Abstract
Oral habits, if persist beyond certain developmental age, can pose great harm to the developing teeth, occlusion, and surrounding oral tissues. In the formative years, almost all children engage in some non-nutritive sucking habits. Clinicians, by proper differential diagnosis and thorough understanding of natural growth and developmental processes, should take a decision for intervening. This article describes case series reports of thumb sucking, finger sucking, and tongue thrusting habits, which have been successfully treated by both removable and fixed orthodontic appliances. The cases shown are ranging from the age group of 9-19 years presenting combination of both mixed and permanent dentition development. All cases show satisfactory correction of habits and stable results.
Keywords: Correcting appliances, damaging oral habits, intervention, patient counseling
Introduction
Various oral habits such as thumb sucking, finger biting, or finger sucking, tongue thrusting, lip biting, or lip sucking, bruxism, mouth breathing can produce destructive effects on the dentoalveolar structures. Trident of factors, like duration of the habit per day, degree, and intensity of habit, are responsible for any habit to produce detrimental and lasting effects.
A habit is a repetitive action that is being done automatically.1 The mouth is the primary and permanent location for expression of emotions and is a source of relief in passion and anxiety in both children and adults, stimulation of this region with tongue, finger, nail or cigarette can be a palliative action.2
Dental changes due to thumb sucking or finger sucking do not need any treatment if the habit is stopped before the age of 5 years, and as soon as giving up the habit, dental changes will be corrected spontaneously.3,4 Thumb sucking habit can be defined as the repeated forceful sucking of the thumb with associated strong buccal and lip musculature contraction. Digit or thumb sucking results in various side-effects as follows:
Anterior open bite5
Increased overjet6
Lingual inclination of lower incisors and the labial inclination of upper incisors
Tongue thrusting can take place because of delayed transition between the infantile and adult swallowing pattern. Normally, the transition begins around the age of 2 years, and by the age of 6 years 50%, has completed the transition. Tongue thrust can also result in open bite, cross bite, overjet and Class II malocclusions.7
In treating these types of cases, following stages should be sequentially carried out to get the best possible results.8 These are:
Direct counseling of the patient by dental surgeon
Reminder therapy
Rewards concept
Orthodontic appliance treatment.
Four different cases of thumb sucking, finger sucking, and tongue thrusting are presented.
Discussion
Tongue crib appliances are extremely effective in breaking the tongue thrusting habit.9-12 According to Proffit and Fields, the anterior tongue position at rest may have a greater impact on the tooth position rather than the tongue pressure during thrusting. Hence, the aim of the treatment primarily is to train the tongue to rest in its normal superior position.3 Case 1, (Figures 1-3) a boy 10 years old presented with a gaping hole in the anterior region from where tongue was protruding. He had mixed dentition and localized malocclusion. He was given a removable appliance with a labial bow, an Adam’s clasp, and tongue crib. The spikes were bent posteriorly to prevent interference with lower anteriors. Patient was trained for placing the tip of the tongue on the palate, close the teeth, close the lip, and then asked to swallow.13 He was told to do this tongue exercises at least 4-5 times a day, and each time for 5 min. Same plate, (Figure 2a and b), was used for initial correction of tongue thrusting habit and later for retroclination of upper anterior teeth. During palatal movement of upper anterior teeth one has to be careful to trim palatal acrylic so as to allow smooth movement of maxillary anteriors.
Figure 1.
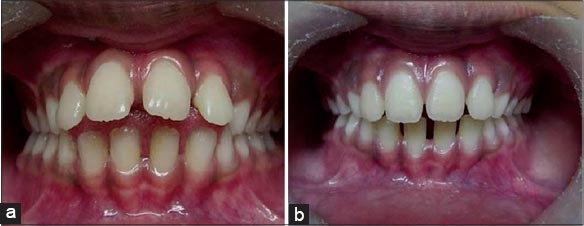
Tongue thrusting: (a) Open bite due to tongue thrusting, (b) post correction.
Figure 2.
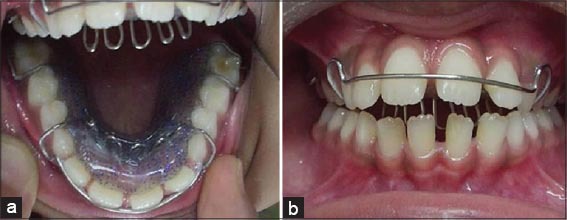
Tongue thrusting: (a and b) Removable plate with palatal crib which were bent posteriorly to avoid lower interference.
Figure 3.
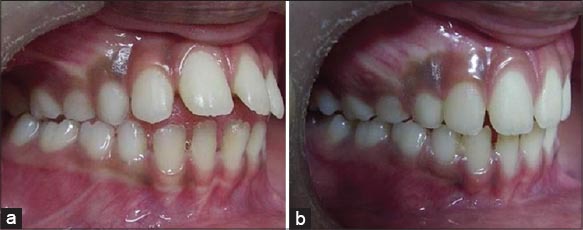
Tongue thrusting: (a) Ill effects of tongue thrusing habit, (b) marked improvement post appliance wear.
Digit and dummy-sucking were the lowest among children who had a good opportunity for breastfeeding.14 Thumb sucking or finger sucking habit is carried out for self-satisfaction. Ceasing an entrenched addictive habit is hard. Keeping progress report card will motivate patients in correction.
