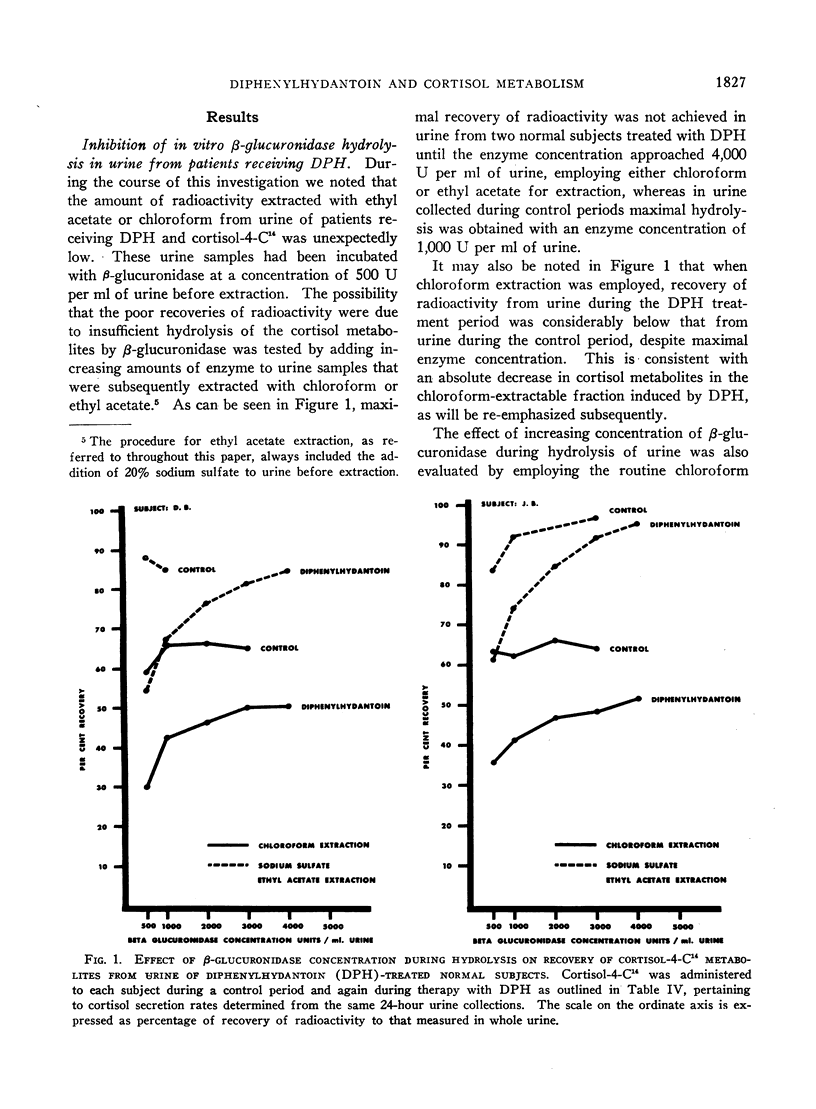
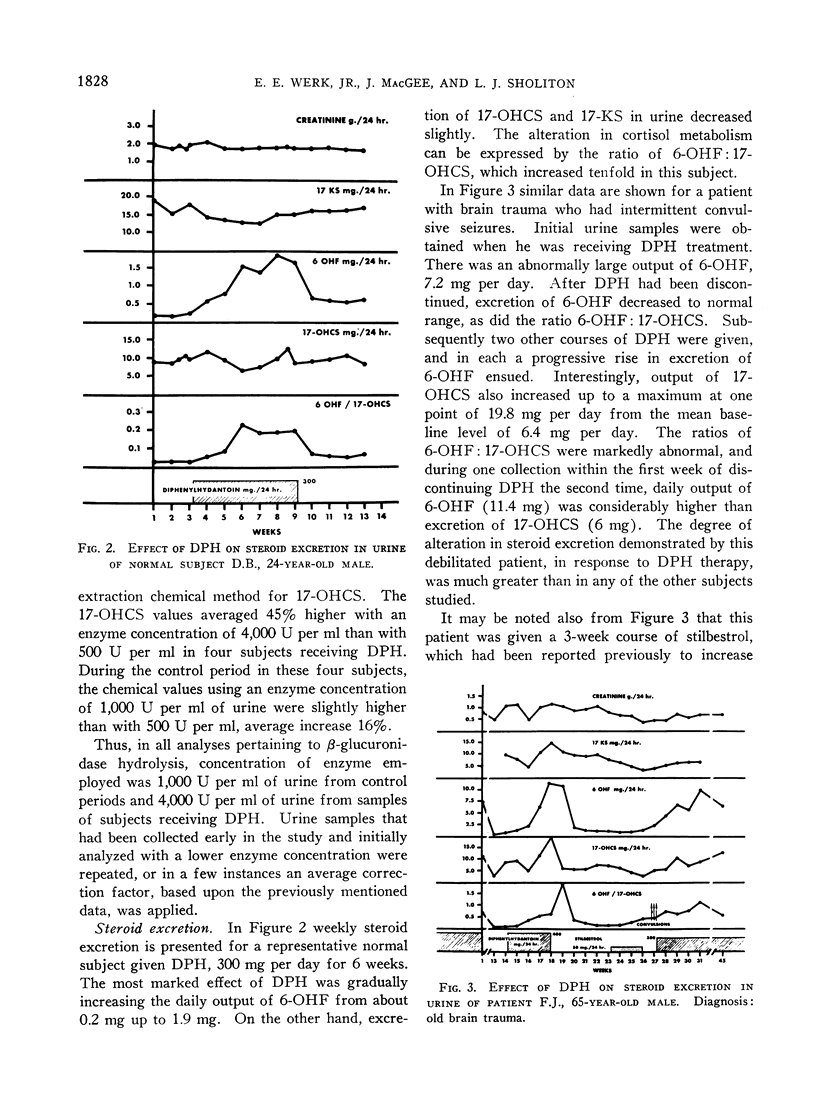
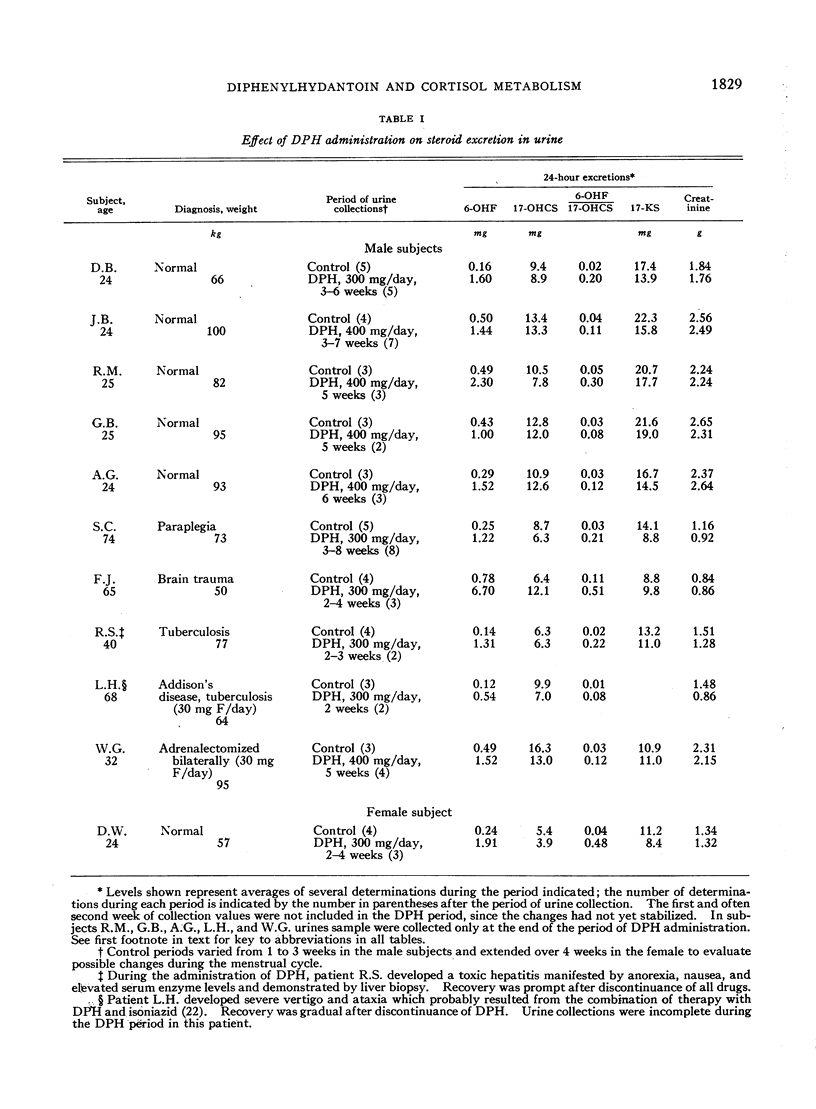
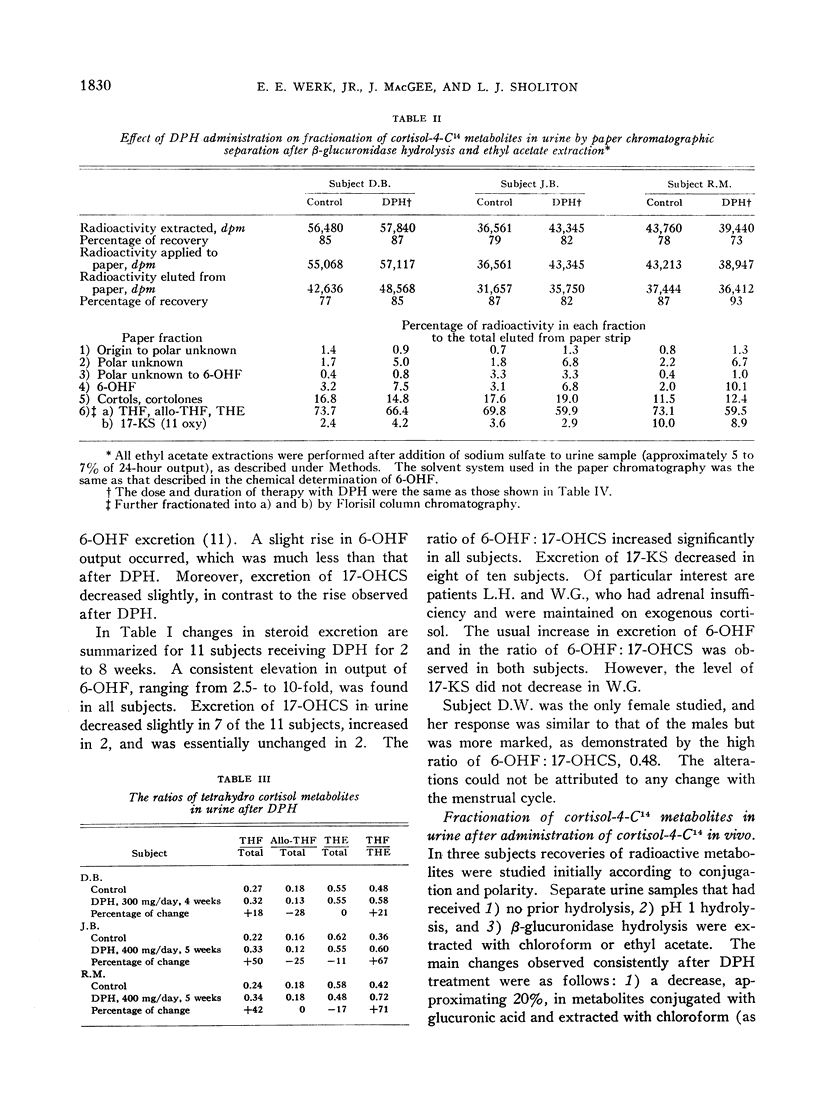
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BONNYCASTLE D. D., BRADLEY A. J. Diphenylhydantoin and the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone in the albino rat. Endocrinology. 1960 Mar;66:355–363. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER T. C. The metabolic conversion of 5, 5-diphenyl hydantoin to 5-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-5-phenyl hydantoin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Jan;119(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTY N. P., HOFMANN A. D. Effects of diphenylhydantoin upon adrenal cortical function in man. Neurology. 1959 Apr;9(4):245–248. doi: 10.1212/wnl.9.4.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTA P. J., GLASER G. H., BONNY-CASTLE D. D. Effects of diphenylhydantoin (dilantin) on adrenal cortical function; a study in nonepileptic human subjects. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1955 Jul;74(1):88–91. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1955.02330130090010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREKTER I. J., HEISLER A., SCISM G. R., STERN S., PEARSON S., McGAVACK T. H. The determination of urinary steroids. I. The preparation of pigment-free extracts and a simplified procedure for the estimation of total 17-ketosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1952 Jan;12(1):55–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-12-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOOD C., LAYNE D. S., RAMCHARAN S., ROSSIPAL E., TAIT J. F., TAIT S. A. An investigation of the urinary metabolites and secretion rates of aldosterone and cortisol in man and a description of methods for their measurement. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Feb;36:237–264. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0360237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANTZ A. G., KATZ F. H., JAILER J. W. 6beta-Hydroxycortisol and other polar corticosteroids: measurement and significance in human urine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Oct;21:1290–1303. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-10-1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENN E. M., NELSON D. H. Chemical method for the determination of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids and 17-ketosteroids in urine following hydrolysis with beta-glucuronidase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1953 Aug;13(8):911–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-13-8-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEN A. A., TROOP R. C. Influence of age, sex and adrenocortical status on hepatic reduction of cortisone in vitro. Endocrinology. 1960 Aug;67:194–203. doi: 10.1210/endo-67-2-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUCK J. C., JACOB R. A. Connective tissue. VII. Factors inhibiting the dermal chemical response to cortisol. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jul;113:692–694. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ F. H., LIPMAN M. M., FRANTZ A. G., JAILER J. W. The physiologic significance of 6beta-hydroxycortisol in human corticoid metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Jan;22:71–77. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITTINGER G. W. The determination of adrenal cortical alpha-ketolic steroids by quantitative paper chromatography. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 May;55:796–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER D. T. Effect of diphenylhydantoin on pituitary-adrenal interrelations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 May;22:490–493. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-5-490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAGAI A., OTOMO M., YANO S., TAKEUCHI N., NISHINO K., UEDA H., KO S., KITAMURA M. Inhibition of cortisol metabolism in the liver by other steroids. Endocrinol Jpn. 1959 Jun;6(2):86–92. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.6.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPMAN M. M., KATZ F. H., JAILER J. W. An alternate pathway for cortisol metabolism. 6 beta-hydroxycortisol production by human tissue slices. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Mar;22:268–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-3-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYNERT E. W. The metabolic fate of diphenylhydantoin in the dog, rat and man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Nov;130:275–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY F. J. Outbreak of unexpected reactions among epileptics taking isoniazid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Nov;86:729–732. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.86.5.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., TAVERNETTI R. R. Studies on the thyroxine-diphenylhydantoin interaction: effect of 5,5'-diphenylhydantoin on the displacement of L-thyroxine from thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Endocrinology. 1962 Sep;71:496–504. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-3-496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON W. A., ENGLE W. A., SMITH D. L. Effect of diphelhydantoin sodium on liver restitution in the rat following hepatectomy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:477–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANOFF L. P., RODRIGUEZ R. M., SEELYE J. M., PARENT C., PINCUS G. The urinary excretion of tetrahydrocortisol, 3 alpha-allotetrahydrocortisol and tetrahydrocortisone in young and elderly men and women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1285–1295. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD S., SWILLER A. I., SHENOY Y. M., MORRISON A. N. Syndrome simulatingqymphosarcoma induced by diphenylhydantoin sodium. JAMA. 1961 May 13;176:491–493. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040190013004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTZSTEIN S. L., ACKERMAN L. V. Lymphadenopathy induced by anticonvulsant drugs and mimicking clinically pathologically malignant lymphomas. Cancer. 1959 Jan-Feb;12(1):164–182. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195901/02)12:1<164::aid-cncr2820120122>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILBER R. H., PORTER C. C. The determination of 17,21-dihydroxy-20-ketosteroids in urine and plasma. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):923–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEMPFEL R. S., Jr, SIDBURY J. B., Jr, MIGEON C. J. beta-Glucuronidase hydrolysis of urinary corticosteroid conjugates: the effect of salicylate glucuronoside as a competing substrate and the effect of enzyme inactivation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Jun;20:814–824. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-6-814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULSTROM R. A., COLLE E., BURLEY J., GUNVILLE R. Adrenocortical steroid metabolism in newborn infants. II. Urinary excretion of 6beta-hydroxycortisol and other polar metabolites. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Aug;20:1080–1094. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-8-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES F. E., HERBST A. L., URQUHART J. Sex difference in rate of ring A reduction of delta 4-3-keto-steroids in vitro by rat liver. Endocrinology. 1958 Dec;63(6):887–902. doi: 10.1210/endo-63-6-887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



