Abstract
Posterior acoustic shadowing (PAS) can bias breast tumor segmentation and classification in ultrasound images. In this paper, half-contour features are proposed to classify benign and malignant breast tumors with PAS, considering the fact that the upper half of the tumor contour is less affected by PAS. Adaptive thresholding and disk expansion are employed to detect tumor contours. Based on the detected full contour, the upper half contour is extracted. For breast tumor classification, six quantitative feature parameters are analyzed for both full contours and half contours, including standard deviation of degree (SDD), which is proposed to describe tumor irregularity. Fifty clinical cases (40 with PAS and 10 without PAS) were used. Tumor circularity (TC) and SDD were both effective full- and half-contour parameters in classifying images without PAS. Half-contour TC [74 % accuracy, 72 % sensitivity, 76 % specificity, 0.78 area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), p > 0.05] significantly improved the classification of breast tumors with PAS compared to that with full-contour TC (54 % accuracy, 56 % sensitivity, 52 % specificity, 0.52 AUC, p > 0.05). Half-contour SDD (72 % accuracy, 76 % sensitivity, 68 % specificity, 0.81 AUC, p < 0.05) improved the classification of breast tumors with PAS compared to that with full-contour SDD (62 % accuracy, 80 % sensitivity, 44 % specificity, 0.61 AUC, p > 0.05). The proposed half-contour TC and SDD may be useful in classifying benign and malignant breast tumors in ultrasound images affected by PAS.
Keywords: Ultrasound, Breast tumor, Posterior acoustic shadowing (PAS), Half-contour feature, Standard deviation of degree (SDD)
Introduction
Breast cancer is a health problem for women worldwide [1]. Ultrasound has become a useful adjunct modality for breast tumor diagnosis because it is cost-effective, noninvasive, and performed in real time [2]. However, certain inherent characteristics of ultrasound images, including low contrast, speckle noise, and tissue-related textures, may cause difficulties for radiologists [3]. Moreover, inter- or intraobserver differences in the understanding and diagnosis of ultrasound images might occur [4]. Hence, developing a computer-aided detection/diagnosis (CAD) system for analyzing ultrasound images is crucial [3, 5–7]. The diagnosis result of a CAD system can provide a second opinion for radiologists in the detection and diagnosis of breast lesions [4, 8, 9].
Typically, an ultrasound CAD system is composed of four parts: preprocessing, segmentation, feature extraction and selection, and classification [10]. Breast ultrasound image segmentation techniques include histogram thresholding [11], region growing [11, 12], model-based methods (such as active contour models or snakes [12, 13], level sets [14], and Markov random fields [15]), graph-based methods [16–18], neural networks [11, 19, 20], and watersheds [21, 22]. For ultrasound image classification, many features have been proposed to describe breast tumors, such as shape, margin, calcification, echogenicity, posterior echo, and echo texture. The features of ultrasound images can be classified into four categories: texture features, morphologic features, model-based features, and descriptor features [10]. Identifying most of these features relies on accurate segmentation of tumor contours, but ultrasound image segmentation and classification can be difficult when posterior acoustic shadowing (PAS) occurs. PAS occurs in ultrasound images when a strong attenuation effect caused by the tumor growth weakens the strength of the ultrasonic beam. PAS is frequently observed for malignant tumors [5, 23], and can bias the computerized segmentation and classification of breast tumors in ultrasound images. However, few of the current ultrasound image segmentation or classification techniques address the PAS problem [3, 5–7, 10–23].
Since the upper half of the tumor contour is less affected by the PAS effect than is the lower half, the present study proposes using features based on the upper half contour to classify benign and malignant breast tumors in ultrasound images with PAS. Adaptive thresholding and disk expansion (DE) [24] are employed for breast tumor segmentation, and half-contour feature parameters are analyzed for breast tumor classification. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, 50 clinical cases were obtained from a hospital to calculate half-contour feature parameters. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to evaluate the method, and a t test was applied to estimate the diagnostic performance of this method.
Materials and Methods
Data Acquisition
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of National Taiwan University Hospital and the patients signed informed consent forms. Ultrasound images were collected using a commercial portable ultrasound scanner (Model 3000, Terason, Burlington, MA, USA). The probe comprised a wideband linear array with a central frequency of 7.5 MHz and 256 elements. Fifty female patients volunteered to participate in the study. A sonographer performed the ultrasound scanning, and breast tumors were identified as benign (fibroadenoma) or malignant (invasive ductal carcinoma) according to biopsy reports. There were 40 cases with PAS and 10 cases without PAS.
