Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., KOCH G., MOUNTAIN I. M., VAN DAMME O. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid from poliovirus in human cell monolayers. J Exp Med. 1958 Oct 1;108(4):493–506. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.4.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., FRIEDMAN R. M., BUCKLER C. E. Properties of poliovirus inhibitor from monkey brain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 May;113:107–110. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., ISAACS A. Mechanism of recovery from viral infection in the chick embryo. Nature. 1961 Jul 1;191:97–98. doi: 10.1038/191097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEHBEHANI A. M., SULKIN S. E., WALLIS C. Factors influencing susceptibility of mice to Coxsackie virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1962 Mar-Apr;110:147–154. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIG J. M., MACAULEY J. C., WELLER T. H., WIRTH P. Isolation of intranuclear inclusion producing agents from infants with illnesses resembling cytomegalic inclusion disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):4–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALLDORF G. The Coxsackie viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1955;9:277–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.09.100155.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARNELL J. E., Jr, SAWYER T. K. The basis for variation in susceptibility to poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology. 1960 Aug;11:665–675. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY B. E., STEWART S. E. Characteristics of the SE polyoma virus. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1959 Nov;49:1486–1492. doi: 10.2105/ajph.49.11.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGGERS H. J., SABIN A. B. Factors determining pathogenicity of variants of ECHO 9 virus for newborn mice. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:951–967. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS C. A., HOSHIWARA I. Local increase of poliomyelitis virus in healing wound tissue of cynomolgus monkeys. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 May;89(1):86–89. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEBERG H., GOLD E., ROBBINS F. C. DIFFERENCES IN INTERFERON CONTENT IN TISSUES OF MICE OF VARIOUS AGES INFECTED WITH COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Apr;115:947–953. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. IV. Infection of naturally insusceptible cells with enterovirus ribonucleic acid. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):65–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C. The location and nature of enterovirus receptors in susceptible cells. J Exp Med. 1961 Aug 1;114:161–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Receptor affinities as major determinants of enterovirus tissue tropisms in humans. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:312–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S. Comparison of susceptible and resistant cells to infection with poliomyelitis virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Sep 27;61(4):830-8; discussion, 838-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILBOURNE E. D., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Studies of herpes simplex virus in newborn mice. J Immunol. 1951 Oct;67(4):321–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILBOURNE E. D., WILSON C. B., PERRIER D. The induction of gross myocardial lesions by a Coxsackie (pleurodynia) virus and cortisone. J Clin Invest. 1956 Apr;35(4):362–370. doi: 10.1172/JCI103286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILHAM L., MURPHY H. W. Propagation of mumps virus in suckling mice and in mouse embryo tissue cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Jul;80(3):495–498. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., JORDAN W. S., Jr In vitro absorption of poliovirus by noncultured tissues. Effect of species, age and malignancy. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:245–257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
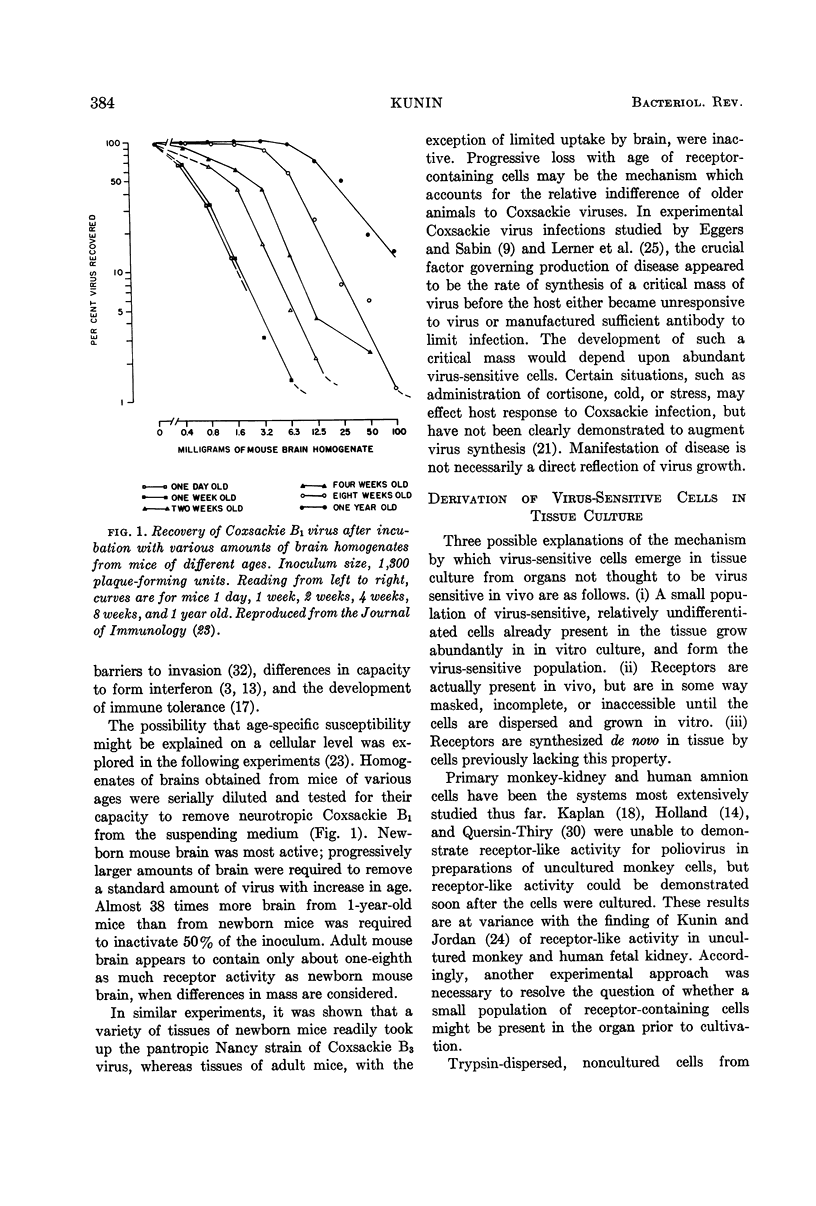
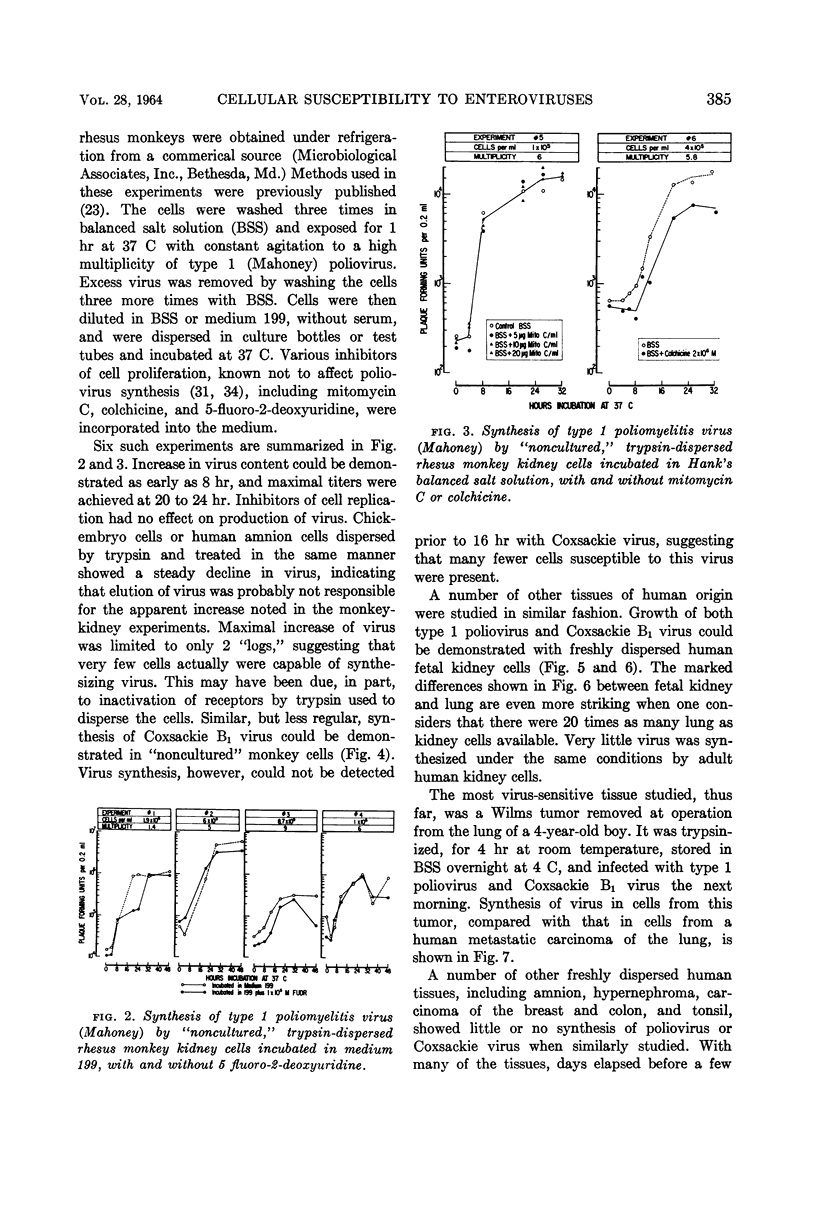
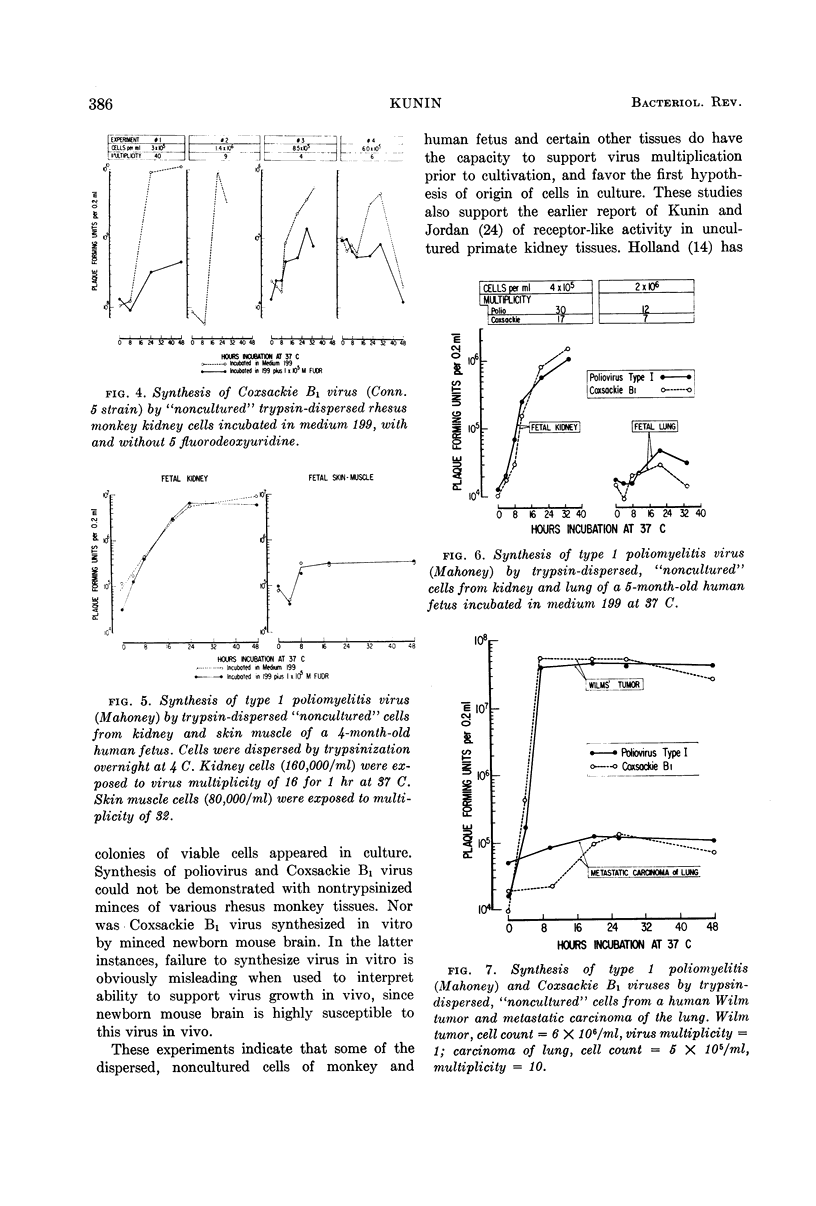
- KUNIN C. M. Virus-tissue union and the pathogenesis of enterovirus infections. J Immunol. 1962 May;88:556–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER A. M., LEVIN H. S., FINLAND M. Age and susceptibility of mice to Coxsackie A viruses. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:745–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE A. E. Effects of viruses on tumors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1954;8:393–410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.08.100154.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLAREN L. C., HOLLAND J. J., SYVERTON J. T. The mammalian cell-virus relationship. I. Attachment of poliovirus to cultivated cells of primate and non-primate origin. J Exp Med. 1959 May 1;109(5):475–485. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.5.