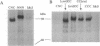Abstract
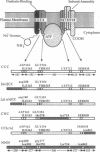
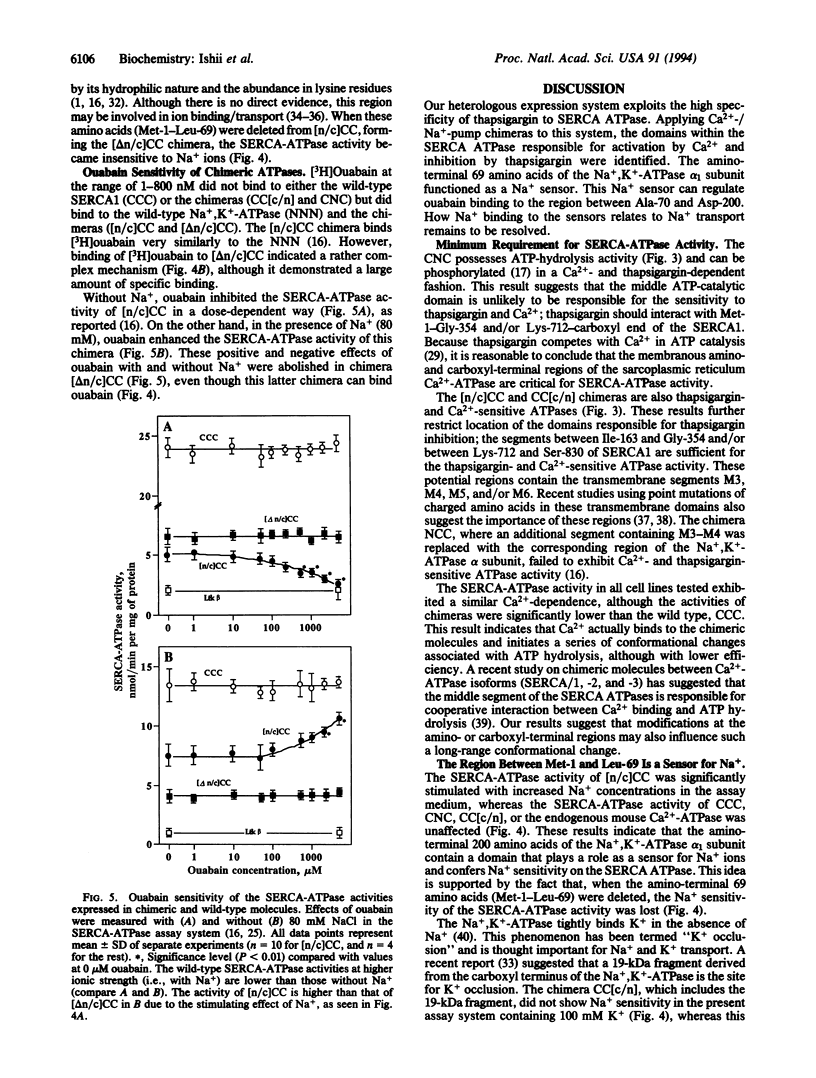
Using the chicken sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ (SERCA)-ATPase as a parental molecule and replacing various portions with the corresponding portions of the chicken Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit, Ca2+/thapsigargin- and Na+/ouabain-sensitive domains critical for these P-type ATPase activities were identified. In the chimera, [n/c]CC, the amino-terminal amino acids Met-1 to Asp-162 of the SERCA (isoform 1) (SERCA1) ATPase were replaced with the corresponding portion (Met-1-Asp-200) of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit. In the chimera CC[c/n], the carboxyl-terminal amino acids (Ser-830 to COOH) of the SERCA1 ATPase were replaced with the corresponding segment (Leu-861 to COOH) of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit, and in the chimera CNC, the middle part (Gly-354-Lys-712) of the SERCA1 ATPase was exchanged with the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit (Gly-378-Lys-724). None of the chimeric molecules exhibited any detectable ouabain-sensitive Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity, but they did exhibit thapsigargin-sensitive Ca(2+)-ATPase activity. Therefore, the segments Ile-163-Gly-354 and Lys-712-Ser-830 of the SERCA1 ATPase are sufficient for Ca2+ and thapsigargin sensitivity. The SERCA1-ATPase activity of [n/c]CC, but not of CCC, CNC, or CC[c/n], was further stimulated by addition of Na+ in the assay medium containing Ca2+. This additional stimulation of SERCA1-ATPase activity by Na+ was abolished when the amino-terminal region (Met-1-Leu-69) of [n/c]CC was deleted ([delta n/c]CC). In the absence of Na+, the SERCA1-ATPase activity of [n/c]CC was inhibited by ouabain, and, in the presence of Na+, its activity was stimulated by this drug. On the other hand, the ATPase activity of [delta n/c]CC was not affected by ouabain, although [delta n/c]CC can still bind [3H]ouabain. These results suggest that a distinct Na(+)-sensitive domain (Na+ sensor) located within the restricted amino-terminal region (Met-1-Leu-69) of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit regulates ATPase activity. The Na+ sensor also controls ouabain action in concert with the major ouabain-binding region between Ala-70 and Asp-200 of alpha 1 subunit.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. P., Vilsen B. Functional consequences of alterations to Glu309, Glu771, and Asp800 in the Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19383–19387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blostein R., Zhang R., Gottardi C. J., Caplan M. J. Functional properties of an H,K-ATPase/Na,K-ATPase chimera. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10654–10658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgener-Kairuz P., Horisberger J. D., Geering K., Rossier B. C. Functional expression of N-terminal truncated alpha-subunits of Na,K-ATPase in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81231-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Kessler P. D., Sagara Y., Inesi G., Fambrough D. M. Nucleotide sequences of avian cardiac and brain SR/ER Ca(2+)-ATPases and functional comparisons with fast twitch Ca(2+)-ATPase. Calcium affinities and inhibitor effects. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16050–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Louvard D., Rossier B. C. Mutation of a cysteine in the first transmembrane segment of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit confers ouabain resistance. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1681–1687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Mutation of a tyrosine in the H3-H4 ectodomain of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit confers ouabain resistance. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17722–17726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. G., Zhou X. M., Cunha M. J., Epstein J., Cantley L. C. Ouabain-resistant transfectants of the murine ouabain resistance gene contain mutations in the alpha-subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17271–17278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso J. M., Hoving S., Tal D. M., Goldshleger R., Karlish S. J. Extensive digestion of Na+,K(+)-ATPase by specific and nonspecific proteases with preservation of cation occlusion sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1150–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowson M. S., Shull G. E. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding the putative distal colon H+,K(+)-ATPase. Similarity of deduced amino acid sequence to gastric H+,K(+)-ATPase and Na+,K(+)-ATPase and mRNA expression in distal colon, kidney, and uterus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13740–13748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Kim K. S., Kabalin M. A., Farley R. A. High-affinity ouabain binding by yeast cells expressing Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha subunits and the gastric H+, K(+)-ATPase beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd Overview: occluded ions and Na, K-ATPase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268A:229–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldshleger R., Tal D. M., Moorman J., Stein W. D., Karlish S. J. Chemical modification of Glu-953 of the alpha chain of Na+,K(+)-ATPase associated with inactivation of cation occlusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6911–6915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Taylor W. R., Brandl C., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Structural and mechanistic implications of the amino acid sequence of calcium-transporting ATPases. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;122:93–114. doi: 10.1002/9780470513347.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. H., Ganjeizadeh M., Wang Y. H., Chiu I. N., Askari A. Autoregulation of the phosphointermediate of Na+/K(+)-ATPase by the amino-terminal domain of the alpha-subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1030(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90239-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Takeyasu K. The amino-terminal 200 amino acids of the plasma membrane Na+,K+-ATPase alpha subunit confer ouabain sensitivity on the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8881–8885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Primary sequence and functional expression of a novel ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase. The beta subunit modulates potassium activation of the Na,K-pump. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16895–16903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell E. A., Lingrel J. B. Comparison of the substrate dependence properties of the rat Na,K-ATPase alpha 1, alpha 2, and alpha 3 isoforms expressed in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16925–16930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Andersen J. P. Structural basis for E1-E2 conformational transitions in Na,K-pump and Ca-pump proteins. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(2):95–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaprielian Z., Fambrough D. M. Expression of fast and slow isoforms of the Ca2+-ATPase in developing chick skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1987 Dec;124(2):490–503. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90502-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin N. J., Kaprielian Z., Fambrough D. M. Expression of avian Ca2+-ATPase in cultured mouse myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1978–1986. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemas M. V., Takeyasu K., Fambrough D. M. The carboxyl-terminal 161 amino acids of the Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit are sufficient for assembly with the beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20987–20991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi P. A., Sweadner K. J. Postnatal changes in Na,K-ATPase isoform expression in rat cardiac ventricle. Conservation of biphasic ouabain affinity. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9327–9331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Boyd K. L., Takeyasu K. Ouabain- and Ca2(+)-sensitive ATPase activity of chimeric Na- and Ca-pump molecules. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80400-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Lemas V., Boyd K. L., Fambrough D. M., Takeyasu K. Molecular dissection of functional domains of the E1E2-ATPase using sodium and calcium pump chimeric molecules. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):220–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81807-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsenko S., Kaplan J. H. An essential role for the extracellular domain of the Na,K-ATPase beta-subunit in cation occlusion. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 6;32(26):6737–6743. doi: 10.1021/bi00077a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Westlin M., Hanley M. R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17067–17071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda M., Oshiman K., Tamura S., Futai M. Human gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase gene. Similarity to (Na+ + K+)-ATPase genes in exon/intron organization but difference in control region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9027–9032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedemonte C. H., Kaplan J. H. Chemical modification as an approach to elucidation of sodium pump structure-function relations. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C1–23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y., Fernandez-Belda F., de Meis L., Inesi G. Characterization of the inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ transport ATPases by thapsigargin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12606–12613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y., Wade J. B., Inesi G. A conformational mechanism for formation of a dead-end complex by the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase with thapsigargin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultheis P. J., Lingrel J. B. Substitution of transmembrane residues with hydrogen-bonding potential in the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase reveals alterations in ouabain sensitivity. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):544–550. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultheis P. J., Wallick E. T., Lingrel J. B. Kinetic analysis of ouabain binding to native and mutated forms of Na,K-ATPase and identification of a new region involved in cardiac glycoside interactions. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22686–22694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Young R. M., Greeb J., Lingrel J. B. Overview: amino acid sequences of the alpha and beta subunits of the Na,K-ATPase. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;268A:3–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stults N. L., Asta L. M., Lee Y. C. Immobilization of proteins on oxidized crosslinked Sepharose preparations by reductive amination. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumbilla C., Cantilina T., Collins J. H., Malak H., Lakowicz J. R., Inesi G. Structural perturbation of the transmembrane region interferes with calcium binding by the Ca2+ transport ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12682–12689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumbilla C., Lu L., Lewis D. E., Inesi G., Ishii T., Takeyasu K., Feng Y., Fambrough D. M. Ca(2+)-dependent and thapsigargin-inhibited phosphorylation of Na+,K(+)-ATPase catalytic domain following chimeric recombination with Ca(2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21185–21192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Kaneko K. Ouabain-sensitive H+-K+ exchange mechanism in the apical membrane of guinea pig colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):G979–G988. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.6.G979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Kadoma M., Inui M., Fujii J. Regulation of Ca2+-pump from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:107–154. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Lemas V., Fambrough D. M. Stability of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms in evolution. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C619–C630. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Renaud K. J., Fambrough D. M. Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the alpha-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4347–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Siegel N. R., Fambrough D. M. Expression of hybrid (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules after transfection of mouse Ltk-cells with DNA encoding the beta-subunit of an avian brain sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10733–10740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyofuku T., Kurzydlowski K., Lytton J., MacLennan D. H. The nucleotide binding/hinge domain plays a crucial role in determining isoform-specific Ca2+ dependence of organellar Ca(2+)-ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14490–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Omay H. S., Ohta T., Noguchi S., Kawamura M., Schwarz W. Stimulation of the Na+/K+ pump by external [K+] is regulated by voltage-dependent gating. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16285–16288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilsen B., Andersen J. P. CrATP-induced Ca2+ occlusion in mutants of the Ca(2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25739–25743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Suzuki T., Suzuki Y. Ouabain-sensitive K(+)-ATPase in epithelial cells from guinea pig distal colon. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):G506–G511. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.4.G506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Engelhardt W., Burmester M., Hansen K., Becker G., Rechkemmer G. Effects of amiloride and ouabain on short-chain fatty acid transport in guinea-pig large intestine. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:455–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]