Abstract
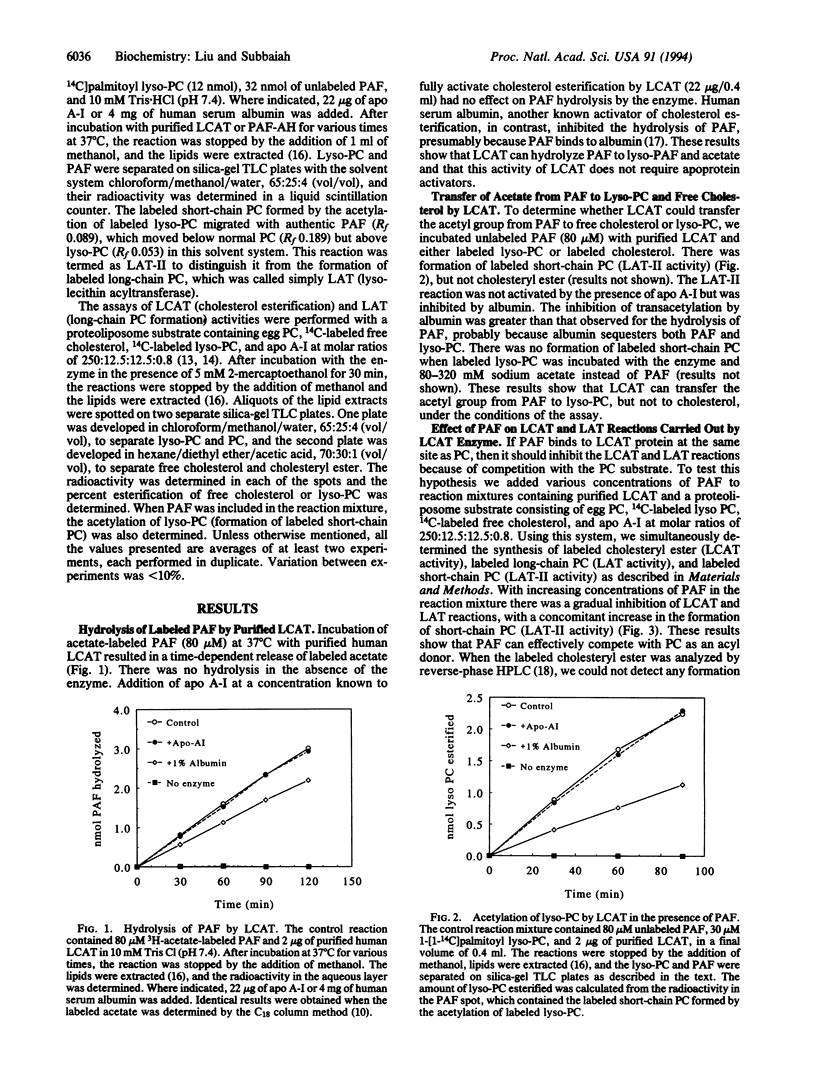
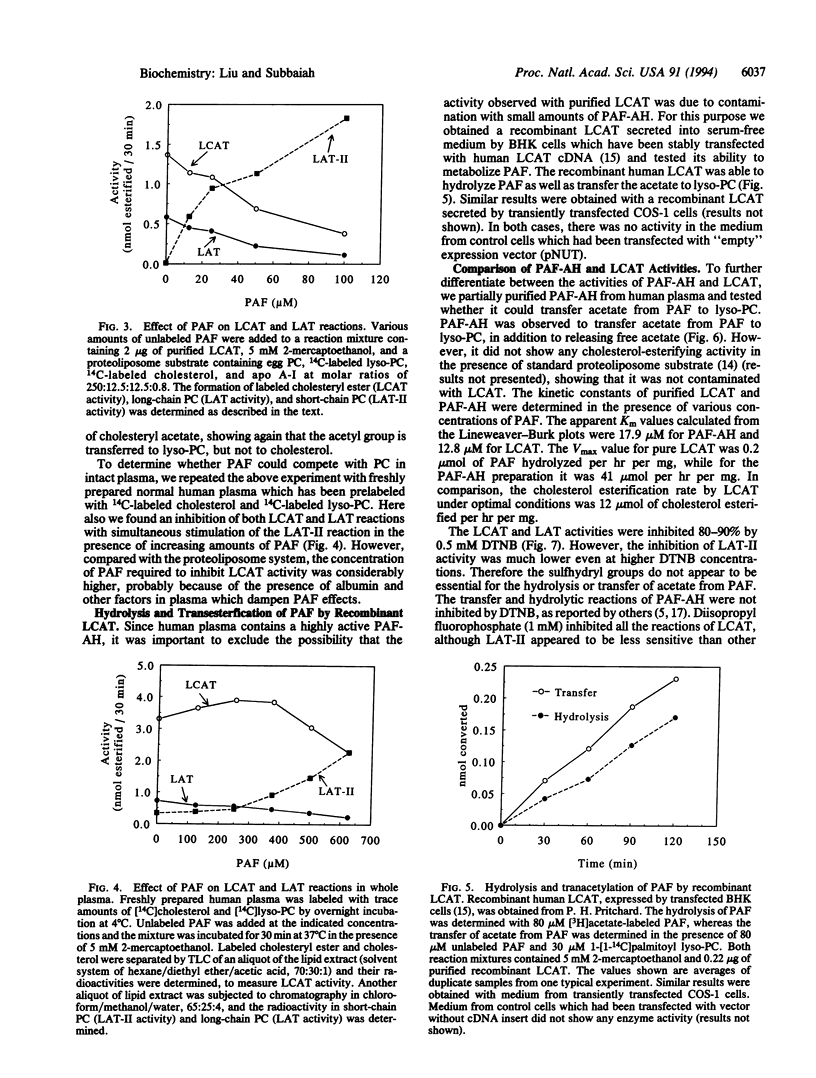
Purified lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT, EC 2.3.1.43) from human plasma was found to hydrolyze platelet-activating factor (PAF) to lyso-PAF and acetate. In addition, it catalyzed the transfer of the acetate group from PAF to lysophosphatidylcholine, forming lyso-PAF and a 1-acyl analog of PAF. In contrast to the cholesterol-esterification reaction carried out by the enzyme, the hydrolysis and transacetylation of PAF by LCAT did not require an apoprotein activator and were not inhibited by sulfhydryl inhibitors but were inhibited by serum albumin. When added to a proteoliposome substrate of LCAT or to whole plasma, PAF inhibited cholesterol esterification by LCAT competitively. PAF acetylhydrolase (EC 3.1.1.47), purified from human plasma, also catalyzed the transfer of acetate from PAF to lysophosphatidylcholine. However, the LCAT-catalyzed reactions of PAF were not due to contamination with PAF acetylhydrolase, since the ratio of acetyl transfer to acetyl hydrolysis was 3 times greater for LCAT, when compared with PAF acetylhydrolase under identical conditions. Furthermore, recombinant human LCAT secreted by baby hamster kidney cells also catalyzed the hydrolysis and transacetylation of PAF. These results demonstrate that LCAT can inactivate PAF in plasma by transacetylation and suggest that it may have a role in the metabolism of PAF, and possibly of oxidized phospholipids, in plasma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam I., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Metabolism of platelet-activating factor by blood platelets and plasma. Lipids. 1983 Aug;18(8):534–538. doi: 10.1007/BF02535393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aron L., Jones S., Fielding C. J. Human plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. Characterization of cofactor-dependent phospholipase activity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7220–7226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank M. L., Hall M. N., Cress E. A., Snyder F. Inactivation of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine by a plasma acetylhydrolase: higher activities in hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):666–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91778-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonelli F. S., Jonas A. Reaction of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase with water-soluble substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14723–14728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Albers J. J. Characterization of proteoliposomes containing apoprotein A-I: a new substrate for the measurement of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):680–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobiásová M. Lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase and the regulation of endogenous cholesterol transport. Adv Lipid Res. 1983;20:107–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francone O. L., Fielding C. J. Effects of site-directed mutagenesis at residues cysteine-31 and cysteine-184 on lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1716–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. S., O K., Wang X., Paranjape S., Dimitrijevich D., Lacko A. G., Pritchard P. H. Expression and characterization of recombinant human lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res. 1993 Jul;34(7):1245–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Uemura Y., Snyder F. A novel CoA-independent transacetylase produces the ethanolamine plasmalogen and acyl analogs of platelet-activating factor (PAF) with PAF as the acetate donor in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):19992–20001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Krul E. S., Subbaiah P. V. Effect of apoprotein B conformation on the activation of lysolecithin