Breast Tumor Segmentation
Let I denote an ultrasound image with M × N pixels and I(x, y) denote a pixel at (x, y). The threshold TH x for each column of I is defined as:
| 1 |
The image I can then be binarized with TH x to form a binary image B:
| 2 |
To incorporate regional information into the binarization, the mean gray value in a neighboring window of size (2n + 1) × (2n + 1), n = 1, 2, 3,…, is considered:
| 3 |
Adaptive thresholding is performed to obtain the binary image B:
| 4 |
The DE segmentation method [24] is employed to detect the tumor contour in the binary image B. Figure 1b shows the result of using the proposed adaptive thresholding for an ultrasound image. Figure 1c shows the tumor contour extracted from the ultrasound image using DE.
Fig. 1.
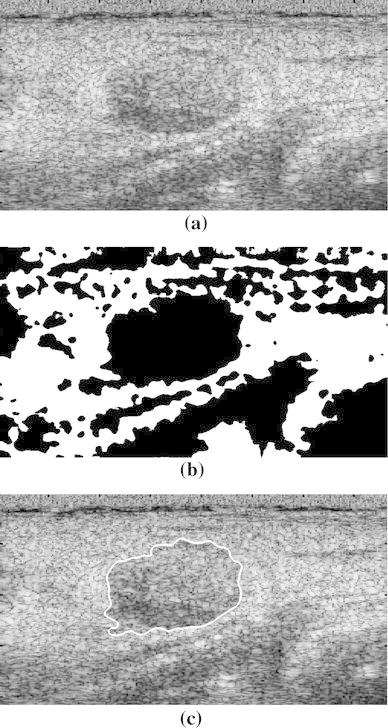
a Breast ultrasound image. b Image after adaptive thresholding. c Tumor contour extracted using DE
Breast Tumor Classification
In the ultrasound image with the extracted tumor contour C, the half contour was detected by determining the leftmost and rightmost pixels P l and P r, respectively, of the tumor region, excluding the portion affected by PAS, as shown in Fig. 2. A line L lr was drawn to connect P l and P r. The half contour was defined as the upper part of C, between P l and P r.
Fig. 2.
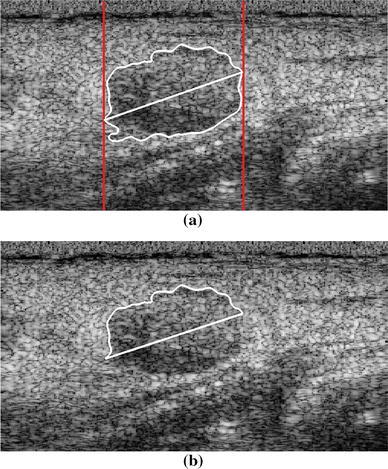
a Leftmost and rightmost pixels (indicated by the two red lines) detected from the extracted tumor full contour. b Detected tumor half contour
The features of the tumor half contour, including its shape and margin, are described using six typical feature parameters: tumor circularity (TC), mean of the normalized radial length (NRLM), standard deviation of the NRL (NRLSTD), area ratio (AR), roughness index (RI), and standard deviation of degree (SDD). TC, NRLM, NRLSTD, and AR are parameters that describe tumor shape (the degree of irregularity), RI describes the margin (the degree of spiculation), and SDD is a contour feature parameter proposed here to characterize the half-contour irregularity. To compare the six half-contour features with full-contour features, six full-contour feature parameters were also calculated.
TC is a gross contour feature descriptor that has been shown to be useful in classifying breast masses [25]. TC was calculated using:
| 5 |
where P is the perimeter and A is the area of the tumor half contour. The perimeter P was measured by summing the number of pixels corresponding to the tumor contour, and the area A was calculated by the number of pixels inside the contour.
Similar to TC, NRLM, and NRLSTD reflect macroscopic boundary changes, but they can also indicate subtle boundary changes [26]. NRL was first computed using:
| 6 |
where d(i) denotes the distance from the ith contour pixel to the tumor centroid. NRLM and NRLSTD were then respectively computed using:
| 7 |
and
| 8 |
where N is the number of contour pixels.
