Figure 6. PRMT7 promotes MMP9 expression.
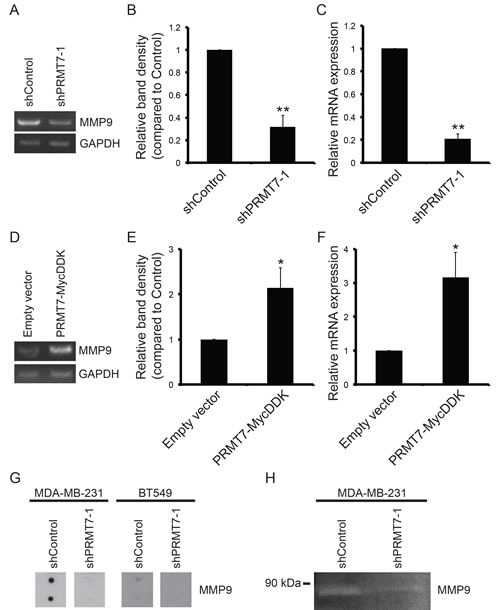
Total RNA was isolated from MDA-MB-231 cells stably depleted of PRMT7 and assessed for mRNA levels by RT-PCR and quantitative RT-PCR. Representative PCR (A) and band density quantitation of MMP9 mRNA levels (B) are shown. GAPDH served as a loading control. Data represents the mean ± standard error of six independent experiments (**p < 0.01). Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MMP9 expression in PRMT7-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells (C). Data represents the mean ± standard error of five independent experiments (**p < 0.01). Total RNA was isolated from MCF7 cells stably expressing PRMT7-MycDDK and assessed for MMP9 mRNA levels by PCR analysis. Representative PCR (D) and band density quantitation of MMP9 mRNA levels (E) are shown. GAPDH served as a loading control. Data represents the mean ± standard error of four independent experiments (*p < 0.05). Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MMP9 expression in MCF7 cells expressing PRMT7-MycDDK compared to empty vector control expressing cells (F). Data represents the mean ± standard error of four independent experiments (*p < 0.05). Secreted MMP9 protein levels were examined in conditioned media using an MMP antibody array. A reduction in secreted MMP9 protein levels was observed in both MDA-MB-231 and BT549 cells with PRMT7 knockdown (G). Gelatin zymography was used to determine the MMP9 enzymatic activity in conditioned media collected from MDA-MB-231 cells expressing a control shRNA (non-targeting) or PRMT7-targeted shRNA. PRMT7 depletion resulted in a reduction in MMP9 enzymatic activity (H).
