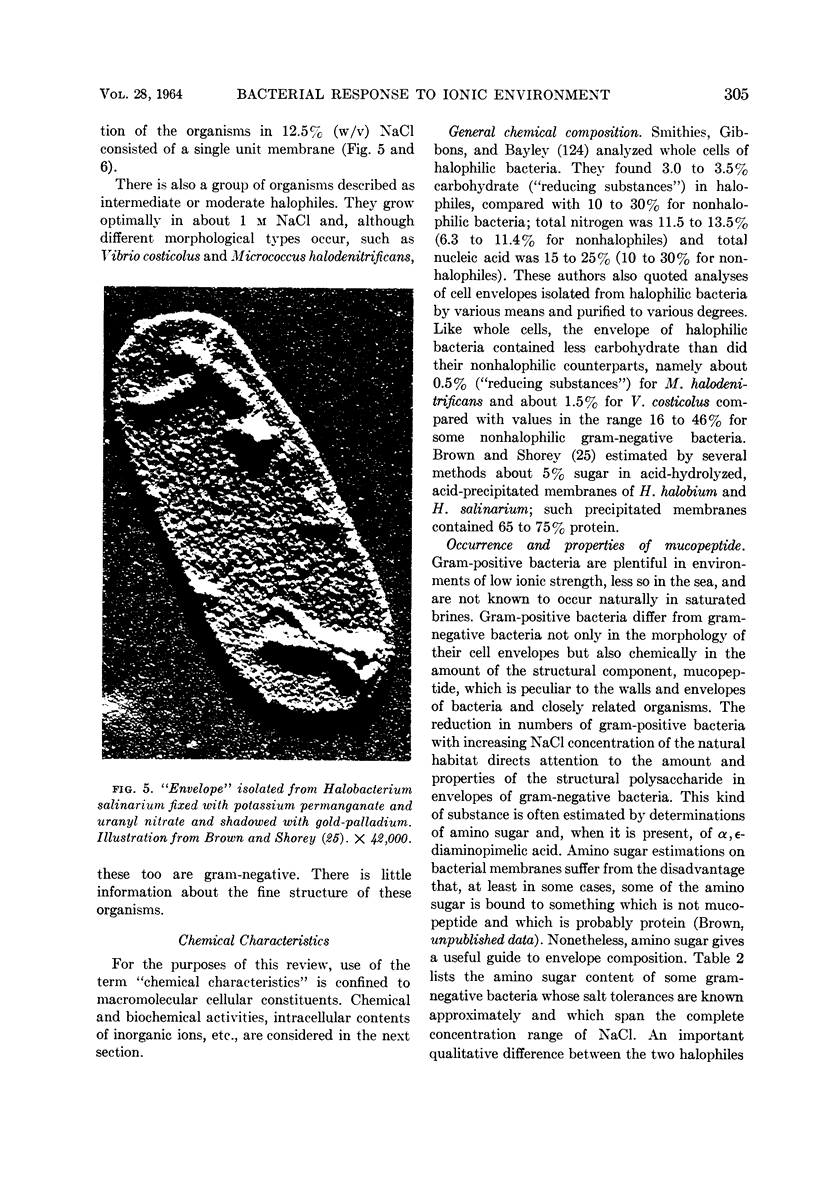
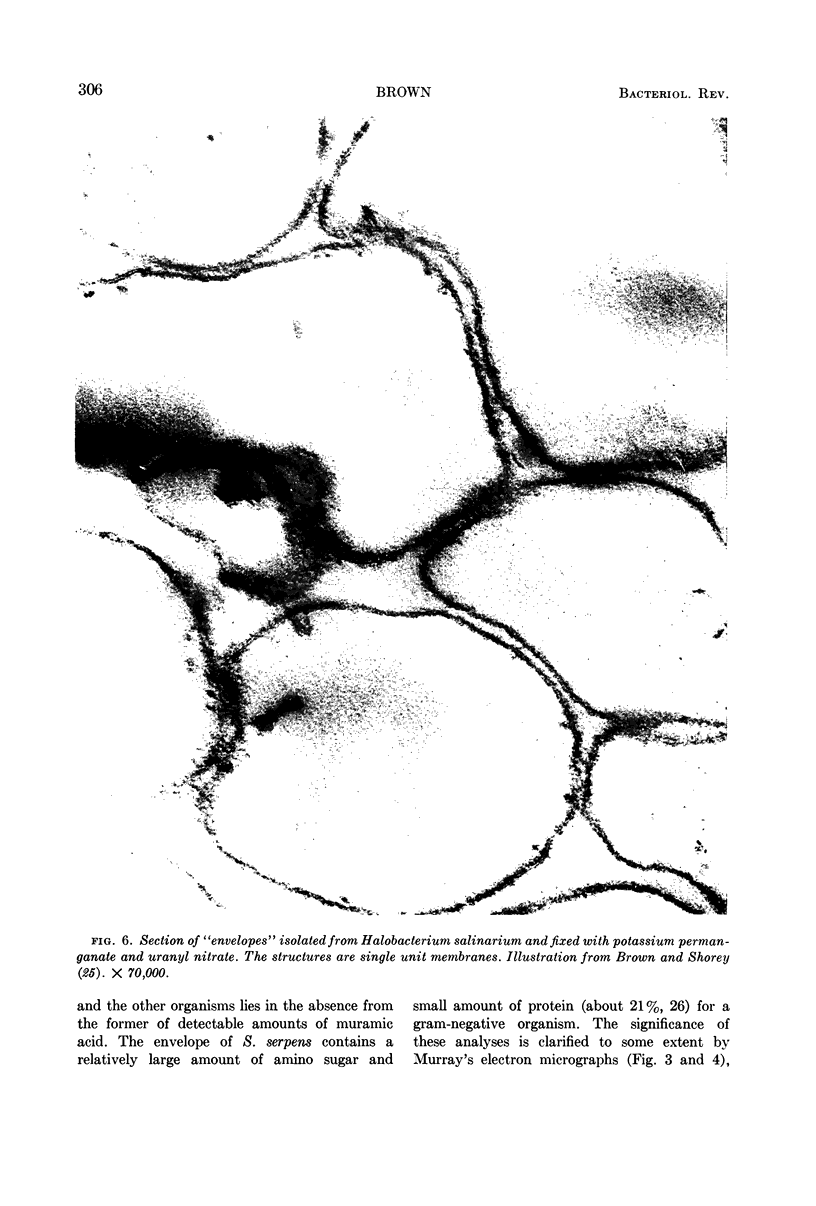
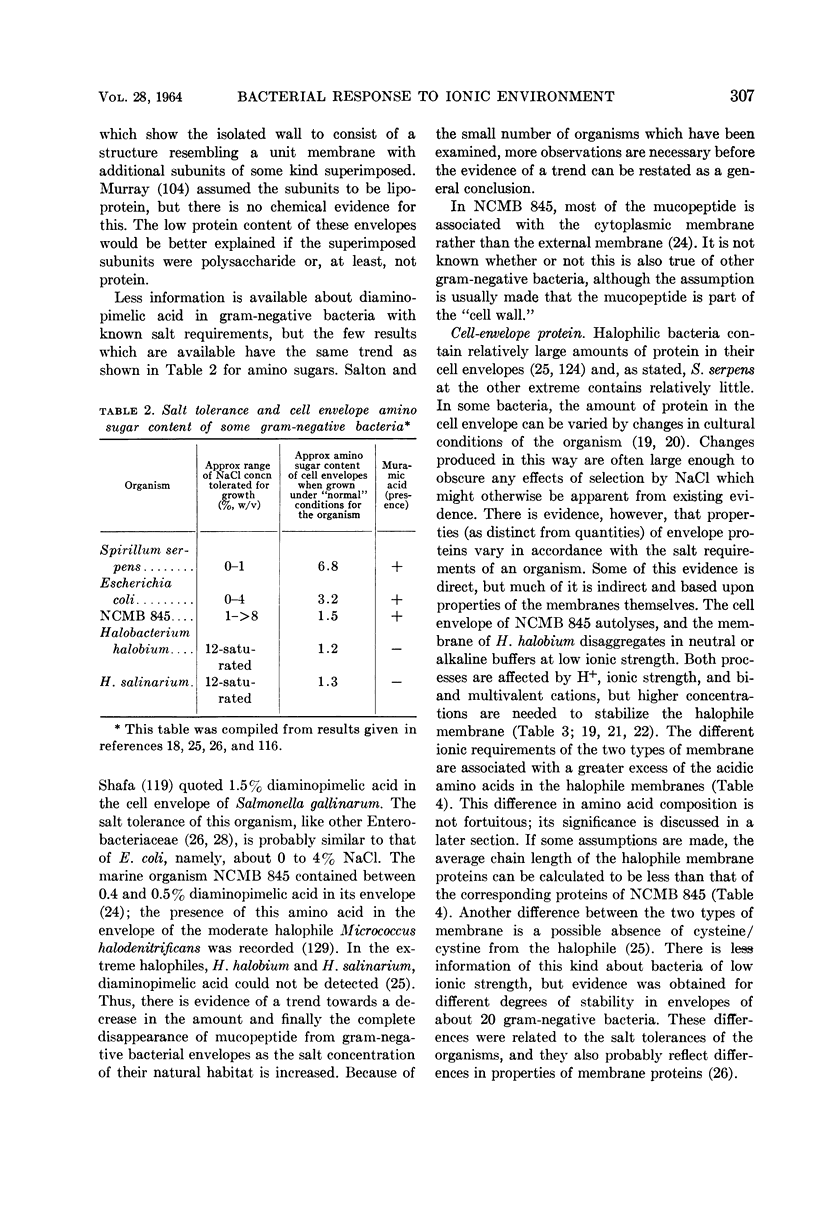
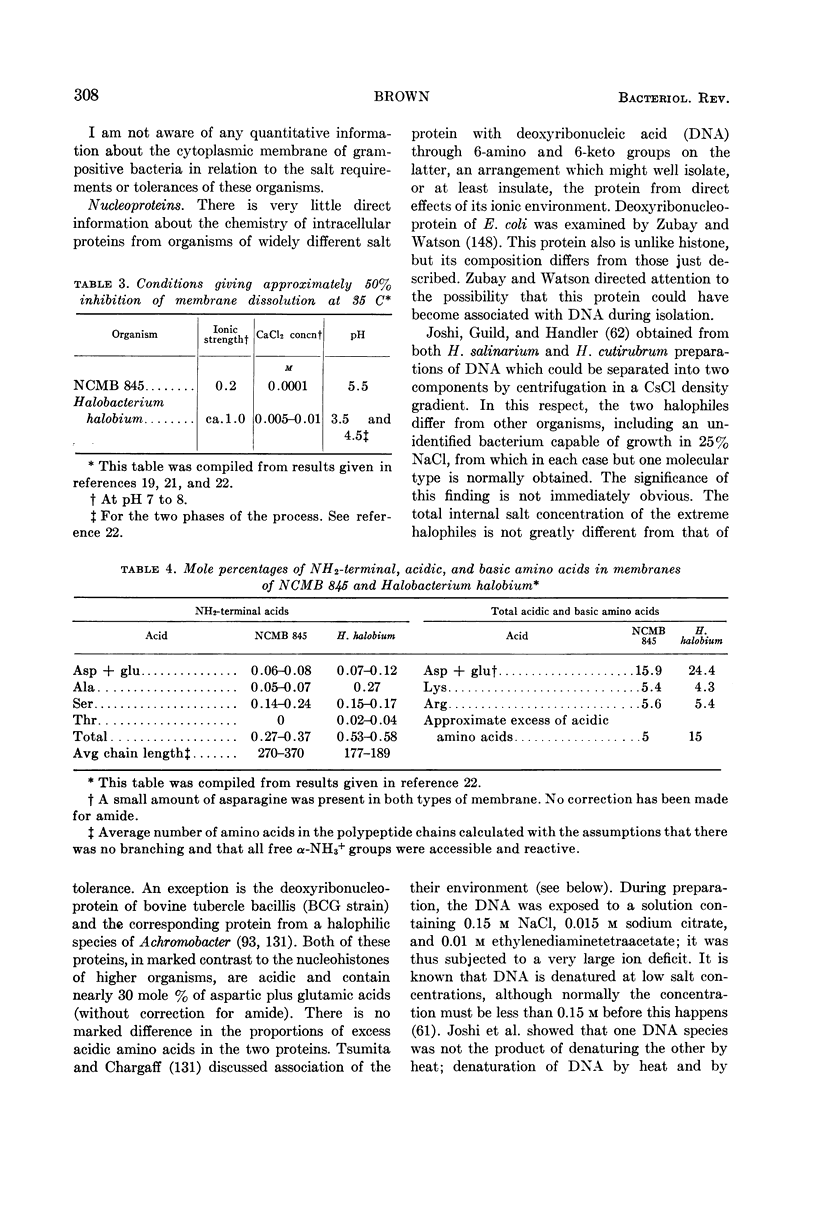
Full text
PDF






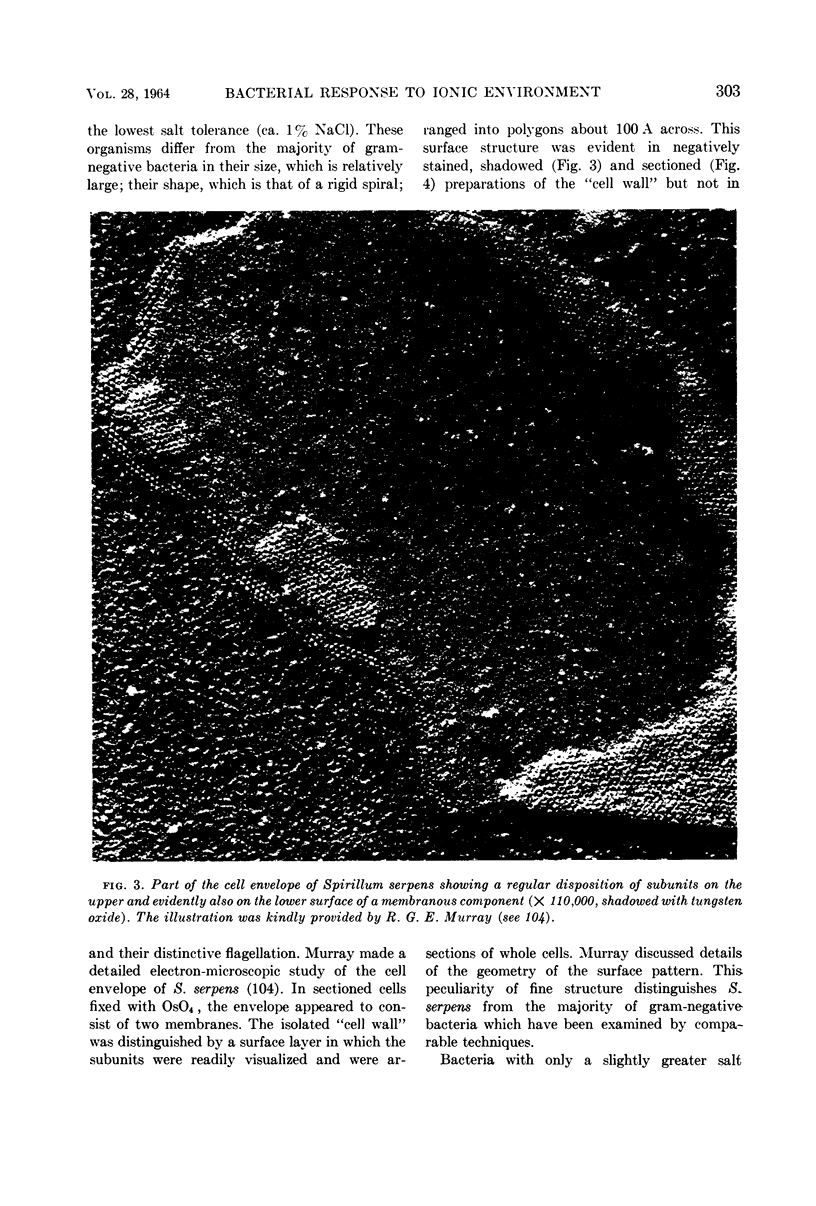
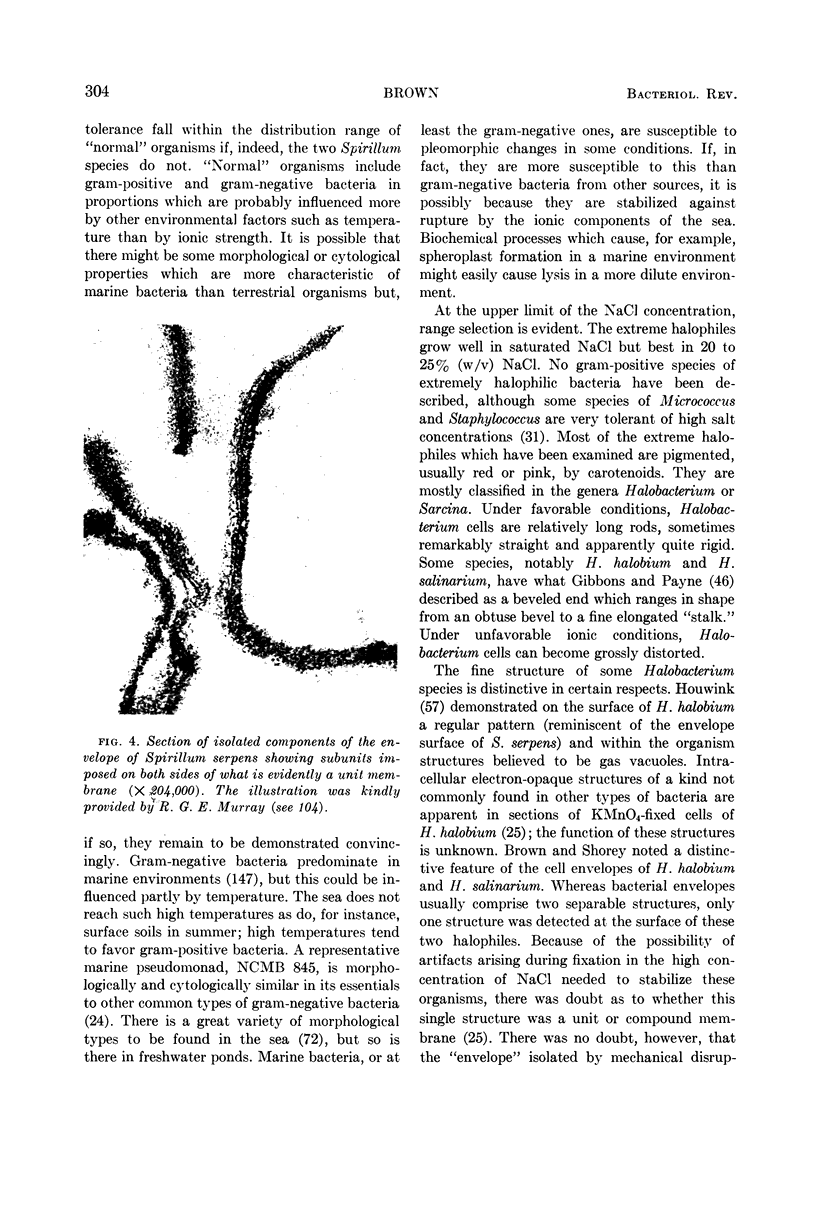

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., KOKETSU K., MIYAMOTO S. Outflux of various phosphates during membrane depolarization of excitable tissues. Am J Physiol. 1962 Mar;202:469–474. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABOOD L. G., KOYAMA I., KIMIZUKA H. A possible mechanism of action of calcium and some psychotomimetic agents on membranes. Nature. 1963 Jan 26;197:367–368. doi: 10.1038/197367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAM D., GIBBONS N. E. The effect of chlorides of monovalent cations, urea, detergents, and heat on morphology and the turbidity of suspensions of red halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Oct;7:741–750. doi: 10.1139/m61-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAM D., GIBBONS N. E. Turbidity of suspensions and morphology of red halophilic bacteria as influenced by sodium chloride concentration. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Oct;6:535–543. doi: 10.1139/m60-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABRAMS A. Reversible metabolic swelling of bacterial protoplasts. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M. An interpretation of the effects of salts on the lactic dehydrogenase of Halobacterium salinarium. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Feb;5(1):47–57. doi: 10.1139/m59-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. Effects of sodium and potassium chloride on certain enzymes of Micrococcus halodenitrificans and Pseudomonas salinaria. Can J Microbiol. 1956 Oct;2(6):599–606. doi: 10.1139/m56-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. The cysteine desulphydrase of Pseudomonas salinaria. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;3(3):461–465. doi: 10.1139/m57-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. The glycerol dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas salinaria, Vibrio costicolus, and Escherichia coli in relation to bacterial halophilism. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1954 May;32(3):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAMENT J. W. Electrical properties of orientated lipid on a biological membrane. An electrostatic diffusion barrier and ion pump. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:217–221. doi: 10.1038/191217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIER M., NORD F. F. On the mechanism of enzyme acition. XLVI. The effect of certain ions on crystalline trypsin and reinvestigation of its isoelectric point. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):320–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D., SHOREY C. D. THE CELL ENVELOPES OF TWO EXTREMELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA. J Cell Biol. 1963 Sep;18:681–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE PERIPHERAL STRUCTURES OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA.IV. THE CATION-SENSITIVE DISSOLUTION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OF THE HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM, HALOBACTERIUM HALOBIUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:425–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D., TURNER H. P. MEMBRANE STABILITY AND SALT TOLERANCE IN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Nature. 1963 Jul 20;199:301–302. doi: 10.1038/199301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. The peripheral structures of gram-negative bacteria. III. Effects of cations of proteolytic degradation of the cell envelope of a marine pseudomonad. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 30;62:132–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN H. N. Reactive sites and biological transport. Adv Protein Chem. 1960;15:239–314. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., SCOTT W. J. Water relations of Salmonellae at 30 degrees C. Aust J Biol Sci. 1953 Nov;6(4):565–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 17;65:506–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. Polyamines and ribosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2112–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLBOURN J. L., WITHERSPOON B. H., HERBST E. J. Effect of intracellular spermine on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 May 13;49:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRISLEY F. D. EFFECT OF SODIUM CHLORIDE ON GROWTH, GLUCOSE UTILIZATION, AND ACID PRODUCTION IN PROTEUS VULGARIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Aug;86:346–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.2.346-347.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK D. A. Osmotic properties of living cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1959;8:387–448. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62736-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNIS H. L., LUBIN M. Dissociation of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in bacteria deprived of potassium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 24;50:399–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90355-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS N. E., PAYNE J. I. Relation of temperature and sodium chloride concentration to growth and morphology of some halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Aug;7:483–489. doi: 10.1139/m61-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBY A. R., FEW A. V., McQUILLEN K. The chemical composition of the protoplast membrane of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jul;29(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBY A. R., FEW A. V. Osmotic properties of protoplasts of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Apr;20(2):321–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., AUDRAIN L. Action de quelques métaux bivalents sur la sensibilité de la sérumalbumine á l'action de la trypsine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952;9(2):180–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L. Rôle du calcium dans le système trypsine-sérumalbumine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1951 Jul;7(2):318–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(51)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURD F. R., WILCOX P. E. Complex formation between metallic cations and proteins, peptides and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1956;11:311–427. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORI K. Electron transporting components participating in nitrate and oxygen respirations from a halotolerant Micrococcus. I. Purification and properties of cytochromes b4 (I) and b4 (II). J Biochem. 1961 Nov;50:440–449. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORI K. Electron transporting components participating in nitrate and oxygen respirations from a halotolerant Micrococcus. II. Properties of cytochrome c551 and brown protein. J Biochem. 1961 Dec;50:481–485. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORI K. Electron transporting components participating in nitrate and oxygen respirations from a halotolerant Micrococcus. III. The pathways of electron transfer. J Biochem. 