AR is a measure of the percentage of the tumor located outside the circular region defined by the mean of the x–y line plot [26]. It was computed using:
| 9 |
where
RI represents the degree of tumor spiculation and was computed using [26]:
| 10 |
To clearly describe the shape irregularity of the tumor half contour, SDD is proposed to classify tumors. θ s is defined as the relationship between the sth contour pixel and the (s − k)th and (s + k)th pixels:
| 11 |
where denotes the position vector from the sth to the (s − k)th pixels, and is the length of the vector. SDD is defined as the standard deviation of θ s:
| 12 |
where is the mean of θ s.
Statistical Analysis
By using t-tests, the probability value (p value) of each of the six feature parameters was determined to classify benign and malignant breast tumors. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the features were then respectively computed using:
| 13 |
where TP (true positive) denotes the number of malignant cases truly classified as positive, TN (true negative) denotes the number of benign cases truly classified as negative, FP (false positive) denotes the benign cases falsely classified as positive, and FN (false negative) denotes the malignant cases falsely classified as negative. The tumor classification performance of each feature parameter was evaluated using the ROC curve.
Results
Classification of Breast Tumors Without PAS
The feasibility of using the six feature parameters in discriminating between benign and malignant breast tumors was validated using images without PAS. The full- and half-contour features were identified for the 10 cases without PAS. One benign case and one malignant case without PAS are shown in Figs. 3 and 4, respectively. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of each feature parameter in classifying benign and malignant breast tumors was analyzed using images without PAS (n = 10). The results are shown in Table 1. Among the six feature parameters, TC and SDD were most effective for classifying tumors without PAS, both for full contours and half contours.
Fig. 3.
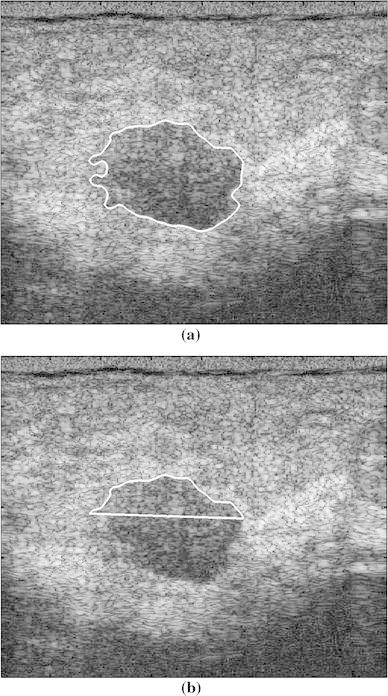
Benign case without shadowing. a Full contour and b half contour
Fig. 4.
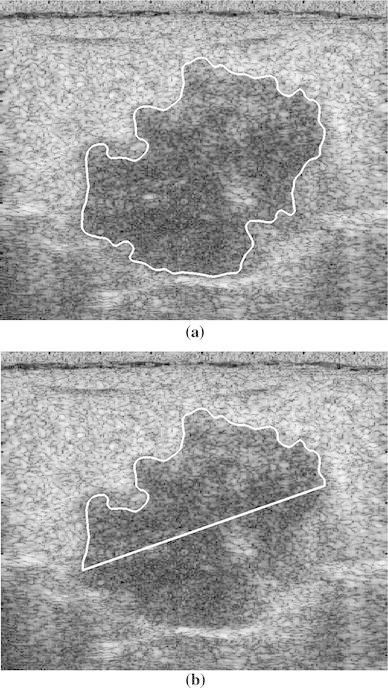
Malignant case without shadowing. a Full contour and b half contour
Table 1.
Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of each parameter in classifying benign and malignant breast tumors without PAS (n = 10)
| Parameters | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | |||
| Full contour | 90 | 100 | 80 |
| Half contour | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| σ s | |||
| Full contour | 90 | 100 | 80 |
| Half contour | 90 | 80 | 100 |
| Full contour | 60 | 40 | 80 |
| Half contour | 60 | 80 | 40 |
| σ d | |||
| Full contour | 60 | 80 | 40 |
| Half contour | 50 | 20 | 80 |
| A | |||
| Full contour | 60 | 80 | 40 |
| Half contour | 60 | 100 | 20 |
| RI | |||
| Full contour | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Half contour | 80 | 60 | 100 |
TC tumor circularity, σ s standard deviation of degree, mean of the normalized radial length, σ d standard deviation of the normalized radial length, A area ratio, RI roughness index
Classification of Breast Tumors with PAS
As TC and SDD yielded the best performance for breast tumors without PAS, these two parameters were evaluated in discriminating between benign and malignant tumors in images with PAS. Two benign cases and two malignant cases with PAS are shown in Figs. 5 and 6, respectively. Table 2 shows the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the two parameters (n = 50). Half-contour TC was significantly more accurate, sensitive, and specific than full-contour TC, indicating the capability of using half-contour TC to manage the PAS effect. Half-contour SDD was slightly less sensitive, but considerably more accurate and specific than full-contour SDD. This reflects the capability of using the half-contour SDD to discriminate between benign and malignant breast tumors in images with PAS.
