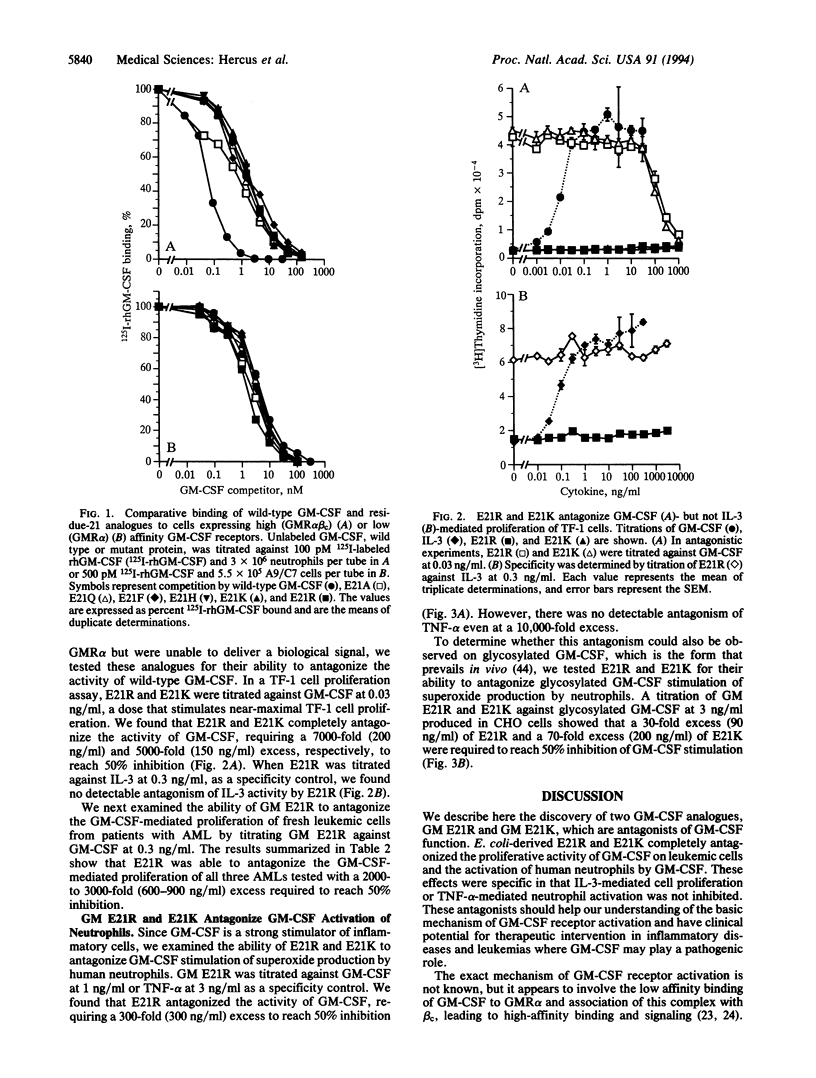
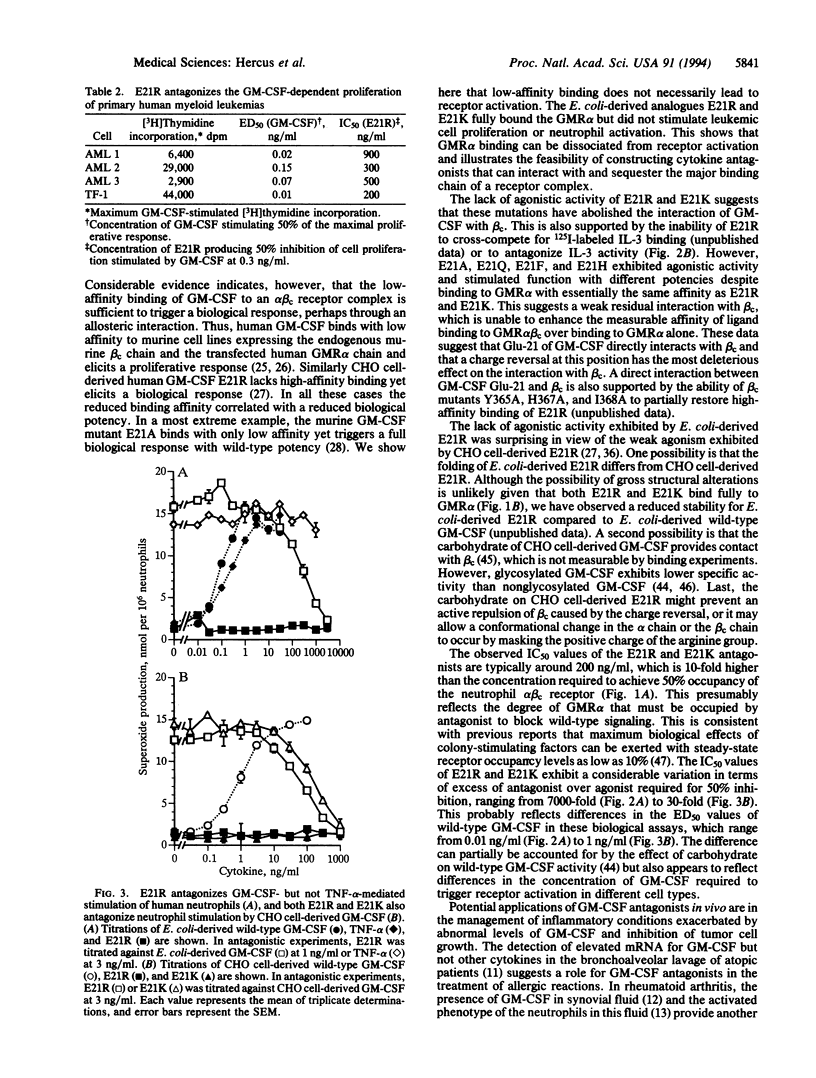
Abstract
Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is a pleiotropic hemopoietic growth factor and activator of mature myeloid cell function. We have previously shown that residue 21 in the first helix of GM-CSF plays a critical role in both biological activity and high-affinity receptor binding. We have now generated analogues of GM-CSF mutated at residue 21, expressed them in Escherichia coli, and examined them for binding, agonistic, and antagonistic activities. Binding experiments showed that GM E21A, E21Q, E21F, E21H, E21R, and E21K bound to the GM-CSF receptor alpha chain with a similar affinity to wild-type GM-CSF and had lost high-affinity binding to the GM-CSF receptor alpha-chain-common beta-chain complex. From these mutants, only the charge reversal mutants E21R and E21K were completely devoid of agonistic activity. Significantly we found that E21R and E21K antagonized the proliferative effect of GM-CSF on the erythroleukemic cell line TF-1 and primary acute myeloid leukemias, as well as GM-CSF-mediated stimulation of neutrophil superoxide production. This antagonism was specific for GM-CSF in that no antagonism of interleukin 3-mediated TF-1 cell proliferation or tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated stimulation of neutrophil superoxide production was observed. E. coli-derived GM E21R and E21K were effective antagonists of both nonglycosylated and glycosylated wild-type GM-CSF. These results show that low-affinity GM-CSF binding can be dissociated from receptor activation and have potential clinical significance for the management of inflammatory diseases and certain leukemias where GM-CSF plays a pathogenic role.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin G. C., Gasson J. C., Quan S. G., Fleischmann J., Weisbart R., Oette D., Mitsuyasu R. T., Golde D. W. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances neutrophil function in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2763–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry S. C., Bagley C. J., Phillips J., Dottore M., Cambareri B., Moretti P., D'Andrea R., Goodall G. J., Shannon M. F., Vadas M. A. Two contiguous residues in human interleukin-3, Asp21 and Glu22, selectively interact with the alpha- and beta-chains of its receptor and participate in function. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8488–8492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebon J., Nicola N., Ward M., Gardner I., Dempsey P., Layton J., Dührsen U., Burgess A. W., Nice E., Morstyn G. Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor from human lymphocytes. The effect of glycosylation on receptor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4483–4491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras M. A., Bale W. F., Spar I. L. Iodine monochloride (IC1) iodination techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:277–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederichs K., Boone T., Karplus P. A. Novel fold and putative receptor binding site of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1779–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1837174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Lopez A. F., Burns G. F., Vadas M. A. Synovial fluid neutrophils of patients with rheumatoid arthritis have membrane antigen changes that reflect activation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Jan;47(1):34–39. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Grunberger T., Correa P., Axelrad A. A., Dube I. D., Cohen A. Autocrine and paracrine growth control by granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):3068–3075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Kaufman S. E., Weisbart R. H., Tomonaga M., Golde D. W. High-affinity binding of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghrayeb J., Kimura H., Takahara M., Hsiung H., Masui Y., Inouye M. Secretion cloning vectors in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2437–2442. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groopman J. E., Mitsuyasu R. T., DeLeo M. J., Oette D. H., Golde D. W. Effect of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on myelopoiesis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 3;317(10):593–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709033171003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida K., Kitamura T., Gorman D. M., Arai K., Yokota T., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9655–9659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasama T., Strieter R. M., Standiford T. J., Burdick M. D., Kunkel S. L. Expression and regulation of human neutrophil-derived macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):63–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Liu M. C., Stealey B. A., Friedman B., Lichtenstein L. M., Permutt S., Schleimer R. P. Production of granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human airways during allergen-induced late-phase reactions in atopic subjects. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1992 Dec;11(6):287–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., O'Hara P. J., Hart C. E., Forstrom J. W., Hagen F. S. Role of carbohydrate in the function of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4861–4867. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Hayashida K., Sakamaki K., Yokota T., Arai K., Miyajima A. Reconstitution of functional receptors for human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): evidence that the protein encoded by the AIC2B cDNA is a subunit of the murine GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5082–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Tange T., Terasawa T., Chiba S., Kuwaki T., Miyagawa K., Piao Y. F., Miyazono K., Urabe A., Takaku F. Establishment and characterization of a unique human cell line that proliferates dependently on GM-CSF, IL-3, or erythropoietin. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Aug;140(2):323–334. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Botstein D. Secretion of beta-lactamase requires the carboxy end of the protein. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):749–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Cuthbertson R. A., Lyons I., Stanley E., Kelso A., Kannourakis G., Williamson D. J., Klintworth G. K., Gonda T. J. Transgenic mice expressing a hemopoietic growth factor gene (GM-CSF) develop accumulations of macrophages, blindness, and a fatal syndrome of tissue damage. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Metcalf D., Battye F. L., Sewell W. A., Vadas M. Activation of granulocyte cytotoxic function by purified mouse colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Shannon M. F., Hercus T., Nicola N. A., Cambareri B., Dottore M., Layton M. J., Eglinton L., Vadas M. A. Residue 21 of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is critical for biological activity and for high but not low affinity binding. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):909–916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Gamble J. R., Begley C. G., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Waltersdorph A., Wong G., Clark S. C., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates in vitro mature human neutrophil and eosinophil function, surface receptor expression, and survival. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI112705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCain R. W., Dessypris E. N., Christman J. W. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates human polymorphonuclear leukocytes to produce interleukin-8 in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;8(1):28–34. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. B. Response. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):412–413. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5068.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Williamson D. J., Nice E. C., De Lamarter J., Mermod J. J., Thatcher D., Schmidt A. Hemopoietic responses in mice injected with purified recombinant murine GM-CSF. Exp Hematol. 1987 Jan;15(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Gearing D. P., Gough N. M. Low-affinity placenta-derived receptors for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor can deliver a proliferative signal to murine hemopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4670–4674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The molecular biology and functions of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):257–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Hassell A. M., Lambert M. H., Jordan S. R., Proudfoot A. E., Graber P., Wells T. N. A novel dimer configuration revealed by the crystal structure at 2.4 A resolution of human interleukin-5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):172–176. doi: 10.1038/363172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Mui A. L., Ogorochi T., Sakamaki K. Receptors for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-3, and interleukin-5. Blood. 1993 Oct 1;82(7):1960–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Peterson L., Hilton D. J., Metcalf D. Cellular processing of murine colony-stimulating factor (Multi-CSF, GM-CSF, G-CSF) receptors by normal hemopoietic cells and cell lines. Growth Factors. 1988;1(1):41–49. doi: 10.3109/08977198809000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Wycherley K., Boyd A. W., Layton J. E., Cary D., Metcalf D. Neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor alpha-chain. Blood. 1993 Sep 15;82(6):1724–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opdenakker G., Rudd P. M., Ponting C. P., Dwek R. A. Concepts and principles of glycobiology. FASEB J. 1993 Nov;7(14):1330–1337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.14.8224606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. H. Autocrine growth factors and leukaemic haemopoiesis. Blood Rev. 1992 Sep;6(3):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(92)90026-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt A. B., Kastelein R. A. High affinity ligand binding is not essential for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25466–25472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt A. B., Miyajima A., Kitamura T., Kastelein R. A. The amino-terminal helix of GM-CSF and IL-5 governs high affinity binding to their receptors. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4105–4112. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. J., Redfield C., Boyd J., Lawrence G. M., Edwards R. G., Smith R. A., Dobson C. M. Human interleukin 4. The solution structure of a four-helix bundle protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):899–904. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90457-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Activation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of human neutrophils and eosinophils by separate colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):795–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. J., Begley C. G., Vadas M. A., Metcalf D. The detection and initial characterization of colony-stimulating factors in synovial fluid. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Apr;72(1):67–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. C., Griffin J. D. Autocrine secretion of GM-CSF in acute myeloblastic leukemia. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1178–1181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



