The title compound shows two packing polymorphs, in which the molecular structures are planar and essentially similar. One crystal shows intermolecular C—H⋯O and π–π interactions, while the other crystal exhibits several modes of intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, packing polymorphism, 2-nitrobenzyl ester, π–π interactions, C—H⋯O interactions
Abstract
The title compound, C11H13NO6, shows two polymorphs, orange and yellow forms, both of which crystallize in the space group P21/c. The molecular structures in the two polymorphs are essentially similar and adopt a planar structure, the maximum deviations for the non-H atoms being 0.1836 (13) and 0.1276 (13) Å, respectively, for the orange and yellow forms. In the orange crystal, molecules are linked by an intermolecular C—H⋯O interaction into a helical chain along the b-axis direction. The chains are stacked along the c axis through a π–π interaction [centroid–centroid distance = 3.6087 (11) Å], forming a layer parallel to the bc plane. In the yellow crystal, molecules are connected through C—H⋯O interactions into a sheet structure parallel to (-302). No significant π–π interaction is observed. The unit-cell volume of the orange crystal is larger than that of the yellow one, and this accounts for the predominant growth of the yellow crystal.
Chemical context
Polymorphism is of interest in crystallization, phase transition, material synthesis and the pharmaceutical industry because differences in the crystal packing and/or conformation of compounds with the same formula can change the chemical and physical properties, including solubility, bioavailability and so forth (Moulton & Zaworotko, 2001 ▸; Matsuo & Matsuoka, 2007 ▸; Yu, 2010 ▸). We have been investigating silane coupling agents and thiols with distal functional groups protected by photolabile 2-nitrobenzyl groups (Edagawa et al., 2012 ▸). During the course of photoremoval studies of these materials, we found that the simple ester, 4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate, which releases acetic acid on photo-irradiation, forms two different types of crystals, orange rods and yellow needles. Here, we report the crystal structures of these two polymorphs of the title compound.
Structural commentary
The molecular structures of the two crystals are approximately planar and almost identical, as shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The C2—C1—C7—O3, C9—C8—O3—C7, C5—C4—O5—C10 and C4—C5—O6—C11 torsion angles in the two crystals are approximately 180°. The dihedral angles between the benzene ring (C1–C6) and the nitro group (O1/N1/O2) are 9.54 (11) and 4.15 (7)° for the orange and yellow polymorphs, respectively.
Figure 1.
The molecular structures of the title compound polymorphs, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
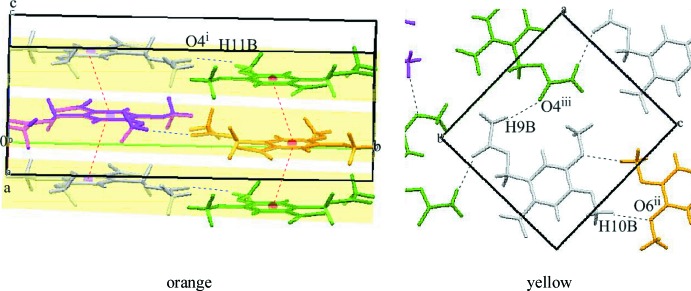
Although the two crystals crystallize in the same space group (P21/c) with Z′ = 1, their packing modes are different. In the orange crystal, the molecules are connected by an intermolecular C—H⋯O interaction [C11—H11B⋯O4i; symmetry code: (i) 1 − x, − + y,
+ y,  − z; Table 1 ▸] between the methoxy group and the carbonyl group, forming a helical chain along the b axis as shown in Fig. 2 ▸, left. In addition, a π–π interaction between the benzene rings with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.6087 (11) Å links the chains to be stacked along the c axis. In the yellow crystal, the molecules located in the plane perpendicular to the ac plane are connected by C—H⋯O interactions (Table 2 ▸) between methoxy groups [C10—H10B⋯O6ii; symmetry code: (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z] and between acetyl groups [C9—H9B⋯O4iii; symmetry code: (iii) −x, −
− z; Table 1 ▸] between the methoxy group and the carbonyl group, forming a helical chain along the b axis as shown in Fig. 2 ▸, left. In addition, a π–π interaction between the benzene rings with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.6087 (11) Å links the chains to be stacked along the c axis. In the yellow crystal, the molecules located in the plane perpendicular to the ac plane are connected by C—H⋯O interactions (Table 2 ▸) between methoxy groups [C10—H10B⋯O6ii; symmetry code: (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z] and between acetyl groups [C9—H9B⋯O4iii; symmetry code: (iii) −x, − + y,
+ y,  − z], forming a sheet structure parallel to (
− z], forming a sheet structure parallel to ( 02) (Fig. 2 ▸, right).
