Previously considered to be nonpathogenic, Clostridium bifermentans has been implicated in a wide variety of infections over the past three decades, ranging from septic arthritis to endocarditis. The authors of this article describe a case involving a 60-year-old man who was found to have an empyema caused by C bifermentans. The authors review similar cases and discuss the course of treatment for this infection.
Keywords: Clostridium bifermentans, Empyema, Pneumonia
Abstract
A case of pneumonia with associated empyema caused by Clostridium bifermentans is described. C bifermentans is an anaerobic, spore-forming, Gram-positive bacillus. This organism is infrequently reported as a cause of infection in humans, and older publications tended to regard it as nonpathogenic. However, in more recent reports, C bifermentans has been documented as a cause of septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, soft tissue infection, abdominal infections, brain abscess, bacteremia and endocarditis. The present case is the third reported case of empyema caused by C bifermentans, and it serves to further define the spectrum of illness due to this uncommon organism.
Abstract
Les auteurs décrivent un cas de pneumonie associé à de l’empyème attribuable à un Clostridium bifermentans. Le C bifermentans est un bacille anaérobique sporulé Gram positif. Il est rarement signalé comme cause d’infection chez les humains, et les publications plus anciennes ont tendance à le considérer comme non pathogène. Cependant, dans des rapports plus récents, le C bifermentans est attesté comme cause d’arthrite septique, d’ostéomyélite, d’infection des tissus mous, d’infection abdominale, d’abcès du cerveau, de bactériémie et d’endocardite. Le présent cas, qui est le troisième cas déclaré d’empyème attribuable au C bifermentans, contribue à mieux définir le spectre de maladie causé par cet organisme peu courant.
CASE PRESENTATION
A 60-year-old man with a medical history significant only for an anxiety disorder presented to a community hospital in Winnipeg, Manitoba with a four-day history of increasing fatigue, weakness, cough and shortness of breath. The patient also complained of sharp right-sided pleuritic chest pain, as well as right upper quadrant abdominal pain associated with deep breathing. He denied nausea and vomiting. A review of systems was otherwise negative. The patient was a heavy smoker and reported occasional alcohol consumption. He denied the use of intravenous recreational drugs.
On physical examination at the time of presentation, the patient was noted to be febrile, with an oral temperature of 39.2°C. He was otherwise hemodynamically stable. The patient was edentulous. On respiratory examination, decreased air entry was noted in the right lower and middle lobes. Bronchial breath sounds were noted at the right lung base, and crepitations were heard with auscultation over the rest of the right lung. The abdomen was tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant. The remainder of the physical examination was unremarkable. Laboratory investigations performed on presentation demonstrated an elevated total leukocyte count (17.8×109 cells/L) with a neutrophil predominance (neutrophil count 16.12×109 cells/L). Blood cultures (aerobic and anaerobic) were negative. On chest radiography, a right-sided pneumothorax with right lower lobe consolidation and associated pleural fluid was apparent (Figure 1). The patient underwent a noncontrast computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen to rule out a subdiaphragmatic abscess in view of the right upper quadrant abdominal pain. No intra-abdominal abnormality was noted; however, the assessment did confirm a right-sided hydropneumothorax, with areas of pulmonary consolidation and loculated pleural fluid.
Figure 1).