The role of the dental surgeon is very important to achieve the desired result. Showing them photographs of damaged dentition may work as a deterrent. No treatment approach should be labeled as punishment. The child should be encouraged to visit the dental office and confide in dentist. Case 2, (Figures 4 and 5a-c), presents localized damage due to finger sucking habit. The damage was restricted on the right lateral side of the mouth. The case responded extremely well with fixed habit correcting appliance. This was followed with fixed appliance therapy for correction of anterior overjet.
Figure 4.
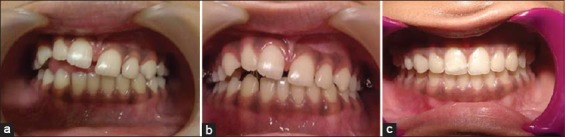
Finger sucking: (a) Localised open bite due to finger sucking, (b) fixed habit breaking appliance, (c) ideal occlusion.
Figure 5.
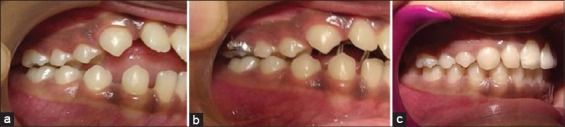
Finger sucking: (a) Tongue protruding from open bite, (b) change within 10 weeks, (c) well settled dentition.
A young girl aged 19 years presented with the extreme case of thumb sucking habit. It had created severe anterior open bite, which was causing a lot of inferiority complex. The habit resulted in extreme proclination of upper anterior teeth. The girl and parents had tried all possible methods to stop the habit, but unfortunately nothing worked. Children who suck vigorously, but intermittently may not displace the incisors much if at all, whereas others who produce 6 h or more of pressure, particularly, those who sleep with a thumb or finger pressure between teeth all night, can cause significant malocclusion.3 Case 3, (Figure 6a and b) was treated with Fixed orthodontic appliances with a habit breaking spikes soldered to molar bands. She responded well to counseling and treatment mechanics. Post-correction of habit, it is necessary to let the appliance act as a retainer to prevent recurrence of the habit.
Figure 6.
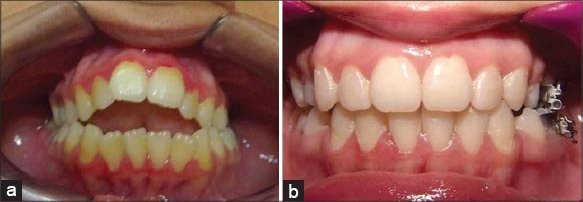
Thumb sucking: (a) Severe dentoalveolar effect due to thumb sucking in a girl aged 19 years, (b) satisfactory correction of habit and malocclusion.
Conclusions
This case reports will help clinician in treating simple and complex malocclusion cases due to damaging oral habits. In today’s highly stressed environment, school/college going kids are subjected to various kinds of pressure/stress in different forms. Oral habit can be a form of destressing. Anterior open bite can become a great source of embarrassment for kids resulting in lack of self-confidence. Clinician should play the role of friend, philosopher and guide to both parents and child indulging in damaging oral habits. Clinician should try initially to break the habit by non-invasive means and if not successful, then pursuing orthodontic correction.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None
Source of Support: Nil
References
- 1.Shahraki N, Yassaei S, Moghadam MG. Abnormal oral habits: A review. J Dent Oral Hyg. 2012;4(2):12–5. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baer PN, Lester M. The thumb, the pacifier, the erupting tooth and a beautiful smile. J Pedod. 1987;11:113–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Proffit WR, Fields HW. Contemporary Orthodontics. 3rd ed. USA: Mosby; 2000. pp. 129–35. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Warren JJ, Bishara SE, Steinbock KL, Yonezu T, Nowak AJ. Effects of oral habits’ duration on dental characteristics in the primary dentition. J Am Dent Assoc. 2001;132(12):1685–93. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2001.0121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gale EN, Ayer WA. Thumb-sucking revisited. Am J Orthod. 1969;55(2):167–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(69)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yemitan TA, daCosta OO, Sanu OO, Isiekwe MC. Effects of digit sucking on dental arch dimensions in the primary dentition. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2010;39(1):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Melsen B, Stensgaard K, Pedersen J. Sucking habits and their influence on swallowing pattern and prevalence of malocclusion. Eur J Orthod. 1979;1(4):271–80. doi: 10.1093/ejo/1.4.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Maguire JA. The evaluation and treatment of pediatric oral habits. Dent Clin North Am. 2000;44(3):659–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sayin MO, Akin E, Karaçay S, Bulakbasi N. Initial effects of the tongue crib on tongue movements during deglutition: A Cine-Magnetic resonance imaging study. Angle Orthod. 2006;76:400–5. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(2006)076[0400:IEOTTC]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Haryett RD, Hansen FC, Davidson PO, Sandilands ML. Chronic thumb-sucking: The psychologic effects and the relative effectiveness of various methods of treatment. Am J Orthod. 1967;53(8):569–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(67)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Villa NL, Cisneros GJ. Changes in the dentition secondary to palatal crib therapy in digit-suckers: A preliminary study. Pediatr Dent. 1997;19(5):323–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schwestka-Polly R, Engelke W, Hoch G. Electromagnetic articulography as a method for detecting the influence of spikes on tongue movement. Eur J Orthod. 1995;17(5):411–7. doi: 10.1093/ejo/17.5.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Premkumar S. Orthodontics Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates. New Delhi, India: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2011. pp. 535–42. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Farsi NM, Salama FS. Sucking habits in Saudi children: Prevalence, contributing factors and effects on the primary dentition. Pediatr Dent. 1997;19(1):28–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


