Figure 4. Effect of NRs on cell cycle and apoptosis.
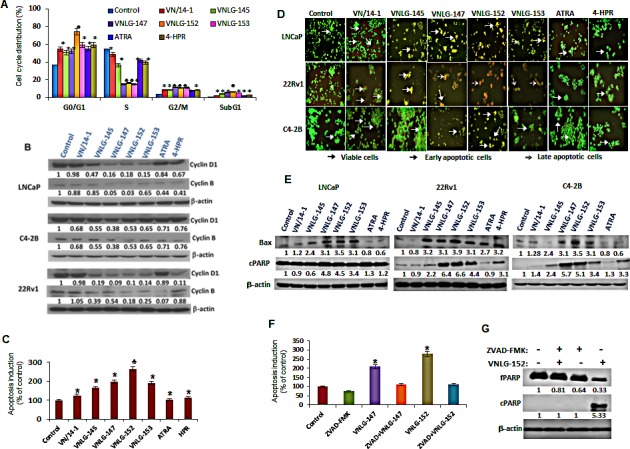
(A) LNCaP cells treated with 5 μM of NRs and other compounds for 24 h were stained with PI and analysed with a FACS calibur flow cytometer. (B) Total cell lysates from PCa cells treated with 20 μM of NRs were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with cyclin D1 and B antibodies. Vehicle treated cells were included as a control and all blots were reprobed for β-actin for equal protein loading and transfer. (C) LNCaP cells were treated with indicated compounds (5 μmol/L) for 24 h and apoptosis induction was examined by oligonucleosomal fragmentation. Data are shown relative to vehicle treated control and the bars are means of three replicate determinations plus standard deviations. *, P< 0.01; ♣, P<0.05 compared with vehicle treated control. (D) PCa cells as indicated were seeded in 24 well plate, and treated with 5 μmol/L of NRs the subsequent day. After 24 h the plates were analyzed for apoptotic and viable cells using acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining. (E) Western blot analysis of apoptosis associated Bax and cPARP in PCa cells treated with NRs (20 μmol/L) for 24 h. (F) Apoptosis induction in LNCaP cells treated with 5 μmol/L of VNLG-147 and -152 in the presence or absence of ZVAD (5 μmol/L) was assessed by oligonucleosomal fragmentation after 24 h incubation. *, P< 0.05 compared with vehicle treated control. (G) Expression of full-length and cleaved PARP protein was investigated by Western blot in LNCaP cells treated with lead NR (VNLG-152, 20 μM) with or without caspase inhibitor ZVAD (5 μmol/L).