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L., BENGTSSON S., BRISHAMMAR S., SVENNERHOLM L., ZETTERQVIST O. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF THE ERYTHROCYTE RECEPTOR FOR HEMAGGLUTINATING ENTEROVIRUSES. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:580–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M. Effect of mitomycin C on the growth of some animal viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Aug;47:1212–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.8.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALZMAN N. P., SHATKIN A. J., SEBRING E. D. Viral protein and DNA synthesis in vaccinia virus-infected HeLacell cultures. Virology. 1963 Apr;19:542–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS M. I., LAVENDER J. F. Studies on the interrelationship between the blood-brain barrier and entry of viruses into the central nervous system. I. The effect of carbon dioxide on type II poliovirus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:107–130. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSKIND R. G., HUEBNER R. J., ROWE W. P., LOVE R. Viral agents oncolytic for human tumors in heterologous host; oncolytic effect of Coxsackie B viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Feb;94(2):309–318. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato G., Zaroff L., Mills S. E. TISSUE CULTURE POPULATIONS AND THEIR RELATION TO THE TISSUE OF ORIGIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jul;46(7):963–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.7.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAINIO T., GWATKIN R., KOPROWSKI H. Production of interferon by brains of genetically resistant and susceptible mice infected with West Nile virus. Virology. 1961 Jul;14:385–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILCEK J. PRODUCTION OF INTERFERON BY NEWBORN AND ADULT MICE INFECTED WITH SINDBIS VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:651–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R. Cellular resistance to viral infection, with particular reference to endogenous interferon. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:72–86. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.72-86.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENNER H. A., KAMITSUKA P. Further observations on the widespread distribution of poliomyelitis virus in body tissues following intramuscular inoculation of cynomolgus monkeys. Virology. 1956 Feb;2(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