1963 May;53:354–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUWINK A. L. Flagella, gas vacuoles and cell-wall structure in Halobacterium halobium; an electron microscope study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):146–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY B., VINCENT J. M. Calcium in cell walls of Rhizobium trifolii. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Nov;29:557–561. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-3-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARNEFELT J. Mechanism of sodium transport in cellular membranes. Nature. 1961 May 20;190:694–697. doi: 10.1038/190694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSHI J. G., GUILD W. R., HANDLER P. The presence of two species of DNA in some halobacteria. J Mol Biol. 1963 Jan;6:34–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., SEHGAL S. N., GIBBONS N. E. The lipid composition of Micrococcus halodenitrificans as influenced by salt concentration. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Aug;7:427–435. doi: 10.1139/m61-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNELSON H., LOCHHEAD A. G. Growth factor requirements of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.1.97-103.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNELSON H., ROBINSON J. Observations on the respiratory activity of certain obligately halophilic bacteria with high salt requirements. J Bacteriol. 1956 Feb;71(2):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.2.244-249.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. A physical interpretation of the phenomenological coefficients of membrane permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Sep;45:143–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONO T., COLOWICK S. P. Isolation of skeletal muscle cell membrane and some of its properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Jun;93:520–533. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(61)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKOWSKI M., WU F. C. Temporary inhibition of trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):797–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS S. M., CORPE W. A. PRODIGIOSIN-PRODUCING BACTERIA FROM MARINE SOURCES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:13–17. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.13-17.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDERSTRØM-LANG K. Structure and enzymatic break-down of proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1950;14:117–126. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1950.014.