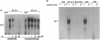Abstract
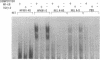
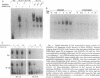
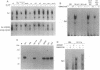
Modified analogues of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs), particularly phosphorothioates ([S]ODNs), have been extensively used to inhibit gene expression. The potential sequence specificity of antisense oligomers makes them attractive as molecular drugs for human diseases. The use of antisense [S]ODNs to inhibit gene expression has been complicated by frequent nonspecific effects. In this study we show in diverse cell types that [S]ODNs, independent of their base sequence, mediated the induction of an Sp1 nuclear transcription factor. The [S]ODN-mediated Sp1 induction was rapid and was associated with elevated levels of Sp1 protein. This induction was dependent on NF-kappa B activity, since inhibition of NF-kappa B activity abolished the [S]ODN-induced Sp1 activity. [S]ODN-induced Sp1 activity was seen in mouse spleen cells following in vivo administration. Sp1 activity induced by [S]ODNs required the tyrosine kinase pathway and did not have transactivating potential. These results may help to explain some of the non-specific effects often seen with [S]ODNs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branda R. F., Moore A. L., Mathews L., McCormack J. J., Zon G. Immune stimulation by an antisense oligomer complementary to the rev gene of HIV-1. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 May 25;45(10):2037–2043. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90014-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B. Inhibition of protooncogene expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides: biological and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res. 1991 Sep 1;51(17):4505–4510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck S. L., Perkins N. D., Carr D. P., Nabel G. J. Inhibition of phorbol ester-induced cellular adhesion by competitive binding of NF-kappa B in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6530–6536. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins K. A., Perez J. R., Coleman T. A., Dorshkind K., McComas W. A., Sarmiento U. M., Rosen C. A., Narayanan R. Antisense inhibition of the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B blocks tumorigenicity and causes tumor regression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9901–9905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Ghersa P., DeRaemy-Schenk A. M., Chen B. P., Hai T., DeLamarter J. F., Whelan J. Cyclic AMP-independent ATF family members interact with NF-kappa B and function in the activation of the E-selectin promoter in response to cytokines. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7180–7190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Wamsley P., Schmitt M. J., Boyer T. G., Zhou Q., Berk A. J., Verma I. M. Association between proto-oncoprotein Rel and TATA-binding protein mediates transcriptional activation by NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):412–419. doi: 10.1038/365412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima I., Shinohara T., Bilakovics J., Brown D. A., Xu X., Nerenberg M. Ablation of transplanted HTLV-I Tax-transformed tumors in mice by antisense inhibition of NF-kappa B. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1792–1795. doi: 10.1126/science.1299224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke S. L., Stein C. A., Zhang X. H., Mori K., Nakanishi M., Subasinghe C., Cohen J. S., Neckers L. M. Characterization of oligonucleotide transport into living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3474–3478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Higgins K. A., Perez J. R., Coleman T. A., Rosen C. A. Evidence for differential functions of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B with a cell adhesion model. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3802–3810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Lawlor K. G., Schaapveld R. Q., Cho K. R., Vogelstein B., Bui-Vinh Tran P., Osborne M. P., Telang N. T. Antisense RNA to the putative tumor-suppressor gene DCC transforms Rat-1 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):553–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Edwards N. L., Duckett C. S., Agranoff A. B., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. A cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV-1 enhancer activation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3551–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak M. Z., Kant J. A., Luger S. M., Hijiya N., Zhang J., Zon G., Gewirtz A. M. In vivo treatment of human leukemia in a scid mouse model with c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11823–11827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Jackson S. P., Annarella M. B. Developmental expression of Sp1 in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2189–2199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Meier B., Männel D. N., Dröge W., Baeuerle P. A. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1181–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Edelman E. R., DeKeyser J. L., Langer R., Rosenberg R. D. Antisense c-myb oligonucleotides inhibit intimal arterial smooth muscle cell accumulation in vivo. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):67–70. doi: 10.1038/359067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloski J. A., Sartorelli A. C., Rosen C. A., Narayanan R. Antisense oligonucleotides to the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B block CD11b expression and alter adhesion properties of differentiated HL-60 granulocytes. Blood. 1993 Jul 15;82(2):625–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Ballard D. W., Greene W. C., Angel P., Herrlich P. Cross-coupling of the NF-kappa B p65 and Fos/Jun transcription factors produces potentiated biological function. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3879–3891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B., Baldwin A. S., Jr Distinct mechanisms for regulation of the interleukin-8 gene involve synergism and cooperativity between C/EBP and NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7191–7198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Tonkinson J. L., Zhang L. M., Yakubov L., Gervasoni J., Taub R., Rotenberg S. A. Dynamics of the internalization of phosphodiester oligodeoxynucleotides in HL60 cells. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4855–4861. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Golanov E., Yamamoto S., Yee F., Ericson H., Yoo H., Inturrisi C. E., Reis D. J. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to NMDA-R1 receptor channel protect cortical neurons from excitotoxicity and reduce focal ischaemic infarctions. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):260–263. doi: 10.1038/363260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Prorock C., Ishikawa H., Maldonado E., Ito Y., Gélinas C. Functional interaction of the v-Rel and c-Rel oncoproteins with the TATA-binding protein and association with transcription factor IIB. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6733–6741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]