02) (Fig. 2 ▸, right).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for orange .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11—H11B⋯O4i | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.369 (2) | 147 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 2.
Intermolecular C—H⋯O (black dashed lines) and π–π (red dashed lines) interactions in the orange crystal (left), and intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions (black dashed lines) between methoxy groups and between acetyl groups in the yellow crystal (right). [Symmetry codes: (i) 1 − x, − + y,
+ y,  − z; (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z; (iii) −x, −
− z; (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 2 − z; (iii) −x, − + y,
+ y,  − z.]
− z.]
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for yellow .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9—H9B⋯O4iii | 0.98 | 2.40 | 3.375 (2) | 174 |
| C10—H10B⋯O6ii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.472 (2) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
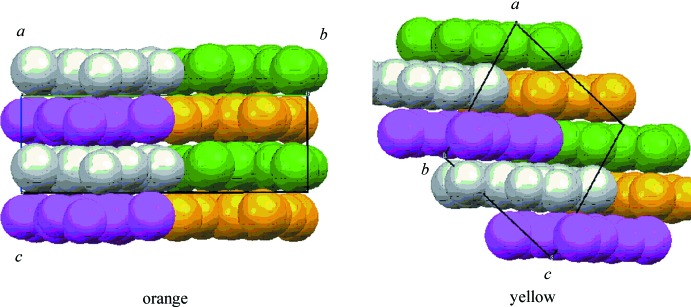
In the orange crystal, the molecules are stacked in columnar structures via π–π interactions along the c axis (Fig. 3 ▸, left). In contrast, no π–π interactions are observed in the yellow crystal. The molecules are therefore terraced along the diagonal line of the a and c axes as shown in Fig. 3 ▸, right. As a result of these packing differences, the volume of the unit cell of the orange crystal is larger than that of the yellow one, i.e., the orange crystal contains slightly more void space than the yellow one. This would account for the predominant growth of the yellow crystals.
Figure 3.
Side views of space-filling models of molecular packing of the orange (left) and yellow (right) crystals.
Synthesis and crystallization
4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl alcohol (0.714 g, 3.35 mmol), acetic anhydride (0.63 ml, 6.66 mmol), Et3N (1 ml) and CH2Cl2 (20 ml) were placed in a 100 mL flask, and the mixture was stirred at ambient temperature overnight. The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (20 ml × 3), washed with brine, dried over MgSO4, and evaporated to give a yellow solid (0.773 g, 90% yield). The solid was crystallized by slow evaporation from a mixed solution of ethyl acetate and hexane (1:1). Orange crystals were occasionally obtained in small amounts, but the yellow crystals grew predominantly.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All H atoms were located geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.99 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for methylene H atoms, C—H = 0.95 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) for aromatic H atoms, and C—H = 0.98 Å and U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| orange | yellow | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C11H13NO6 | C11H13NO6 |
| M r | 255.22 | 255.22 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 93 | 93 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.8751 (13), 19.555 (2), 6.8688 (9) | 10.476 (3), 10.714 (3), 10.266 (3) |
| β (°) | 106.298 (6) | 105.077 (10) |
| V (Å3) | 1144.2 (3) | 1112.6 (6) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.45 × 0.42 × 0.39 | 0.56 × 0.54 × 0.25 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Mercury375R | Rigaku Mercury375R |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (REQAB; Rigaku, 1998 ▸) | Multi-scan (REQAB; Rigaku, 1998 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.960, 0.970 | 0.797, 0.970 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 11495, 2612, 2098 | 9498, 2058, 1769 |
| R int | 0.047 | 0.033 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 | 0.606 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.051, 0.132, 1.11 | 0.049, 0.130, 1.13 |
| No. of reflections | 2612 | 2058 |
| No. of parameters | 166 | 166 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters not refined | H-atom parameters not refined |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.39, −0.30 | 0.38, −0.35 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) orange, yellow, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) orange. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) yellow. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup5.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Kanagawa University for the general support of our studies.
