Abstract
In the title compound, C11H7Br3ClN, the quinoline ring system is approximately planar (r.m.s. = 0.011 Å). In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯Br interactions forming chains along [10-1]. The chains are linked by C—H⋯π and π–π interactions involving inversion-related pyridine rings [intercentroid distance = 3.608 (4) Å], forming sheets parallel to (10-1). Within the sheets, there are two significant short interactions involving a Br⋯Cl contact of 3.4904 (18) Å and a Br⋯N contact of 3.187 (6) Å, both of which are significantly shorter than the sum of their van der Waals radii.
Keywords: crystal structure, quinoline, bromoquinolines, halogen–halogen contacts, Br⋯Cl contacts, Br⋯N contacts, C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions
Related literature
The title compound is an important intermediate in the manufacture of materials such as organic light-emitting devices. For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Jones (1977 ▸); Lyle et al. (1972 ▸). For the biological activity of quinoline derivatives, see: Chauhan & Srivastava (2001 ▸); Ferrarini et al. (2000 ▸); Chen et al. (2001 ▸); Sahin et al. (2008 ▸).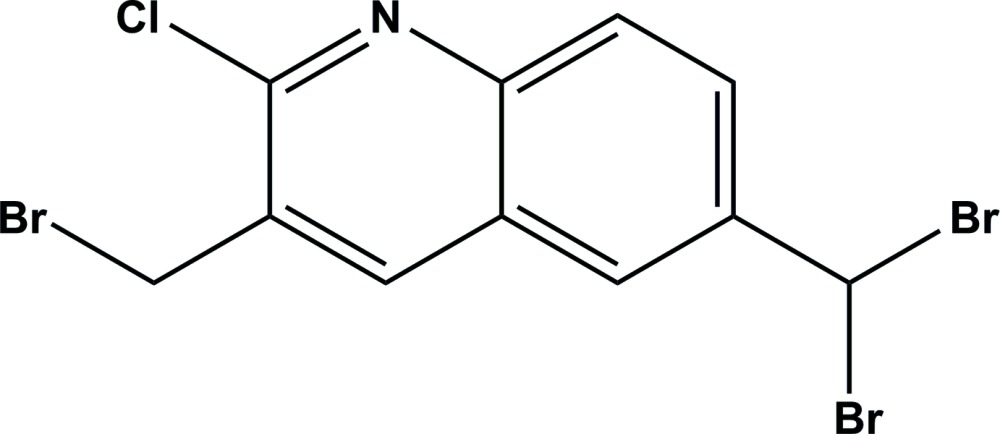
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H7Br3ClN
M r = 428.36
Monoclinic,

a = 8.9042 (5) Å
b = 9.3375 (4) Å
c = 15.5107 (7) Å
β = 104.553 (5)°
V = 1248.23 (11) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 9.88 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.42 × 0.36 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 Gemini ultra diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸) T min = 0.056, T max = 0.153
8597 measured reflections
2259 independent reflections
1889 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.143
S = 1.09
2259 reflections
145 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.65 e Å−3
Δρmin = −1.19 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▸); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL2014 and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096fig2.tif
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯π interactions (Table 1) and the Br⋯Cl and Br⋯N short contacts are shown as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 902598
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4C9 ring.
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11H11Br1i | 1.00 | 2.92 | 3.709(8) | 137 |
| C10H10B Cg2ii | 0.99 | 2.70 | 3.438(8) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
HAS is grateful to the Leverhulme Trust and Durham University for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was prepared in line with literature methods (Jones, 1977; Lyle et al., 1972). 2-Chloro-3,6-dimethyl-quinoline (0.001 mole) was dissolved in CCl4. To this benzoyl peroxide (50 mg) was added and the mixture was stirred under ice-cold conditions. To this mixture N-bromosuccinimide (0.005 mole) was added portion wise. The whole mixture was further stirred under ice-cold condition for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then refluxed for about 10 hours. After completion of the reaction, the succinimide was removed (it was insoluble in CCl4) by filtration and washed with 20 ml of CCl4. The contents of the filtrate were reduced to half, and the residue was chromatographed on silica gel using petroleum ether and ethyl acetate as eluent (99:1), which gave the titled product (yield: 52%). The white solid obtained was then recrystallized using acetone yielding colourless block-like crystals.
S2. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.95 - 1.0 Å with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The highest peak in the final difference Fourier map (1.654 eÅ-3) is close to atom Cl1. Attempts to split this atom were unsuccessful.
S3. Structural commentary
The presence of the quinoline skeleton in the frameworks of pharmacologically active compounds and natural products has spurred on the development of different strategies for their synthesis (Chauhan et al., 2001; Ferrarini et al., 2000; Chen et al., 2001). Bromoquinolines have been of interest for chemists as precursors for heterocyclic compounds with multifunctionality, giving accessibility to a wide variety of compounds. These building blocks have been used in medicinal chemistry as starting materials for numerous compounds with pharmacological activity (Sahin et al., 2008).
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The quinoline ring is planar (r.m.s. = 0.011 Å).
In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H···Br interactions forming chains along [101]; Table 1 and Fig. 2. The chains are linked by C—H···π (Table 1), and π-π interactions involving inversion related pyridine rings (N1/C1—C5) with an inter-centroid distance of 3.608 (4) Å, forming sheets parallel to (101). Within the sheets, there are two significant short interactions: A Br1···Cli contact of 3.4904 (18) Å and a Br3···Nii contact of 3.187 (6) Å [symmetry codes: (i) -x+3/2, y-1/2, -z+3/2; (ii) x-1/2, -y+3/2, z-1/2], both are significantly shorter than the sum of their van der Waals radii [1.85 Å for Br; 1.75 Å for Cl; 1.55 Å for N; PLATON (Spek, 2009)].
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The C—H···Br hydrogen bonds, C—H···π interactions (Table 1) and the Br···Cl and Br···N short contacts are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C11H7Br3ClN | F(000) = 808 |
| Mr = 428.36 | Dx = 2.279 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9042 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 4382 reflections |
| b = 9.3375 (4) Å | θ = 2.6–29.0° |
| c = 15.5107 (7) Å | µ = 9.88 mm−1 |
| β = 104.553 (5)° | T = 120 K |
| V = 1248.23 (11) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.42 × 0.36 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 Gemini ultra diffractometer | 2259 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 1889 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1511 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.4° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.056, Tmax = 0.153 | l = −18→12 |
| 8597 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.143 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0713P)2 + 10.6242P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2259 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmax = 1.65 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −1.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.63474 (10) | 0.04489 (9) | 0.60991 (6) | 0.0370 (3) | |
| Br3 | 0.45280 (10) | 0.74291 (9) | 0.12751 (6) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| Br2 | 0.70035 (11) | 0.53886 (11) | 0.08299 (6) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.8069 (2) | 0.38929 (19) | 0.67965 (10) | 0.0226 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.7951 (7) | 0.4817 (7) | 0.5207 (4) | 0.0242 (13) | |
| C1 | 0.7245 (8) | 0.3973 (8) | 0.5630 (4) | 0.0215 (15) | |
| C2 | 0.5903 (8) | 0.3156 (7) | 0.5249 (4) | 0.0179 (14) | |
| C3 | 0.5309 (8) | 0.3292 (7) | 0.4361 (5) | 0.0201 (14) | |
| H3 | 0.4411 | 0.2763 | 0.4074 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 0.6012 (8) | 0.4213 (7) | 0.3857 (4) | 0.0175 (14) | |
| C5 | 0.7359 (8) | 0.4957 (8) | 0.4305 (5) | 0.0197 (14) | |
| C6 | 0.8084 (8) | 0.5892 (9) | 0.3828 (5) | 0.0274 (17) | |
| H6 | 0.8991 | 0.6397 | 0.4129 | 0.033* | |
| C7 | 0.7505 (9) | 0.6079 (9) | 0.2946 (5) | 0.0279 (17) | |
| H7 | 0.8002 | 0.6722 | 0.2631 | 0.034* | |
| C8 | 0.6160 (8) | 0.5326 (8) | 0.2483 (5) | 0.0217 (15) | |
| C9 | 0.5450 (8) | 0.4423 (7) | 0.2927 (4) | 0.0201 (14) | |
| H9 | 0.4555 | 0.3916 | 0.2612 | 0.024* | |
| C10 | 0.5174 (9) | 0.2212 (8) | 0.5792 (5) | 0.0234 (15) | |
| H10A | 0.4102 | 0.1981 | 0.5456 | 0.028* | |
| H10B | 0.5120 | 0.2718 | 0.6344 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 0.5499 (9) | 0.5552 (8) | 0.1511 (5) | 0.0250 (16) | |
| H11 | 0.4683 | 0.4809 | 0.1295 | 0.030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0423 (5) | 0.0311 (5) | 0.0363 (5) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0073 (4) | 0.0085 (3) |
| Br3 | 0.0415 (5) | 0.0292 (5) | 0.0416 (5) | 0.0098 (4) | 0.0068 (4) | 0.0091 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.0437 (5) | 0.0546 (6) | 0.0369 (5) | 0.0031 (4) | 0.0225 (4) | −0.0033 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.0252 (9) | 0.0296 (9) | 0.0114 (7) | −0.0033 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| N1 | 0.022 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.024 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.000 (3) |
| C1 | 0.020 (4) | 0.026 (4) | 0.018 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.005 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.019 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C3 | 0.020 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.027 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C4 | 0.017 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.008 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C5 | 0.019 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.021 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C6 | 0.018 (4) | 0.030 (4) | 0.031 (4) | −0.003 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C7 | 0.023 (4) | 0.033 (4) | 0.029 (4) | −0.007 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C8 | 0.022 (4) | 0.018 (4) | 0.026 (4) | 0.005 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C9 | 0.021 (4) | 0.016 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.001 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C10 | 0.024 (4) | 0.023 (4) | 0.025 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C11 | 0.030 (4) | 0.021 (4) | 0.026 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C10 | 1.944 (7) | C4—C9 | 1.417 (9) |
