Abstract
The lethal effects of endotoxin, a bacterial product shed into the blood during bacteremia, are thought to be due to macrophage release of mediators such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1. Although much is known about the pathophysiology of endotoxemia, relatively little is known about the cellular signaling mechanisms that are involved. The data in this study suggest that extracellular adenine nucleotides can influence the development of endotoxin shock. An adenine nucleotide analog, 2-methylthio-ATP, inhibited the endotoxin-stimulated release of toxic mediators (i.e., tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1), and it protected mice from endotoxin-induced death. These studies suggest a fundamental and unusual role for adenine nucleotides on endotoxin action, and they provide a potentially new therapeutic approach for the control of the pathophysiology of Gram-negative septicemia.
Full text
PDF
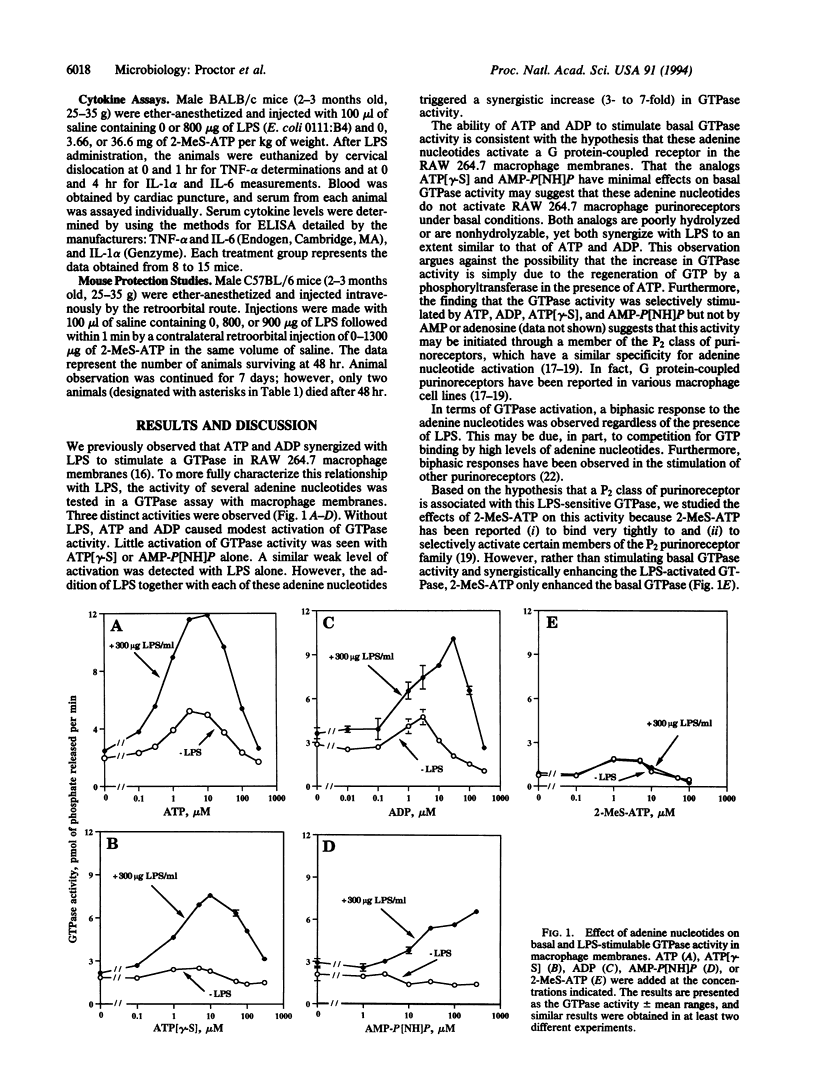
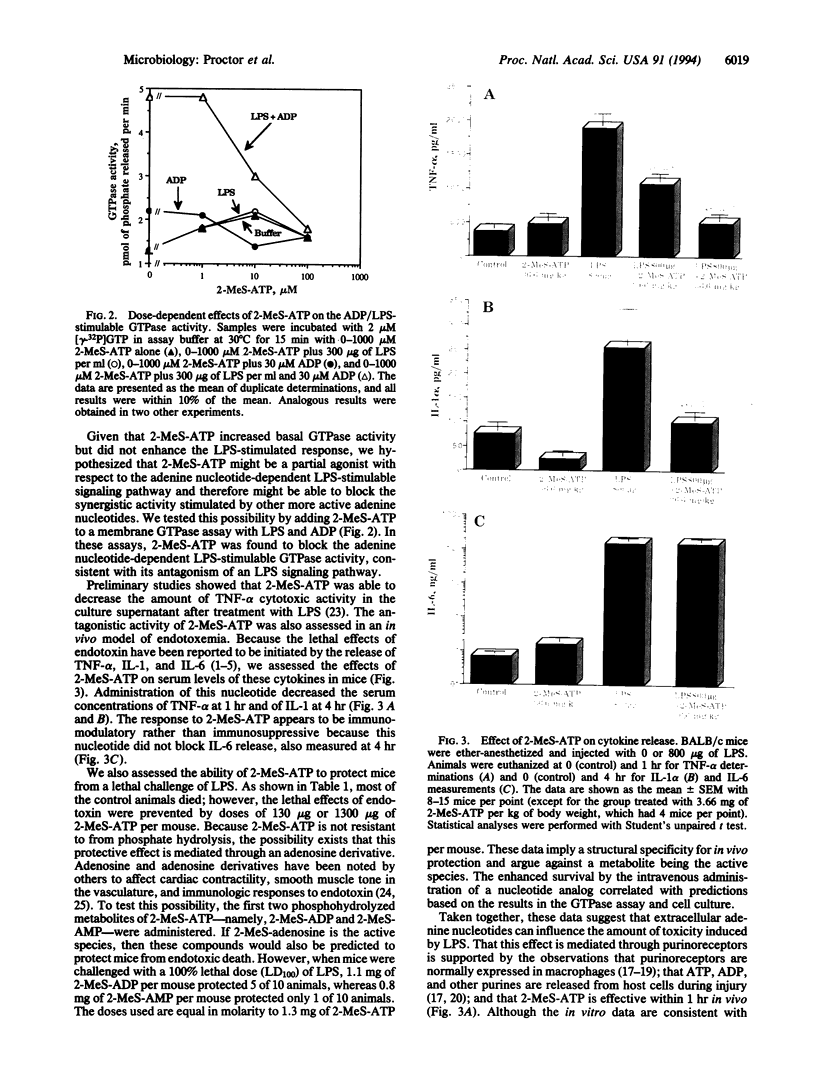

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Overview. Purinergic mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel-Issakani S., Spiegel A. M., Strulovici B. Lipopolysaccharide response is linked to the GTP binding protein, Gi2, in the promonocytic cell line U937. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20240–20247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R. Signal transduction by P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;4(4):295–300. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Pertussis toxin inhibition of B cell and macrophage responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):743–746. doi: 10.1126/science.3095921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. A., Golenbock D. T. Lipopolysaccharide antagonists. Immunol Today. 1992 Jul;13(7):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90009-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Moore R. N., McGhee J. R., Rosenstreich D. L., Mergenhagen S. E. The primary role of lymphoreticular cells in the mediation of host responses to bacterial endotoxim. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Zhou W. W., Edwards C. K., 3rd, Borcherding D. R., Silverstein R., Morrison D. C. Adenosine and a related carbocyclic nucleoside analogue selectively inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha production and protect mice against endotoxin challenge. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I., Corcoran M. L., Horak E. M., Wahl L. M., Bolen J. B., Horak I. D. Lipopolysaccharide induces activation of CD14-associated protein tyrosine kinase p53/56lyn. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20725–20728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6451–6454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanke T., van de Loo J. W., Rhim H., Leventhal P. S., Proctor R. A., Bertics P. J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated GTPase activity in RAW 264.7 macrophage membranes. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):379–385. doi: 10.1042/bj2770379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W. The role of G proteins in transmembrane signalling. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 15;272(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2720001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Wei F. S., Stacey D. W. The effect of GTPase activating protein upon ras is inhibited by mitogenically responsive lipids. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):522–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2536192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein S. L., June C. H., DeFranco A. L. Lipopolysaccharide-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation in human macrophages is mediated by CD14. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3829–3838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing M., Thévenod F., Mattera R. Dual regulation of arachidonic acid release by P2U purinergic receptors in dibutyryl cyclic AMP-differentiated HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6602–6610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Morrison D. C. Pertussis toxin-sensitive factor differentially regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide production in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dornand J., Mani J. C. Extracellular ATP and cell signalling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 19;1134(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]