Abstract
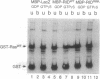
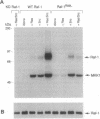
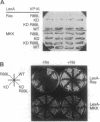
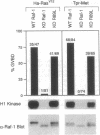
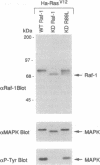
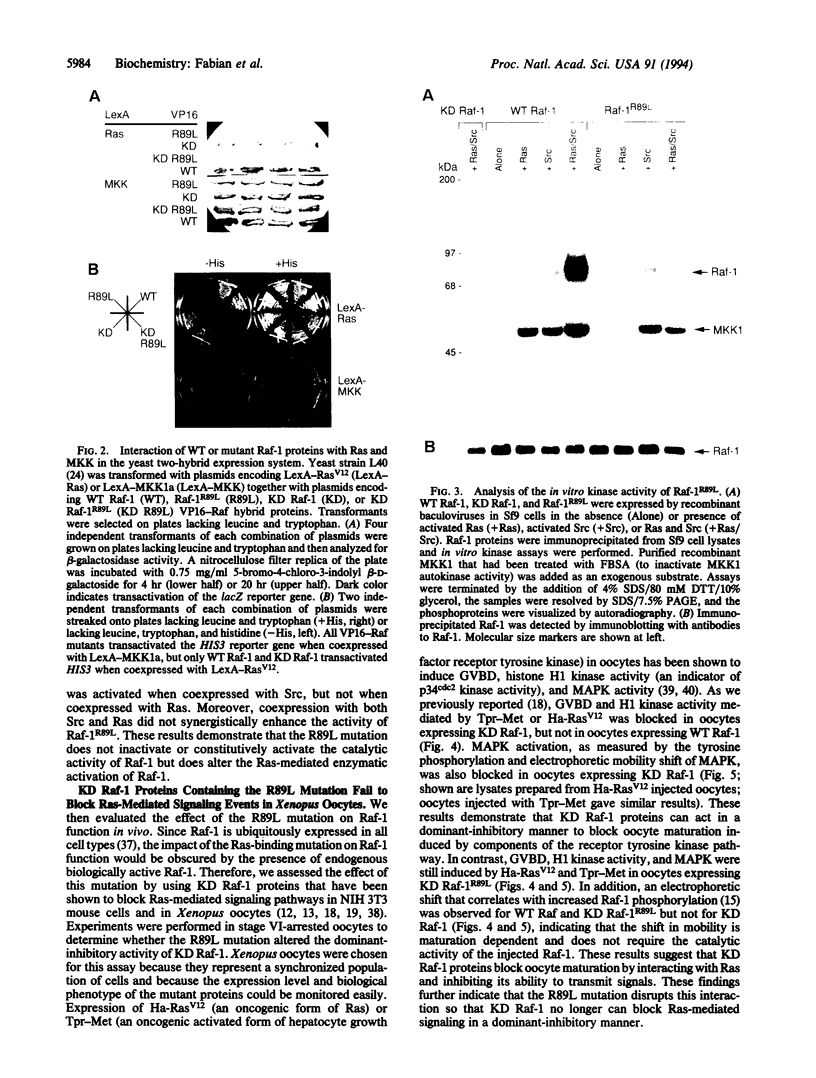
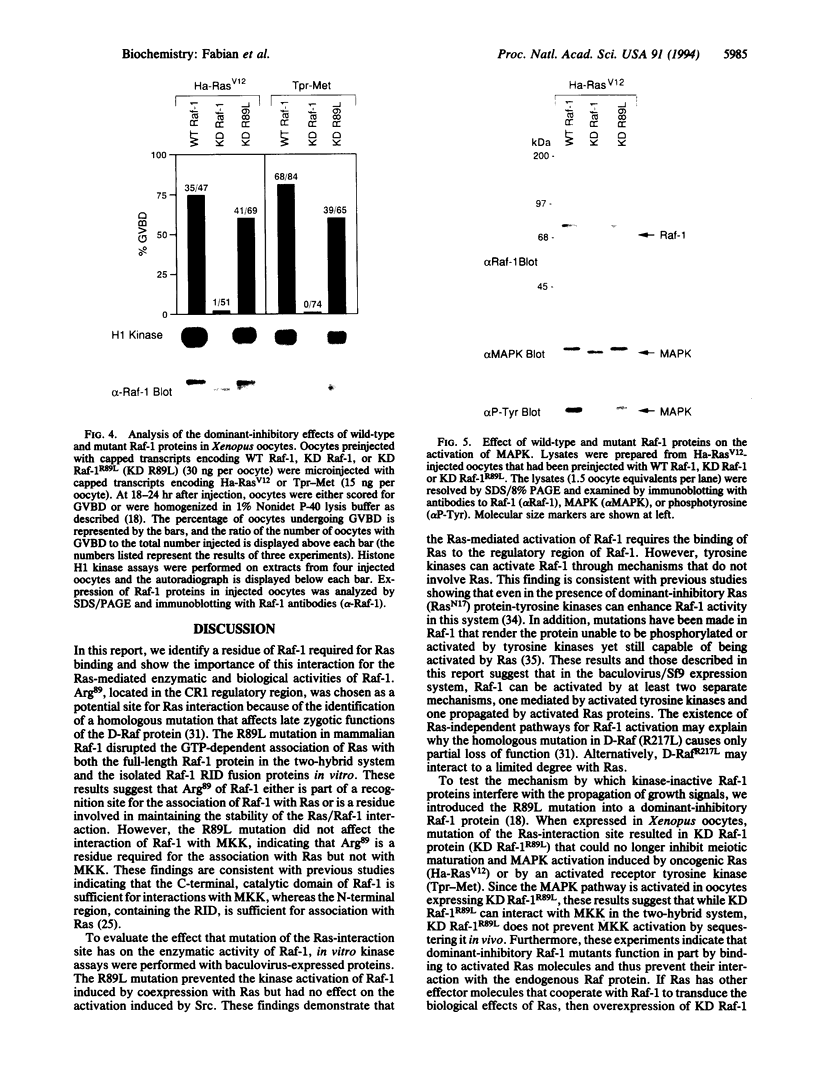
Ras and Raf-1 are key proteins involved in the transmission of developmental and proliferative signals generated by receptor and nonreceptor tyrosine kinases. Genetic and biochemical studies demonstrate that Raf-1 functions downstream of Ras in many signaling pathways. Although Raf-1 directly associates with GTP-bound Ras, an effect of this interaction on Raf-1 activity in vivo has not been established. To examine the biological consequence of the Ras/Raf-1 interaction in vivo, we set out to identify key residues of Raf-1 required for Ras binding. In this report, we show that a single amino acid mutation in Raf-1 (Arg89 to Leu) disrupted the interaction with Ras in vitro and in the yeast two-hybrid system. This mutation prevented Ras-mediated but not tyrosine kinase-mediated enzymatic activation of Raf-1 in the baculovirus/Sf9 expression system. Furthermore, kinase-defective Raf-1 proteins containing the Arg89-->Leu mutation were no longer dominant-inhibitory or capable of blocking Ras-mediated signal transduction in Xenopus laevis oocytes. These results demonstrate that the association of Raf-1 and Ras modulates both the kinase activity and the biological function of Raf-1 and identify Arg89 as a critical residue involved in this interaction. In addition, the finding that tyrosine kinases can stimulate the enzymatic activity of Raf-1 proteins containing a mutation at the Ras-interaction site suggests that Raf-1 can be activated by Ras-independent pathways.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruder J. T., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R. Serum-, TPA-, and Ras-induced expression from Ap-1/Ets-driven promoters requires Raf-1 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):545–556. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., White G. A., Schuh S. M., Ferris D. K., Vande Woude G. F. tpr-met oncogene product induces maturation-producing factor activation in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5985–5991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I., Yew N., Vande Woude G. F. Inhibition of mos-induced oocyte maturation by protein kinase A. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1197–1202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson B., Sprenger F., Morrison D., Hafen E. Raf functions downstream of Ras1 in the Sevenless signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):600–603. doi: 10.1038/360600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian J. R., Morrison D. K., Daar I. O. Requirement for Raf and MAP kinase function during the meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):645–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney R. E., Robbins S. M., Bishop J. M. Association of pRas and pRaf-1 in a complex correlates with activation of a signal transduction pathway. Curr Biol. 1993 Dec 1;3(12):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg B., Rayter S. I., Downward J. Interaction of Ras and Raf in intact mammalian cells upon extracellular stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):3913–3916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Golden A., Han Y., Sternberg P. W. C. elegans lin-45 raf gene participates in let-60 ras-stimulated vulval differentiation. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):133–140. doi: 10.1038/363133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W., Alessandrini A., Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Raf-1 forms a stable complex with Mek1 and activates Mek1 by serine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10947–10951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide H., Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. GTP-dependent association of Raf-1 with Ha-Ras: identification of Raf as a target downstream of Ras in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8683–8686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Kochs G., Hummel R., Vahidi H., Mischak H., Finkenzeller G., Marmé D., Rapp U. R. Protein kinase C alpha activates RAF-1 by direct phosphorylation. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):249–252. doi: 10.1038/364249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Lloyd P., Rapp U. R. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):426–428. doi: 10.1038/349426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNicol A. M., Muslin A. J., Williams L. T. Raf-1 kinase is essential for early Xenopus development and mediates the induction of mesoderm by FGF. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):571–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90143-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick M. B., Perkins L. A., Lee M., Ambrosio L., Perrimon N. Developmental and molecular characterization of mutations in the Drosophila-raf serine/threonine protein kinase. Development. 1993 May;118(1):127–138. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. R., Greenwald I. Two novel transmembrane protein tyrosine kinases expressed during Caenorhabditis elegans hypodermal development. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7133–7143. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Copeland T. D. Identification of the major phosphorylation sites of the Raf-1 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17309–17316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K. The Raf-1 kinase as a transducer of mitogenic signals. Cancer Cells. 1990 Dec;2(12):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muslin A. J., MacNicol A. M., Williams L. T. Raf-1 protein kinase is important for progesterone-induced Xenopus oocyte maturation and acts downstream of mos. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4197–4202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R. Role of Raf-1 serine/threonine protein kinase in growth factor signal transduction. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M. Cell biology. A signal chain of events. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):534–535. doi: 10.1038/360534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., van der Wal J., Howe L. R., Marshall C. J., van Blitterswijk W. J. A dominant-negative mutant of raf blocks mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by growth factors and oncogenic p21ras. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20232–20236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Copeland T. D., Mark G. E., Rapp U. R., Oroszlan S. Detection of the myristylated gag-raf transforming protein with raf-specific antipeptide sera. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):78–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Seger D., Lozeman F. J., Ahn N. G., Graves L. M., Campbell J. S., Ericsson L., Harrylock M., Jensen A. M., Krebs E. G. Human T-cell mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases are related to yeast signal transduction kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25628–25631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm S. M., Cleveland J. L., Rapp U. R. Expression of raf family proto-oncogenes in normal mouse tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeberényi J., Cai H., Cooper G. M. Effect of a dominant inhibitory Ha-ras mutation on neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troppmair J., Bruder J. T., App H., Cai H., Liptak L., Szeberényi J., Cooper G. M., Rapp U. R. Ras controls coupling of growth factor receptors and protein kinase C in the membrane to Raf-1 and B-Raf protein serine kinases in the cytosol. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1867–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. G., Roberts T. M., Li P. Both p21ras and pp60v-src are required, but neither alone is sufficient, to activate the Raf-1 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2922–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]