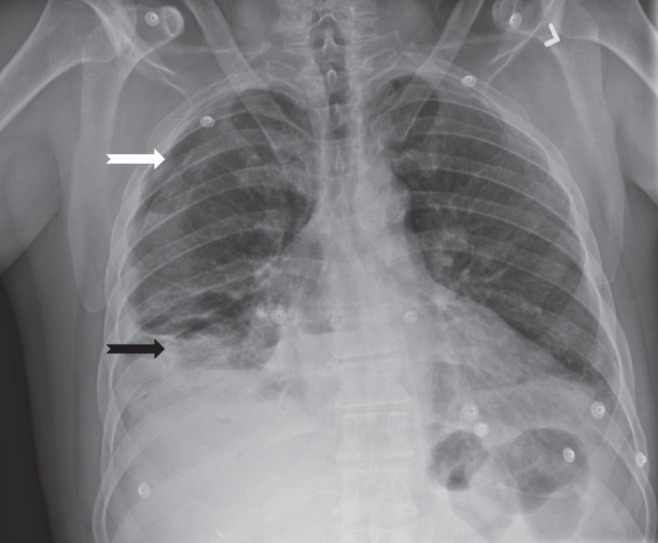
Chest radiograph demonstrating a right-sided pneumothorax (white arrow) and right lower lobe consolidation (black arrow)
The patient was admitted to hospital. A chest tube was placed, and empirical antimicrobial therapy with a combination of levofloxacin and metronidazole was initiated. A sample of pleural fluid was submitted to the microbiology laboratory for further analysis. No polymorphonuclear cells or bacteria were observed on Gram stain. The aerobic culture did not demonstrate any bacterial growth following 72 h of incubation. However, after 48 h of incubation, a large Gram-positive spore-forming bacillus was recovered on anaerobic culture. The organism was subsequently identified as Clostridium bifermentans using a Vitek™ 2 ANC card (bioMérieux, Canada). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed by E-test (bioMérieux, Canada), with minimum inhibitory concentrations interpreted according to 2012 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute breakpoints for anaerobic bacteria (1). The isolate was susceptible to amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefoxitin, clindamycin, meropenem, metronidazole and penicillin.
On the third day postadmission, the patient continued to complain of significant dyspnea and chest pain. A CT scan of the chest was performed with contrast and this demonstrated a right main pulmonary artery embolus. The patient clinically deteriorated and ultimately required admission to the intensive care unit. His antimicrobial therapy was changed to a combination of piperacillin-tazobactam and levofloxacin, and heparin was initiated as treatment for the pulmonary embolus. Fifteen days postadmission, the patient underwent a thoracotomy and decortication of the right lung. Empyema fluid obtained at the time of surgery was submitted to the microbiology laboratory. C bifermentans was once again recovered on anaerobic culture. Postoperatively, antimicrobial therapy with piperacillin-tazobactam alone was continued.
Following surgery, the patient experienced intermittent low-grade fevers (approximately 38°C) and ongoing hypoxia requiring 2 L of oxygen via nasal prongs. Repeat chest radiography revealed a loculated right-sided pneumothorax with a small amount of fluid remaining in the empyema cavity. Twenty-nine days after the initial surgical procedure (44 days postadmission), the patient was taken back to the operating room for a second thoracotomy, right rib resection and empyema drainage. Lung tissue obtained at the time of this surgery for aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culture was found to be sterile. After the second surgery, the antimicrobial therapy was changed to a combination of ceftriaxone and metronidazole. An echocardiogram was performed, which did not demonstrate any evidence of endocarditis or other valvular pathology. The patient gradually improved over a period of several weeks. He was ultimately discharged home 76 days post-admission with a prescription for oral metronidazole to complete an additional 10 days of therapy as an outpatient (arbitrary treatment duration of six weeks following the final surgical drainage procedure).
DISCUSSION
Bacteria belonging to the genus Clostridium are anaerobic Gram-positive rods with the ability to form endospores (2,3). More than 200 species and subspecies have been recognized to date. Clostridium species are ubiquitous in the environment. They may be found in soil, sewage, marine sediment and feces (2,3). Clostridium species are part of the normal flora of the intestinal tract of humans and other animals, and may also be isolated from the female genital tract and the oral mucosa (2).
C bifermentans was first described in 1902 under the name Bacillus bifermentans sporogenes (4). The name ‘bifermentans’ relates to the ability of this organism to ferment both carbohydrates and amino acids (5). It may be differentiated from other members of the genus Clostridium, in part, by a negative urease test, and positive indole and lecithinase tests (2). Older publications in the literature tended to regard C bifermentans as nonpathogenic (4,6). In somewhat dated animal studies involving mice and guinea pigs, C bifermentans did not demonstrate any lethal or dermatonecrotic properties (4,6). Furthermore, before 1970, only two cases of human infection due to this organism had been reported (7,8). These included a contaminated war wound with very poor documentation describing the infection, and a case of food poisoning (7,8). However, over the past three decades, several case reports have been published in the English language documenting a variety of clinical infectious due to this bacteria. C bifermentans has been described as a cause of septic arthritis, liver abscess following blunt abdominal trauma, abdominal abscess (in association with Cardiobacterium hominis), delayed brain abscess due to a retained foreign body, metastatic osteomyelitis, soft tissue infection and endocarditis (7,9–15). Furthermore, in various published series of Clostridium species bacteremia, C bifermentans typically accounts for a small percentage of cases (16–18). It is likely that the increased reporting of this organism reflects, at least in part, improved laboratory methods for detection and identification.