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBIN M. A priming reaction in protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., HORI A., FOX S. M. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. IX. Ion requirements for obtaining and stabilizing isocitric dehydrogenase from a marine bacterium. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Jul;38:693–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., HORI A., FOX S. M. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. X. The glyoxylate cycle in a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Dec;6:639–644. doi: 10.1139/m60-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., HORI A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. VIII. Tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in a marine bacterium and their response to inorganic salts. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:464–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.464-471.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E., NORRIS M. E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. I. Survey of nutritional requirements. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):680–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.680-686.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. II. Observations on the relation of sea water to the growth of marine bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jun;71(6):661–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.6.661-667.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. III. The relation of sodium and potassium to growth. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Dec;50(3):389–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. VI. Quantitative requirements for halides, magnesium, calcium, and iron. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Aug;3(5):753–759. doi: 10.1139/m57-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAEDA A. Some properties of ribonucleic acid from yeast 80S particle; effect of magnesium ions. J Biochem. 1961 Nov;50:377–385. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J. Spermine as a protective agent against osmotic lysis. Nature. 1959 Jun 27;183:1827–1828. doi: 10.1038/1831827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J. The stabilizing effect of spermine and related polyamines and bacterial protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:529–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASUI M., IWATA T., ISHIMITSU A., UMEBAYASHI Y. Deoxyribonucleoprotein of halophilic Achromobacter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Mar 5;55:384–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90795-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Liberation and osmotic properties of the protoplasts of Micrococcus lysodeikticus and Sarcina lutea. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Dec;15(3):512–520. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Permeability of the envelopes of Staphylococcus aureus to some salts, amino acids, and non-electrolytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Apr;20(2):434–441. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-2-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Transport of phosphate across the surface of Micrococcus pyogenes; nature of the cell inorganic phosphate. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Oct;9(2):273–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-9-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P., RUDIN D. O., TIEN H. T., WESCOTT W. C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:979–980. doi: 10.1038/194979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUNUKI K. Denaturation and inactivation of enzyme proteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1961;23:29–82. doi: 10.1002/9780470122686.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITZURRA M., SZYBALSKI W. Formation and multiplication of spheroplasts of Escherichia coli in the presence of lithium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):614–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.614-620.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F., STRANGE R. E. Biochemical changes occurring during sporulation in Bacillus species. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):661–668. doi: 10.1042/bj0630661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN A. Role of the cell membrane in the metabolism of inorganic electrolytes by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Dec;23(4):175–201. doi: 10.1128/br.23.4.175-201.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS H. A stabilized enzyme system for amino acid incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):23–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R., SHAFA F. Some changes in the surface structure of gram-negative bacteria induced by penicillin action. Nature. 