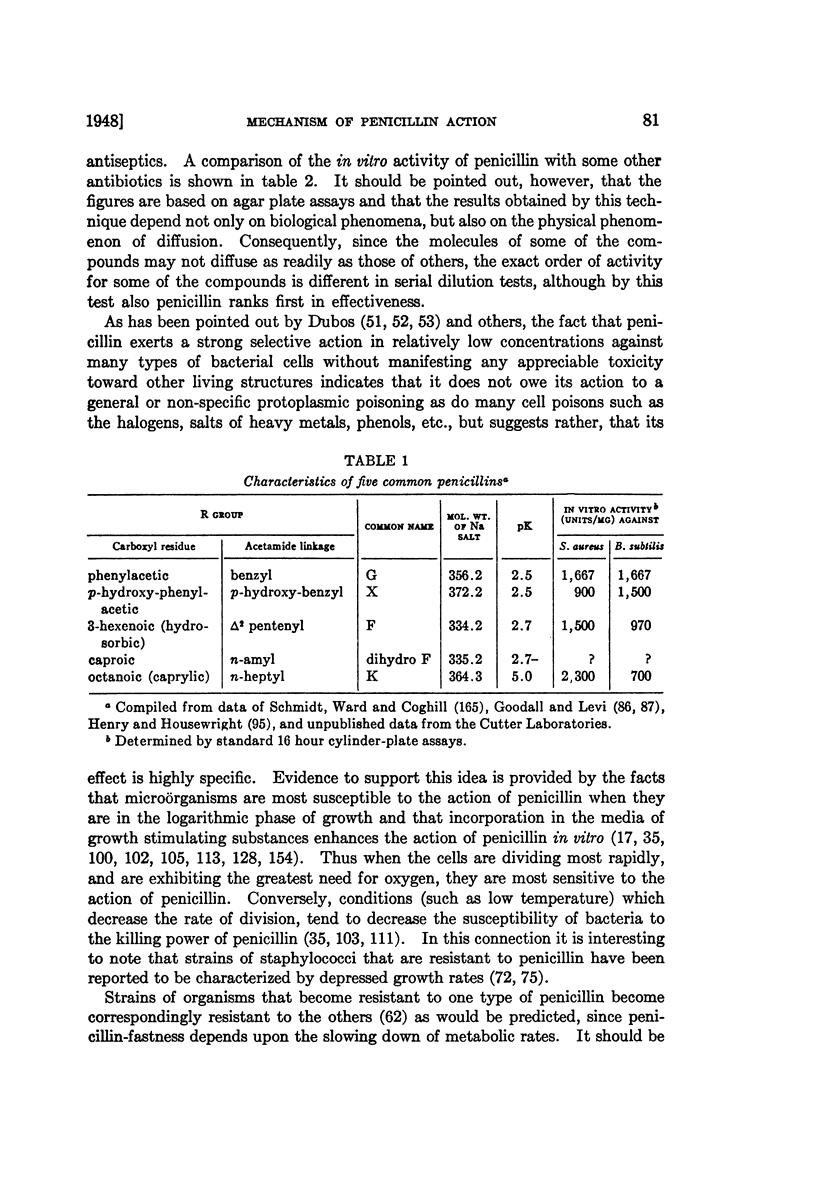
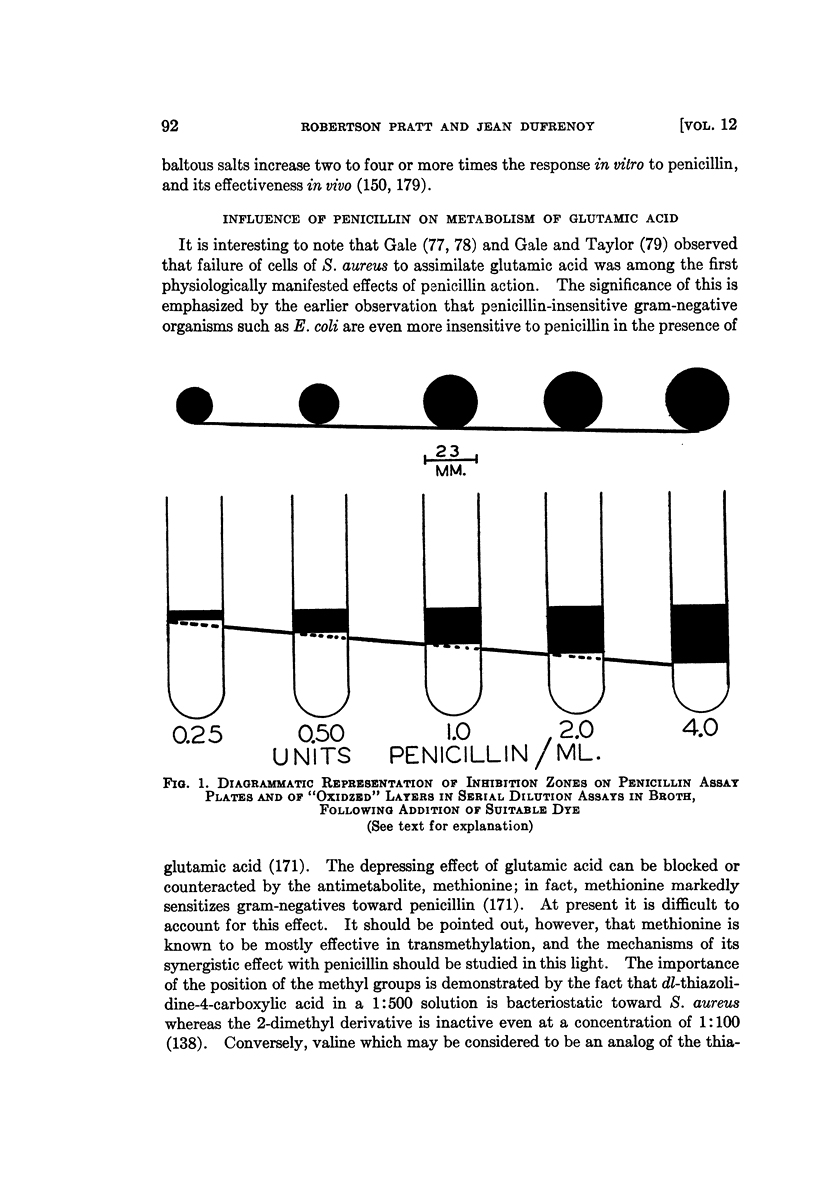
Full text
PDF






















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alture-Werber E., Lipschitz R., Kashdan F., Rosenblatt P. The Effect of Incompletely Inhibitory Concentrations of Penicillin on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1945 Sep;50(3):291–295. doi: 10.1128/jb.50.3.291-295.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anslow W. K., Raistrick H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: Fumigatin (3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-2:5-toluquinone), and spinulosin (3:6-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-2:5-toluquinone), metabolic products respectively of Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius and Penicillium spinulosum Thom. Biochem J. 1938 Apr;32(4):687–696. doi: 10.1042/bj0320687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anslow W. K., Raistrick H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: Spinulosin (3:6-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-2:5-toluquinone) a metabolic product of a strain of Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius. Biochem J. 1938 Dec;32(12):2288–2289. doi: 10.1042/bj0322288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkinshaw J. H., Oxford A. E., Raistrick H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: Penicillic acid, a metabolic product of Penicillium puberulum Bainier and P. cylopium Westling. Biochem J. 1936 Mar;30(3):394–411. doi: 10.1042/bj0300394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallito C. J., Bailey J. H. PRELIMINARY NOTE ON THE INACTIVATION OF ANTIBIOTICS. Science. 1944 Oct 27;100(2600):390–390. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2600.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallito C. J. Penicillin Site of Action. Science. 1947 Feb 28;105(2722):235–236. doi: 10.1126/science.105.2722.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck P. W., Raistrick H. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: The molecular constitution of the metabolic products of Penicillium brevi-compactum Dierckx and related species. II. Mycophenolic acid. Biochem J. 1933;27(3):654–667. doi: 10.1042/bj0270654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghill R. D., Osterberg A. E., Hazel G. R. The Relative Effectiveness of Pure Penicillins G, X, and K. Science. 1946 Jun 14;103(2685):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2685.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornman I. SURVIVAL OF NORMAL CELLS IN PENICILLIN SOLUTIONS LETHAL TO MALIGNANT CELLS. Science. 1944 Mar 24;99(2569):247–247. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2569.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufrenoy J., Pratt R. Cytochemical Mechanisms of Penicillin Action: I. Oxidation-Reduction Levels. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):657–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufrenoy J., Pratt R. Cytochemical Mechanisms of Penicillin Action: III. Effect on Reaction to the Gram Stain in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):283–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Musselman A. The Low Therapeutic Activity of Penicillin K Relative to That of Penicillins F, G, and X, and Its Pharmacological Basis. Science. 1946 May 17;103(2681):618–620. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2681.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisman P. C., Marsh W. S., Mayer R. L. Differentiation of Antibiotics by Resistant Strains. Science. 