supplementary crystallographic information
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Crystal data
| C11H13NO6 | F(000) = 536 |
| Mr = 255.22 | Dx = 1.48 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2655 reflections |
| a = 8.8751 (13) Å | θ = 3.1–27.5° |
| b = 19.555 (2) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 6.8688 (9) Å | T = 93 K |
| β = 106.298 (6)° | Platelet, orange |
| V = 1144.2 (3) Å3 | 0.45 × 0.42 × 0.39 mm |
| Z = 4 |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury375R (2x2 bin mode) diffractometer | 2612 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2098 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.047 |
| Detector resolution: 13.6612 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.2° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (REQAB; Rigaku, 1998) | k = −25→25 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.970 | l = −8→8 |
| 11495 measured reflections |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.132 | H-atom parameters not refined |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0597P)2 + 0.5862P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2612 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 166 parameters | Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.19328 (19) | 0.29434 (8) | 0.7664 (2) | 0.0124 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.04911 (19) | 0.26435 (9) | 0.7614 (3) | 0.0139 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.02606 (19) | 0.19342 (8) | 0.7577 (3) | 0.0140 (3) | |
| H3 | −0.0739 | 0.1752 | 0.7541 | 0.017* | |
| C4 | 0.1487 (2) | 0.15013 (8) | 0.7593 (3) | 0.0139 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.29755 (19) | 0.17865 (8) | 0.7678 (2) | 0.0125 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.31701 (19) | 0.24911 (8) | 0.7700 (2) | 0.0128 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.4171 | 0.2673 | 0.7740 | 0.015* | |
| C7 | 0.22141 (19) | 0.37064 (8) | 0.7674 (3) | 0.0138 (3) | |
| H7A | 0.1502 | 0.3919 | 0.6450 | 0.017* | |
| H7B | 0.2010 | 0.3916 | 0.8887 | 0.017* | |
| C8 | 0.4225 (2) | 0.44786 (9) | 0.7575 (3) | 0.0155 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.5882 (2) | 0.45412 (9) | 0.7490 (3) | 0.0218 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.5938 | 0.4425 | 0.6124 | 0.033* | |
| H9B | 0.6550 | 0.4227 | 0.8475 | 0.033* | |
| H9C | 0.6247 | 0.5012 | 0.7816 | 0.033* | |
| C10 | −0.0084 (2) | 0.05009 (9) | 0.7387 (3) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| H10A | −0.0436 | 0.0632 | 0.8565 | 0.030* | |
| H10B | 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.7344 | 0.030* | |
| H10C | −0.0848 | 0.0660 | 0.6144 | 0.030* | |
| C11 | 0.5657 (2) | 0.15867 (9) | 0.7809 (3) | 0.0187 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.5598 | 0.1883 | 0.6639 | 0.028* | |
| H11B | 0.6370 | 0.1205 | 0.7803 | 0.028* | |
| H11C | 0.6051 | 0.1850 | 0.9063 | 0.028* | |
| N1 | −0.08677 (17) | 0.30611 (7) | 0.7608 (2) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| O1 | −0.08009 (15) | 0.36827 (7) | 0.7379 (2) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| O2 | −0.20491 (15) | 0.27751 (7) | 0.7846 (2) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.38271 (14) | 0.38139 (6) | 0.7701 (2) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.33181 (16) | 0.49408 (7) | 0.7520 (2) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.14161 (14) | 0.08062 (6) | 0.7543 (2) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.41110 (14) | 0.13243 (6) | 0.7695 (2) | 0.0164 (3) |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0088 (8) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0112 (8) | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0121 (8) | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0127 (8) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0147 (8) | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0133 (8) | −0.0031 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0152 (8) | 0.0095 (8) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0113 (8) | 0.0160 (8) | 0.0117 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0043 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0105 (8) | 0.0147 (8) | 0.0177 (9) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0164 (9) | −0.0025 (6) | 0.0063 (7) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0182 (9) | 0.0347 (11) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0094 (8) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0271 (10) | −0.0074 (7) | 0.0075 (7) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0277 (10) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0065 (7) | −0.0011 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0171 (7) | 0.0177 (8) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0041 (6) | −0.0007 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0119 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0133 (6) | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0364 (8) | −0.0016 (5) | 0.0111 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0227 (7) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0063 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0018 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0160 (6) | 0.0120 (6) | 0.0264 (7) | −0.0022 (5) | 0.0085 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0244 (7) | 0.0013 (5) | 0.0071 (5) | 0.0005 (5) |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.399 (2) | C8—O3 | 1.356 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.405 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.494 (2) |
