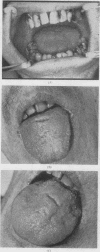
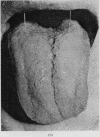
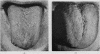
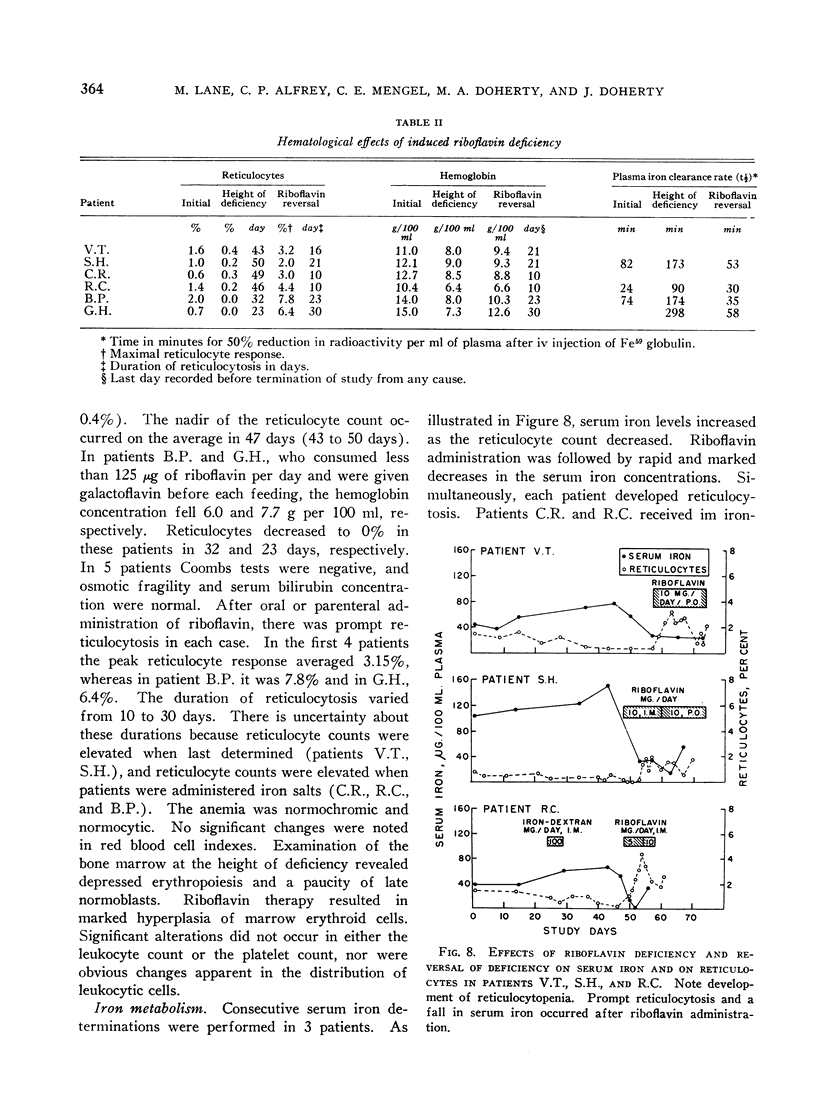
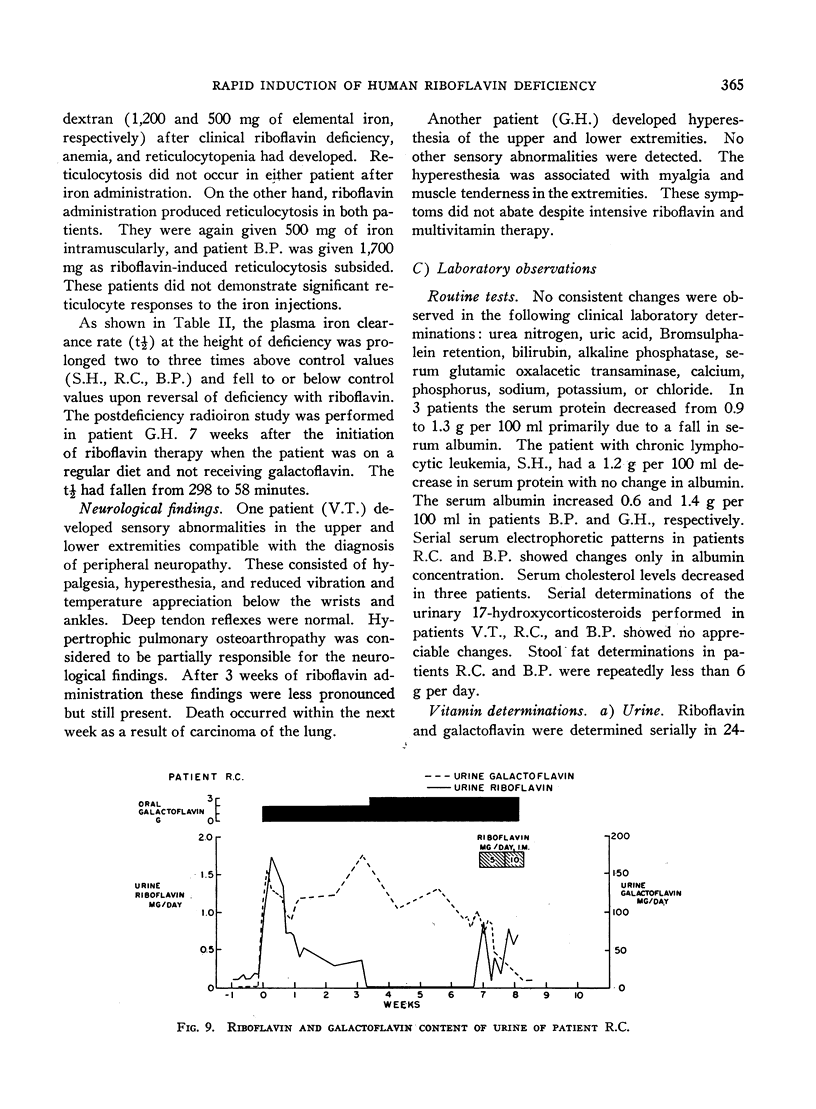
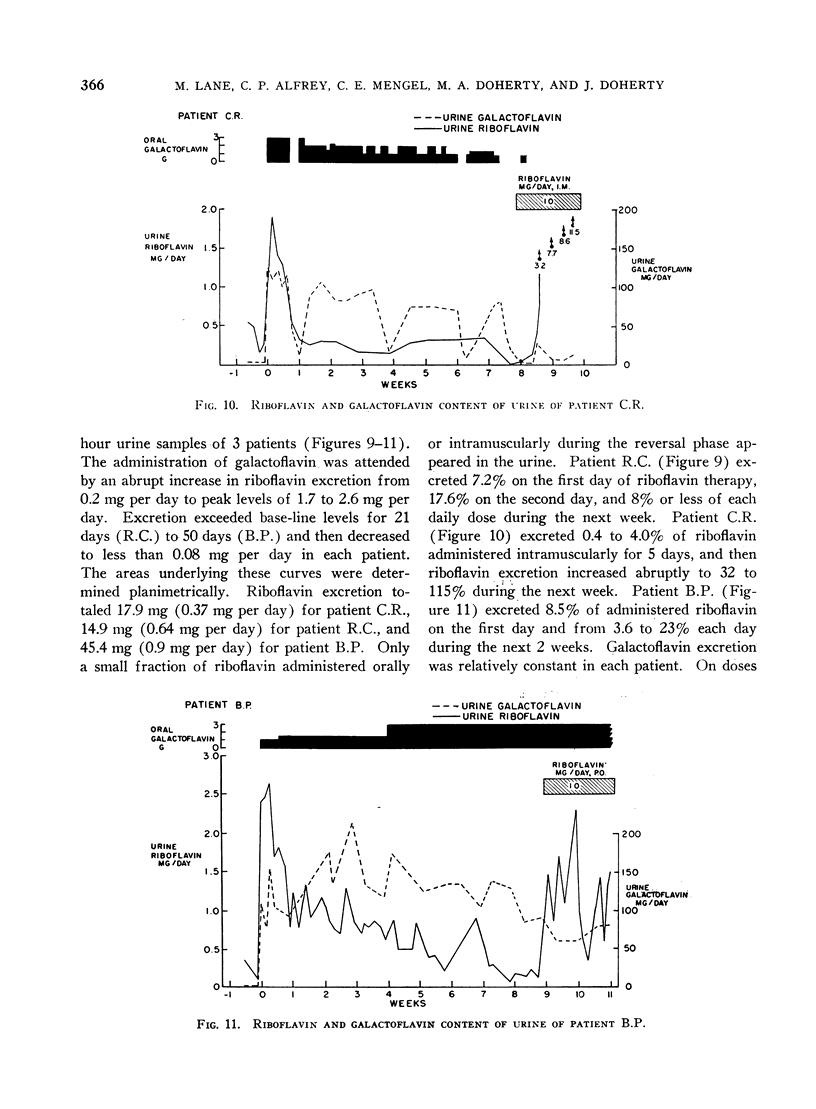
Full text
PDF

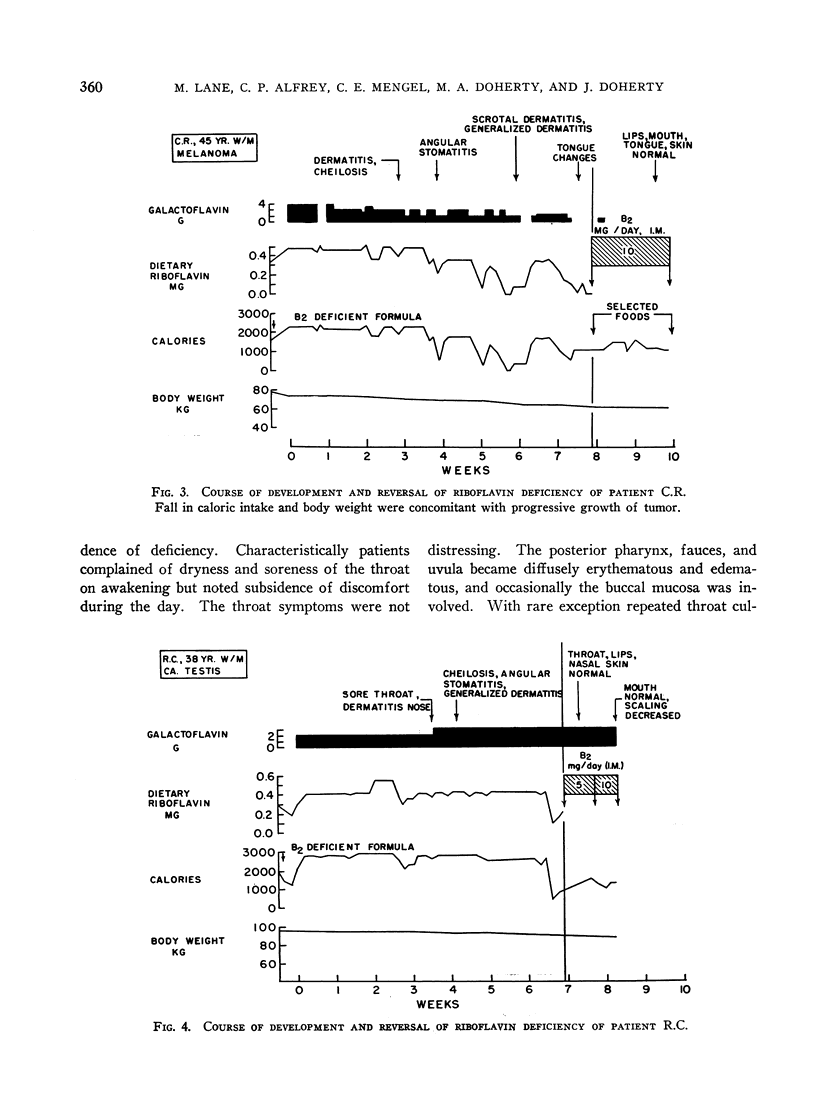
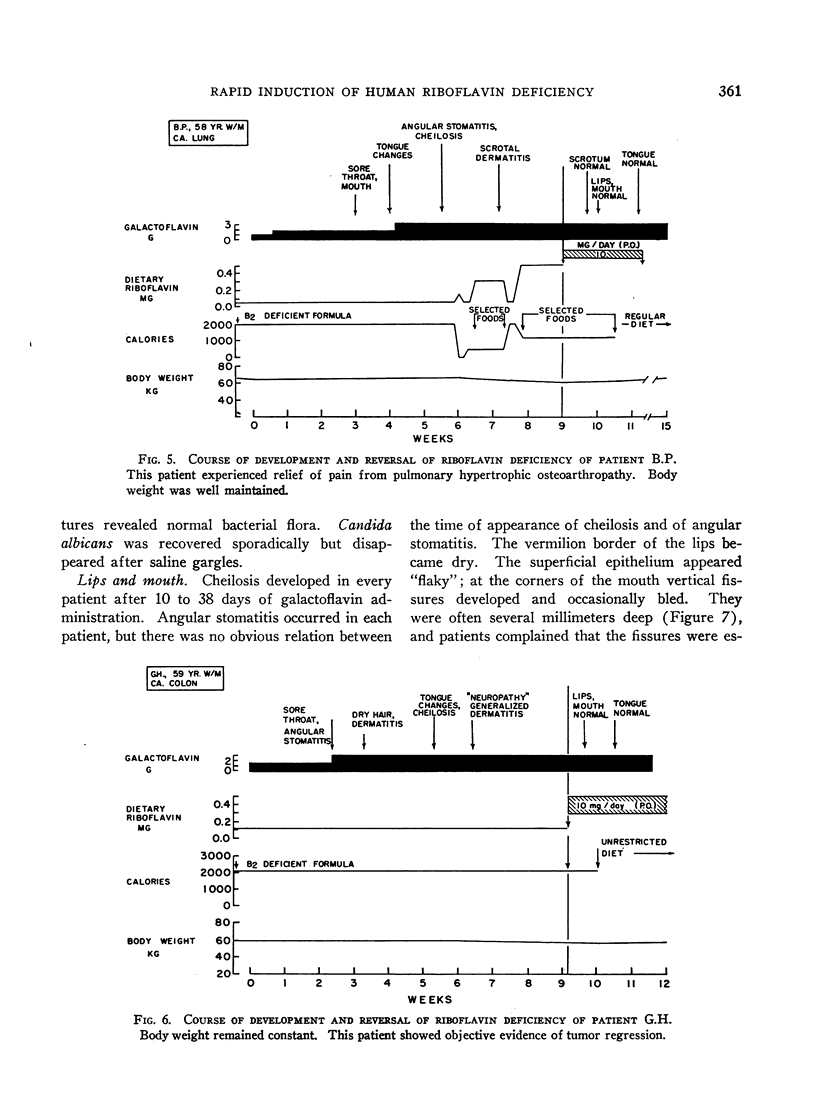
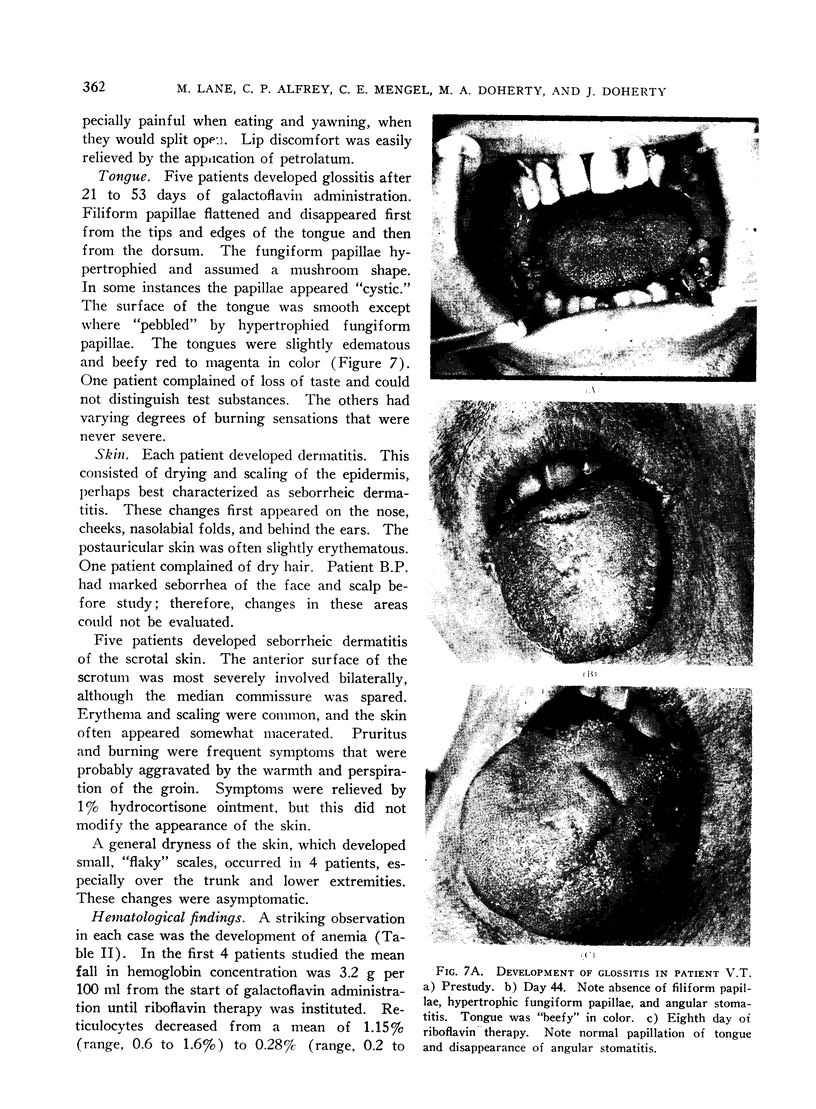
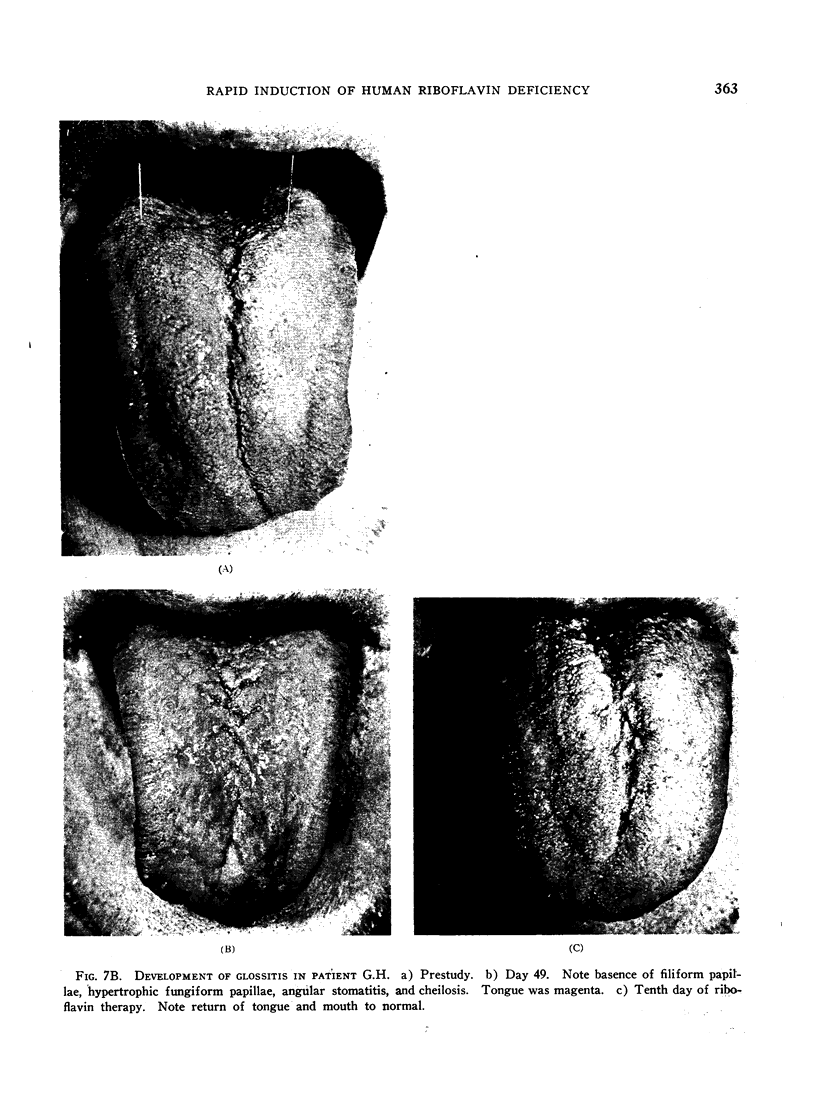







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APOSHIAN H. V., LAMBOOY J. P. Retardation of growth of Walker rat carcinoma 256 by administration of diethyl riboflavin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Oct;78(1):197–199. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., SCHNEIDERMAN M. A time-saving device for the counting of reticulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Nov;20(11):1079–1083. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/20.11_ts.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER K. J., KODICEK E. The blood pictures of pyridoxine and riboflavin-deficient rats. Int Z Vitaminforsch. 1952;24(3):241–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capps B. F., Hobbs N. L., Fox S. H. A Dehydrated Experimental Medium for the Microbiological Assay of Folic Acid. J Bacteriol. 1948 Jun;55(6):869–870. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAULKNER R. D., LAMBOOY J. P. Intestinal synthesis of riboflavin in the rat. J Nutr. 1961 Dec;75:373–378. doi: 10.1093/jn/75.4.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOY H., KONDI A. A case of true redcell aplastic anaemia successfully treated with riboflavin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(2):559–564. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOY H., KONDI A., MACDOUGALL L. Pure red-cell aplasia in marasmus and kwashiorkor treated with riboflavine. Br Med J. 1961 Apr 1;1(5230):937–941. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5230.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha B. C., Mapson L. W. The rôle of certain dietary factors in the formation of erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1931;25(5):1674–1686. doi: 10.1042/bj0251674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRILL I., KYLEN A. M., WEIS A., DYAR E. Relation of dietary fat and supplementary riboflavin to tissue levels of cholesterol, riboflavin and total lipids in the rat. J Nutr. 1959 Dec;69:356–364. doi: 10.1093/jn/69.4.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLS O. W., LIEBERT E., STEINBERG D. L., HORWITT M. K. Clinical aspects of dietary depletion of riboflavin. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 May;87(5):682–693. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810050058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORWITT M. K., HARVEY C. C., HILLS O. W., LIEBERT E. Correlation of urinary excretion of riboflavin with dietary intake and symptoms of ariboflavinosis. J Nutr. 1950 Jun 10;41(2):247–264. doi: 10.1093/jn/41.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORWITT M. K., HILLS O. W. Effects of dietary depletion of riboflavin. J Nutr. 1949 Nov;39(3):357–373. doi: 10.1093/jn/39.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUNITZ H., WIESINGER H., BLODI F. C., JOHNSON R. E., SLANETZ C. A. Relation of protein and fat intake to growth and corneal vascularization in galactoflavin-produced ariboflavinosis. J Nutr. 1954 Mar;52(3):467–482. doi: 10.1093/jn/52.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSELL L. W., MICHAELS G. D., PARTRIDGE F. W., BOLING L. A., BALCH H. E., COCHRANE G. C. Effect upon serum cholesterol and phospholipids of diets containing large amounts of vegetable fat. J Clin Nutr. 1953 Mar-Apr;1(3):224–231. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/1.3.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE M., FAHEY J. L., SULLIVAN R. D., ZUBROD C. G. The comparative pharmacology in man and the rat of the riboflavin analogu 6,7-dimethyl-9-(2-acetoxyethyl)-isoalloxazine, U-2112. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Mar;122(3):315–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE M., PETERING H. G., BRINDLEY C. O. Synthesis, pharmacology, and clinical trial of the riboflavine analogue, sodium-6, 7-dimethyl-9-(2'-hemisuccinoxyethyl)-isoalloxazine, U-6538. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Feb;22(2):349–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOOKERJEA S., HAWKINS W. W. Haematopoiesis in the rat in riboflavin deficiency. Br J Nutr. 1960;14:239–246. doi: 10.1079/bjn19600029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSSER E. A., HEINLE R. W. The effect of riboflavin antagonist upon leukocytes of normal and Shay myeloid chloroleukemic rats. Blood. 1958 May;13(5):464–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydenstricker V. P., Hail W. K., Hock C. W., Pund E. R. Amino Acid and Protein Deficiencies as Causes of Corneal Vascularization: A Preliminary Report. Science. 1946 Feb 15;103(2668):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.103.2668.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall F. F., McCreary J. F., Pearce H. The Effect of Riboflavin on Corneal Vascularization and Symptoms of Eye Fatigue in R.C.A.F. Personnel. Can Med Assoc J. 1943 Jul;49(1):5–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]