1946 May 31;103(2683):673–674. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2683.673-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING A., FISH E. W. Influence of penicillin on the coagulation of blood with especial reference to certain dental operations. Br Med J. 1947 Aug 16;2(4519):242–242. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4519.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach H., Eble T. E., Levine J. Ortho-Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid From an Amorphous Penicillin. Science. 1947 Oct 17;106(2755):373–374. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2755.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. M. A Study on the Mechanism of Action of Penicillin as Shown by Its Effect on Bacterial Morphology. J Bacteriol. 1946 Nov;52(5):539–554. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.5.539-554.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florey H. W. Use of Micro-organisms for Therapeutic Purposes. Br Med J. 1945 Nov 10;2(4427):635–642. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4427.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod L. P. Action of Penicillin on Bacteria. Br Med J. 1945 Jan 27;1(4386):107–110. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4386.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossowicz N. Growth Requirements and Metabolism of Neisseria intracellularis. J Bacteriol. 1945 Jul;50(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jb.50.1.109-115.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey R. J. STERILITY TEST FOR PENICILLIN EMPLOYING CYSTEINE FOR INACTIVATION. Science. 1945 Mar 2;101(2618):232–234. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2618.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobby G. L., Lenert T. F., Hyman B. The Effect of Impurities on the Chemotherapeutic Action of Crystalline Penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):305–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.3.305-323.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kalter S. S. The Combined Action of Penicillin and the Sulfonamides in Vitro: The Nature of the Reaction. J Bacteriol. 1946 Jan;51(1):95–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kimmelman L. J. The Correlation between the Inhibition of Drug Resistance and Synergism in Streptomycin and Penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.3.363-370.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Foley E. J., Epstein J. A. Mode of Action of Penicillin: I. Bacterial Growth and Penicillin Activity-Staphylococcus aureus FDA. J Bacteriol. 1944 Oct;48(4):393–399. doi: 10.1128/jb.48.4.393-399.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. R. THE FAILURE OF PURIFIED PENICILLIN TO RETARD THE GROWTH OF GRAFTS OF SARCOMA IN MICE. Science. 1944 Oct 6;100(2597):314–315. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2597.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loofbourow J. R. Intercellular hormones: 7. Release of amino-acids by damaged living yeast cells. Biochem J. 1947;41(1):119–122. doi: 10.1042/bj0410119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldavsky L. F., Hasselbrock W. B., Cateno C., Goodwin D. STUDIES IN MECHANISMS OF PENICILLIN ACTION. I. PENICILLIN EFFECTS ON BLOOD COAGULATION. Science. 1945 Jul 13;102(2637):38–40. doi: 10.1126/science.102.2637.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir R. D., Valley G. A SUGGESTED STERILITY TEST FOR PENICILLIN. Science. 