| C1—C7 | 1.512 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C2—N1 | 1.456 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.377 (2) | C10—O5 | 1.436 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| C4—O5 | 1.361 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.420 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C5—O6 | 1.351 (2) | C11—O6 | 1.446 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.388 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C7—O3 | 1.4419 (19) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9900 | N1—O1 | 1.229 (2) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9900 | N1—O2 | 1.2390 (19) |
| C8—O4 | 1.204 (2) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 116.20 (15) | O3—C8—C9 | 110.96 (15) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 124.21 (15) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 119.59 (15) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.90 (15) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 121.08 (15) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 116.02 (15) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.83 (15) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 | O5—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 | O5—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O5—C4—C3 | 125.67 (15) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O5—C4—C5 | 115.43 (15) | O5—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.90 (15) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O6—C5—C6 | 125.00 (15) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O6—C5—C4 | 114.87 (15) | O6—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.12 (15) | O6—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.03 (15) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.0 | O6—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.0 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C1 | 107.82 (13) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—H7A | 110.1 | O1—N1—O2 | 122.43 (15) |
| C1—C7—H7A | 110.1 | O1—N1—C2 | 119.04 (14) |
| O3—C7—H7B | 110.1 | O2—N1—C2 | 118.53 (14) |
| C1—C7—H7B | 110.1 | C8—O3—C7 | 114.47 (13) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.5 | C4—O5—C10 | 116.93 (13) |
| O4—C8—O3 | 122.58 (16) | C5—O6—C11 | 117.20 (13) |
| O4—C8—C9 | 126.45 (16) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (2) | C7—C1—C6—C5 | −179.55 (15) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 179.08 (16) | C2—C1—C7—O3 | −179.18 (15) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | 178.95 (15) | C6—C1—C7—O3 | 0.6 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—N1 | −1.2 (3) | C1—C2—N1—O1 | 9.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (3) | C3—C2—N1—O1 | −170.83 (16) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.59 (15) | C1—C2—N1—O2 | −170.13 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4—O5 | −179.39 (16) | C3—C2—N1—O2 | 9.6 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.0 (2) | O4—C8—O3—C7 | 2.5 (2) |
| O5—C4—C5—O6 | 0.1 (2) | C9—C8—O3—C7 | −176.69 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—O6 | 179.78 (15) | C1—C7—O3—C8 | 175.79 (14) |
| O5—C4—C5—C6 | 178.91 (14) | C3—C4—O5—C10 | 2.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.4 (2) | C5—C4—O5—C10 | −177.96 (15) |
| O6—C5—C6—C1 | 179.47 (15) | C6—C5—O6—C11 | 2.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.8 (2) | C4—C5—O6—C11 | −179.17 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (2) |
(orange) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl acetate. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11B···O4i | 0.98 | 2.50 | 3.369 (2) | 147 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Crystal data
| C11H13NO6 | F(000) = 536 |
| Mr = 255.22 | Dx = 1.52 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2424 reflections |
| a = 10.476 (3) Å | θ = 3.1–27.5° |
| b = 10.714 (3) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| c = 10.266 (3) Å | T = 93 K |
| β = 105.077 (10)° | Neecle, yellow |
| V = 1112.6 (6) Å3 | 0.56 × 0.54 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury375R (2x2 bin mode) diffractometer | 2058 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1769 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.033 |
| Detector resolution: 13.6612 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 3.1° |
| profile data from ω–scan | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (REQAB; Rigaku, 1998) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.797, Tmax = 0.970 | l = −12→12 |
