Abstract
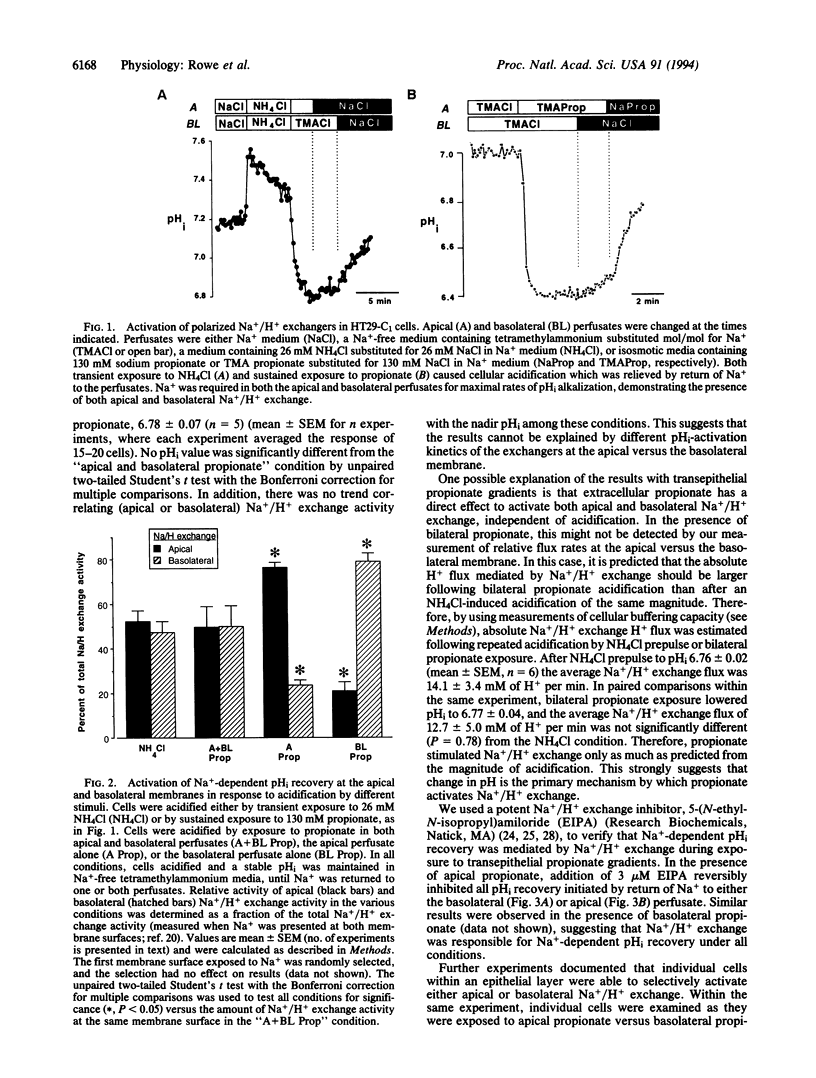
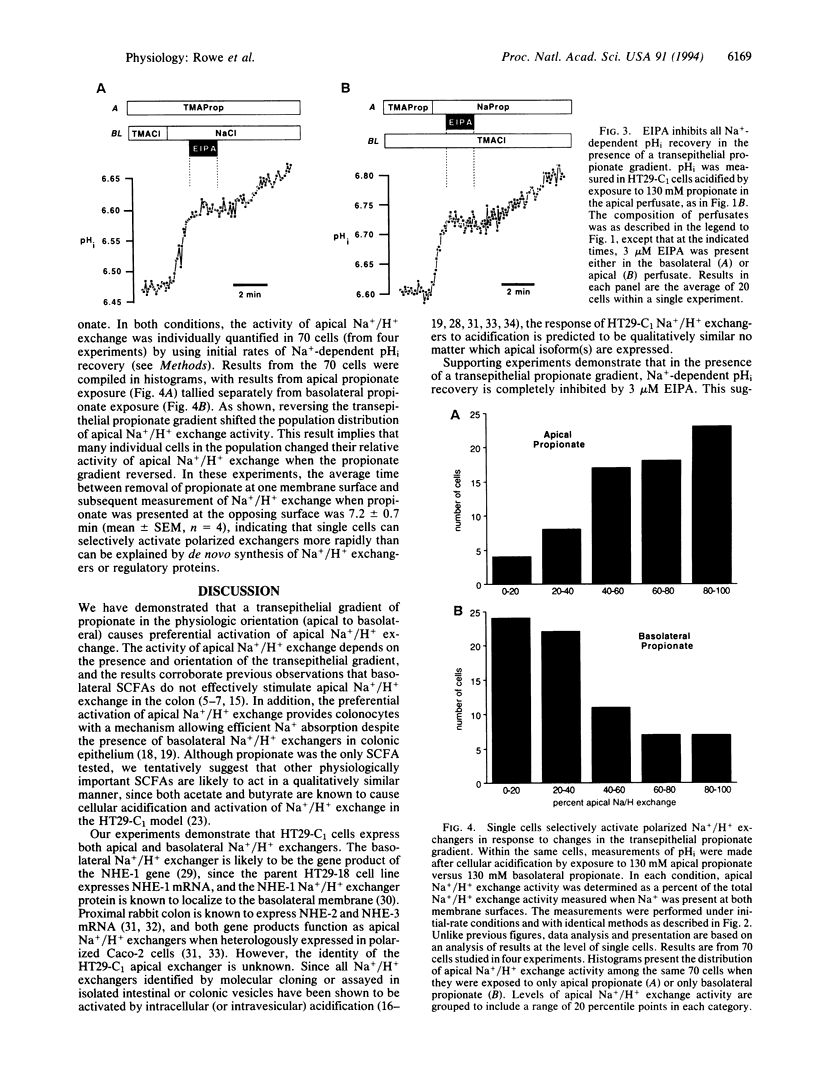
Short-chain fatty acids are produced at high concentration in the colonic lumen and stimulate electroneutral Na+ absorption by activating apical Na+/H+ exchange in colonocytes. We used an epithelial cell line derived from a human colon carcinoma (HT29-18-C1) to study activation of apical and basolateral Na+/H+ exchange by a short-chain fatty acid, propionate. Confluent cell monolayers on membrane filters were loaded with 2',7'-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-5 (and 6)-carboxyfluorescein (a fluorescent pH indicator) and intracellular pH was monitored with a digital fluorescence imaging microscope. Cells acidified by transient exposure to NH4Cl demonstrated both apical and basolateral Na+/H+ exchange. In this condition, apical Na+/H+ exchange was 50% of the total Na+/H+ exchange activity. Similar results were obtained when cells were bilaterally perfused with apical and basolateral propionate in an isosmotic medium (130 mM propionate at each membrane surface). However, apical Na+/H+ exchange was a significantly larger fraction (76%) of the total Na+/H+ exchange activity when cells were acidified by exposure to apical propionate alone. Conversely, in cells acidified by basolateral propionate alone, apical Na+/H+ exchange was 21% of the total Na+/H+ exchange activity. The change in relative activity was observed in individual cells which expressed both apical and basolateral Na+/H+ exchange and occurred rapidly (within 7 min). In the presence of transepithelial propionate gradients, all Na(+)-dependent alkalinization was sensitive to 3 microM 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)amiloride, a potent Na+/H+ exchange inhibitor. These results suggest that transepithelial gradients of short-chain fatty acids, which occur in vivo, can cause preferential activation of apical Na+/H+ exchange.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Mehta P. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate active sodium and chloride absorption in vitro in the rat distal colon. Gastroenterology. 1989 Apr;96(4):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91614-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Stange G., Murer H., Stieger B., Hauri H. P. Sodium-proton exchange in colon brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):G382–G390. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.3.G382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmon D. L., Watson A. J., Montrose M. H. Assay of apical membrane enzymes based on fluorogenic substrates. Anal Biochem. 1992 Feb 1;200(2):352–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90478-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Pomare E. W., Branch W. J., Naylor C. P., Macfarlane G. T. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut. 1987 Oct;28(10):1221–1227. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.10.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudeja P. K., Foster E. S., Brasitus T. A. Na+-H+ antiporter of rat colonic basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):G624–G632. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.4.G624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Dudeja P. K., Brasitus T. A. Na+-H+ exchange in rat colonic brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):G781–G787. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.6.G781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäbel G., Vogler S., Martens H. Short-chain fatty acids and CO2 as regulators of Na+ and Cl- absorption in isolated sheep rumen mucosa. J Comp Physiol B. 1991;161(4):419–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00260803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harig J. M., Soergel K. H., Barry J. A., Ramaswamy K. Transport of propionate by human ileal brush-border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):G776–G782. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.5.G776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildmann B., Storelli C., Haase W., Barac-Nieto M., Murer H. Sodium ion/L-lactate co-transport in rabbit small-intestinal brush-border-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):169–176. doi: 10.1042/bj1860169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtug K., McEwan G. T., Skadhauge E. Effects of propionate on the acid microclimate of hen (Gallus domesticus) colonic mucosa. Comp Biochem Physiol Comp Physiol. 1992 Dec;103(4):649–652. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(92)90160-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtug K. Mechanisms of absorption of short chain fatty acids--coupling to intracellular pH regulation. Acta Vet Scand Suppl. 1989;86:126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Sahuquillo-Merino C., Coudrier E., Louvard D. Absorptive and mucus-secreting subclones isolated from a multipotent intestinal cell line (HT-29) provide new models for cell polarity and terminal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):345–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane G. T., Gibson G. R., Cummings J. H. Comparison of fermentation reactions in different regions of the human colon. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;72(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb04882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascolo N., Rajendran V. M., Binder H. J. Mechanism of short-chain fatty acid uptake by apical membrane vesicles of rat distal colon. Gastroenterology. 1991 Aug;101(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose-Rafizadeh C., Guggino W. B., Montrose M. H. Cellular differentiation regulates expression of Cl- transport and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mRNA in human intestinal cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4495–4499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose M. H., Friedrich T., Murer H. Measurements of intracellular pH in single LLC-PK1 cells: recovery from an acid load via basolateral Na+/H+ exchange. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(1):63–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01869615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrose M. H., Murer H. Polarity and kinetics of Na(+)-H+ exchange in cultured opossum kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C121–C133. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhoul N. L., Lopes A. G., Chaillet J. R., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH regulation in the S3 segment of the rabbit proximal tubule in HCO3- -free solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Sep;92(3):369–393. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen K. U., Wood J. R., Schulze G., Heintze K. Stimulation of gallbladder fluid and electrolyte absorption by butyrate. J Membr Biol. 1981;62(3):183–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01998164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran V. M., Oesterlin M., Binder H. J. Sodium uptake across basolateral membrane of rat distal colon. Evidence for Na-H exchange and Na-anion cotransport. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1379–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI115444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechkemmer G., Wahl M., Kuschinsky W., von Engelhardt W. pH-microclimate at the luminal surface of the intestinal mucosa of guinea pig and rat. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Jul;407(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00580717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. A., Rajendran V. M., Binder H. J. Bicarbonate-stimulated [14C]butyrate uptake in basolateral membrane vesicles of rat distal colon. Gastroenterology. 1993 Sep;105(3):725–732. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90889-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. A., Blackmon D. L., Montrose M. H. Propionate activates multiple ion transport mechanisms in the HT29-18-C1 human colon cell line. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):G564–G571. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.3.G564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen K., von Engelhardt W. Absorption of Na, H ions and short chain fatty acids from the sheep colon. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):141–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00657005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Levine S. A., Yun C. H., Brant S. R., Pouyssegur J., Montrose M. H., Donowitz M. Functional characteristics of a cloned epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE3): resistance to amiloride and inhibition by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9110–9114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Levine S. A., Yun C. H., Montrose M. H., Little P. J., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and expression of a rabbit cDNA encoding a serum-activated ethylisopropylamiloride-resistant epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-2). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11917–11924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Ma A. I., Yang V. W., Watson A. J., Levine S., Montrose M. H., Potter J., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the rabbit ileal villus cell basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1957–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse M., Levine S., Yun C., Brant S., Counillon L. T., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Structure/function studies of the epithelial isoforms of the mammalian Na+/H+ exchanger gene family. J Membr Biol. 1993 Aug;135(2):93–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00231435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., METCALFE-GIBSON A., MORRISON R. B., NG S. T., HOWARD A. V. IN VIVO DIALYSIS OF FAECES AS A METHOD OF STOOL ANALYSIS. I. TECHNIQUE AND RESULTS IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. Clin Sci. 1965 Apr;28:357–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., Levine S., Donowitz M., Montrose M. H. Kinetics and regulation of a polarized Na(+)-H+ exchanger from Caco-2 cells, a human intestinal cell line. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):G229–G238. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.2.G229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