Pleuropulmonary disease, including pneumonia and/or empyema, is an uncommon manifestation of infection due to Clostridium species in the absence of preceding trauma (19). Several clostridial species have been documented as a cause of pleuropulmonary infection, including Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium sordellii, Clostridium sporogenes, Clostridium paraputrificum, Clostridium difficile, Clostridium septicum, Clostridium cadaveris and Clostridium tetani (19–23). C bifermentans has only been reported as a cause of pulmonary infection/empyema in two other publications (24,25). Jonsson et al (24) described a 60-year-old man who presented with fever, cough and pleuritic chest pain. A large pleural effusion was demonstrated on chest radiography. Cultures of the pleural fluid grew C bifermentans and Bacillus cereus. The patient improved following thoracotomy with decortication and appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Misra and Hurst (25) reported a 41-year-old woman who presented with cough, hemoptysis and pleuritic chest pain. A lung scan performed on admission was consistent with pulmonary emboli and the patient was treated with heparin. She subsequently deteriorated in hospital, with repeat chest radiography demonstrating pulmonary infiltrates and a pneumothorax that appeared to communicate with a cavitary lesion in the chest. C bifermentans was recovered from blood and pleural fluid cultures. The patient succumbed to complications of the illness (25).
In both of the previously published cases of C bifermentans empyema as well as the current case, it is unclear whether infection occurred secondary to hematogenous spread, inhalation or aspiration of the organism, although inhalation was favoured in the report by Jonsson et al (24). The case presented here is similar to the case described by Misra and Hurst (25) in that the infection occurred in the setting of a pulmonary embolus. Given the reported low virulence of C bifermentans, it is tempting to speculate that tissue injury/infarction secondary to a pulmonary embolus may have predisposed our patient to develop this infection. A septic embolus would also be possible as a mechanism of infection, although blood cultures were negative. Unfortunately, the lack of an infused chest CT scan on presentation prevents determination of whether the pulmonary embolus was present at the start of the illness or whether it occurred in hospital once the infection was already established. Alternatively, the infection may have occurred secondary to aspiration, although the patient did not have any risk factors for aspiration specifically identified. It should be noted that the possibility of polymicrobial infection could not be completely excluded because all pleural fluid and tissue specimens were obtained after the start of antimicrobial therapy. Thus, the patient remained on broad-spectrum antimicrobials during his stay in hospital. The etiology of the pneumothorax in the present case also remains uncertain, as is its association (if any) with the development of infection. With the history of smoking, it is possible that our patient did, in fact, have underlying pulmonary disease, and this may have been a predisposing factor for the pneumothorax and/or the empyema.
CONCLUSION
The present report describes a case of pneumonia/empyema caused by C bifermentans. Infections due to C bifermentans are infrequently reported, potentially due to the relatively low virulence of this organism. Older publications tended to regard C bifermentans as nonpathogenic (4,6). However, in more recent reports, this organism has been documented as a cause of septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, soft tissue infection, abdominal infections, brain abscess, bacteremia and endocarditis (7,9–18). The present article describes the third reported case of empyema caused by C bifermentans, and serves to further define the spectrum of illness due to this uncommon organism.