Fig. 5.
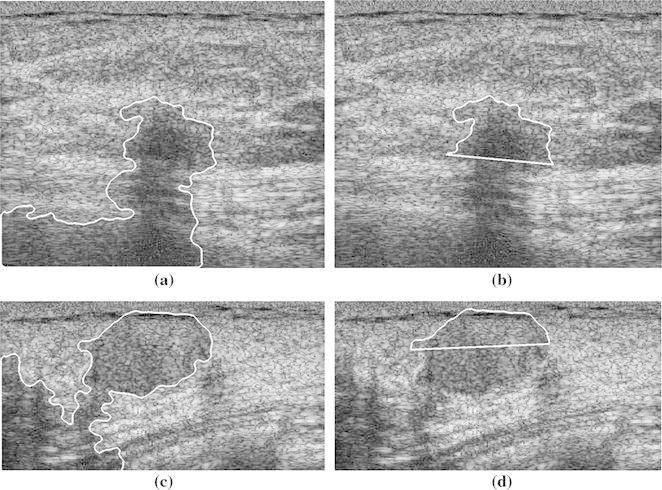
Two benign cases with shadowing. a, c Full contour and b, d half contour
Fig. 6.
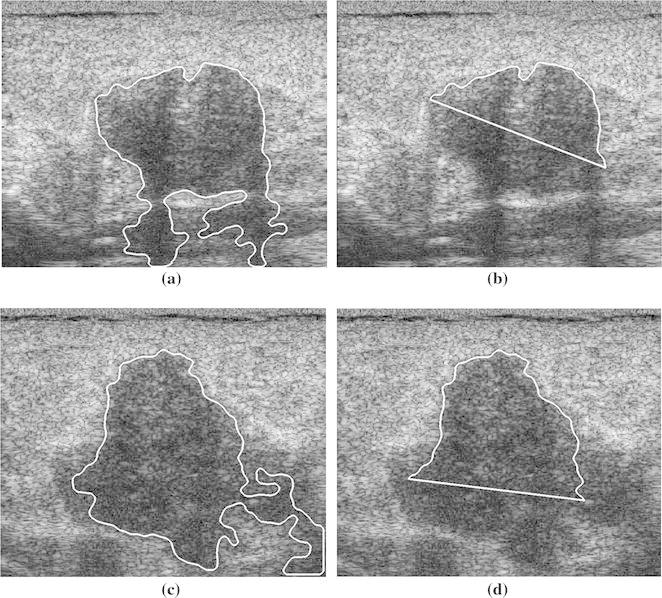
Two malignant cases with shadowing. a, c Full contour and b, d half contour
Table 2.
Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of TC and SDD in classifying benign and malignant breast tumors with PAS (n = 50)
| Performance parameters | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC | |||
| Full contour | 54 | 56 | 52 |
| Half contour | 74 | 72 | 76 |
| σ s | |||
| Full contour | 62 | 80 | 44 |
| Half contour | 72 | 76 | 68 |
TC tumor circularity, σ s standard deviation of degree
Figure 7a shows the ROC curve for full-contour TC. Full-contour TC presented a low discrimination accuracy because it was affected by the PAS effect; its area under the ROC curve (AUC) was only 0.52. Figure 7b shows that half-contour TC can be used for classifying breast tumors more accurately, with an AUC of 0.78. Figure 7c, d show the ROC curves of the half- and full-contour SDD, respectively; half-contour SDD presented a higher AUC (0.81) than that of full-contour SDD (0.61). As the ROC curves show, half-contour TC and half-contour SDD may be effectively used to classify benign and malignant breast tumors. Figure 8 shows the t-test results of using the full- and half-contour TCs as well as full- and half-contour SDDs on images with PAS. Half-contour SDD had a p value of <0.05, indicating discrimination capability, whereas full-contour TC and SDD both had p values of >0.05.
