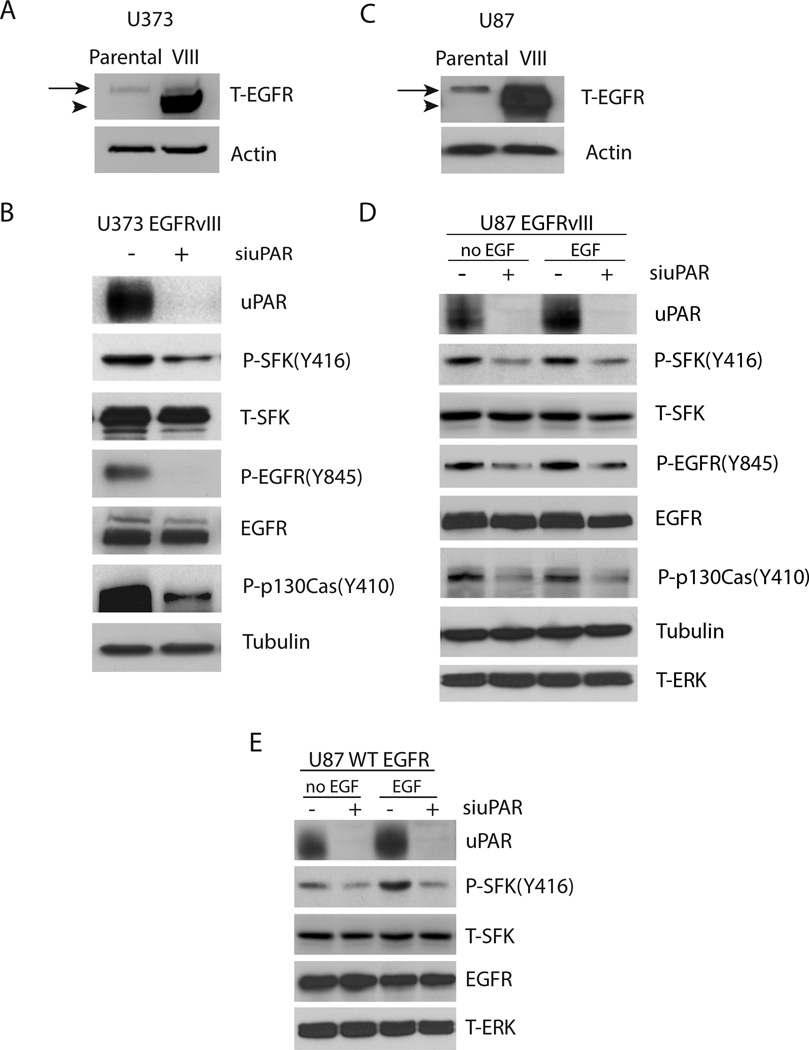
Figure 1.
Regulation of SFK activation by uPAR in EGFRvIII-expressing U373MG and U87MG cells. (a) Cell extracts from parental and EGFRvIII-expressing U373MG cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect total EGFR (T-EGFR) and actin as a loading control. The mobility of wild-type EGFR is shown with an arrow and the mobility of EGFRvIII is shown with an arrowhead. (b) EGFRvIII-expressing U373MG cells were transfected with uPAR-specific (+) or NTC siRNA (−), allowed to recover, and then cultured in SFM for 24 h. Cell extracts were prepared and subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect uPAR, phospho-Tyr-416 in SFKs (P-SFK(Y416)), total SFKs (T-SFK), phosphorylated Tyr-845 in the EGFR (P-EGFR(Y845)), total EGFR, phosphorylated Tyr-410 in p130Cas (P-p130Cas(Y410)) and tubulin. (c) Cell extracts from parental and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect total EGFR (T-EGFR) and actin as a loading control. (d) EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were transfected with uPAR-specific (+) or NTC siRNA (−), allowed to recover, and then cultured in SFM for 24 h. The cells were then treated with EGF (2 ng/mL) for 10 min as specified (the two right-hand lanes). Immunoblot analysis was performed. (e) wt-EGFR-over-expressing U87MG cells and EGFRvIII-expressing U87MG cells were transfected with uPAR-specific (+) or NTC (−) siRNA, transferred to SFM, and treated with EGF (2 ng/mL) or vehicle for 10 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed.