Abstract
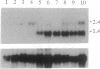
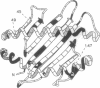
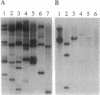
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I genes typically encode polymorphic peptide-binding chains which are ubiquitously expressed and mediate the recognition of intracellular antigens by cytotoxic T cells. They constitute diverse gene families in different species and include the numerous so-called nonclassical genes in the mouse H-2 complex, of which some have been adapted to variously modified functions. We have identified a distinct family of five related sequences in the human MHC which are distantly homologous to class I chains. These MIC genes (MHC class I chain-related genes) evolved in parallel with the human class I genes and with those of most if not all mammalian orders. The MICA gene in this family is located near HLA-B and is by far the most divergent mammalian MHC class I gene known. It is further distinguished by its unusual exon-intron organization and preferential expression in fibroblasts and epithelial cells. However, the presence of diagnostic residues in the MICA amino acid sequence translated from cDNA suggests that the putative MICA chain folds similarly to typical class I chains and may have the capacity to bind peptide or other short ligands. These results define a second lineage of evolutionarily conserved MHC class I genes. This implies that MICA and possibly other members in this family have been selected for specialized functions that are either ancient or derived from those of typical MHC class I genes, in analogy to some of the nonclassical mouse H-2 genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjorkman P. J., Parham P. Structure, function, and diversity of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:253–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson S. K., Pei J., Taillon-Miller P., Chorney M. J., Geraghty D. E., Chaplin D. D. Isolation and characterization of yeast artificial chromosome clones linking the HLA-B and HLA-C loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1676–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Katzman P., Alicot E. M., Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Linkage map of the human major histocompatibility complex including the tumor necrosis factor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBrino M., Parker K. C., Shiloach J., Turner R. V., Tsuchida T., Garfield M., Biddison W. E., Coligan J. E. Endogenous peptides with distinct amino acid anchor residue motifs bind to HLA-A1 and HLA-B8. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 15;152(2):620–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Koller B. H., Hansen J. A., Orr H. T. The HLA class I gene family includes at least six genes and twelve pseudogenes and gene fragments. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1934–1946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Pei J., Lipsky B., Hansen J. A., Taillon-Miller P., Bronson S. K., Chaplin D. D. Cloning and physical mapping of the HLA class I region spanning the HLA-E-to-HLA-F interval by using yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Wei X. H., Orr H. T., Koller B. H. Human leukocyte antigen F (HLA-F). An expressed HLA gene composed of a class I coding sequence linked to a novel transcribed repetitive element. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D., Parham P. Reptilian class I major histocompatibility complex genes reveal conserved elements in class I structure. Immunogenetics. 1992;36(3):166–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00661093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberg R., Eghtesady P., Sydora B., Brorson K., Cheroutre H., Modlin R., Kronenberg M. Expression of the thymus leukemia antigen in mouse intestinal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9727–9731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V., Allsopp C. E., Kwiatkowski D., Anstey N. M., Twumasi P., Rowe P. A., Bennett S., Brewster D., McMichael A. J., Greenwood B. M. Common west African HLA antigens are associated with protection from severe malaria. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):595–600. doi: 10.1038/352595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Van Kaer L., Bonneville M., Hsu S., Murphy D. B., Tonegawa S. Recognition of the product of a novel MHC TL region gene (27b) by a mouse gamma delta T cell receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90019-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J., Andersen R., Avila D., Engberg J., Lambris J., Salomonsen J., Welinder K., Skjødt K. Different features of the MHC class I heterodimer have evolved at different rates. Chicken B-F and beta 2-microglobulin sequences reveal invariant surface residues. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1532–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Shimizu Y., DeMars R., Orr H. T. HLA-E. A novel HLA class I gene expressed in resting T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):897–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovats S., Main E. K., Librach C., Stubblebine M., Fisher S. J., DeMars R. A class I antigen, HLA-G, expressed in human trophoblasts. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):220–223. doi: 10.1126/science.2326636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The three-dimensional structure of HLA-B27 at 2.1 A resolution suggests a general mechanism for tight peptide binding to MHC. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. H., Calabi F., Milstein C. Isolation of CD1 genes: a family of major histocompatibility complex-related differentiation antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9154–9158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamer E. G., Wang C. R., Flaherty L., Lindahl K. F., Bevan M. J. H-2M3 presents a Listeria monocytogenes peptide to cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90097-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Benjamin R. J., Wesley P. K., Buxton S. E., Garrett T. P., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M., Norment A. M., Littman D. R., Parham P. A binding site for the T-cell co-receptor CD8 on the alpha 3 domain of HLA-A2. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):41–46. doi: 10.1038/345041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher B. T., Nairn R., Coligan J. E., Hood L. E. DNA sequence of the mouse H-2Dd transplantation antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1175–1179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., DeMars R. Production of human cells expressing individual transferred HLA-A,-B,-C genes using an HLA-A,-B,-C null human cell line. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3320–3328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simister N. E., Mostov K. E. An Fc receptor structurally related to MHC class I antigens. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):184–187. doi: 10.1038/337184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan D., Sun H., Lindahl K. F., Meyer E., Hämmerling G., Hood L., Steinmetz M. Organization and evolution of D region class I genes in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1227–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng H., Green H. Basonuclin: a keratinocyte protein with multiple paired zinc fingers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10311–10315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidović D., Roglić M., McKune K., Guerder S., MacKay C., Dembić Z. Qa-1 restricted recognition of foreign antigen by a gamma delta T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):646–650. doi: 10.1038/340646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. R., Lindahl K. F. Organization and structure of the H-2M4-M8 class I genes in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(4):258–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00188802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. R., Loveland B. E., Lindahl K. F. H-2M3 encodes the MHC class I molecule presenting the maternally transmitted antigen of the mouse. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90623-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Geliebter J., Tonkonogy S., Flaherty L. Expression of the Q2 gene of the MHC in thymus and intestinal epithelial cells. Immunogenetics. 1993;38(5):370–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00210481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S., Davis A. C., Gaut B., Wheeler C., Hill L., Goodenow R. S. Organization and structure of the Qa genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the C3H mouse: implications for Qa function and class I evolution. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1749–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]