Abstract
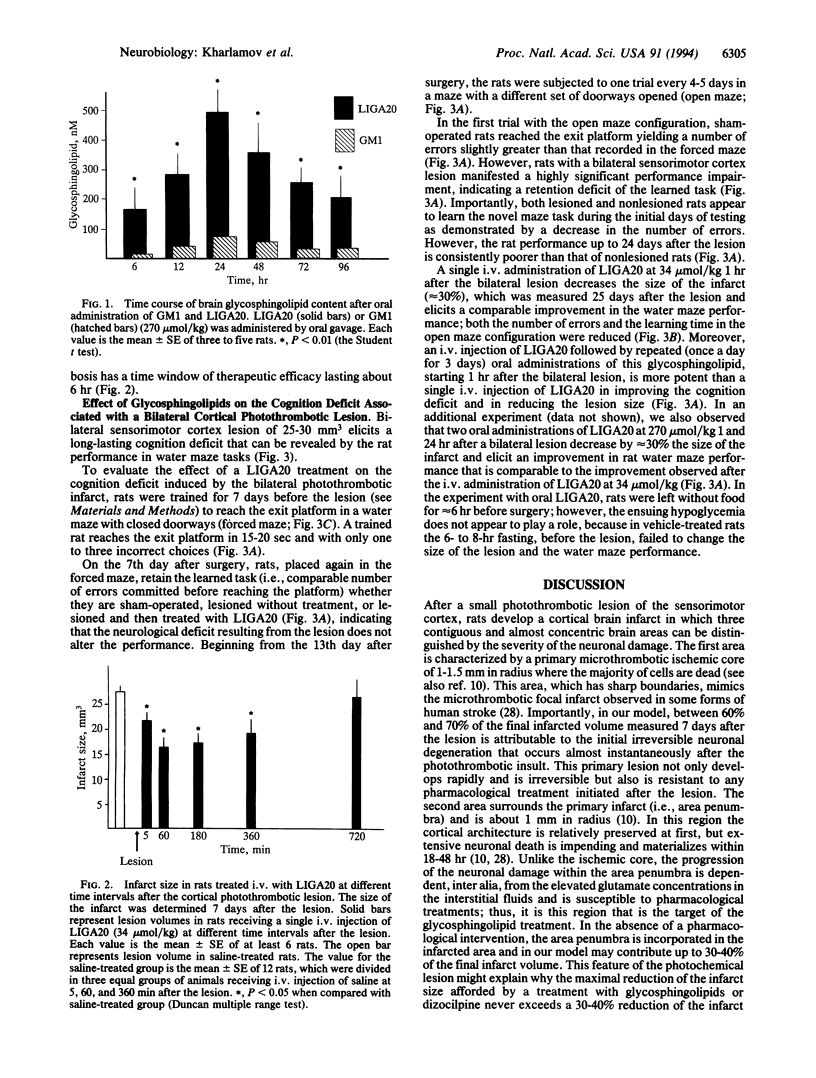
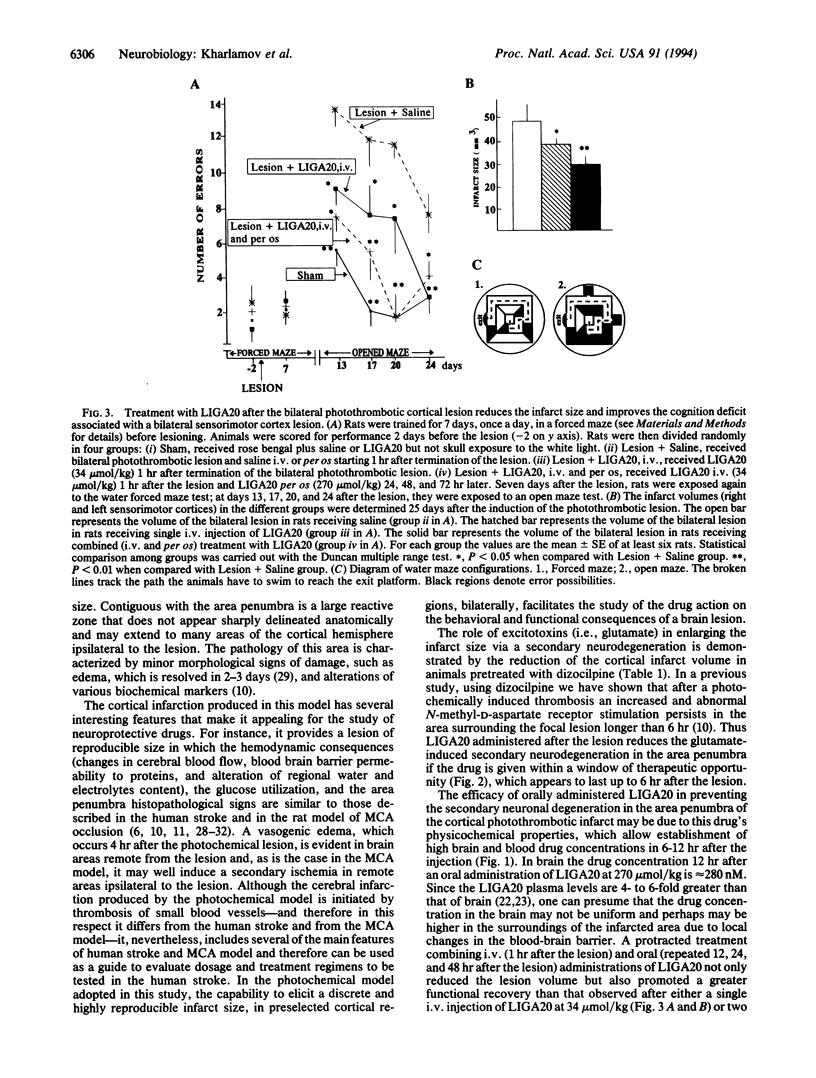
A bilateral photochemically induced thrombotic lesion of rat sensorimotor cortex (approximately 3 mm in diameter and 25 mm3 in volume) is associated with a persistent cognition (learning and memory) deficit, which was evaluated with water maze tasks. The N-dichloroacetylsphingosine derivative of lysoGM1 (LIGA20) administered after the lesion either i.v. or per or reduces the infarct size by 30-40% and attenuates the associated cognition deficits, presumably by limiting the extent of damage of neurons at risk located in the surroundings of the infarcted core (i.e., area penumbra). The LIGA20 protection is dose and time dependent. Maximal protection is afforded by a single dose of LIGA20 of 34 mumol/kg i.v. 1 hr after lesion or by a dose of 270 mumol/kg per os when administered 1 hr and 24 hr after the lesion. The protective effect of LIGA20 can be observed when the drug is administered i.v. up to 6 hr after the lesion. The protective efficacy of the oral administration of LIGA20 is related to its physiochemical properties, which, unlike those of GM1, allow absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. LIGA20 given orally reaches the brain promptly and rapidly inserts into the neuronal membranes. Here, by an unknown molecular mechanism, LIGA20 selectively reduces the pathological amplification of Ca2+ signaling elicited by persistent stimulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors in the area penumbra.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bederson J. B., Pitts L. H., Germano S. M., Nishimura M. C., Davis R. L., Bartkowski H. M. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1304–1308. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharucha V. A., Wakade C. G., Mahadik S. P., Karpiak S. E. GM1 ganglioside treatment reduces functional deficits associated with cortical focal ischemia. Exp Neurol. 1991 Oct;114(1):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90091-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carolei A., Fieschi C., Bruno R., Toffano G. Monosialoganglioside GM1 in cerebral ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1991 Summer;3(2):134–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Aporti F., Finesso M. Effects of brain gangliosides on functional recovery in experimental regeneration and reinnervation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;71:275–293. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4614-9_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Kharlamov A., Guidotti A., Hayes R., Armstrong D. Sequelae of biochemical events following photochemical injury of rat sensory-motor cortex: mechanism of ganglioside protection. Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 1992 Jul-Aug;(4):17–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. D., Ginsberg M. D., Busto R., Watson B. D. Photochemically induced cortical infarction in the rat. 1. Time course of hemodynamic consequences. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1986 Apr;6(2):184–194. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1986.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. D., Watson B. D., Busto R., Ginsberg M. D., Bethea J. R. Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. I. Early microvascular alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;72(4):315–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00687262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaron M., Manev H., Alho H., Bertolino M., Ferret B., Guidotti A., Costa E. Gangliosides prevent glutamate and kainate neurotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures of neonatal rat cerebellum and cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7351–7355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari G., Batistatou A., Greene L. A. Gangliosides rescue neuronal cells from death after trophic factor deprivation. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):1879–1887. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-01879.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo L., Cuello A. C. Nerve growth factor and the monosialoganglioside GM1: analogous and different in vivo effects on biochemical, morphological, and behavioral parameters of adult cortically lesioned rats. Exp Neurol. 1994 Feb;125(2):195–217. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler F. H., Dorsey F. C., Coleman W. P. Recovery of motor function after spinal-cord injury--a randomized, placebo-controlled trial with GM-1 ganglioside. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 27;324(26):1829–1838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106273242601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. D., Busto R. Rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 1989 Dec;20(12):1627–1642. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.12.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kant G. J., Yen M. H., D'Angelo P. C., Brown A. J., Eggleston T. Maze performance: a direct comparison of food vs. water mazes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Oct;31(2):487–491. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpiak S. E., Mahadik S. P., Wakade C. G. Ganglioside reduction of ischemic injury. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1990;5(3):221–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharlamov A., Guidotti A., Costa E., Hayes R., Armstrong D. Semisynthetic sphingolipids prevent protein kinase C translocation and neuronal damage in the perifocal area following a photochemically induced thrombotic brain cortical lesion. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2483–2494. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02483.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manev H., Costa E., Wroblewski J. T., Guidotti A. Abusive stimulation of excitatory amino acid receptors: a strategy to limit neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2789–2797. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2165013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manev H., Favaron M., Vicini S., Guidotti A., Costa E. Glutamate-induced neuronal death in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells: protection by synthetic derivatives of endogenous sphingolipids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jan;252(1):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perillo M. A., Polo A., Guidotti A., Costa E., Maggio B. Molecular parameters of semisynthetic derivatives of gangliosides and sphingosine in monolayers at the air-water interface. Chem Phys Lipids. 1993 Oct;65(3):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(93)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli C., Righini A., Linfante I., Tao-Cheng J. H., Alger J. R., Di Chiro G. Histopathologic correlates of abnormal water diffusion in cerebral ischemia: diffusion-weighted MR imaging and light and electron microscopic study. Radiology. 