| 9498 measured reflections |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | H-atom parameters not refined |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0689P)2 + 0.4454P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2058 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 166 parameters | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Special details
| Experimental. Rigaku (1998). REQAB. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.22297 (15) | 0.82305 (16) | 0.58154 (16) | 0.0158 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.29963 (16) | 0.88543 (15) | 0.69423 (17) | 0.0154 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.37895 (16) | 0.82230 (16) | 0.80564 (16) | 0.0168 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.4307 | 0.8681 | 0.8801 | 0.020* | |
| C4 | 0.38181 (16) | 0.69396 (16) | 0.80717 (16) | 0.0167 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.30317 (15) | 0.62775 (16) | 0.69555 (17) | 0.0154 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.22676 (16) | 0.69258 (16) | 0.58567 (16) | 0.0158 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.1754 | 0.6469 | 0.5109 | 0.019* | |
| C7 | 0.13844 (16) | 0.88840 (15) | 0.45857 (17) | 0.0166 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.0754 | 0.9456 | 0.4852 | 0.020* | |
| H7B | 0.1948 | 0.9379 | 0.4140 | 0.020* | |
| C8 | −0.01205 (16) | 0.83679 (16) | 0.25084 (16) | 0.0175 (4) | |
| C9 | −0.08377 (18) | 0.73342 (16) | 0.16403 (18) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H9A | −0.1781 | 0.7378 | 0.1603 | 0.032* | |
| H9B | −0.0481 | 0.6529 | 0.2022 | 0.032* | |
| H9C | −0.0721 | 0.7418 | 0.0728 | 0.032* | |
| C10 | 0.53711 (16) | 0.68572 (16) | 1.02246 (16) | 0.0186 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.6026 | 0.7354 | 0.9923 | 0.028* | |
| H10B | 0.5826 | 0.6245 | 1.0895 | 0.028* | |
| H10C | 0.4834 | 0.7409 | 1.0630 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 0.22990 (18) | 0.43083 (16) | 0.59702 (17) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.1368 | 0.4538 | 0.5832 | 0.032* | |
| H11B | 0.2410 | 0.3417 | 0.6185 | 0.032* | |
| H11C | 0.2574 | 0.4480 | 0.5146 | 0.032* | |
| O1 | 0.23683 (12) | 1.08224 (11) | 0.60592 (12) | 0.0219 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.36433 (12) | 1.07109 (11) | 0.80903 (12) | 0.0228 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.06713 (11) | 0.79354 (11) | 0.36698 (12) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| O4 | −0.02320 (12) | 0.94638 (11) | 0.22241 (12) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.45330 (11) | 0.62196 (11) | 0.90924 (12) | 0.0183 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.30975 (12) | 0.50251 (11) | 0.70663 (12) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.30069 (14) | 1.02142 (14) | 0.70366 (14) | 0.0175 (3) |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0052 (7) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0084 (8) | 0.0189 (9) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0064 (7) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0159 (8) | 0.0154 (8) | −0.0026 (7) | 0.0023 (7) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0189 (8) | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0136 (9) | 0.0158 (8) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0033 (7) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0177 (8) | 0.0137 (9) | 0.0153 (8) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0033 (7) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0193 (8) | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0163 (8) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0188 (9) | 0.0148 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0006 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0025 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0181 (9) | 0.0144 (8) | −0.0017 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0134 (9) | 0.0188 (9) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0029 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0277 (7) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0204 (7) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0035 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0189 (7) | −0.0016 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | −0.0052 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0215 (6) | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0173 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | −0.0027 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0277 (7) | 0.0140 (6) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0001 (5) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | −0.0040 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0245 (6) | 0.0095 (6) | 0.0183 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | −0.0001 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0195 (7) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0168 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.395 (2) | C8—O3 | 1.345 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.496 (2) |
