Abstract
To evaluate the possible role of posttranscriptional mechanisms in the acute phase response, we determined the kinetics of transcription (by nuclear run-on assay) and mRNA accumulation of five human acute phase genes in Hep 3B cells incubated with conditioned medium from LPS-stimulated monocytes. Increase in mRNA accumulation was comparable to increase in transcription rate for fibrinogen-alpha and alpha-1 protease inhibitor, suggesting largely transcriptional regulation. In contrast, mRNA accumulation was about 10-20-fold greater than transcriptional increase for serum amyloid A, C3, and factor B, suggesting participation of posttranscriptional mechanisms. Since finding a disparity between the magnitudes of increase in mRNA and transcription does not definitively establish involvement of posttranscriptional mechanisms, we subjected our data to modeling studies and dynamic mathematical analysis to evaluate this possibility more rigorously. In modeling studies, accumulation curves resembling those observed for these three mRNAs could be generated from the nuclear run-on results only if posttranscriptional regulation was assumed. Dynamic mathematical analysis of relative transcription rates and relative mRNA abundance also strongly supported participation of posttranscriptional mechanisms. These observations suggest that posttranscriptional regulation plays a substantial role in induction of some, but not all acute phase proteins.
Full text
PDF

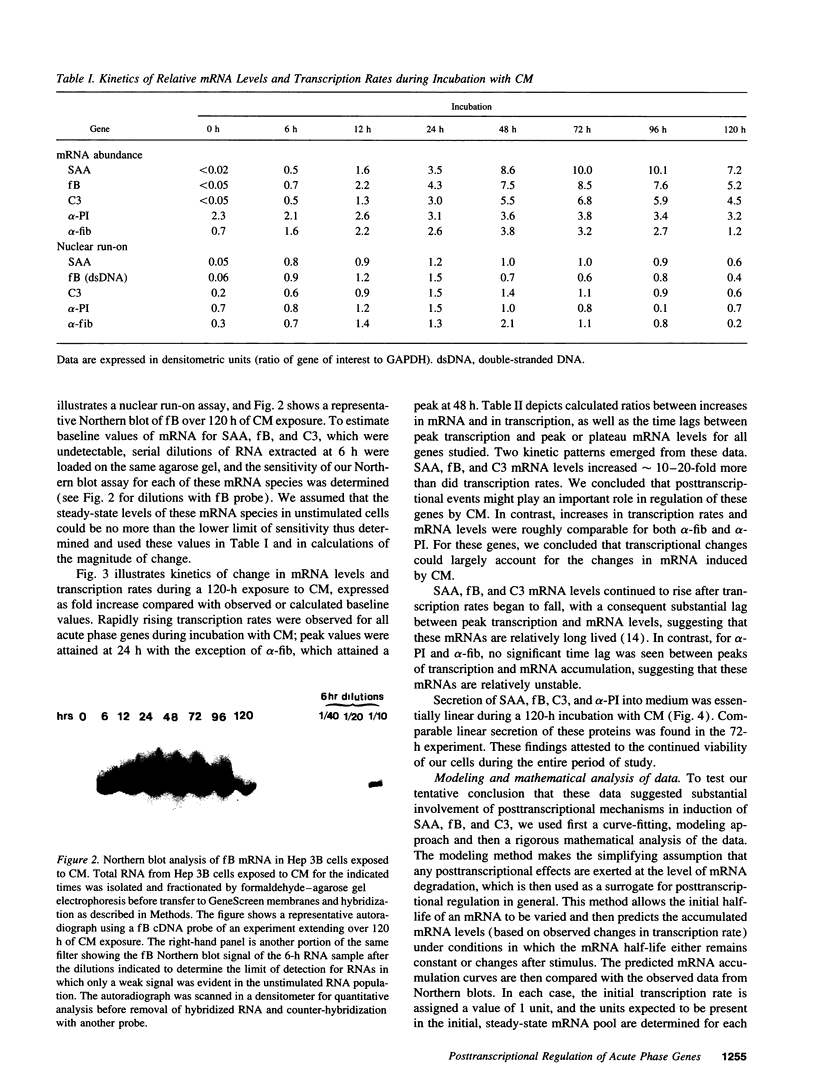
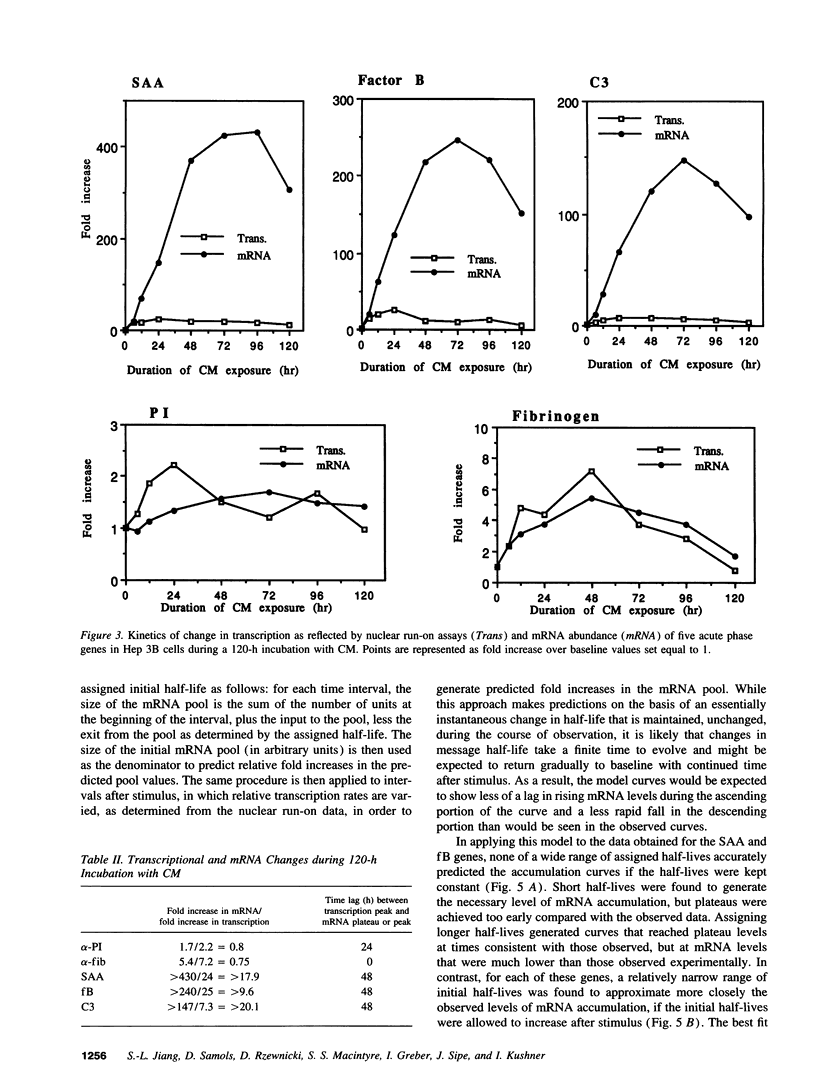
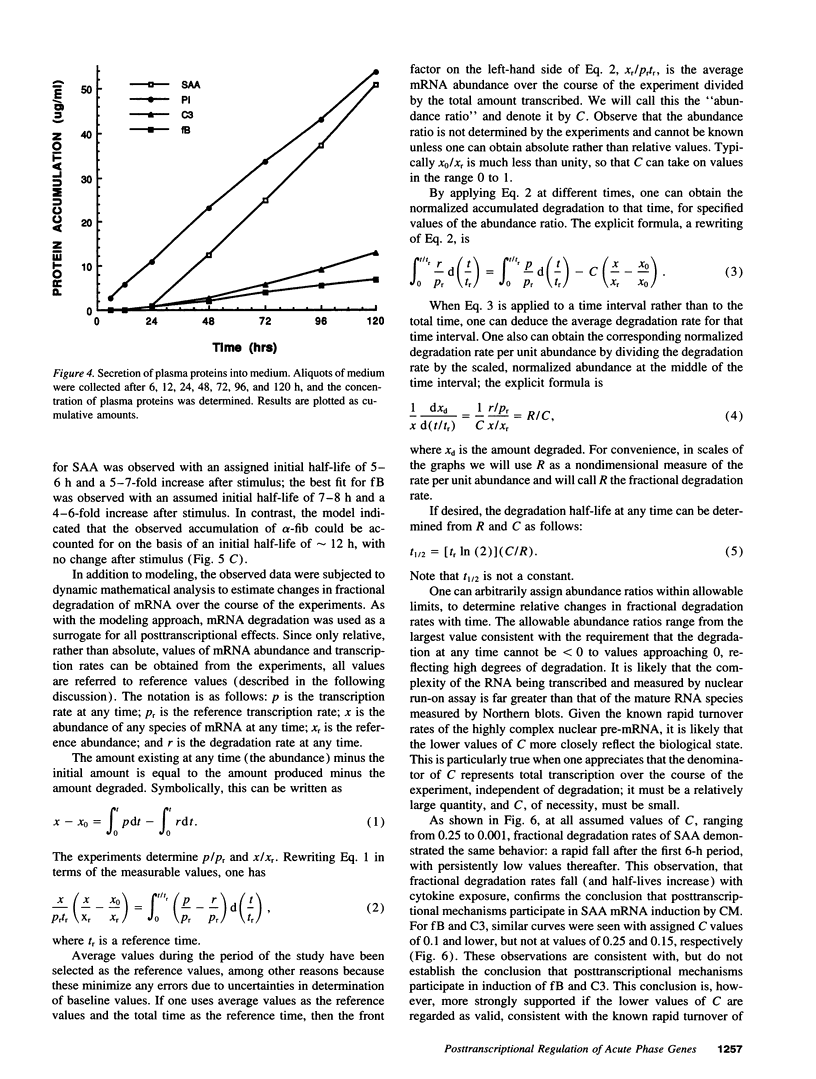
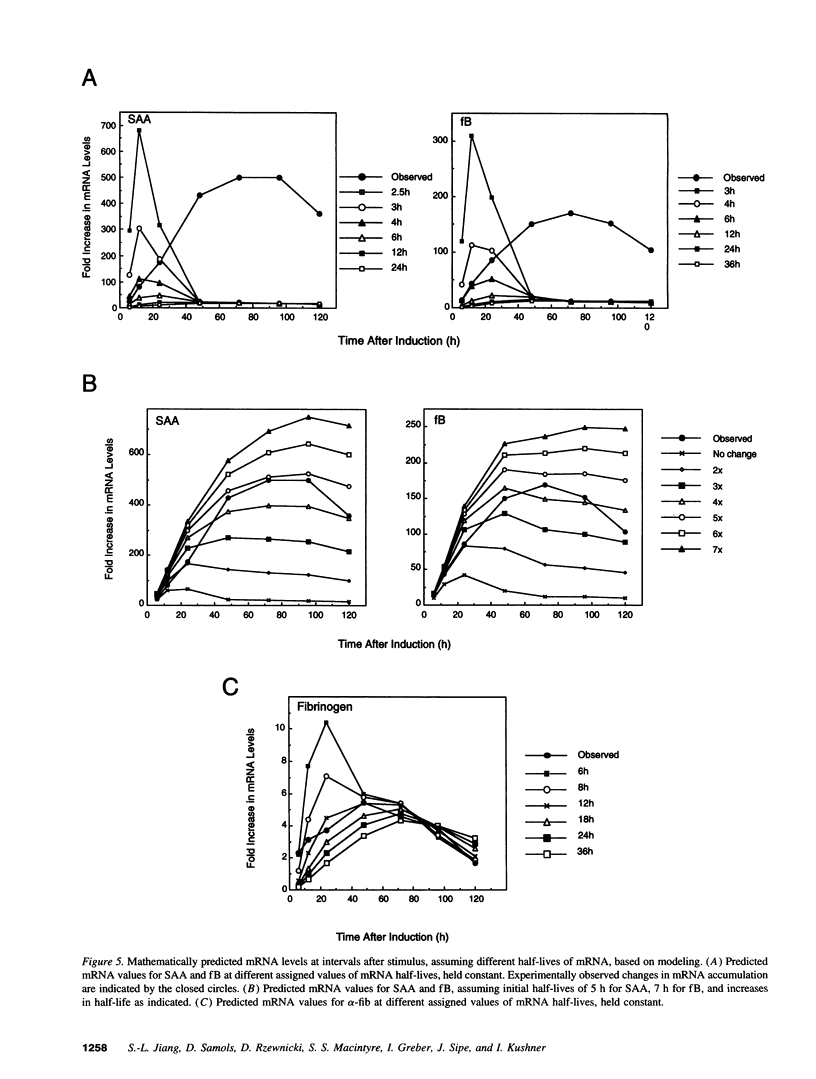
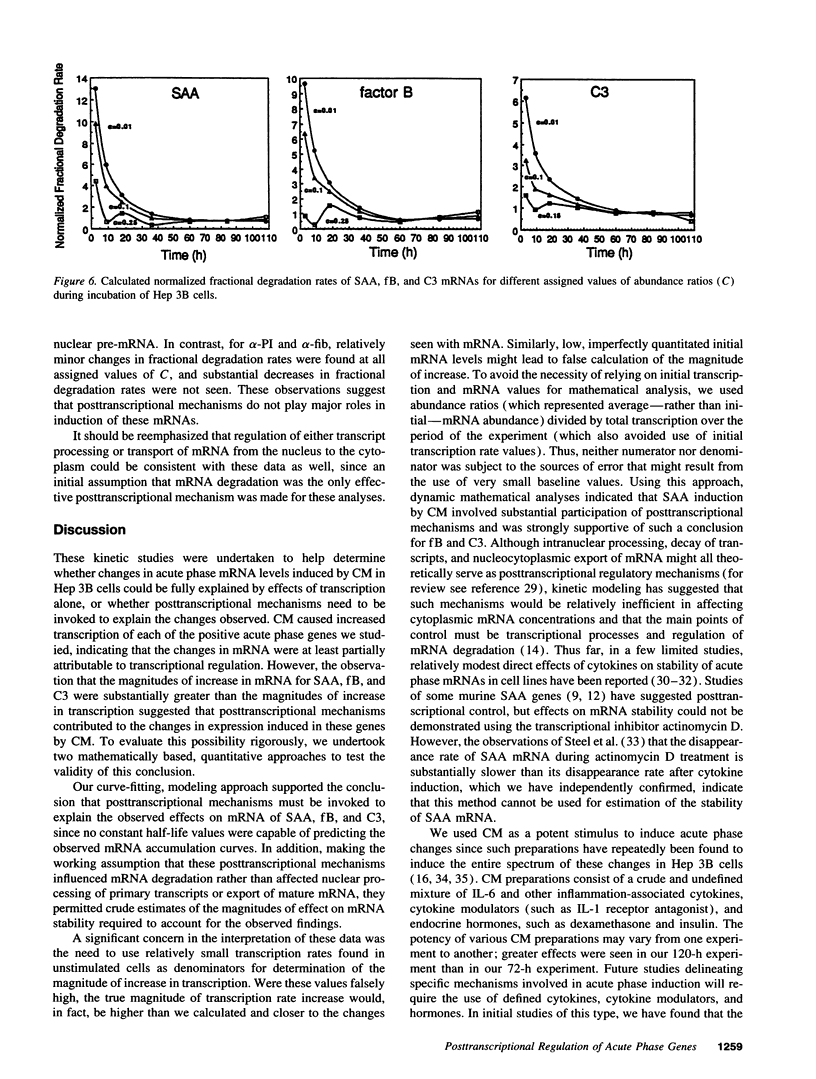