acyltransferase and lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Studies with subfractions of low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5139–5147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Subbaiah P. V. Activation of plasma lysolecithin acyltransferase reaction by apolipoproteins A-I, C-I and E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 12;1168(2):144–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90118-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone B., Lee T., Snyder F. Inactivation of platelet activating factor by rabbit platelets. Lyso-platelet activating factor as a key intermediate with phosphatidylcholine as the source of arachidonic acid in its conversion to a tetraenoic acylated product. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1531–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Barnett J. Phospholipase A2 activity of low density lipoprotein: evidence for an intrinsic phospholipase A2 activity of apoprotein B-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9741–9745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17381–17384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard P. H. The degradation of platelet-activating factor by high-density lipoprotein in rat plasma. Effect of ethynyloestradiol administration. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):791–794. doi: 10.1042/bj2460791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Imaizumi T., Kawamura Y., Yoshida H., Takamatsu S., Takamatsu M. Increased activity of the platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in plasma low density lipoprotein from patients with essential hypertension. Prostaglandins. 1989 Jun;37(6):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(89)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini D. M., Carter M. E., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Lipoproteins alter the catalytic behavior of the platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2393–2397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini D. M., McIntyre T. M., Carter M. E., Prescott S. M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Association with lipoprotein particles and role in the degradation of platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4215–4222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafforini D. M., Prescott S. M., McIntyre T. M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4223–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Pritchard P. H. Hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine during LDL oxidation is mediated by platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremler K. E., Stafforini D. M., Prescott S. M., McIntyre T. M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Oxidatively fragmented phospholipids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11095–11103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Albers J. J., Chen C. H., Bagdade J. D. Low density lipoprotein-activated lysolecithin acylation by human plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. Identity of lysolecithin acyltransferase and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9275–9280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Chen C. H., Bagdade J. D., Albers J. J. Substrate specificity of plasma lysolecithin acyltransferase and the molecular species of lecithin formed by the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5308–5314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Liu M., Bolan P. J., Paltauf F. Altered positional specificity of human plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase in the presence of sn-2 arachidonoyl phosphatidyl cholines. Mechanism of formation of saturated cholesteryl esters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 22;1128(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90261-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