| Br3—C11 | 1.948 (7) | C5—C6 | 1.404 (11) |
| Br2—C11 | 1.910 (8) | C6—C7 | 1.345 (10) |
| Cl1—C1 | 1.776 (7) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.286 (10) | C7—C8 | 1.419 (10) |
| N1—C5 | 1.371 (9) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.416 (10) | C8—C9 | 1.343 (10) |
| C2—C3 | 1.352 (10) | C8—C11 | 1.489 (10) |
| C2—C10 | 1.478 (10) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.409 (10) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.409 (10) | C11—H11 | 1.0000 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 117.8 (6) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 126.0 (6) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| N1—C1—Cl1 | 114.6 (5) | C9—C8—C7 | 119.9 (7) |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 119.5 (5) | C9—C8—C11 | 119.4 (7) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 116.6 (6) | C7—C8—C11 | 120.7 (7) |
| C3—C2—C10 | 121.5 (6) | C8—C9—C4 | 121.2 (6) |
| C1—C2—C10 | 121.9 (6) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.5 (6) | C4—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C2—C10—Br1 | 111.0 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C2—C10—H10A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.0 (6) | Br1—C10—H10A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.2 (6) | C2—C10—H10B | 109.4 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 123.8 (6) | Br1—C10—H10B | 109.4 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 119.2 (6) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.0 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 121.2 (6) | C8—C11—Br2 | 113.3 (5) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.6 (6) | C8—C11—Br3 | 111.2 (5) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.5 (7) | Br2—C11—Br3 | 107.9 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.8 | C8—C11—H11 | 108.1 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 | Br2—C11—H11 | 108.1 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.6 (7) | Br3—C11—H11 | 108.1 |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 0.4 (11) | N1—C5—C6—C7 | −178.3 (7) |
| C5—N1—C1—Cl1 | −178.6 (5) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.2 (11) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (11) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.5 (12) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.3 (5) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.4 (12) |
| N1—C1—C2—C10 | 180.0 (7) | C6—C7—C8—C11 | 178.8 (7) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C10 | −1.0 (9) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.5 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (10) | C11—C8—C9—C4 | −177.9 (6) |
| C10—C2—C3—C4 | 179.1 (6) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | −1.2 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.2 (10) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | 179.4 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | −179.4 (7) | C3—C2—C10—Br1 | 103.9 (7) |
| C1—N1—C5—C6 | 178.7 (7) | C1—C2—C10—Br1 | −76.8 (8) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.7 (10) | C9—C8—C11—Br2 | −131.1 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −1.5 (10) | C7—C8—C11—Br2 | 50.5 (8) |
| C9—C4—C5—N1 | 179.1 (6) | C9—C8—C11—Br3 | 107.2 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.5 (7) | C7—C8—C11—Br3 | −71.3 (8) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | 1.0 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the C4–C9 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11···Br1i | 1.00 | 2.92 | 3.709 (8) | 137 |
| C10—H10B···Cg2ii | 0.99 | 2.70 | 3.438 (8) | 131 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU5096).
References
- Chauhan, P. M. S. & Srivastava, S. K. (2001). Curr. Med. Chem. 8, 1535–1542. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y. L., Fang, K. C., Sheu, J. Y., Hsu, S. L. & Tzeng, C. C. (2001). J. Med. Chem. 44, 2374–2377. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ferrarini, P. L., Mori, C., Badawneh, M., Calderone, V., Greco, R., Manera, C., Martinelli, A., Nieri, P. & Saccomanni, G. (2000). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 35, 815–826. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jones, G. (1977). Quinolines, Part-I. Wiley Interscience Publication, John Wiley & Sons.
- Lyle, R. E., Portlock, D. E., Kane, M. J. & Bristol, J. A. (1972). J. Org. Chem. 37, 3967–3968. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Oxford Diffraction (2010). CrysAlis PRO. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Sahin, A., Cakmak, O., Demirtas, I., Okten, S. & Tutar, A. (2008). Tetrahedron, 64, 10068–10074.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008002/su5096fig2.tif
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯π interactions (Table 1) and the Br⋯Cl and Br⋯N short contacts are shown as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 902598
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


