Abstract
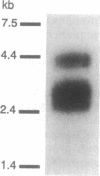
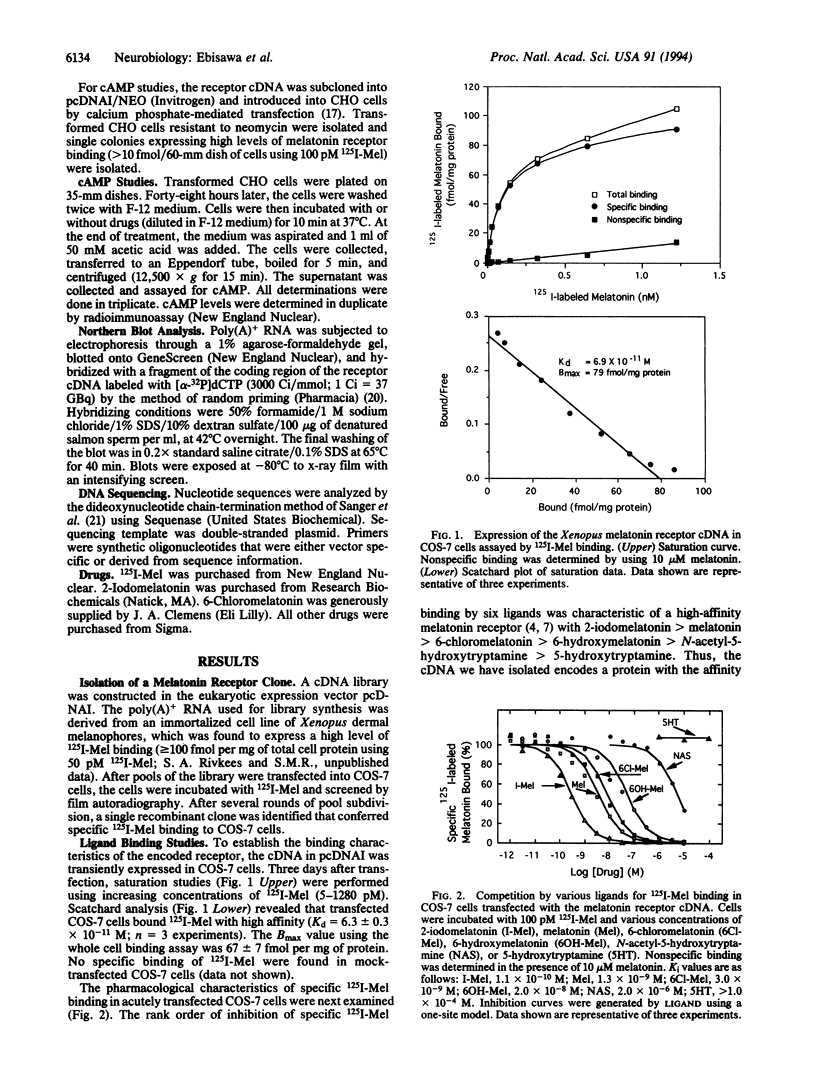
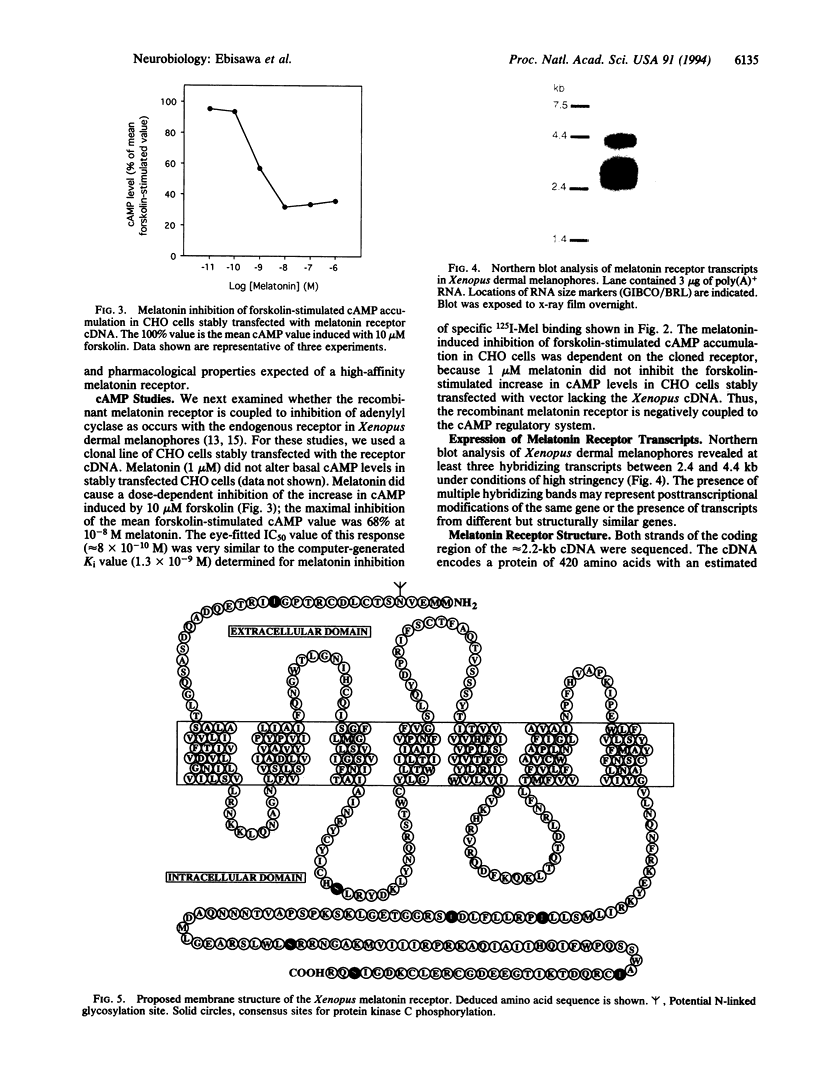
Using an expression cloning strategy, a high-affinity melatonin receptor cDNA has been isolated from Xenopus laevis dermal melanophores. Transient expression of the cDNA in COS-7 cells resulted in high-affinity 2-[125I]-iodomelatonin binding (Kd = 6.3 +/- 0.3 x 10(-11) M). In addition, six ligands exhibited a rank order of inhibition of specific 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding that was identical to that reported for endogenous high-affinity receptors. Functional studies of CHO cells stably expressing the receptor cDNA showed that melatonin acting through the cloned receptor inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in a dose-dependent manner. Northern blot analysis showed that melatonin receptor transcripts are moderately expressed in Xenopus dermal melanophores. The cDNA encodes a protein of 420 amino acids, which contains seven hydrophobic segments. Structural analysis revealed that the receptor protein is a newly discovered member of the guanine nucleotide binding protein-coupled receptor family.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Robison G. A., Liddle G. W., Butcher R. W., Nicholson W. E., Baird C. E. Role of cyclic AMP in mediating the effects of MSH, norepinephrine, and melatonin on frog skin color. Endocrinology. 1969 Oct;85(4):674–682. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-4-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. L., Weaver D. R., Reppert S. M. Melatonin signal transduction in hamster brain: inhibition of adenylyl cyclase by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Endocrinology. 1989 Nov;125(5):2670–2676. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-5-2670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone V. M. Effects of melatonin on vertebrate circadian systems. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Nov;13(11):457–464. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90099-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniolos A., Lerner A. B., Lerner M. R. Action of light on frog pigment cells in culture. Pigment Cell Res. 1990 Jan-Feb;3(1):38–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.1990.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Register R. B., Scattergood W., Rands E., Strader C. D. Structural features required for ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3269–3275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubocovich M. L., Takahashi J. S. Use of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin to characterize melatonin binding sites in chicken retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J., Eliopoulos E. Three-dimensional modelling of G protein-linked receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):492–499. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90050-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibert M. F., Trumpp-Kallmeyer S., Bruinvels A., Hoflack J. Three-dimensional models of neurotransmitter G-binding protein-coupled receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;40(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüppner H., Abou-Samra A. B., Freeman M., Kong X. F., Schipani E., Richards J., Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Hock J., Potts J. T., Jr, Kronenberg H. M. A G protein-linked receptor for parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone-related peptide. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1024–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1658941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karne S., Jayawickreme C. K., Lerner M. R. Cloning and characterization of an endothelin-3 specific receptor (ETC receptor) from Xenopus laevis dermal melanophores. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19126–19133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolakowski L. F., Jr GCRDb: a G-protein-coupled receptor database. Receptors Channels. 1994;2(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen J. T., Saavedra J. M. Characterization of melatonin receptors in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: modulation of affinity with cations and guanine nucleotides. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):2110–2115. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Harris T. L., Flannery M. S., Aruffo A., Kaji E. H., Gorn A., Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Lodish H. F., Goldring S. R. Expression cloning of an adenylate cyclase-coupled calcitonin receptor. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.1658940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):760–765. doi: 10.1038/349760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T., Hsu H., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Organization of African green monkey DNA at junctions between alpha-satellite and other DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. J., Lawson W., Davidson G., Howell H. E. Guanine nucleotides regulate the affinity of melatonin receptors on the ovine pars tuberalis. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Sep;50(3):359–362. doi: 10.1159/000125245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst W. C., Snyder L. A., Schuster D. I., Brosius J., Sealfon S. C. Sequence alignment of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–20. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter R. J. Pineal melatonin: cell biology of its synthesis and of its physiological interactions. Endocr Rev. 1991 May;12(2):151–180. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reppert S. M., Weaver D. R., Rivkees S. A., Stopa E. G. Putative melatonin receptors in a human biological clock. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):78–81. doi: 10.1126/science.2845576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkees S. A., Carlson L. L., Reppert S. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein regulation of melatonin receptors in lizard brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3882–3886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood H., Goldman B. D. Vertebrate circadian and photoperiodic systems: role of the pineal gland and melatonin. J Biol Rhythms. 1987 Winter;2(4):279–315. doi: 10.1177/074873048700200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanecek J. Melatonin binding sites. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1436–1440. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. H., Sekura R. D., Rollag M. D. Pertussis toxin blocks melatonin-induced pigment aggregation in Xenopus dermal melanophores. J Comp Physiol B. 1987;157(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00692359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]