Background: Channelrhodopsins, light-gated cation channels, are widely used for optogenetics.
Results: Channelrhodopsin-1/2 chimeras exhibit light-induced conformational changes with reduced Glu-129 deprotonation (Glu-90 in channelrhodopsin-2).
Conclusion: First and second channelrhodopsin-1 transmembrane helices are prerequisite for converting photostationary state of channelrhodopsin-2 into reduced desensitized state.
Significance: Channelrhodopsin-2 has some structural differences from a channelrhodopsin chimera whose x-ray crystal structure has been solved.
Keywords: Fourier Transform IR (FTIR), Gating, Ion Channel, Photobiology, Rhodopsin, Proton Transfer, Channel Desensitization, Channelrhodopsin
Abstract
Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii functions as a light-gated cation channel that has been developed as an optogenetic tool to stimulate specific nerve cells in animals and control their behavior by illumination. The molecular mechanism of ChR2 has been extensively studied by a variety of spectroscopic methods, including light-induced difference Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, which is sensitive to structural changes in the protein upon light activation. An atomic structure of channelrhodopsin was recently determined by x-ray crystallography using a chimera of channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and ChR2. Electrophysiological studies have shown that ChR1/ChR2 chimeras are less desensitized upon continuous illumination than native ChR2, implying that there are some structural differences between ChR2 and chimeras. In this study, we applied light-induced difference FTIR spectroscopy to ChR2 and ChR1/ChR2 chimeras to determine the molecular basis underlying these functional differences. Upon continuous illumination, ChR1/ChR2 chimeras exhibited structural changes distinct from those in ChR2. In particular, the protonation state of a glutamate residue, Glu-129 (Glu-90 in ChR2 numbering), in the ChR chimeras is not changed as dramatically as in ChR2. Moreover, using mutants stabilizing particular photointermediates as well as time-resolved measurements, we identified some differences between the major photointermediates of ChR2 and ChR1/ChR2 chimeras. Taken together, our data indicate that the gating and desensitizing processes in ChR1/ChR2 chimeras are different from those in ChR2 and that these differences should be considered in the rational design of new optogenetic tools based on channelrhodopsins.
Introduction
Channelrhodopsin-1 and -2 (ChR1 and ChR2)3 are photoreceptive proteins expressed in the eyespot of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (1–4). They have seven transmembrane helices and possess all-trans retinal as their chromophore. Photoisomerization of the retinal chromophore upon light absorption causes conformational changes in these proteins that result in opening of the channel gate and the flow of cations.
Recently, ChR2 and its derivative mutants with particular electrophysiological properties have been developed for use as powerful optogenetic tools, particularly in neuroscience (5–12). Optogenetics is a rapidly growing technique for manipulating specific neural activities by light stimulation, instead of invasive electrode methods. ChR2 is preferentially activated by blue light due to its absorption maximum at ∼470 nm. It inwardly conducts protons and Na+ ions in a light-dependent manner, resulting in the depolarization of ChR2-expressing cells. Since 2005, ChR2 has been genetically introduced into nerve cells in various animals to regulate their behavior by light illumination (5, 12, 13).
The time course of the photocurrent upon continuous illumination of ChR2 shows a peak-and-plateau, whereas that of ChR1 shows a rectangular shape (2). The suppression just after the transient maximum photocurrent seen in ChR2 is denoted the “desensitization” (14). A photocurrent without the desensitization process would be favorable for use in optogenetics, but heterologous expression of ChR1 in mammalian cells is usually very difficult. Therefore, ChR2 has been preferred over ChR1 for applications in optogenetics.
In 2009, several types of ChR1/ChR2 chimeras were characterized using electrophysiological techniques (14). One of these chimeras, originally named “channelrhodopsin/wide receiver,” consists of the first five transmembrane helices (TM1 to TM5) from ChR1 and the last two transmembrane helices (TM6 and TM7) from ChR2. This chimera is referred to as ChR5/2. Another chimera, originally named channelrhodopsin/fast receiver, consists of TM1 and TM2 from ChR1 and TM3 to TM7 from ChR2. This chimera is referred to as ChR2/5 (for details, see Figs. 1 and 2). These ChR1/ChR2 chimeras show larger photocurrents than the wild types, and their desensitization is significantly reduced upon continuous illumination (14). These features can overcome the principal disadvantage of ChR2 as an optogenetic tool: that the high level of desensitization that reduces the photocurrent by ∼80% at the plateau (2, 13, 15, 16). In addition, ChR5/2 is relatively sensitive to green light, and ChR2/5 exhibits faster on and off kinetics of the channel gating. These properties are advantages for their use in optogenetic applications.
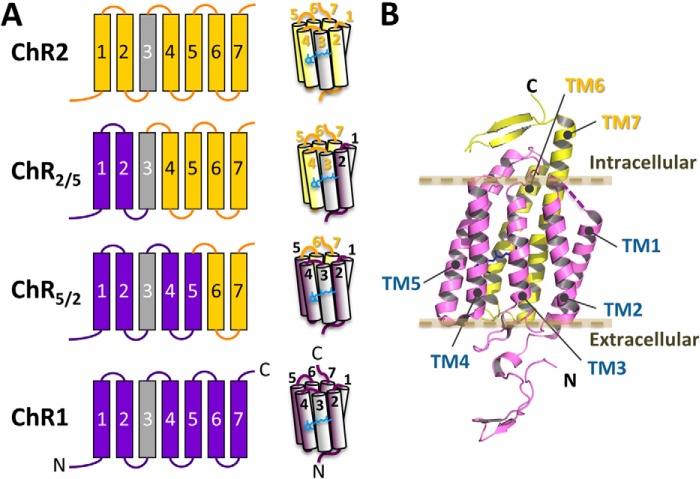
FIGURE 1.
Arrangement of the helices in chimeras of ChR1 and ChR2. A, schematic representation of the chimeric channel rhodopsins. The segments from ChR2 are colored yellow, and those from ChR1 are colored purple. Note that the amino acid sequences of TM3 in ChR1 and ChR2 (colored gray) are identical. A chimeric channelrhodopsin that has TM1 and TM2 from ChR1 and the other transmembrane regions from ChR2 is denoted ChR2/5. Also, a chimera that has TM1 to TM5 from ChR1 and the other transmembrane regions from ChR1 is denoted ChR5/2. B, the x-ray crystal structure of a chimeric channelrhodopsin called C1C2, which is nearly identical to ChR5/2.
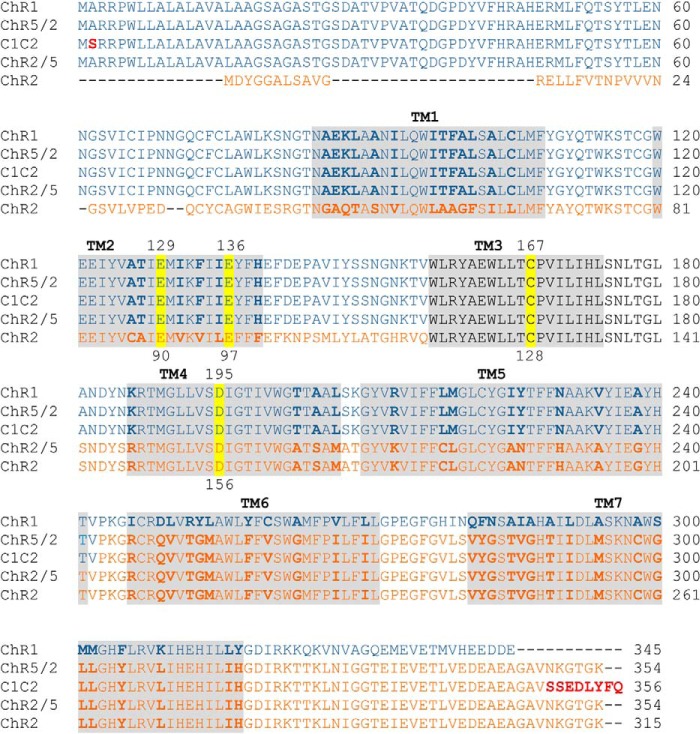
FIGURE 2.
Amino acid sequence alignment of ChR1, ChR2, and their chimeras (ChR5/2, ChR2/5, and C1C2). The amino acid sequences were aligned by ClustalW. The helix regions are shaded. The amino acid residues that are different between ChR1 and ChR2 are indicated in bold. The red residues in C1C2 are different from those in ChR5/2. The residues that are substituted in this work are highlighted in yellow. Note that the amino acid sequence of TM3 is identical between ChR1 and ChR2 (black).