1993 Nov;189(2):439–448. doi: 10.1148/radiology.189.2.8210373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polo A., Kirschner G., Guidotti A., Costa E. Brain content of glycosphingolipids after oral administration of monosialogangliosides GM1 and LIGA20 to rats. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1994 Jan;21(1):41–53. doi: 10.1007/BF03160083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. M., Gillinov A. M., Blue M. E., Zehr K. J., Troncoso J. C., Cameron D. E., Johnston M. V., Baumgartner W. A. The monosialoganglioside, GM1, reduces neurologic injury associated with hypothermic circulatory arrest. Surgery. 1993 Aug;114(2):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seren M. S., Lazzaro A., Yang C. L., Canella R., Bassan M., Zanoni R., Manev H. Orally administered glycolipid derivative LIGA20 reduces infarct volume and behavioral impairment after focal cerebral ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seren M. S., Rubini R., Lazzaro A., Zanoni R., Fiori M. G., Leon A. Protective effects of a monosialoganglioside derivative following transitory forebrain ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1990 Nov;21(11):1607–1612. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.11.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. P., Chen J., Graham S. H. GM1 ganglioside treatment of focal ischemia: a dose-response and microdialysis study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaper S. D., Leon A., Facci L. Death of cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons induced by pathological activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors is reduced by monosialogangliosides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaper S. D., Leon A., Toffano G. Ganglioside function in the development and repair of the nervous system. From basic science to clinical application. Mol Neurobiol. 1989 Fall;3(3):173–199. doi: 10.1007/BF02935630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnino S., Cantu L., Corti M., Acquotti D., Kirschner G., Tettamanti G. Aggregation properties of semisynthetic GM1 ganglioside (II3Neu5AcGgOse4Cer) containing an acetyl group as acyl moiety. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Nov;56(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettamanti G., Bonali F., Marchesini S., Zambotti V. A new procedure for the extraction, purification and fractionation of brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):160–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanics R., Greenberg J. H., Toffano G., Reivich M. Effect of GM1 ganglioside after focal cerebral ischemia in halothane-anesthetized cats. Stroke. 1989 Jun;20(6):795–802. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.6.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B. D., Dietrich W. D., Busto R., Wachtel M. S., Ginsberg M. D. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 1985 May;17(5):497–504. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Erausquin G. A., Manev H., Guidotti A., Costa E., Brooker G. Gangliosides normalize distorted single-cell intracellular free Ca2+ dynamics after toxic doses of glutamate in cerebellar granule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8017–8021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