1958 May 10;181(4619):1321–1324. doi: 10.1038/1811321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. The lysis of micro-organisms by lysozyme and related enzymes. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):481–490. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLAMOWITZ M., PETERSON L. U. The effect of sodium chloride on peptic digestion of bovine serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 15;46:381–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90762-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOSTRAND F. S. Morphology of ordered biological structures. Radiat Res. 1960;Suppl 2:349–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES W. R., GIBBONS N. E., BAYLEY S. T. The chemical composition of the cell and cell wall of some halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1955 Oct;1(8):605–613. doi: 10.1139/m55-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH L. Structure of the bacterial respiratory-chain system. Respiration of Bacillus subtilis spheroplasts as a function of the osmotic pressure of the medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 30;62:145–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90499-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOECKENIUS W. An electron microscope study of myelin figures. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):491–500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR H. The stabilization of Bacillus subtilis transforming principle by spermine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Mar 10;4:228–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I., GIBBONS N. E. Effect of salt concentration on the morphology and chemical composition of Micrococcus halodenitrificans. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Feb;5(1):25–35. doi: 10.1139/m59-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TCHAN Y. T., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A., JENSEN H. L. The ultrastructure of vegetative cells and cysts of Azotobacter chroococcum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:50–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00408395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUMITA T., CHARGAFF E. Studies on nucleoproteins. VI. The deoxyribonucleoprotien and the deoxyribonucleic acid of bovine tubercle bacilli. (BCG). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):568–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W. STABILIZATION OF PROTOPLASTS AND SPHEROPLASTS BY SPERMINE AND OTHER POLYAMINES. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83(5):1101–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1101-1111.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGAR G., ROMANO D. V. Diffusion across rat diaphragm. I. Movement of sodium and potassium; effect of excitation and correlation with protein structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 15;66:110–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINCENT J. M., HUMPHREY B., NORTH R. J. Some features of the fine structure and chemical composition of Rhizobium trifolii. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Nov;29:551–555. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-3-551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C., BERGSTROM L. The chemical nature of the cytoplasmic membrane and cell wall of Bacillus megaterium, strain M. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Nov;30(2):340–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. Osmotic properties of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Oct;9(2):294–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. The localisation of a permeability barrier in the cells of Bacillus megatherium. Exp Cell Res. 1955 Aug;9(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(55)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., LEUTGEB W. Autolytic enzymes as a source of error in the preparation and study of gram-negative cell walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:127–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., MARTIN H. H. The rigid layer of the cell wall of Escherichia coli strain B. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:158–166. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLMER E. N. Amoeba-flagellate transformation. Exp Cell Res. 1961;Suppl 8:32–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLMER E. N. Steroids and cell surfaces. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1961 Aug;36:368–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1961.tb01295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YON J. [Action of metals on proteolytic enzymes]. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1960;42:1263–1277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUBAY G., WATSON M. R. The absence of histone in the bacterium Escherichia coli. I. Preparation and analysis of nucleoprotein extract. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):51–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]