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy has revealed the molecular mechanisms underlying the photo-induced structural dynamics of various microbial rhodopsins, such as bacteriorhodopsin and halorhodopsin (17–20). Using FTIR spectroscopy, the molecular mechanisms of ChR2 upon activation and desensitization have also been extensively studied (21–26). After the all-trans to 13-cis photoisomerization of the retinal chromophore in the ground (closed) state of ChR2, several intermediates (P1500, P2390, P3520, and P4480) are formed and then return to the ground state. From a comparison between photocurrent and flash photolysis experiments, P2390 and P3520 are considered to be conductive, whereas the desensitization occurs in P4480, which exhibits a large conformational change of the protein (21, 23).
In 2012, the three-dimensional structure of a chimeric channelrhodopsin was solved at atomic resolution using x-ray crystallography (27). This structure opened a way to understand the molecular mechanisms of channelrhodopsins in greater detail. Interestingly, the crystal structure was determined using a ChR1/ChR2 chimera. This chimera, called C1C2, consists of TM1 to TM5 from ChR1 and TM6 and TM7 from ChR2. The amino acid sequence of C1C2 is virtually the same as that of ChR5/2 (Fig. 2), and it shows a reduced desensitization upon continuous illumination, like ChR5/2 (27). The molecular mechanism of ChR2 has been discussed based on the C1C2 structure or a ChR2 homology model (10, 28). However, as noted above, ChR2 has a different amino acid sequence and different photocurrent properties than those of C1C2 (ChR5/2). Furthermore, the light-dependent structural changes exhibited by the chimera C1C2 and a ChR1 homologue from Chlamydomonas augustae have been studied by light-induced difference FTIR spectroscopy. These studies suggested the structural changes that occur during the photocycles of these channelrhodopsins are different from those in ChR2 (29–32).
In this study ChR1/ChR2 chimeras and ChR2 were studied by light-induced difference FTIR spectroscopy with an aim to reveal the molecular basis underlying the differences in electrophysiological properties between them. We also investigated the effects of the mutation of key residues on the photocyclic reaction and photocurrent profiles. Glu-90 in ChR2 is considered to be crucial for gating properties and ion selectivity (22, 28). Glu-129 in the chimeras (corresponding to Glu-90 in ChR2) was substituted with Gln to assign the vibrational bands of protonated carboxylate groups. Asp-195 and Cys-167 (corresponding to Asp-156 and Cys-128 in ChR2, respectively) constitute the so-called “DC-gate” in channelrhodopsins; mutations at these positions affect the kinetics of the P2 and P3 intermediates in the photocycle (11, 33). Electrophysiological measurements on DC-gate mutants of ChR2/5 and ChR5/2 have recently demonstrated that the cation-permeable states are markedly prolonged, like corresponding mutants of ChR2 (34). Here, we spectroscopically investigated DC-gate mutants of the chimeras to compare the structural changes in their P2 and P3 intermediates with those of ChR2.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Constructions of ChRs
The cDNA of ChR2 (GenBankTM AB058891/AF461397 (encoding amino acids 1–315)), ChR5/2 (chimera of ChR1; GenBankTM AB058890/AF385748 (amino acids 1–242) and ChR2 (amino acids 204–315)), and ChR2/5 (chimera of ChR1 (amino acids 1–164) and ChR2 (amino acids 126–315)) (14) were used in this study. A His9-tag sequence was fused to the C-terminal end of each ChR construct using a PCR reaction with DNA polymerase KOD Plus Neo (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan). The cDNAs were cloned into the mammalian expression vector pMT (a kind gift from Dr. David Farrens, Oregon Health and Science University) via its EcoRI and NotI sites using In-Fusion (Clontech). Point mutations (E129Q, E136Q, C167S, and D195N in chimeras and E90Q, C128S, and D156N in ChR2) were introduced using conventional PCR methods. The amino acid sequence of C1C2 (27) is virtually the same as the sequence of ChR5/2, with minor differences at position 2 at the N terminus and the last several residues at the C terminus (Fig. 2). It should be noted that the N- and C-terminal residues are far from the retinal and the ion-conducting pathway in the crystal structure of C1C2 (27). An amino acid sequence alignment is shown in Fig. 2.
Expression, Purification, and Reconstitution of ChRs
ChR2, ChR5/2, ChR2/5, and their mutants were expressed in COS-1 cells (a kind gift from Dr. David Farrens, Oregon Health and Science University) as previously described (35). The harvested cell membranes were mixed with 4 mm all-trans retinal for ∼6 h. The membranes were subsequently solubilized in a solution containing 20 mm HEPES (pH 7.0), 140 mm NaCl, and 1% DDM for 1 h. After centrifugation at 55,000 rpm for 20 min, Ni-Sepharose resin (GE Healthcare) was added to the supernatant. After 2 h of incubation, the sample was loaded into a Bio-spin disposable column (Bio-Rad) and washed with a buffer containing 50 mm Tri-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mm NaCl, 20 mm imidazole, 0.05% DDM, and 5% glycerol and subsequently washed with a buffer containing 50 mm Tri-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mm NaCl, 50 mm imidazole, 0.05% DDM, and 5% glycerol. The ChR samples were eluted with a buffer containing 50 mm Tri-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mm NaCl, 300 mm imidazole, 0.05% DDM, and 5% glycerol. For reconstitution of the ChRs into lipid vesicles, a mixture of the purified sample and phosphatidylcholine from egg yolk (Sigma) in a buffer containing 20 mm HEPES (pH 7.0), 140 mm NaCl, and 0.75% CHAPS was dialyzed against a buffer containing 20 mm HEPES (pH 7.0) and 140 mm NaCl using Spectra/Por7 (MWCO 15,000) (Spectrum Laboratories Inc.). The protein versus lipid molar ratio was 1:50, and the mixture was dialyzed for 8 days. Finally, the sample was centrifuged at 45,000 rpm for 25 min, and the pellet was washed twice and suspended in a buffer containing 2 mm phosphate (pH 7.5), 10 mm NaCl, and 0.05% glycerol to reach to an approximate concentration of 2 mg/ml. For time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy of C1C2 (see Figs. 8 and 9), C1C2 samples were prepared as described previously (27) (see below).
FIGURE 8.
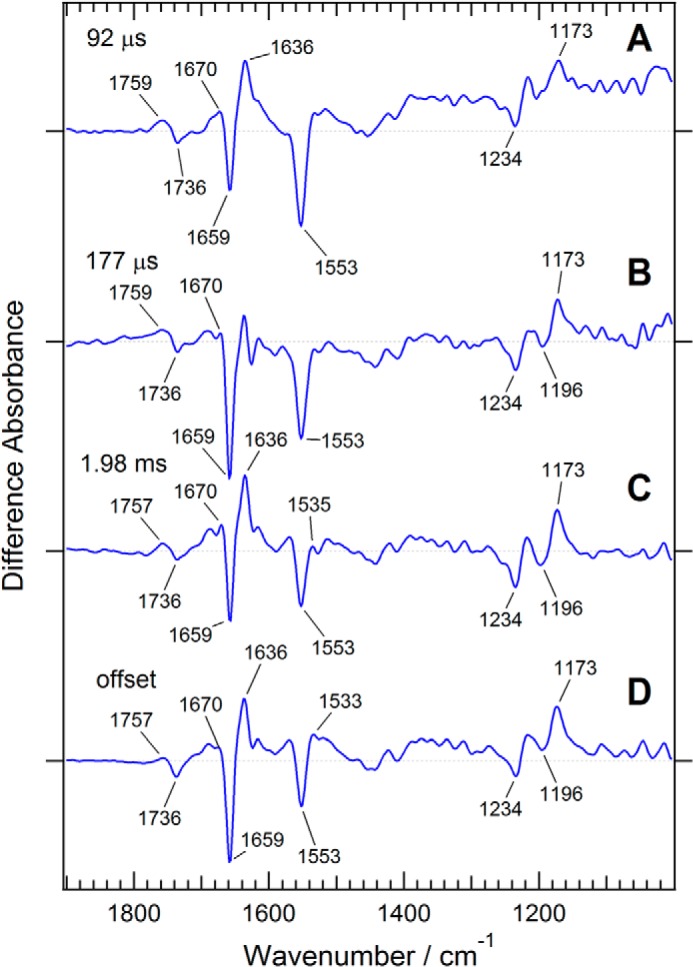
Time-resolved FTIR measurement of a ChR1/ChR2 chimera, C1C2, which is nearly identical to ChR5/2. The intermediate spectra (blue) are reconstituted from decay-associated spectra obtained by global exponential fitting with three time constants: 92 μs (A), 177 μs (B), and 1.98 ms (C) as well as D (the spectral component at the infinite time).
FIGURE 9.