Fig. 7.
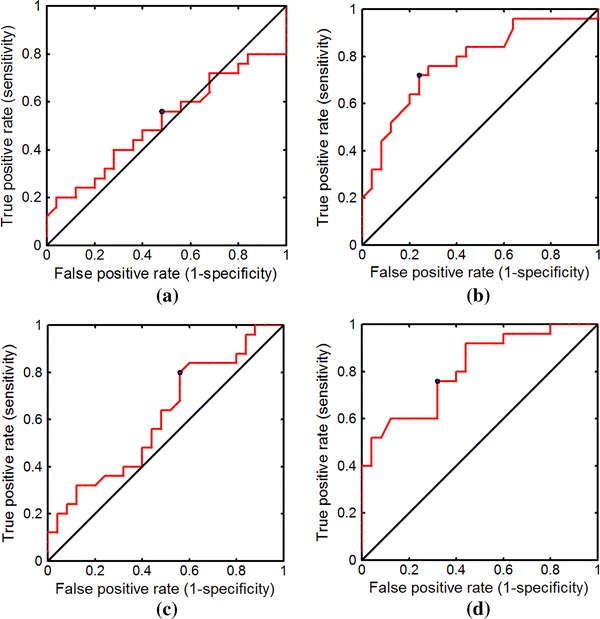
ROC curves obtained using a full- and b half-contour TC and c full- and d half-contour SDD to classify benign and malignant tumors with PAS
Fig. 8.
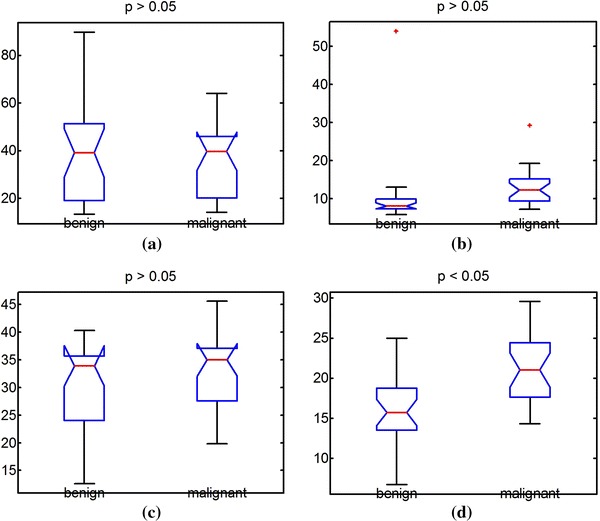
Results of t-test obtained using a full- and b half-contour TC and c full- and d half-contour SDD to classify benign and malignant tumors with PAS
Discussion
As ultrasonic waves propagate through biological tissue, their energy is reduced or attenuated exponentially with depth. The energy is lost because of absorption, scattering, and specular reflection at the boundary between two layers of tissue. When little energy is transmitted through a mass, such as a solid tumor composed of mainly connective tissues, an acoustic shadow may be created behind such a mass [27]. The energy attenuation coefficient increases with the ultrasonic transmission frequency. A higher frequency is required to obtain a higher ultrasonic imaging resolution. The PAS effect can affect ultrasound image segmentation, and thus may affect the tumor contour-based classification of benign and malignant breast tumors.
The present study proposes using half-contour feature parameters to classify benign and malignant breast tumors in ultrasound images with PAS. It was demonstrated that full-contour features are inadequate for managing PAS. Half-contour features improve the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity in classifying benign and malignant breast tumors. Our findings indicate that PAS may be addressed by using half-contour features to diagnose breast tumors using ultrasound images. The half contour can be delineated manually by a radiologist, or partially or fully extracted automatically by a computer. However, to reduce inter- and intraoperator variance, fully automated breast tumor segmentation is preferable. Additional studies on the half-contour analysis of ultrasound images with PAS are necessary.
It should be noted that computerized breast tumor segmentation of ultrasound images remains a challenging task, due to such factors as the partial volume effect and the side acoustic shadow. The DE segmentation method used in this study could yield acceptable half contours according to the identification by the physician, and the half-contour features have been demonstrated to be capable of classifying benign and malignant breast tumors with PAS. The segmentation and classification accuracy of breast tumors may be increased by improving the DE method or employing more accurate segmentation methods. Nevertheless, this paper focuses on the feasibility of using half-contour features in differentiating begin tumors from malignant ones. In the future, more advanced breast tumor segmentation techniques can be studied to improve the recognition accuracy of breast tumors with PAS.
