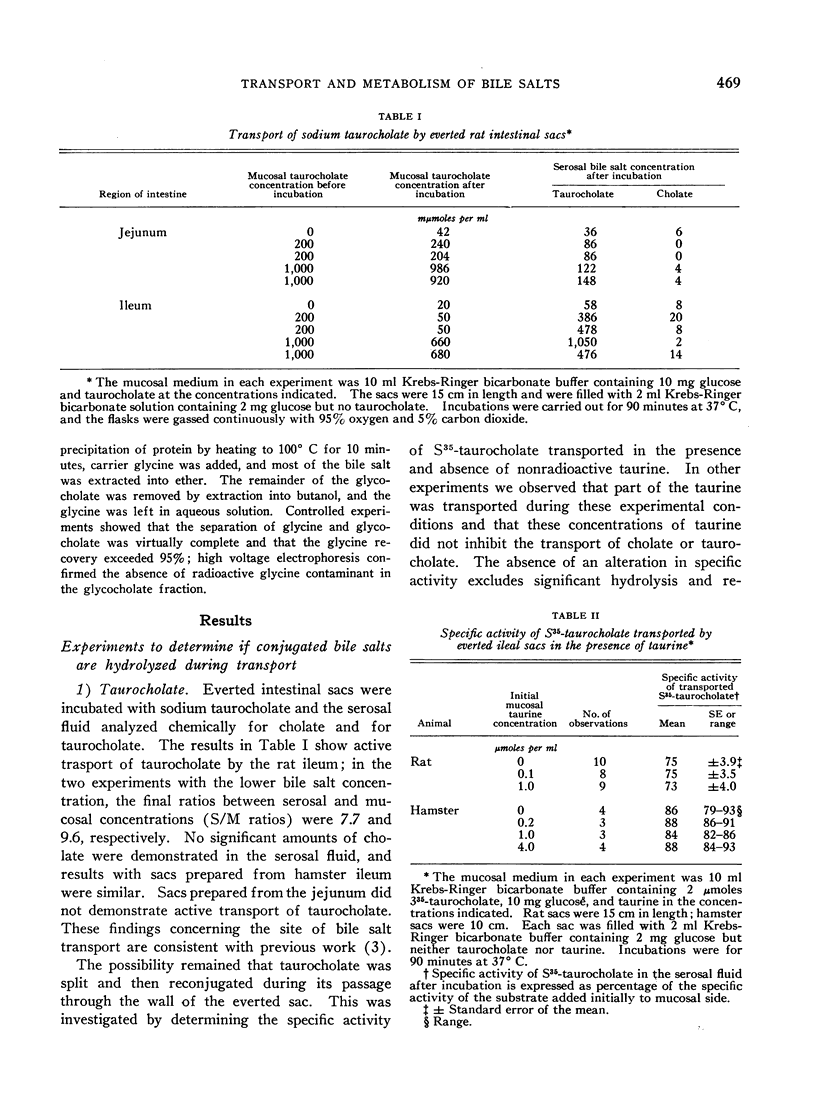
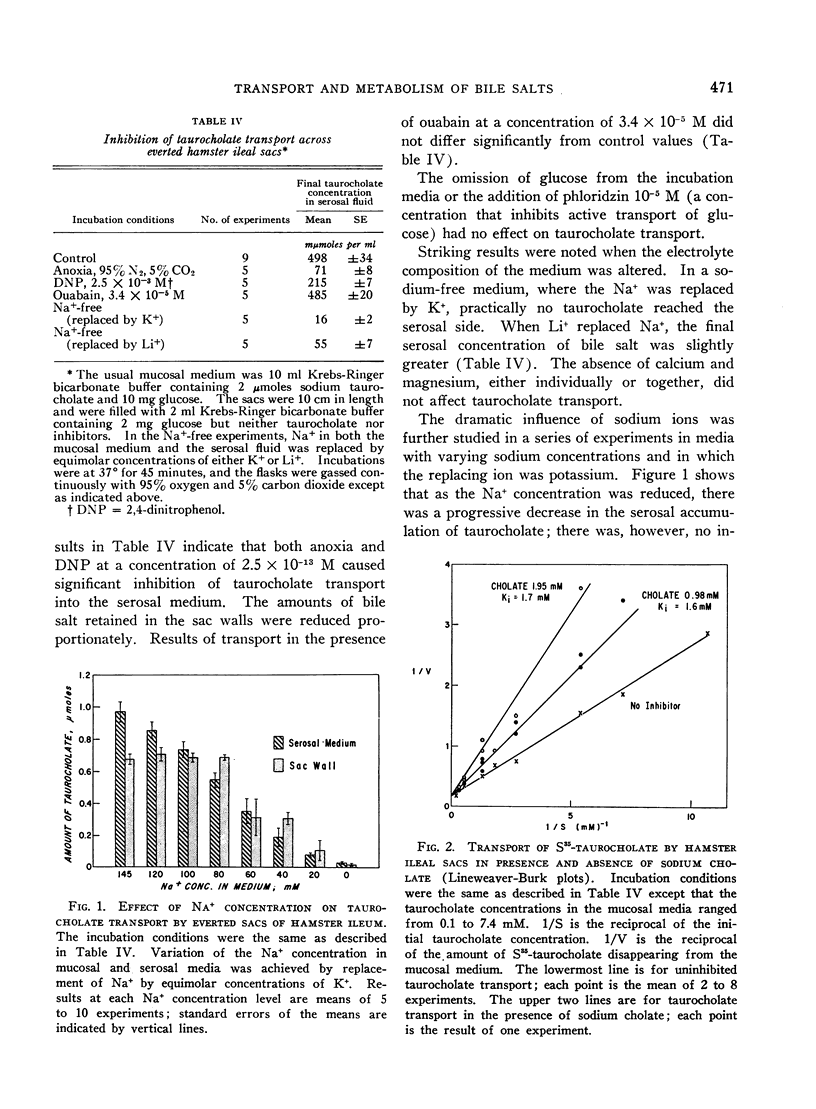
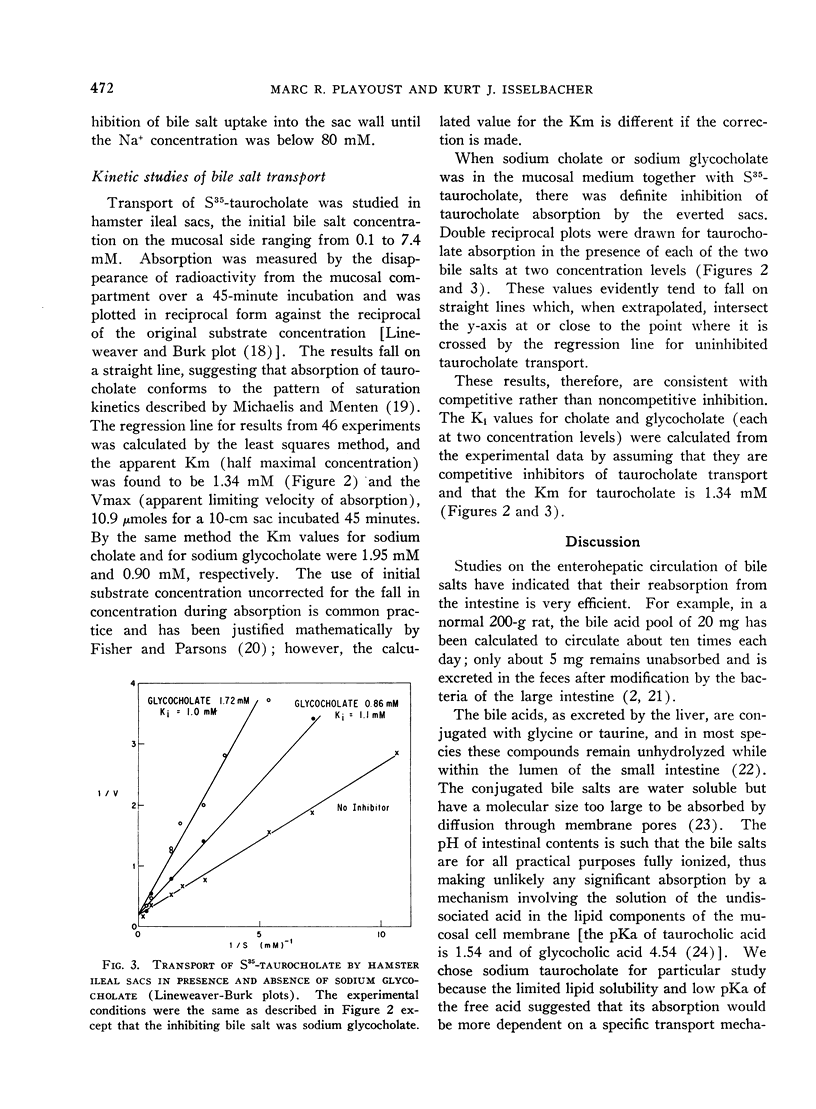
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIHLER I., CRANE R. K. Studies on the mechanism of intestinal absorption of sugars. V. The influence of several cations and anions on the active transport of sugars, in vitro, by various preparations of hamster small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:78–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90699-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIHLER I., HAWKINS K. A., CRANE R. K. Studies on the mechanism of intestinal absorption of sugars. VI. The specificity and other properties of Na ion-dependent entrance of sugars into intestinal tissue under anaerobic conditions, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:94–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90700-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON T. W., CROSS A. C., TOOLE S. R. Electrical potentials across isolated small intestine of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1233–1235. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKAY T. Z. A possible link between active transport of electrolytes and nonelectrolyes. Fed Proc. 1963 Jan-Feb;22:3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z., HARTZOG H. G., 3rd, FERNALD G. W. Effect of digitalis on active intestinal sugar transport. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:459–460. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z. Significance of sodium ions in active intestinal transport of nonelectrolytes. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:999–1001. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAUST R. G. The effect of anoxia and lithium ions on the absorption of D-glucose by the rat jejunum, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 16;60:604–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90879-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., PARSONS D. S. Glucose movements across the wall of the rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):210–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., NORMAN A., SJOVALL J. Influence of E. coli infection on turnover and metabolism of cholic acid in germ-free rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Nov;91:93–100. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90460-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E., HARRISON H. C. Sodium, potassium, and intestinal transport of glucose, 1-tyrosine, phosphate, and calcium. Am J Physiol. 1963 Jul;205:107–111. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZ R., Jr, TAPLEY D. F., ROSS J. E. Glucuronide formation in the transport of thyroxine analogues by rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:273–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90440-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J. Fat absorption and the esterification of fatty acids by intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1961 Feb;40:259–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ A. M., DREYER W. J., ANFINSEN C. B. Peptide separation by two-dimensional chromatography and electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2897–2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINZELLER A., KOTYK A. Cations and transport of galactose in kidney-cortex slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 9;54:367–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L., WEINER I. M. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF BILE SALTS AND SOME BIOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS. Fed Proc. 1963 Nov-Dec;22:1334–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L., WEINER I. M. In vitro absorption of bile salts by small intestine of rats and guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1961 Feb;200:313–317. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R., SCHMID R. Intestinal absorption of bile pigments. I. The enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI104766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R., SCHMID R. Intestinal absorption of bile pigments. II. Bilirubin absorption in man. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jul 25;269:178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196307252690402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. I. An intracellular locus of disaccharide and sugar phosphate ester hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:281–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90677-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWEY H., SMYTH D. H. Intracellular hydrolysis of dipeptides during intestinal absorption. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:367–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENTZ E. I., DAVENPORT C. H., GLOVER W., SMITH D. D. A test for the determination of taurine in urine. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):433–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKLIS E., QUASTEL J. H. Effects of cations on sugar absorption by isolated surviving guinea pig intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):347–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium- und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(4):346–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. The interaction between active sodium transport and active sugar transport in the isolated rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:503–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENIOR J. R., ISSELBACHER K. J. Direct esterification of monoglycerides with palmityl coenzyme A by intestinal epithelial subcellular fractions. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1454–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH F. R., TAPLEY D. F., ROSS J. E. Glucuronide formation in the transport of estradiol by rat intestine in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 1;69:68–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPLEY D. F., HERZ R., Jr, ROSS J. E., DEUEL T. F., LEVENTER L. Glucuronide formation in the active transport of amino acid and thyroxine analogues by rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Sep 23;43:344–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., LACK L. Absorption of bile salts from the small intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jan;202:155–157. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTAM R. The asymmetrical stimulation of a membrane adenosine triphosphatase in relation to active cation transport. Biochem J. 1962 Jul;84:110–118. doi: 10.1042/bj0840110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILBRANDT W., ROSENBERG T. The concept of carrier transport and its corollaries in pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Jun;13:109–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON J. D., SIPERSTEIN M. D. Effect of saturated and unsaturated fats on fecal excretion of end products of cholesterol-4-C14 metabolism in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Mar;196(3):596–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., KAZYAK L. Acid-base changes across the wall of hamster and rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Apr;24(1):124–132. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., WISEMAN G. The use of sacs of everted small intestine for the study of the transference of substances from the mucosal to the serosal surface. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):116–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. A model of a poorly-permeable membrane as an alternative to the carrier hypothesis of cell membrane penetration. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1961 Jul;109:35–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