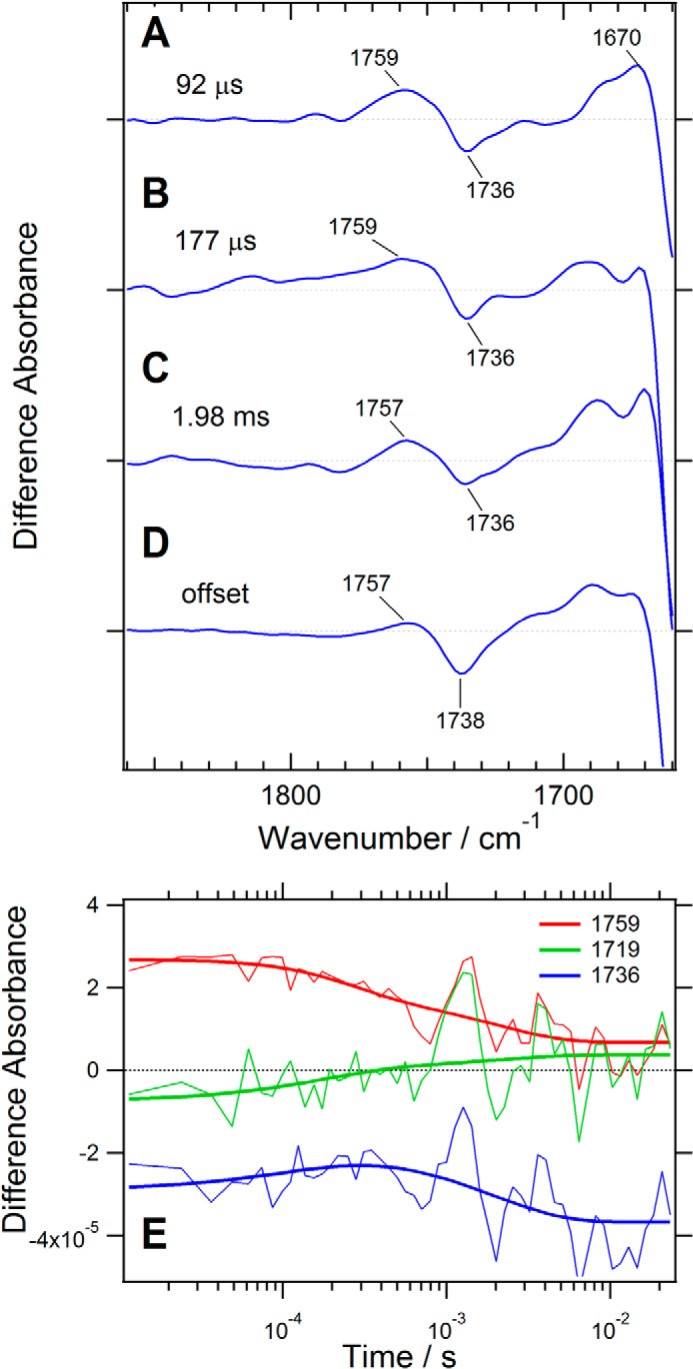
Upper panel, the spectral region of the carboxyl group C=O stretching vibration in the time-resolved FTIR spectra of a ChR1/ChR2 chimera, C1C2, which is virtually identical to ChR5/2. The intermediate spectra are reconstituted from decay-associated spectra obtained by global exponential fitting with three time constants: 92 μs (A), 177 μs (B), and 1.98 ms (C), as well as D (the spectral component at the infinite time). These spectra are reproduced from Fig. 8. Lower panel, time courses of the absorption changes at 1759 cm−1 (red), 1719 cm−1 (green), and 1736 cm−1 (blue) are shown with their global exponential fitting lines (thick lines, E).
Light-induced FTIR Measurements of the Photostationary State of Channelrhodopsin
A 5-μl aliquot of reconstituted ChR was dried on a nine reflectance attenuated total reflection crystal (DuraSamplIR II, Smiths Detection) and rehydrated with 8 μl of H2O water; the drops were placed close to the sample and sealed with a CaF2 window and a silicone spacer. The sample was kept for >2.5 h to stabilize the hydration level. The sample temperature was controlled using a homemade thermo-jacket circulating water from a thermo-regulated bath (Alpha RA8, Lauda) set to 25 °C. An FTIR spectrometer (Vertex70, Bruker Optics) equipped with a mercury-cadmium-telluride detector was used to measure IR spectra by using the rapid scan mode with a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1. For each measurement, the photostationary state of the ChRs was measured for 30 s with illumination from a metal halide lamp (IMH-250, Sigma-Koki) equipped with a short bandpath filter (460 nm, Sigma-Koki). The samples were rested in the dark for 5 min between measurements so that the ChRs can recover to the ground state, which was measured just before subsequent light illumination. The measurement was repeatedly performed until the data set met a fine signal-to-noise ratio. Then, the FTIR difference spectra (photostationary state minus ground state) were calculated. Because the FTIR difference spectra showed distortion, probably due to continuous illumination of the attenuated total reflection crystal, we bleached the ChR samples with hydroxylamine and performed the same procedure on the next day to measure the distorted background component. Finally, the pure FTIR difference spectra of photoactive ChRs were calculated by subtracting the distorted background component from the previously measured difference spectra.
Time-resolved FTIR Spectroscopy
The step-scan time-resolved FTIR measurement requires repetitive laser irradiation in order to construct a series of interferograms. This process, which gradually degrades the sample, requires a relatively large amount of protein compared with conventional FTIR measurements. Therefore, samples of C1C2, which was used for the previous x-ray crystallographic study (27) and is virtually identical to ChR5/2, were expressed in Sf9 cells, purified after solubilization in DDM detergent micelles, and reconstituted into phosphatidylcholine liposomes in a process similar to that used to prepare the samples for the attenuated total reflection-FTIR experiment. The C1C2 liposomes were suspended in a buffer solution (5 mm HEPES (pH 7.4) and 5 mm NaCl) at a final concentration estimated to be ∼5 optical density at 474 nm. A 30-μl aliquot of the C1C2 liposomes was deposited onto a CaF2 window and slowly dried in a refrigerator. Several drops of 20% (v/v) glycerol solution were placed near the C1C2 film sample and sealed using another CaF2 window with a silicone spacer. Then, the sample was mounted in the temperature-controlled cell. The sample temperature was kept at 25 °C by using a temperature-controlled cell (TFC-M25–3, Harrick) with a thermo-jacket circulating water from a thermostat bath (Alpha RA8, Lauda).
The photocycles of channelrhodopsins have a slow decay component for P4, which lives up to several seconds. Therefore, we introduced an electromagnetic shutter (SH-05, Thorlab) to reduce the repetition rate of a pulsed laser from 10 Hz to 0.25 Hz. The wavelength of the laser pulse was adjusted to 470 nm by use of an OPO system (LT-2214, Lotis TII) with 355 nm of the third harmonic of an Nd:YAG laser (LS-2134UTF, Lotis TII). The pulse duration was ∼7 ns. An FTIR spectrometer (Vertex80, Bruker Optics) with the step-scan mode was used to achieve a time resolution of 12.5 μs and to measure a time series of interferograms from −213.5 μs to ∼25 ms (the total number of time slices is 2000). We introduced an IR filter passing light with frequencies lower than 2000 cm−1 and limited the spectral range to 1950–1000 cm−1 with a spectral resolution of 8 cm−1 to reduce the number of sampling points while collecting an interferogram. Three photoreactions of C1C2 were co-added at each sampling point for a series of interferograms. Eighteen spectra collected before the excitations were averaged as a background for use when calculating the flash-induced difference spectra. We have done 2–4 experiments on one film sample and averaged 92 time-resolved difference spectra in total (corresponding to 276 scans for each spectrum).
Data Analysis for Time-resolved FTIR Spectra
The time-resolved FTIR spectra with 12.5-μs intervals (1982 spectra) were logarithmically averaged to be 20 spectra per log unit, which reduces the number of spectra (55 spectra) and improves the signal-to-noise ratio at later times. Then the data were analyzed by singular value decomposition, and the number of exponentials for reconstituting the experimental data was estimated. Next, the data were globally fitted using the number of exponentials and an offset component at infinite time. The decay-associated spectra obtained using this data analysis were converted to the intermediate spectra, which exhibit the vibrational bands of the decay intermediate components connected with the estimated time constant on the positive side and with those of the unphotolyzed state on the negative side.
RESULTS
Different Conformational Changes at the Photostationary States of ChR2, ChR5/2, and ChR2/5
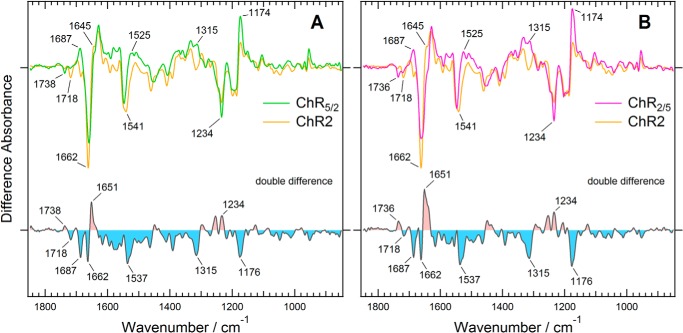
The difference infrared absorption spectra of the photostationary state (under continuous illumination with 460 nm light) minus the ground state (in the dark) were compared between ChR2 and ChR5/2 (Fig. 3A). The difference spectrum of ChR2 is very similar to the previously reported spectra of ChR2 in the photostationary state and the P4 intermediate spectrum constructed from time-resolved spectra (23, 25, 26). Our result also confirms that ChR2 under continuous illumination with blue light, denoted as the photostationary state, is composed mainly of the long-lived intermediate P4 (25, 26). Interestingly, the difference spectrum of ChR5/2 is somewhat different from that of ChR2. Differences in the 1738- and 1718-cm−1 bands in the C=O stretching region of the carboxyl groups, the 1687, 1651, and 1662-cm−1 bands in the amide I region, the 1537-cm−1 band in the regions of the amide II or C=O stretching modes of the retinal chromophore, and the 1234 and 1176-cm−1 bands in the region of the C-C stretching modes of the retinal chromophore were evident in the double difference spectrum (Fig. 3A). This means that replacement of the ChR2 segment with the corresponding ChR1 segment from the N terminus to TM5 altered the light-induced structural changes in the retinal chromophore, protein backbone, and some carboxyl groups of Asp or Glu side chains under the continuous light illumination. The positive 1315-cm−1 band is also characteristic of the photostationary state of ChR5/2, which is probably assignable to a vibrational mode of a side chain.
FIGURE 3.
Difference spectra between the photostationary state and the dark state of two chimeric channelrhodopsins, compared with that of ChR2. A, ChR5/2. B, ChR2/5. The difference spectra of ChR5/2, ChR2/5, and ChR2 are colored green, magenta, and orange, respectively. The double difference spectra were calculated by subtracting the light-induced difference spectrum of ChR2 with that of each chimera.
Next we measured the light-induced difference infrared absorption spectra of ChR2/5 because arrangement of TM1 and TM2 is characteristic of the crystal structure of channelrhodopsin (27). Our data clearly show that the introduction of TM4 and TM5 of ChR1 has little effect on the photostationary state because the difference spectrum of ChR2/5 is almost identical to that of ChR5/2 (Fig. 3B). It strongly suggests that TM1 and TM2 are responsible for the difference in structural changes that occur during continuous illumination between ChR2 and ChR1/ChR2 chimeras.
Protonation and Hydrogen-bonding Change of Asp and Glu Residues in Chimeric Channelrhodopsins
In the region of the carboxyl group C=O stretching vibration (Fig. 4), there are clear differences between ChR2 and the ChR1/ChR2 chimeras. Previous reports have assigned the negative bands at 1738 and 1718 cm−1 to Asp-156 and Glu-90, respectively, in ChR2 (25, 26, 33). Consistent with these previous reports, the 1718-cm−1 band disappeared in the difference spectra of the E90Q mutant of ChR2 (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, the intensity of the negative band at 1718 cm−1 decreased to approximately half in ChR2/5 and almost diminished in ChR5/2 even though both chimeras possess Glu-129 (corresponding to Glu-90 in ChR2) (Fig. 4A). Instead, the negative band at 1738 cm−1 (ChR5/2) or 1736 cm−1 (ChR2/5) and the positive band at 1757 cm−1 increased in intensity. The frequency of the former band indicates that the C=O group of the carboxyl side chain of Glu-129 in the chimeras forms a hydrogen bond in the ground state and that of the later band indicates weak or no hydrogen bond in the photostationary state.
FIGURE 4.
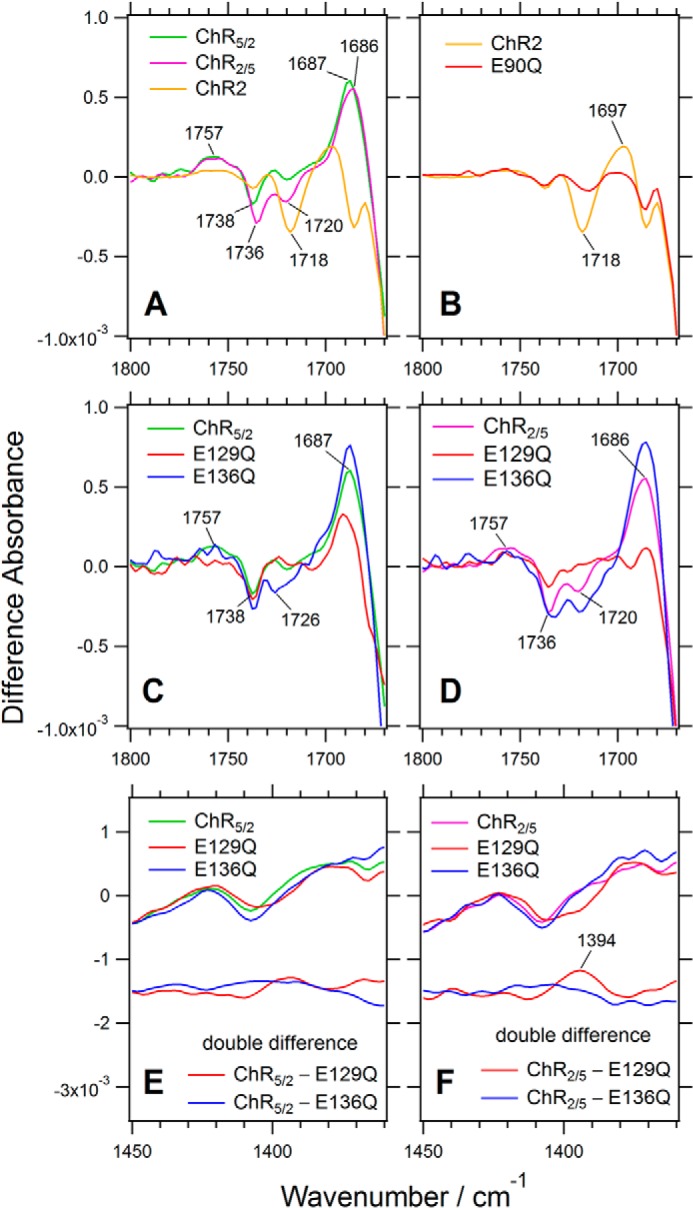
Comparison of the light-induced difference spectra of two chimeric channelrhodopsins (ChR5/2 and ChR2/5) with that of ChR2 in the frequency region of the C=O stretching vibration of carboxyl group (1800–1670 cm−1) and the symmetric COO− stretching vibration (1450–1360 cm−1). A, ChR5/2 (green), ChR2/5 (magenta), and ChR2 (orange). B, ChR2 (orange) and its E90Q mutant (red). C, ChR5/2 (green) and its E129Q (red) and E136Q (blue) mutants. D, ChR2/5 (magenta) and its E129Q (red) and E136Q (blue) mutants. E and F, the symmetric COO− stretching region of C and D with the double difference spectra between the E129Q or E136Q mutant and the chimeras, respectively.
The considerable differences between ChR2 and the ChR1/ChR2 chimeras were observed in the frequency region corresponding to the C=O stretching mode of carboxyl groups. Therefore, we needed to confirm the origins of these bands in ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 because Glu-90 and Asp-156 in ChR2 are located on TM2 and TM4, respectively, both of which are replaced to those from ChR1 in ChR5/2 and one of which is replaced in ChR2/5. We also assessed another nearby Glu residue at position 136 (corresponding to Glu-97 in ChR2) (see Fig. 10A).
FIGURE 10.