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch H. E., Schreiber G. Transcriptional regulation of plasma protein synthesis during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8077–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos S. P., Baumann H. Insulin is a prominent modulator of the cytokine-stimulated expression of acute-phase plasma protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1789–1797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Yen T. J. Multiple determinants of eukaryotic mRNA stability. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Wilson D. R., Lachman L. B. Monocyte-conditioned medium, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the acute phase response in human hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):787–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Mackiewicz A., Samols D., Hu S. I., Brabenec A., Macintyre S. S., Kushner I. Heterogeneous nature of the acute phase response. Differential regulation of human serum amyloid A, C-reactive protein, and other acute phase proteins by cytokines in Hep 3B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring M. R., Shiels B. R., Northemann W., de Bruijn M. H., Kan C. C., Chain A. C., Noonan D. J., Fey G. H. Sequence of rat liver alpha 2-macroglobulin and acute phase control of its messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger T., Andus T., Klapproth J., Northoff H., Heinrich P. C. Induction of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein by recombinant human interleukin-1 in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7141–7146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillaspy G. E., Mapstone T. B., Samols D., Goldthwait D. A. Transcriptional patterns of growth factors and proto-oncogenes in human glioblastomas and normal glial cells. Cancer Lett. 1992 Jul 31;65(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90213-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L. Microcomputer-assisted kinetic modeling of mammalian gene expression. FASEB J. 1993 Sep;7(12):1163–1170. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.12.8375615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang S. L., Lozanski G., Samols D., Kushner I. Induction of human serum amyloid A in Hep 3B cells by IL-6 and IL-1 beta involves both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):825–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant J. A., Lord S. T., Crabtree G. R. Partial mRNA sequences for human A alpha, B beta, and gamma fibrinogen chains: evolutionary and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3953–3957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., Benson M. D. DNA sequence evidence for polymorphic forms of human serum amyloid A (SAA). Biochem Genet. 1986 Dec;24(11-12):795–803. doi: 10.1007/BF00554519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappin D. F., Guc D., Hill A., McShane T., Whaley K. Effect of interferon-gamma on complement gene expression in different cell types. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):437–442. doi: 10.1042/bj2810437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell C. A., Stearman R. S., Morrow J. F. Transcriptional regulation of serum amyloid A gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8453–8461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Brabenec A., Weinstein J., Kelley M. F., Kushner I. Transforming growth factor beta 1 regulates production of acute-phase proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1491–1495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. Is molecular biology yet a science? Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):201–201. doi: 10.1038/355201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milland J., Tsykin A., Thomas T., Aldred A. R., Cole T., Schreiber G. Gene expression in regenerating and acute-phase rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):G340–G347. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.3.G340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Ciliberto G., Oliviero S., Arcone R., Dente L., Content J., Cortese R. Recombinant interleukin 6 regulates the transcriptional activation of a set of human acute phase genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12554–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrone G., Cortese R., Sorrentino V. Post-transcriptional control of negative acute phase genes by transforming growth factor beta. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3767–3771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. S., Chiu J., Cowan K. H. Posttranscriptional control of glutathione S-transferase pi gene expression in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10544–10550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Gitlin J. D., Colten H. R. Regulation of human and murine complement: comparison of 5' structural and functional elements regulating human and murine complement factor B gene expression. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;89(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00228274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Heisig M., Kunz D., Heinrich P. C. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences for rat alpha 2-macroglobulin and measurement of its transcription during experimental inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6200–6205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Brown T. J., Shoyab M., Baumann H., Gauldie J. Recombinant oncostatin M stimulates the production of acute phase proteins in HepG2 cells and rat primary hepatocytes in vitro. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rienhoff H. Y., Jr, Groudine M. Regulation of amyloid A gene expression in cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3710–3716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B. Messenger RNA degradation in eukaryotes. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80043-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooltink H., Stoyan T., Roeb E., Heinrich P. C., Rose-John S. Ciliary neurotrophic factor induces acute-phase protein expression in hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):280–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81489-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiels B. R., Northemann W., Gehring M. R., Fey G. H. Modified nuclear processing of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein RNA during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12826–12831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Colten H. R., Goldberger G., Edge M. D., Tack B. F., Cohen A. S., Whitehead A. S. Human serum amyloid A (SAA): biosynthesis and postsynthetic processing of preSAA and structural variants defined by complementary DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2931–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Gonnerman W. A., Loose L. D., Knapschaefer G., Xie W. J., Franzblau C. Direct binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for serum amyloid A (SAA). J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel D. M., Rogers J. T., DeBeer M. C., DeBeer F. C., Whitehead A. S. Biosynthesis of human acute-phase serum amyloid A protein (A-SAA) in vitro: the roles of mRNA accumulation, poly(A) tail shortening and translational efficiency. Biochem J. 1993 May 1;291(Pt 3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2910701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Whitehead A. S., Cole F. S. Pretranslational regulation of the synthesis of the third component of complement in human mononuclear phagocytes by the lipid A portion of lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):985–990. doi: 10.1172/JCI112099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhausen D. R., Jr, Hopkins W. E., Billadello J. J. Multiple transforming growth factor-beta-inducible elements regulate expression of the plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene in Hep G2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1092–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]