| C1—C7 | 1.512 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.401 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C2—N1 | 1.460 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (3) | C10—O5 | 1.4344 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| C4—O5 | 1.359 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.416 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C5—O6 | 1.347 (2) | C11—O6 | 1.437 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.388 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C7—O3 | 1.4524 (19) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9900 | O1—N1 | 1.2368 (19) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9900 | O2—N1 | 1.2339 (19) |
| C8—O4 | 1.208 (2) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 116.61 (15) | O3—C8—C9 | 111.81 (14) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 123.79 (16) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 119.60 (14) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.48 (16) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—N1 | 121.72 (15) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 115.79 (15) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.91 (15) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | O5—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | O5—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O5—C4—C3 | 125.62 (15) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| O5—C4—C5 | 115.33 (15) | O5—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.04 (15) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O6—C5—C6 | 124.98 (15) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O6—C5—C4 | 115.13 (14) | O6—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.89 (16) | O6—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 122.05 (15) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.0 | O6—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.0 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—C1 | 107.90 (13) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| O3—C7—H7A | 110.1 | C8—O3—C7 | 115.31 (13) |
| C1—C7—H7A | 110.1 | C4—O5—C10 | 116.94 (13) |
| O3—C7—H7B | 110.1 | C5—O6—C11 | 117.37 (13) |
| C1—C7—H7B | 110.1 | O2—N1—O1 | 122.61 (15) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.4 | O2—N1—C2 | 118.78 (14) |
| O4—C8—O3 | 123.19 (15) | O1—N1—C2 | 118.60 (13) |
| O4—C8—C9 | 125.01 (15) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.2 (2) | C7—C1—C6—C5 | 179.61 (14) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −178.75 (15) | C2—C1—C7—O3 | −176.32 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | −178.07 (14) | C6—C1—C7—O3 | 3.7 (2) |
| C7—C1—C2—N1 | 2.0 (2) | O4—C8—O3—C7 | 0.8 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.8 (2) | C9—C8—O3—C7 | −178.75 (13) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.48 (15) | C1—C7—O3—C8 | −179.24 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4—O5 | −179.33 (14) | C3—C4—O5—C10 | −2.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (2) | C5—C4—O5—C10 | 178.28 (13) |
| O5—C4—C5—O6 | 0.4 (2) | C6—C5—O6—C11 | −1.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—O6 | −178.65 (15) | C4—C5—O6—C11 | 178.91 (13) |
| O5—C4—C5—C6 | −179.73 (14) | C1—C2—N1—O2 | 175.79 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.3 (2) | C3—C2—N1—O2 | −3.5 (2) |
| O6—C5—C6—C1 | 179.03 (15) | C1—C2—N1—O1 | −3.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.9 (2) | C3—C2—N1—O1 | 177.02 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (2) |
(yellow) 4,5-Dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzyl Acetate. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C9—H9B···O4i | 0.98 | 2.40 | 3.375 (2) | 174 |
| C10—H10B···O6ii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.472 (2) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
References
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., De Caro, L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2005). J. Appl. Cryst. 38, 381–388.
- Edagawa, Y., Nakanishi, J., Yamaguchi, K. & Takeda, N. (2012). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 99, 20–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Matsuo, K. & Matsuoka, M. (2007). Cryst. Growth Des. 7, 411–415.
- Moulton, B. & Zaworotko, M. J. (2001). Chem. Rev. 101, 1629–1658. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (1998). REQAB. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2011). CrystalClear-SM Expert. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wakita, K. (2001). Yadokari-XG. http://www.hat.hi-ho.jp/k-wakita/yadokari
- Yu, L. (2010). Acc. Chem. Res. 43, 1257–1266. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) orange, yellow, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) orange. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) yellow. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup5.cdx
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391orangesup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006714/is5391yellowsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report