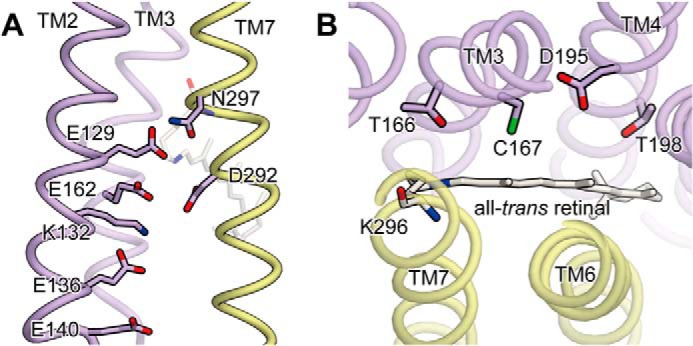
The x-ray crystal structure of C1C2. A, along the cation-conducting pathway. B, in the DC-gate region. Glu-129, Glu-136, Cys-167, and Asp-195, which were substituted in this study, correspond to Glu-90, Glu-97, Cys-128, and Asp-156 in ChR2, respectively. TM2, TM3, and TM4 from ChR1 are colored purple, whereas TM6 and TM7 from ChR2 are colored yellow. The all-trans retinal chromophore, which forms the Schiff base linkage with Lys-296, is rendered as a stick model.
The negative band at 1738 cm−1 was not affected by mutations E129Q or E136Q on TM2 of ChR5/2 (Fig. 4C), which means that the band is not from Glu-129 or Glu-136. As for ChR2/5, the negative band at 1736 cm−1 is preserved in E129Q, although with decreased intensity, and is almost unaffected by E136Q mutation (Fig. 4D). On the other hand, the small 1720-cm−1 band in ChR2/5 disappeared in the E129Q mutant, which supports the idea that the origin of the band is Glu-129 in the chimera, like Glu-90 in ChR2 (Fig. 4D). It should be noted that the E136Q mutation increased the intensity of the bands at 1726 cm−1 in ChR5/2 and 1720 cm−1 in ChR2/5, suggesting that Glu-129 is connected with Glu-136 through some indirect interaction. There is no obvious counterpart of the negative band at 1720 cm−1 in the protonated carboxylate region, whereas a positive band at 1394 cm−1 was observed in the symmetric COO− stretching region (Fig. 4F). Therefore, Glu-129 may be partially deprotonated in the photostationary state in ChR2/5. It should be noted that the positive band was not observed in ChR5/2 (Fig. 4E), which did not show a negative band around at 1720 cm−1. The E136Q mutant of ChR5/2 showed the negative band at 1726 cm−1 (Fig. 4C), whereas it did not exhibit a clear band in the symmetric COO− stretching region (Fig. 4E). Thus, in the E136Q mutant of ChR5/2, Glu-129 may keep its protonation state at the photostationary state.
The negative bands at 1738 cm−1 in ChR5/2 and 1736 cm−1 in ChR2/5 were downshifted to 1699 cm−1 and 1697 cm−1 in their respective D195N mutants (Fig. 5, A and B). In these mutants the additional positive bands at 1687 cm−1 were observed as the counterpart in the photostationary state (Fig. 5, A and B). These features were also seen in the D115N mutant of bacteriorhodopsin (corresponding to the D195N mutants of the ChR chimeras) (36). These results most likely support the assignment of the negative bands at 1736 and 1738 cm−1 to Asp-195 in ChR5/2 and ChR2/5, respectively. Asp-195 is proposed to be a part of the so-called DC-gate, with Cys-167 as a counterpart (Asp-156 and Cys-128 in ChR2 numbering) (33), although direct interaction between the two residues is not observed in the ChR crystal structure (27) (see Fig. 10B). Therefore, we analyzed the C167S mutants of the chimeras as well. The negative band at 1738 cm−1 in ChR5/2 was up-shifted to 1749 cm−1 in its C167S mutant, with the positive counterpart occurring at 1741 cm−1 (Fig. 5C). The mutation probably causes the upshift of the C=O stretching vibration of Asp-195 through some indirect interaction. A similar feature was observed in the C167S mutant of ChR2/5 (Fig. 5D). From these results, we conclude that the negative bands at 1738 cm−1 in ChR5/2 and 1736 cm−1 in ChR2/5 originate from the C=O stretching mode of Asp-195 in both chimeras, as it does in ChR2 (25, 33).
FIGURE 5.
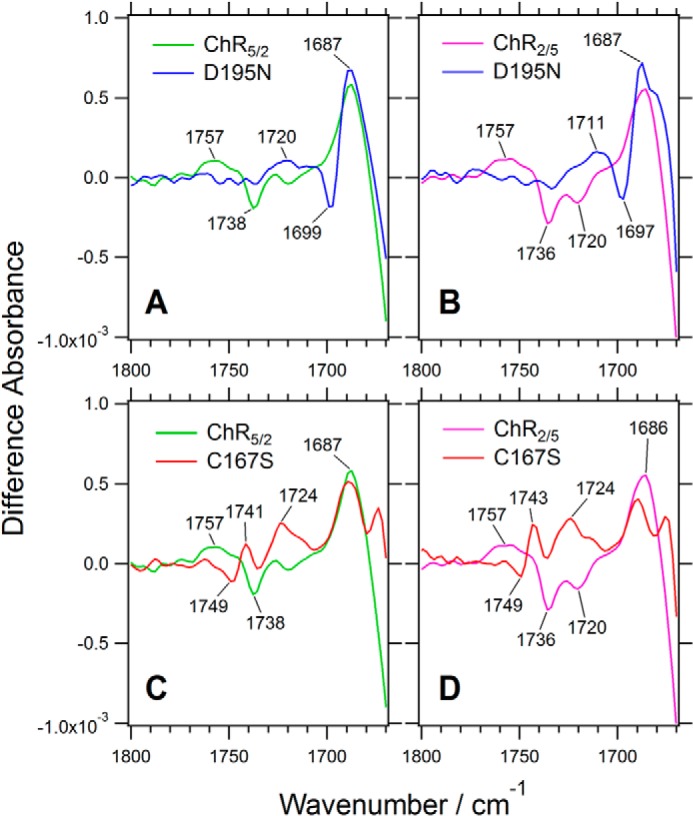
Light-induced difference spectra of two chimeric channelrhodopsins (ChR5/2 and ChR2/5) containing mutations at the DC gate (Asp-195 and Cys-167) in the frequency region of the C=O stretching vibration of carboxyl group (1800–1670 cm−1). A, ChR5/2 (green) and its D195N mutant (blue). B, ChR2/5 (magenta) and its D195N mutant (blue). C, ChR5/2 (green) and its C167S mutant (red). D, ChR2/5 (magenta) and its C167S mutant (red).
What is the origin of the broad positive bands observed at 1757 cm−1 in the chimeric channelrhodopsins? These bands were downshifted to 1720 and 1711 cm−1 in the D195N mutants of ChR5/2 and ChR2/5, respectively (Fig. 5, A and B). The negative bands at 1738 cm−1 in ChR5/2 and 1736 cm−1 in ChR2/5 were downshifted to 1699 and 1697 cm−1 in their respective D195N mutants (Fig. 5, A and B). The counterparts of the negative bands at 1738 cm−1 in ChR5/2 and 1736 cm−1 in ChR2/5 were observed at 1687 cm−1 in both of the mutants. Therefore, some part of the positive bands at 1757 cm−1 should not originate from Asp-195. The bands were downshifted to 1724 cm−1 in the C167S mutants of ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 (Fig. 5, C and D). Although the origin of the band could not be fully assigned by these experiments, it is probably due to protonation of the carboxylate group of an Asp or Glu residue in the chimeras and the mutants in the photostationary state. By analogy with other microbial rhodopsins (37, 38), it is assumed that possible candidates are Glu-162 and Asp-292, both of which are located at positions suitable to be counterions of the protonated Schiff base (see Fig. 10A). However, several groups recently reported various protonation mechanisms of these residues (23, 28, 31). Thus, further studies of mutants at these residues in the chimeras will be needed to completely determine the origin of the broad positive band at 1757 cm−1.
Different Conformational Changes at the Photostationary States of the DC-gate Mutants Stabilizing P2 or P3 Intermediates
The long-lived intermediate P4 is a major component in the photostationary state of ChR2 (21, 26). The differences between the spectrum of ChR2 and the spectra of the chimeras may be attributed to a variety of conformational changes that occur upon P4 formation. However, there is another possibility that the differences between the spectra are due to different intermediate components preserved in the photostationary state; that is, the lifetimes of the intermediates in ChR2/5 and ChR5/2 might be considerably different from those of the intermediates in ChR2. Actually, a ChR1 homologue from C. augustae accumulates P2 intermediate at the photostationary state (29).