1945 Apr 13;101(2624):390–392. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2624.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANDALAI K. M., GEORGE M. A possible mode of action of penicillin. Br Med J. 1947 Aug 9;2(4518):210–210. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4518.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R., Dufrenoy J. Cytochemical Mechanisms of Penicillin Action: II. Changes in Reactions of Staphylococcus aureus to Vital Dyes. J Bacteriol. 1947 Aug;54(2):127–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R., Dufrenoy J. Cytochemical Mechanisms of Penicillin Action: IV. Comparative Responses of Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria to Penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1947 Dec;54(6):719–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R., Dufrenoy J., Strait L. A. The Enhancement of Penicillin Effectiveness in Vivo by Traces of Cobalt. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jan;55(1):75–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.1.75-77.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. Influence of Phosphate on Stability of Crude Penicillin. Plant Physiol. 1947 Jul;22(3):308–314. doi: 10.1104/pp.22.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savard K., Grant G. A. Ergosterol From the Mycelium of Penicillium notatum (Submerged Culture). Science. 1946 Nov 15;104(2707):459–460. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2707.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. H., Ward G. E., Coghill R. D. Penicillin: VI. Effect of Dissociation Phases of Bacillus subtilis on Penicillin Assay. J Bacteriol. 1945 Apr;49(4):411–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.4.411-412.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan A. J., Eisenstark A., Tanner F. W. Morphology of Escherichia coli Exposed to Penicillin as Observed with the Electron Microscope. J Bacteriol. 1947 Aug;54(2):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.2.183-189.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. J. Effect of Penicillin on Seed Germination. Science. 1946 Nov 1;104(2705):411–413. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2705.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y. Simultaneous Adaptation: A New Technique for the Study of Metabolic Pathways. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):339–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.3.339-348.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. R., Levine M. Some Effects of Penicillin on Intestinal Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1945 Jun;49(6):623–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.6.623-627.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. W., Turner G. S., Drew L. G. Temporary Character of "Fastness" of Staphylococci to Penicillin. Br Med J. 1945 Jan 27;1(4386):111–113. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4386.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. M., Loofbourow J. R. Intercellular hormones: 6. Release and synthesis of factors of the vitamin B complex by damaged living cells. Biochem J. 1947;41(1):114–119. doi: 10.1042/bj0410114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. C., Hill J. H. Studies on Antibacterial Products Formed by Molds: I. Aspergillic Acid, a Product of a Strain of Aspergillus Flavus. J Bacteriol. 1943 May;45(5):433–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.5.433-443.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