REFERENCES
- 1.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute . Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Second Informational Supplement. M100-S22. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stevens DL, Bryant AM, Berger A, Von Eichel-Streiber C. Clostridium. In: Versalovic J, Carroll KC, Funke G, Jorgensen JH, Landry ML, Warnock DW, editors. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 10th edn. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2011. pp. 834–57. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Onderdonk AB, Garrett WS. Gas gangrene and other Clostridium-associated diseases. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 7th edn. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2010. pp. 3103–9. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brooks ME, Epps HBG. Taxonomic studies of the genus Clostridium: Clostridium bifermentans and C. sordellii. J Gen Microbiol. 1958;21:144–55. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vos PD, Garrity GM, Jones D, et al., editors. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. 2nd edn. New York: Springer Science+Business Media; 2009. p. 758. Volume 3: The Firmicutes. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nishida S, Tamai K, Yamagishi T. Taxonomy of Clostridium bifermentans and Clostridium sordellii I. Their toxigenicity, urease activity, and sporulating potency. J Bacteriol. 1964;88:1641–6. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1641-1646.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nolan B, Leers WD, Schatzker J. Septic arthritis of the knee due to Clostridium bifermentans. J Bone Joint Surg. 1972;54-A:1275–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.MacLennan JD. Anaerobic infections of war wounds in the Middle East. Lancet. 1943;242:123–6. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nachman S, Kaul A, Li KI, Slim MS, San Filippo JA, Van Horn K. Liver abscess caused by Clostridium bifermentans following blunt abdominal trauma. J Clin Microbiol. 1989;27:1137–8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1137-1138.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rechtman DJ, Nadler JP. Abdominal abscess due to Cardiobacterium hominis and Clostridium bifermentans. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:418–9. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pencek TL, Burchiel KJ. Delayed brain abscess related to a retained foreign body with culture of Clostridium bifermentans. J Neurosurg. 1986;64:813–5. doi: 10.3171/jns.1986.64.5.0813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Scanlan DR, Smith MA, Isenberg HD, Engrassia S, Hilton E. Clostridium bifermentans bacteremia with metastatic osteomyelitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994;32:2867–8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.11.2867-2868.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gorbach SL, Thadepalli H. Isolation of Clostridium in human infections: Evaluation of 114 cases. J Infect Dis. 1975;131:S81–5. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.supplement.s81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moyano R, Gomez-Mateos JM, Lozano de Leon F, Florez C, Jimenez-Ocana C, Gamboa F. Clostridium bifermentans: An exceptional agent of endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;18:837. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kolander SA, Cosgrove EM, Molavi A. Clostridial endocarditis. Report of a case caused by Clostridium bifermentans and review of the literature. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149:455–6. doi: 10.1001/archinte.149.2.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rechner PM, Agger WA, Mruz K, Cogbill TH. Clinical features of clostridial bacteremia: A review from a rural area. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:349–53. doi: 10.1086/321883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Leal J, Gregson DB, Ross T, Church DL, Laupland KB. Epidemiology of Clostridium species bacteremia in Calgary, Canada, 2000–2006. J Infect. 2008;57:198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2008.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Haddy RI, Nadkarni DD, Mann BL, et al. Clostridial bacteremia in the community hospital. Scand J Infect Dis. 2000;32:27–30. doi: 10.1080/00365540050164173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Patel SB, Mahler R. Clostridial pleuropulmonary infections: Case report and review of the literature. J Infect. 1990;21:81–5. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(90)90738-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hudson DA, Gibb AP, Gill MJ. Empyema caused by Clostridium difficile. Can J Infect Dis. 1999;10:170–1. doi: 10.1155/1999/968940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stolk-Engelaar V, Verwiel J, Bongaerts G, Linsen V, Lacquet L, Cox A. Pleural empyema due to Clostridium difficile and Clostridium cadaveris. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:160. doi: 10.1086/516893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Granok AB, Mahon PA, Biesek GW. Clostridium septicum empyema in an immunocompetent woman. Case Rep Med. 2010;231738 doi: 10.1155/2010/231738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mayall BC, Snashall EA, Peel MM. Isolation of Clostridium tetani from anaerobic empyema. Pathology. 1998;30:402–4. doi: 10.1080/00313029800169716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jonsson S, Clarridge J, Young EJ. Necrotizing pneumonia and empyema caused by Bacillus cereus and Clostridium bifermentans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983;127:357–9. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Misra DP, Hurst DJ. Necrotising pneumonia and empyema caused by Clostridium bifermentans. Thorax. 1980;35:310–11. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.4.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