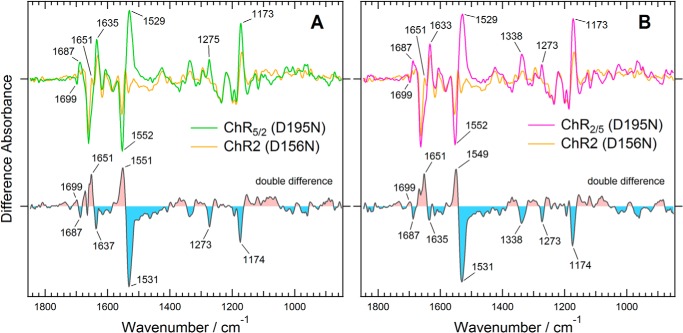
To verify these possibilities as the cause for the large differences in spectral changes between the chimeras and ChR2, we examined two mutants that stabilize the P2 or P3 state in the photostationary state. Previous studies have demonstrated that replacement of Asp-156, a part of the DC gate (see above), with a non-polar residue extends the lifetime of P3 by >35,000-fold (11). Thus, the major fraction in the photostationary state of the mutant was expected to be P3 (39). According to these reports, we analyzed spectral changes of D195N mutants of the chimeras in wavenumber regions other than the carboxylic acid region. As shown in Fig. 6, a large positive peak was observed at 1529 cm−1 in the spectra of the D195N mutants of the chimeras. The peak most likely originates from the ethylenic C=O stretching mode of the retinal chromophore. The frequency of this mode is well known to correlate with the wavelength of the visible absorption maximum of retinal proteins (40). The downshift of the band from 1552 cm−1 to 1529 cm−1 indicates the accumulation of a red-shifted intermediate, which is most likely the P3 state, which has an absorption maximum around at 520 nm. The intensities of the pair of bands at 1552 and 1529 cm−1 are much larger in ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 than in ChR2 (Fig. 6). This can be explained in two ways. One possibility is that the mutation-induced accumulation of the P3 state is more predominant in the chimeras. The increase of the positive band at 1173 cm−1, which originates from the C-C stretching vibration of the retinal and exhibits a greater intensity in protonated retinal, supports this possibility. The other possibility is overlap of the amide II mode in the same frequency region due to a larger conformational change of the protein backbone in the chimeras. This possibility is also supported by the larger spectral change in the amide I modes at around 1635 and 1651 cm−1.
FIGURE 6.
Light-induced difference spectra of the D195N mutants of two chimeric channelrhodopsins compared with that of the corresponding D156N mutant of ChR2. A, ChR5/2. B, ChR2/5. The difference spectra of the Asp mutants of ChR5/2, ChR2/5, and ChR2 are colored green, magenta, and orange, respectively. The double difference spectra were calculated by subtracting the light-induced difference spectrum of ChR2 with that of each chimera.
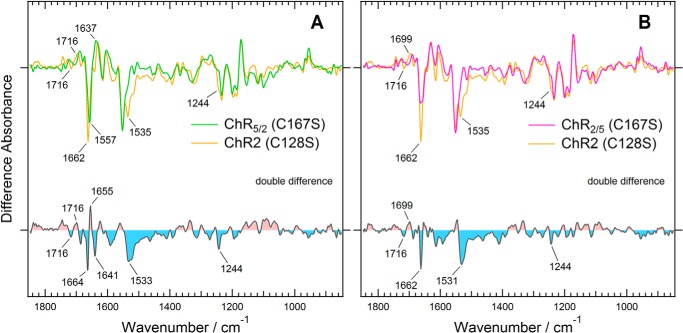
Previous studies on ChR2 showed that substitution of Cys-128 (corresponding to Cys-167 in the chimeras), which is potentially a counterpart to Asp-156 of the DC gate, with Ser causes a large accumulation of the P2 intermediate, whose absorption maximum is located at 390 nm, after illumination with 450-nm light (8). Therefore, the difference infrared spectra induced by continuous illumination with 460-nm light would be expected to reflect a dominant accumulation of the P2 intermediate. That is the case, as shown in Fig. 7. Unlike in the D195N mutants (Fig. 6), the ethylenic C=O stretch of the retinal chromophore exhibited a much reduced intensity at 1529 cm−1 in the photostationary state of the C128S mutant of ChR2 as well as in the corresponding C167S mutants of ChR2/5 and ChR5/2. There are significant differences between the difference spectra of the C167S mutants of the chimeras and the C128S mutant of ChR2 (Fig. 7, A and B). The double difference spectra exhibit large bands in the amide I and II region. The negative bands at 1664 and 1533 cm−1 in the double difference spectra are considered to correspond to the bands at 1662 and 1535 cm−1 in the ground state of the C128S mutant of ChR2, respectively. The positive band at 1655 cm−1 and the negative band at 1641 cm−1 were considered to originate from the photostationary state and the ground state of the C167S mutant of ChR5/2, respectively. Because these bands were not observed in the C167S mutant of ChR2/5 (Fig. 7B), the spectral change suggests a characteristic structural change in the P2 intermediate, which would be caused by a structural difference between ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 in TM4 and TM5.
FIGURE 7.
Light-induced difference spectra of the C167S mutants of two chimeric channelrhodopsins compared with that of corresponding ChR2 C128S mutant. A, ChR5/2. B, ChR2/5. The difference spectra of the Cys mutants of ChR5/2, ChR2/5, and ChR2 are colored green, magenta, and orange, respectively. The double difference spectra were calculated by subtracting the light-induced difference spectrum of ChR2 with that of each chimera.
From these results we conclude that spectral difference observed in ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 (Fig. 3) is attributed to the difference in structural changes in the P4 state. Namely, it was revealed that the structural changes of the chimeras were different not only in the P4 state but also in the P2 and P3 states from those of ChR2 by analyzing the light-induced difference spectra of the DC-gate mutants.
Conformational Changes of a ChR1/ChR2 Chimera, Observed by Time-resolved FTIR Spectroscopy
Based on the FTIR spectra of the photostationary states of ChR2 and the ChR1/ChR2 chimeras as well as spectra of their mutants, we have demonstrated that the structural changes upon formation of the P2, P3, and P4 intermediates are considerably different between ChR2 and ChR1/ChR2 chimeras. However, the structural changes of the intermediate states are more directly captured by the time-resolved spectroscopic method. Such time-resolved measurements have been reported on ChR2 (23, 28). We conducted time-resolved FTIR spectroscopic measurements on the ChR1/ChR2 chimera C1C2, which is virtually identical to ChR5/2 and was used for the crystallographic study (27). C1C2 samples were obtained through large scale expression in Sf9 cells and studied by time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy with 12.5-μs time resolution.
The time-resolved IR spectral data of C1C2 obtained at times up to ∼25 ms were composed of ∼2000 time slices. These data were reduced to 55 slices by logarithmically averaging the data to 20 points per log unit. Then, the data were analyzed using a singular value decomposition method to determine the minimal number of spectral components for reconstituting the data and, thus, remove the noise components. Three singular values were found to exceed those of the noise components. Then, the data were globally fitted by three exponentials and an offset at the end time. The time constants of the three components were estimated to be 92 μs, 180 μs, and 2.0 ms. Finally, the decay-associated spectra were obtained from the analysis.
Fig. 8 shows the intermediate spectra (IS1, IS2, IS3, and ISoffset). All of these spectra were calculated from the decay-associated spectra using an irreversible unidirectional kinetic model. Consistent with the previous time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy on ChR2 (23), IS1 is assumed to be composed of intermediates P1 and P2. IS2 and IS3 are mainly composed of intermediates P2 and P3, respectively. ISoffset is composed of intermediates P3 and P4. Actually, the IS2 spectrum looks very similar to the light-induced difference spectrum of the P2-stabilizing C167S mutant of ChR5/2 (Fig. 7). The IS3 spectrum does not exhibit a large band around at 1535 cm−1, which is characteristic of the P3 intermediate of the D195N mutant of ChR5/2. This suggests that a large negative band of amide II canceled the positive band at 1535 cm−1. The presence of the negative amide II band is supported by a strong negative amide-I band at 1659 cm−1, which indicates α helical structure and would originate from C=O groups of the main chain hydrogen-bonded with the N-H groups of the amide II band.
We did not measure the time-resolved data for ChR2, due to lack of sufficient protein sample, but our data on C1C2 can be compared with the ChR2 data in previous reports (23, 28). The comparison reveals intriguing differences in the C=O stretching vibration of carboxylic acid groups (Fig. 9). The positive band at 1759 cm−1 was found to retain stronger intensity than that of ChR2, especially in the earlier time region (23), but another time-resolved study of ChR2 showed a trend for the 1759-cm−1 band that is similar to the trend in our data (28). It would be considered that an Asp or Glu residue was protonated upon formation of the P2 intermediate and that the lifetime of its protonated state was prolonged until formation of the P3 intermediate in C1C2. The C=O stretching vibration of Glu-129 at 1719 cm−1 did not show substantial spectral changes in the observed time region. This strongly suggests that Glu-129 does not change its protonation state during the photocycle of C1C2, which shows a clear contrast with Glu-90 in ChR2 (23, 28). Glu-90 is considered to be a key residue for the gating of ChR2, although there is still some debate about the functional role of the residue.