One limitation of the proposed method is that the leftmost and rightmost pixels used to determine the half contour may lie in an area with PAS, resulting in biased half-contour detection, as shown in Fig. 9b. In certain cases, a manual exclusion operation may be necessary to detect the tumor half contour, as shown in Fig. 9c, d. This manual interaction may render half-contour detection operator-dependent. Another limitation of this study is the limited number of breast tumor cases and categories, and the large overlap between benign and malignant breast tumors. Additionally, the DE segmentation workflow was offline and time-consuming. To promote the proposed method toward clinical application, online processing is required. A potential approach is to use graphics processing unit-based parallel computing.
Fig. 9.
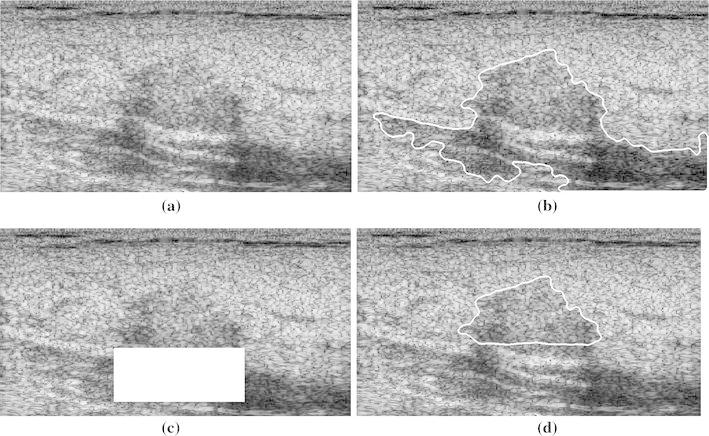
a Breast ultrasound image. b Tumor full contour extracted using adaptive thresholding and DE. c PAS part excluded to detect half contour. d Detected tumor half contour
It is worthwhile to discuss different categories of breast tumors. There are a vast variety of malignant carcinomas, including invasive lobular carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, carcinoma in situ, mucinous carcinoma, and other tumors with abundant mucin. Benign tumors include adenosis, hyperplastic nodule, and adenomatous hyperplasia, whose incidence is high. Phyllodes tumors are also an important variety which can be benign, boarderline, or malignant. They are difficult to distinguish from fibroadenoma. Therefore, a higher number of inclusion cases and categories of disease should be considered in future studies.
Conclusion
This paper proposed using half-contour features to classify benign and malignant breast tumors in ultrasound images with PAS. Two half-contour parameters, TC and SDD, enabled breast tumors to be classified more accurately in ultrasound images affected by PAS. In future studies, a higher number of tumor cases and categories should be considered, and the full automation of the tumor half-contour detection process, especially regarding images with PAS, should be explored.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. This work was supported in part by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant NSC102-2221-E-155-078 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 81127006. This work was also supported by the Doctoral Fund of Innovation of Beijing University of Technology.
Footnotes
Zhuhuang Zhou and Shuicai Wu have contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
King-Jen Chang, Phone: +886-2-23123456, Email: kingjen@ntu.edu.tw.
Yung-Sheng Chen, Phone: +886-3-4638800, Email: eeyschen@saturn.yzu.edu.tw.
