Abstract
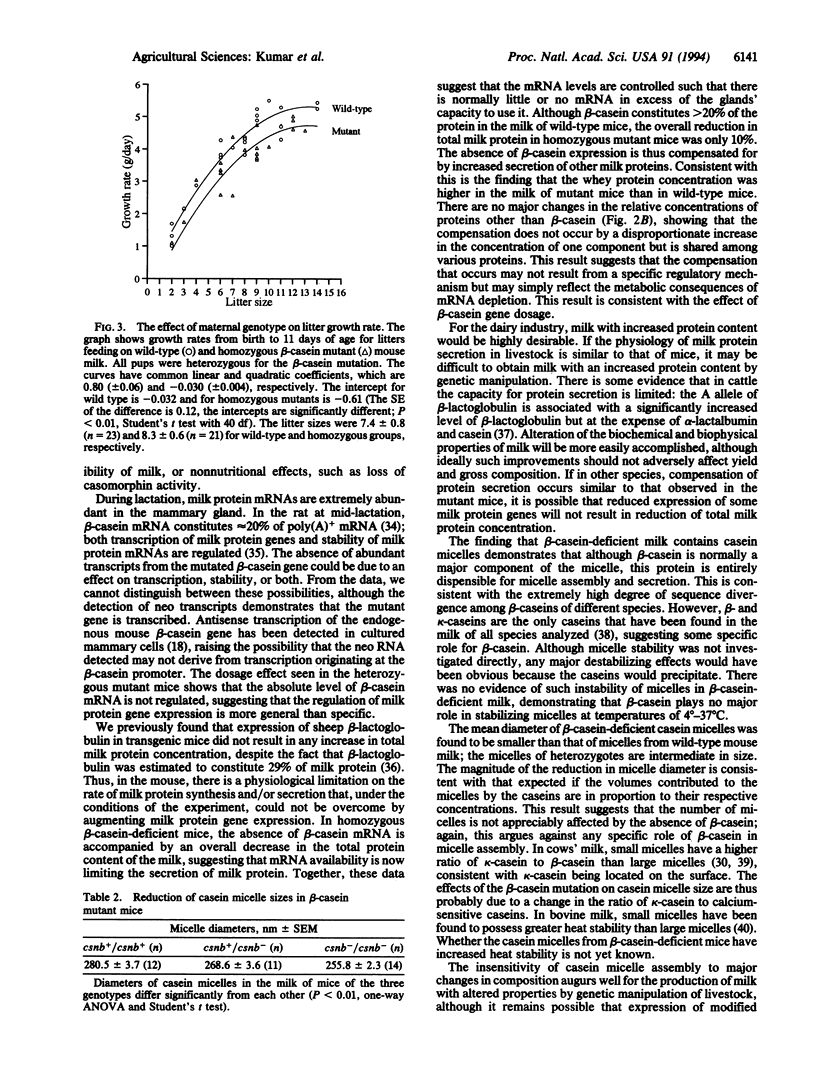
beta-Casein is a major protein component of milk and, in conjunction with the other caseins, it is assembled into micelles. The casein micelles determine many of the physical characteristics of milk, which are important for stability during storage and for milk-processing properties. There is evidence that suggests that beta-casein may also possess other, nonnutritional functions. To address the function of beta-casein, the mouse beta-casein gene was disrupted by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Homozygous beta-casein mutant mice are viable and fertile; females can lactate and successfully rear young. beta-Casein was expressed at a reduced level in heterozygotes and was completely absent from the milk of homozygous mutant mice. Despite the deficiency of beta-casein, casein micelles were assembled in heterozygous and homozygous mutants, albeit with reduced diameters. The absence of beta-casein expression was reflected in a reduced total protein concentration in milk, although this was partially compensated for by an increased concentration of other proteins. The growth of pups feeding on the milk of homozygous mutants was reduced relative to those feeding on the milk of wild-type mice. Various genetic manipulations of caseins have been proposed for the qualitative improvement of cow's milk composition. The results presented here demonstrate that beta-casein has no essential function and that the casein micelle is remarkably tolerant of changes in composition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. L., McClenaghan M., Hornsey V., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. High-level expression of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5178–5182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brantl V., Teschemacher H., Bläsig J., Henschen A., Lottspeich F. Opioid activities of beta-casomorphins. Life Sci. 1981 Apr 27;28(17):1903–1909. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühler T. A., Bruyère T., Went D. F., Stranzinger G., Bürki K. Rabbit beta-casein promoter directs secretion of human interleukin-2 into the milk of transgenic rabbits. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Feb;8(2):140–143. doi: 10.1038/nbt0290-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P. Solubilization in formamide protects RNA from degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3791–3792. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Cowper A., Wallace R., Wright G., Simons J. P. Rescuing transgene expression by co-integration. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Nov;10(11):1450–1454. doi: 10.1038/nbt1192-1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Prospects for the genetic engineering of milk. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Jun;49(2):121–127. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert K. M., Selgrath J. P., DiTullio P., Denman J., Smith T. E., Memon M. A., Schindler J. E., Monastersky G. M., Vitale J. A., Gordon K. Transgenic production of a variant of human tissue-type plasminogen activator in goat milk: generation of transgenic goats and analysis of expression. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Sep;9(9):835–838. doi: 10.1038/nbt0991-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R. S., Rosen J. M. Both cell substratum regulation and hormonal regulation of milk protein gene expression are exerted primarily at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3183–3190. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. S., Rosen J. M. Transcriptional analysis of the mouse beta-casein gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1661–1670. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Mitchell S. C., Nabavi N., Glimcher L. H. Casein expression in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6897–6901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. A., Richards D. A., Kessler D. J., Rosen J. M. Complex hormonal regulation of rat casein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3598–3605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Simons J. P. The effects of terminal heterologies on gene targeting by insertion vectors in embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1541–1548. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H., Gates L., Lacy E., Lonberg N. Bovine alpha S1-casein gene sequences direct high level expression of active human urokinase in mouse milk. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 May;8(5):443–446. doi: 10.1038/nbt0590-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persuy M. A., Stinnakre M. G., Printz C., Mahe M. F., Mercier J. C. High expression of the caprine beta-casein gene in transgenic mice. Eur J Biochem. 1992 May 1;205(3):887–893. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Barash I., Nathan M., Ricca G., Searfoss G. H., Dekel I., Faerman A., Givol D., Hurwitz D. R. Expression of human serum albumin in the milk of transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 1992 Sep;1(5):195–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02524750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. P., McClenaghan M., Clark A. J. Alteration of the quality of milk by expression of sheep beta-lactoglobulin in transgenic mice. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):530–532. doi: 10.1038/328530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velander W. H., Johnson J. L., Page R. L., Russell C. G., Subramanian A., Wilkins T. D., Gwazdauskas F. C., Pittius C., Drohan W. N. High-level expression of a heterologous protein in the milk of transgenic swine using the cDNA encoding human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12003–12007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilotte J. L., Soulier S., Stinnakre M. G., Massoud M., Mercier J. C. Efficient tissue-specific expression of bovine alpha-lactalbumin in transgenic mice. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw C. B., Archibald A. L., Harris S., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. Targeting expression to the mammary gland: intronic sequences can enhance the efficiency of gene expression in transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 1991 Dec;1(1):3–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02512991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. J., Clark A. J., Kerr M. A., Knight C. H., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P. Mammary development and milk secretion in transgenic mice expressing the sheep beta-lactoglobulin gene. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):717–720. doi: 10.1042/bj2840717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G., Carver A., Cottom D., Reeves D., Scott A., Simons P., Wilmut I., Garner I., Colman A. High level expression of active human alpha-1-antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic sheep. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Sep;9(9):830–834. doi: 10.1038/nbt0991-830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]