DISCUSSION
Continuous light-induced difference spectroscopy and time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy clearly demonstrated that the light-induced conformational changes of chimeric channelrhodopsins (ChR5/2 (or C1C2) and ChR2/5) are somewhat different from those of ChR2. Moreover, the similarity of the difference spectra of ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 revealed that introduction of the N terminus, TM1, and TM2 of ChR1 is sufficient to cause most of the differences between the structural changes. Our data from mutants stabilizing the P3 (D195N) and P2 (C167S) states also revealed differences in the structural changes of each photointermediate. We also succeeded in assigning two C=O stretching vibrations around at 1720 and 1738 cm−1 in the chimeras to the carboxyl groups of Glu-129 and Asp-195 (Glu-90 and Asp-156 in ChR2), respectively. In the following paragraphs, we discuss the relevance of IR spectral changes to the molecular mechanism of the photoreaction of channelrhodopsins.
Deprotonation of Glu-129 and Its Correlation with Desensitization
A small, but significant difference was seen in the C=O stretching band of the carboxyl group of Glu-129 (Glu-90 in ChR2). The location of Glu-129 in the C1C2 crystal structure is shown in Fig. 10A. The intensity of the negative band around at 1720 cm−1 was decreased depending on the increase in the lengths of the segments of ChR1 present in the chimera (ChR5/2 < ChR2/5 < ChR2) (Figs. 3 and 4). The light-induced difference spectra of ChR1 from C. augustae that were recently reported did not show a prominent negative band at around 1720 cm−1 (29). Therefore, we conclude that deprotonation of Glu-129 in the photostationary state is partially hampered by TM1 and TM2 of ChR1 and almost completely hampered by the addition of TM4 and TM5 of ChR1.
It should be noted that there is an interesting correlation between these bands and the photocurrent profiles of these chimeric channelrhodopsins. The intensities of the Glu-129 (Glu-90 in ChR2) bands were lower in the chimeras as the number of segments from ChR1 increased. Disappearance of the 1720 cm−1 band in the D195N mutant of ChR2/5 is probably due to enrichment of the P3 intermediate state in the photostationary state. It indicates that Glu-129 may be deprotonated during the transition from P3 to P4 in ChR2/5 and that is the reason why the 1720-cm−1 band was not seen in the D195N mutant. Given the fact that these bands do not appear in the P3-rich photostationary state (in the D195N mutant) but do appear in the P4-rich photostationary state (Fig. 5, A and B), it was assumed that deprotonation of Glu-129 is correlated with the closing of the channel pore and the desensitization of the channel. The authors of a previous time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy study of ChR2 also proposed this interpretation (23). This study is the first to systematically demonstrate the correlation between desensitization and deprotonation of the Glu residue by using chimeric channelrhodopsins.
The Effect of Mutations in the DC Gate of the Chimeric Channelrhodopsins
From previous reports on ChR2, it is well known that one mutation in the DC gate, D156A, delays the decay of the P3 state, whereas a mutation in another part of the DC gate, C128S, stabilizes the P2 state (8, 11). A previous FTIR spectroscopy study on ChR2 suggested that Asp-156 and Cys-128 formed a hydrogen-bonding interaction (33). In this model the carboxyl group of Asp-156 is the hydrogen-bond acceptor and the S-H group of Cys-128 is the donor. However, an S-H stretching vibration at 2577 cm−1 was tentatively assigned to Cys-167 in the ground state of the chimera C1C2; this frequency is higher than the S-H stretching vibrations in microbial rhodopsins (32). Therefore, it was concluded that Cys-167 does not form a hydrogen bond with Asp-195 in C1C2, which is consistent with the x-ray crystal structure (27).
In this study the DC gate mutants of the chimeric channelrhodopsins were investigated by FTIR spectroscopy for the first time. The continuous light-induced difference spectra clearly showed that the D195N mutants and the C167S mutants stabilized the P3 state and the P2 state, respectively. In particular, the carboxyl C=O stretching bands at 1741 (+) and 1749 (−) cm−1 were observed in the C167S mutants (Fig. 5C), which were tentatively assigned to Asp-195. The higher frequency shift of the band suggests disruption of some interaction between Cys-167 and Asp-195. Therefore, these residues are likely to be connected by some sort of indirect interaction. There is a space nearby these residues that could be occupied by a water molecule (Fig. 10B). The presence of a water molecule there was also proposed by a molecular dynamics simulation study (41). It is possible that a hydrogen-bonding network through a water molecule exists in the DC gates of the chimeric channelrhodopsins.
Transient Protonation of a Carboxylate Group in the Photocycles of the Chimeric Channelrhodopsins
A broad positive band at around 1757 cm−1 was observed in the photostationary state of the chimeras (Fig. 4). This band was also observed in the time-resolved spectra of C1C2 (Fig. 9). It may partially originate from Asp-195 and be the result of an upshift of the 1738-cm−1 band upon photoreaction, as shown in the previous time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy on ChR2 (23). However, it seems to downshift to 1720 cm−1 in the D195N mutant of ChR5/2 and to 1711 cm−1 in ChR2/5, as shown in Fig. 5, A and B. Therefore, it would be attributed to transient protonation of an unknown carboxylate group. Interestingly, the band at 1757 cm−1 seems to downshift to 1724 cm−1 in the C167S mutants of ChR5/2 and ChR2/5 (Fig. 5C). Such a downshift was not observed in the early time of the photocycle, as shown in Fig. 9. Therefore, the downshifts would be caused by mutation-induced structural changes around the DC gate, not by accumulation of the P2 or P3 intermediate states. A possible candidate for the band may be Glu-162 and Asp-292 (Glu-123 and Asp-253 in ChR2), which are located at suitable positions to be the counterions of the protonated Schiff base. In the previous report on ChR2 (23), protonation of Asp-253 was observed at 1695 cm−1, which is a much lower frequency than the 1757-cm−1 band observed here. A strong interaction between the protonated Asp-253 and the negatively charged Glu-123 was proposed to explain the extremely low frequency of the 1695-cm−1 band of Asp-253 in ChR2 (23). If the origin of the 1757-cm−1 band is either Glu165 or Asp-292 in the chimeras, a strong interaction between Glu-162 and Asp-292 does not exist in the photostationary states, whereas a relatively weak interaction may exist in the photostationary states of the DC gate mutants. Recently, a similar positive band was observed at 1730 cm−1 in ChR1 from C. augustae (30). This band was tentatively assigned to the proton acceptor for the Schiff base (Glu-169 and Asp-299 correspond to Glu-162 and Asp-292 in the chimeras, respectively).
Conclusion
The molecular mechanism of ChR2 has been extensively studied by light-induced FTIR spectroscopy, electrophysiological methods, and computational methods, including molecular dynamics simulation. Furthermore, the x-ray crystal structure of a ChR1/ChR2 chimera has provided helpful information for understanding the experimental and theoretical data. However, ChR2 has some structural differences from ChR1/ChR2 chimeras, whose light-induced structural changes have been proven to be significantly different from those of ChR2. Therefore, careful consideration is needed to interpret ChR2 behavior based on the crystal structure of the ChR1/ChR2 chimera C1C2. In particular, the consideration is important for the rational design of new optogenetic tools based on ChR2.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Tsuneo Urisu for the opportunity to pursue this collaborative work, Hisashi Yoshida and Tomonori Toyoda at the Equipment Development Center in the Institute for Molecular Science for constructing an electronic circuit and a shutter controller, Dr. Víctor A. Lórenz-Fonfría for using a data analysis program, and Dr. David Farrens for providing COS-1 cells and the pMT expression vector. We thank Enago for the English language review.
This work was supported in part by the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) Program of “Creation of Nanosystems with Novel Function through Process Integration” and the Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO) Program of “Chemical Conversion of Light Energy” from the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST). This work was also supported in part by KAKENHI Japan Society for Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant 22770159 and 24650203 (to Y. F.).
- ChR1
- channelrhodopsin-1
- ChR2
- channelrhodopsin-2
- DDM
- n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside
- TM
- transmembrane helix.