References
- 1.Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2013;63:11–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McCavert M, O’Donnell ME, Aroori S, Badger SA, Sharif MA, Crothers JG, Spence RA. Ultrasound is a useful adjunct to mammography in the assessment of breast tumours in all patients. International Journal of Clinical Practice. 2009;63:1589–1594. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Diao XF, Zhang XY, Wang TF, Chen SP, Yang Y, Zhong L. Highly sensitive computer aided diagnosis system for breast tumor based on color Doppler flow images. Journal of Medical Systems. 2011;35:801–809. doi: 10.1007/s10916-010-9461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Giger ML, Karssemeijer N, Schnabel JA. Breast image analysis for risk assessment, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2013;15:327–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071812-152416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tsui PH, Liao YY, Chang CC, Kuo WH, Chang KJ, Yeh CK. Classification of benign and malignant breast tumors by 2-D analysis based on contour description and scatterer characterization. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2010;29:513–522. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2037147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moon WK, Lo CM, Cho N, Chang JM, Huang CS, Chen JH, Chang RF. Computer-aided diagnosis of breast masses using quantified BI-RADS findings. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 2013;111:84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liao YY, Tsui PH, Yeh CK. Classification of benign and malignant breast tumors by ultrasound B-scan and Nakagami-based images. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2010;30:307–312. doi: 10.5405/jmbe.30.5.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rizzi M, D’Aloia M, Castagnolo B. Review: “Health care CAD systems for breast microcalcification cluster detection”. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2012;32:147–156. doi: 10.5405/jmbe.980. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yuan Y, Giger ML, Li H, Bhooshan N, Sennett CA. Correlative analysis of FFDM and DCE-MRI for improved breast CADx. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2012;32:42–50. doi: 10.5405/jmbe.833. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cheng HD, Shan J, Ju W, Guo Y, Zhang L. Automated breast cancer detection and classification using ultrasound images: A survey. Pattern Recognition. 2010;43:299–317. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.05.012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shan J, Cheng HD, Wang Y. Completely automated segmentation approach for breast ultrasound images using multiple-domain features. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2012;38:262–275. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2011.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Madabhushi A, Metaxas DN. Combining low-, high-level and empirical domain knowledge for automated segmentation of ultrasonic breast lesions. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2003;22:155–169. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2002.808364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen DR, Chang RF, Wu WJ, Moon WK, Wu WL. 3-D breast ultrasound segmentation using active contour model. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2003;29:1017–1026. doi: 10.1016/S0301-5629(03)00059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang YL, Jiang YR, Chen DR, Moon WK. Level set contouring for breast tumor in sonography. Journal of Digital Imaging. 2007;20:238–247. doi: 10.1007/s10278-006-1041-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xiao G, Brady M, Noble JA, Zhang Y. Segmentation of ultrasound B-mode images with intensity inhomogeneity correction. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2002;21:48–57. doi: 10.1109/42.981233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang QH, Lee SY, Liu LZ, Lu MH, Jin LW, Li AH. A robust graph-based segmentation method for breast tumors in ultrasound images. Ultrasonics. 2012;52:266–275. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2011.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gao L, Yang W, Liao Z, Liu X, Feng Q, Chen W. Segmentation of ultrasonic breast tumors based on homogeneous patch. Medical Physics. 2012;39:3299–3318. doi: 10.1118/1.4718565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhou Z, Wu W, Wu S, Tsui PH, Lin CC, Zhang L, Wang T. Semi-automatic breast ultrasound image segmentation based on mean shift and graph cuts. Ultrasonic Imaging. 2014;36:256–276. doi: 10.1177/0161734614524735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Drukker K, Giger ML, Horsch K, Kupinski MA, Vyborny CJ, Mendelson EB. Computerized lesion detection on breast ultrasound. Medical Physics. 2002;29:1438–1446. doi: 10.1118/1.1485995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Madabhushi A, Yang P, Rosen M, Weinstein S. Distinguishing lesions from posterior acoustic shadowing in breast ultrasound via non-linear dimensionality reduction. Conference Proceedings of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 2006;1:3070–3073. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang YL, Chen DR. Watershed segmentation for breast tumor in 2-D sonography. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2004;30:625–632. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gómez W, Leija L, Alvarenga AV, Infantosi AF, Pereira WC. Computerized lesion segmentation of breast ultrasound based on marker-controlled watershed transformation. Medical Physics. 2010;37:82–95. doi: 10.1118/1.3265959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Drukker K, Giger ML, Mendelson EB. Computerized analysis of shadowing on breast ultrasound for improved lesion detection. Medical Physics. 2003;30:1833–1842. doi: 10.1118/1.1584042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yeh CK, Chen YS, Fan WC, Liao YY. A disk expansion segmentation method for ultrasonic breast lesions. Pattern Recognition. 2009;42:596–606. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.09.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kilday J, Palmieri F, Fox MD. Classifying mammographic lesions using computerized image analysis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 1993;12:664–669. doi: 10.1109/42.251116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chou YH, Tiu CM, Hung GS, Wu SC, Chang TY, Chiang HK. Stepwise logistic regression analysis of tumor contour features for breast ultrasound diagnosis. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2001;27:1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/S0301-5629(01)00466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shung KK. Diagnostic ultrasound: Imaging and blood flow measurements. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2005. [Google Scholar]


