Abstract
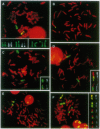
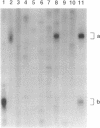
Chromosome-specific DNA libraries can be very useful in molecular and cytogenetic genome mapping studies. We have developed a rapid and simple method for the generation of chromosome-specific DNA sequences that relies on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of a single flow-sorted chromosome or chromosome fragment. Previously reported methods for the development of chromosome libraries require larger numbers of chromosomes, with preparation of pure chromosomes sorted by flow cytometry, generation of somatic cell hybrids containing targeted chromosomes, or a combination of both procedures. These procedures are labor intensive, especially when hybrid cell lines are not already available, and this has limited the generation of chromosome-specific DNA libraries from nonhuman species. In contrast, a single sorted chromosome is a pure source of DNA for library production even when flow cytometric resolution of chromosome populations is poor. Furthermore, any sorting cytometer may be used with this technique. Using this approach, we demonstrate the generation of PCR libraries suitable for both molecular and fluorescence in situ hybridization studies from individual baboon and canine chromosomes, separate human homologues, and a rearranged marker chromosome from a transformed cell line. PCR libraries specific to subchromosomal regions have also been produced by sorting a small chromosome fragment. This simple and rapid technique will allow generation of nonhuman linkage maps and probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization and the characterization of marker chromosomes from solid tumors. In addition, allele-specific libraries generated by this strategy may also be useful for mapping genetic diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beighle C., Karp L. E., Hanson J. W., Hall J. G., Hoehn H. Small structural changes of chromosome 8. Two cases with evidence for deletion. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00295814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlander S. K., Espinosa R., 3rd, Le Beau M. M., Rowley J. D., Díaz M. O. A method for the rapid sequence-independent amplification of microdissected chromosomal material. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1322–1324. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90057-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter N. P., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Perryman M. T., Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Leversha M. A., Glancy M. T., Wood S. L., Cook K., Dyson H. M. Reverse chromosome painting: a method for the rapid analysis of aberrant chromosomes in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):299–307. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. S., Vyas R. C., Deaven L. L., Trujillo J. M., Stass S. A., Hittelman W. N. PCR amplification of chromosome-specific DNA isolated from flow cytometry-sorted chromosomes. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram L. S. Flow cytogenetics and chromosome sorting. Hum Cell. 1990 Jun;3(2):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Cox P. T., Wainwright B. J., Baker K., Mattick J. S. 'Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4008–4008. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Harada N., Yoshiura K., Ohta T., Tohma T., Hirota T., Tsukamoto K., Deng H. X., Oshimura M., Niikawa N. A simple and efficient amplification method of DNA with unknown sequences and its application to microdissection/microcloning. J Biochem. 1992 Jul;112(1):75–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. F., Telenius H., Carter N. P., Miller N. G., Tucker E. M. Chromosome painting using chromosome-specific probes from flow-sorted pig chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;61(3):221–223. doi: 10.1159/000133411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengauer C., Speicher M. R., Popp S., Jauch A., Taniwaki M., Nagaraja R., Riethman H. C., Donis-Keller H., D'Urso M., Schlessinger D. Chromosomal bar codes produced by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization with multiple YAC clones and whole chromosome painting probes. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 May;2(5):505–512. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisitsyn N., Lisitsyn N., Wigler M. Cloning the differences between two complex genomes. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):946–951. doi: 10.1126/science.8438152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Maslen C. L., Smith L., Allen L., Sakai L. Y. Localization of the fibrillin (FBN) gene to chromosome 15, band q21.1. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer P. S., Guan X. Y., Burgess A., Trent J. M. Rapid generation of region specific probes by chromosome microdissection and their application. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander E. A., Jong P. M., Rine J., Duyk G. Construction of small-insert genomic DNA libraries highly enriched for microsatellite repeat sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3419–3423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. P., Bryant E. M., Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Cytogenetic analysis of eight human papillomavirus immortalized human keratinocyte cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1989 Dec 15;44(6):1124–1131. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Borrow J., Goddard A. D. Chromosome aberrations and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1153–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1957167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomfohrde J., Wood S., Schertzer M., Wagner M. J., Wells D. E., Parrish J., Sadler L. A., Blanton S. H., Daiger S. P., Wang Z. Human chromosome 8 linkage map based on short tandem repeat polymorphisms: effect of genotyping errors. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDevanter D. R., Yirdaw G. Recombination between separate MYC amplification structures in COLO320 cells. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Mar;6(3):190–197. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870060310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vooijs M., Yu L. C., Tkachuk D., Pinkel D., Johnson D., Gray J. W. Libraries for each human chromosome, constructed from sorter-enriched chromosomes by using linker-adaptor PCR. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;52(3):586–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Jauch A., Stanyon R., Cremer T. Molecular cytotaxonomy of primates by chromosomal in situ suppression hybridization. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienberg J., Stanyon R., Jauch A., Cremer T. Homologies in human and Macaca fuscata chromosomes revealed by in situ suppression hybridization with human chromosome specific DNA libraries. Chromosoma. 1992 Mar;101(5-6):265–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00346004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. D., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Sillar R., Boyd E. High-resolution analysis of human peripheral lymphocyte chromosomes by flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7727–7731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Prakash O. The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1525–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.7063861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]