REFERENCES
- 1. Nagel G., Ollig D., Fuhrmann M., Kateriya S., Musti A. M., Bamberg E., Hegemann P. (2002) Channelrhodopsin-1: a light-gated proton channel in green algae. Science 296, 2395–2398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Nagel G., Szellas T., Huhn W., Kateriya S., Adeishvili N., Berthold P., Ollig D., Hegemann P., Bamberg E. (2003) Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 13940–13945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Sineshchekov O. A., Jung K. H., Spudich J. L. (2002) Two rhodopsins mediate phototaxis to low- and high-intensity light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 8689–8694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Suzuki T., Yamasaki K., Fujita S., Oda K., Iseki M., Yoshida K., Watanabe M., Daiyasu H., Toh H., Asamizu E., Tabata S., Miura K., Fukuzawa H., Nakamura S., Takahashi T. (2003) Archaeal-type rhodopsins in Chlamydomonas: model structure and intracellular localization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 301, 711–717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Boyden E. S., Zhang F., Bamberg E., Nagel G., Deisseroth K. (2005) Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1263–1268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Berndt A., Lee S. Y., Ramakrishnan C., Deisseroth K. (2014) Structure-guided transformation of channelrhodopsin into a light-activated chloride channel. Science 344, 420–424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Berndt A., Schoenenberger P., Mattis J., Tye K. M., Deisseroth K., Hegemann P., Oertner T. G. (2011) High-efficiency channelrhodopsins for fast neuronal stimulation at low light levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 7595–7600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Berndt A., Yizhar O., Gunaydin L. A., Hegemann P., Deisseroth K. (2009) Bi-stable neural state switches. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 229–234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Wen L., Wang H., Tanimoto S., Egawa R., Matsuzaka Y., Mushiake H., Ishizuka T., Yawo H. (2010) Opto-current-clamp actuation of cortical neurons using a strategically designed channelrhodopsin. PLoS ONE 5, e12893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Wietek J., Wiegert J. S., Adeishvili N., Schneider F., Watanabe H., Tsunoda S. P., Vogt A., Elstner M., Oertner T. G., Hegemann P. (2014) Conversion of channelrhodopsin into a light-gated chloride channel. Science 344, 409–412 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Yizhar O., Fenno L. E., Prigge M., Schneider F., Davidson T. J., O'Shea D. J., Sohal V. S., Goshen I., Finkelstein J., Paz J. T., Stehfest K., Fudim R., Ramakrishnan C., Huguenard J. R., Hegemann P., Deisseroth K. (2011) Neocortical excitation/inhibition balance in information processing and social dysfunction. Nature 477, 171–178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Zhang F., Wang L. P., Boyden E. S., Deisseroth K. (2006) Channelrhodopsin-2 and optical control of excitable cells. Nat. Methods 3, 785–792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ishizuka T., Kakuda M., Araki R., Yawo H. (2006) Kinetic evaluation of photosensitivity in genetically engineered neurons expressing green algae light-gated channels. Neurosci. Res. 54, 85–94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Wang H., Sugiyama Y., Hikima T., Sugano E., Tomita H., Takahashi T., Ishizuka T., Yawo H. (2009) Molecular determinants differentiating photocurrent properties of two channelrhodopsins from chlamydomonas. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 5685–5696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lin J. Y. (2011) A user's guide to channelrhodopsin variants: features, limitations and future developments. Exp. Physiol. 96, 19–25 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Lin J. Y., Lin M. Z., Steinbach P., Tsien R. Y. (2009) Characterization of engineered channelrhodopsin variants with improved properties and kinetics. Biophys. J. 96, 1803–1814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Radu I., Schleeger M., Bolwien C., Heberle J. (2009) Time-resolved methods in biophysics. 10. Time-resolved FT-IR difference spectroscopy and the application to membrane proteins. Photochem Photobiol. Sci. 8, 1517–1528 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gerwert K., Freier E., Wolf S. (2014) The role of protein-bound water molecules in microbial rhodopsins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837, 606–613 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Furutani Y., Fujiwara K., Kimura T., Kikukawa T., Demura M., Kandori H. (2012) Dynamics of dangling bonds of water molecules in pharaonis halorhodopsin during chloride ion transportation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 2964–2969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Furutani Y., Okitsu T., Reissig L., Mizuno M., Homma M., Wada A., Mizutani Y., Sudo Y. (2013) Large spectral change due to amide modes of a β-sheet upon the formation of an early photointermediate of middle rhodopsin. J. Phys. Chem. B 117, 3449–3458 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Bamann C., Kirsch T., Nagel G., Bamberg E. (2008) Spectral characteristics of the photocycle of channelrhodopsin-2 and its implication for channel function. J. Mol. Biol. 375, 686–694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Eisenhauer K., Kuhne J., Ritter E., Berndt A., Wolf S., Freier E., Bartl F., Hegemann P., Gerwert K. (2012) In channelrhodopsin-2 Glu-90 is crucial for ion selectivity and is deprotonated during the photocycle. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 6904–6911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lórenz-Fonfría V. A., Resler T., Krause N., Nack M., Gossing M., Fischer von Mollard G., Bamann C., Bamberg E., Schlesinger R., Heberle J. (2013) Transient protonation changes in channelrhodopsin-2 and their relevance to channel gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, E1273–E1281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Lórenz-Fonfría V. A., Heberle J. (2014) Channelrhodopsin unchained: structure and mechanism of a light-gated cation channel. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837, 626–642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Radu I., Bamann C., Nack M., Nagel G., Bamberg E., Heberle J. (2009) Conformational changes of channelrhodopsin-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 7313–7319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ritter E., Stehfest K., Berndt A., Hegemann P., Bartl F. J. (2008) Monitoring light-induced structural changes of Channelrhodopsin-2 by UV-visible and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 35033–35041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Kato H. E., Zhang F., Yizhar O., Ramakrishnan C., Nishizawa T., Hirata K., Ito J., Aita Y., Tsukazaki T., Hayashi S., Hegemann P., Maturana A. D., Ishitani R., Deisseroth K., Nureki O. (2012) Crystal structure of the channelrhodopsin light-gated cation channel. Nature 482, 369–374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Kuhne J., Eisenhauer K., Ritter E., Hegemann P., Gerwert K., Bartl F. (2014) Early formation of the ion-conducting pore in channelrhodopsin-2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 10.1002/anie.201410180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Lórenz-Fonfría V. A., Muders V., Schlesinger R., Heberle J. (2014) Changes in the hydrogen-bonding strength of internal water molecules and cysteine residues in the conductive state of channelrhodopsin-1. J. Chem. Phys. 141, 22D507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Muders V., Kerruth S., Lórenz-Fonfría V. A., Bamann C., Heberle J., Schlesinger R. (2014) Resonance Raman and FTIR spectroscopic characterization of the closed and open states of channelrhodopsin-1. FEBS Lett. 588, 2301–2306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Ogren J. I., Mamaev S., Russano D., Li H., Spudich J. L., Rothschild K. J. (2014) Retinal chromophore structure and Schiff base interactions in red-shifted channelrhodopsin-1 from Chlamydomonas augustae. Biochemistry 53, 3961–3970 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Ito S., Kato H. E., Taniguchi R., Iwata T., Nureki O., Kandori H. (2014) Water-containing hydrogen-bonding network in the active center of channelrhodopsin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 3475–3482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Nack M., Radu I., Gossing M., Bamann C., Bamberg E., von Mollard G. F., Heberle J. (2010) The DC gate in channelrhodopsin-2: crucial hydrogen bonding interaction between C128 and D156. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 9, 194–198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Hososhima S., Sakai S., Ishizuka T., Yawo H. (2015) Kinetic evaluation of photosensitivity in bi-stable variants of chimeric channelrhodopsins. PLoS ONE 10, e0119558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Tsukamoto H., Farrens D. L. (2013) A constitutively activating mutation alters the dynamics and energetics of a key conformational change in a ligand-free G protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 28207–28216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kandori H., Shimono K., Shichida Y., Kamo N. (2002) Interaction of Asn105 with the retinal chromophore during photoisomerization of pharaonis phoborhodopsin. Biochemistry 41, 4554–4559 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. (1988) Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry 27, 8516–8520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Furutani Y., Iwamoto M., Shimono K., Kamo N., Kandori H. (2002) FTIR spectroscopy of the M photointermediate in pharaonis phoborhodopsin. Biophys. J. 83, 3482–3489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Bamann C., Gueta R., Kleinlogel S., Nagel G., Bamberg E. (2010) Structural guidance of the photocycle of channelrhodopsin-2 by an interhelical hydrogen bond. Biochemistry 49, 267–278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Aton B., Doukas A. G., Callender R. H., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. (1977) Resonance Raman studies of the purple membrane. Biochemistry 16, 2995–2999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Watanabe H. C., Welke K., Sindhikara D. J., Hegemann P., Elstner M. (2013) Towards an understanding of channelrhodopsin function: simulations lead to novel insights of the channel mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 425, 1795–1814 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]