Abstract
In the title compound, C8H7ClFNO, the F atom is disordred over the meta positions of the benzene ring in a 0.574 (4):0.426 (4) ratio and the Cl atom is syn to the O atom [O—C—C—Cl = 5.6 (3)°]. A short intramolecular C—H⋯O contact occurs. In the crystal, molecules are linked into amide C(4) chains propagating in [101] by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, disordered F atom, N-arylamides, hydrogen bonding
Related literature
For compounds in which the meta fluorine substituent of a benzene ring exhibits positional disorder, see: Nayak et al. (2012 ▸); Sanjeevarayappa et al. (2015 ▸).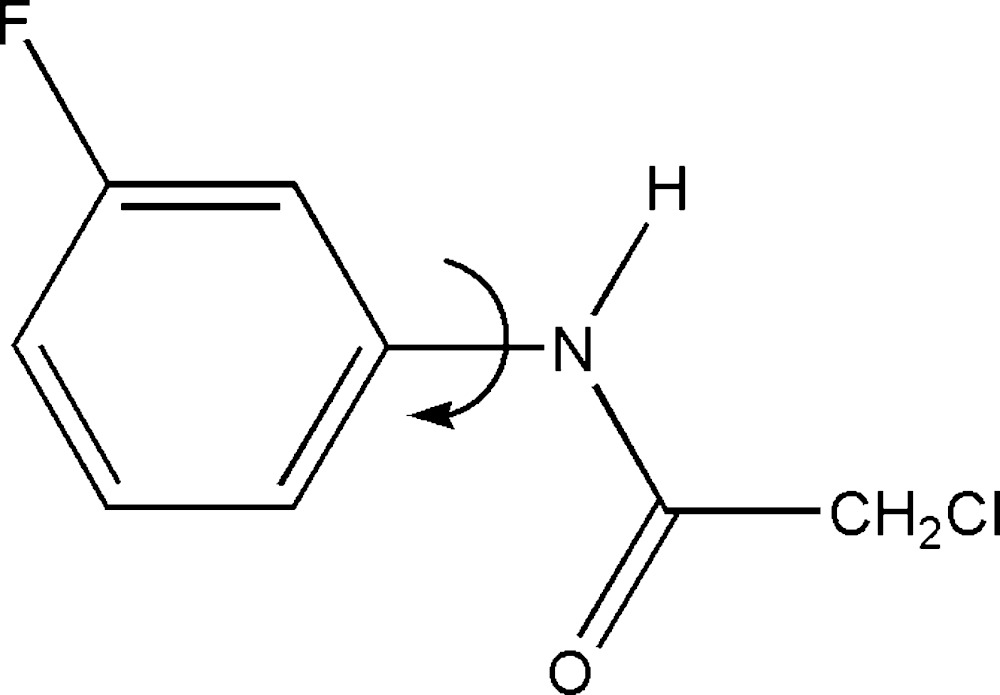
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H7ClFNO
M r = 187.60
Monoclinic,

a = 5.0441 (2) Å
b = 18.2374 (7) Å
c = 8.8653 (3) Å
β = 99.843 (1)°
V = 803.53 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 3.95 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.31 × 0.24 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) T min = 0.368, T max = 0.472
6045 measured reflections
1304 independent reflections
1297 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
1 standard reflections every 1 reflections intensity decay: 1%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.105
S = 1.15
1304 reflections
123 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2009 ▸); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400fig2.tif
Crystal packing of (I). N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
CCDC reference: 1049536
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2H2O1 | 0.93 | 2.33 | 2.885(3) | 118 |
| N1H1O1i | 0.89(2) | 1.99(3) | 2.843(2) | 160(2) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Institution of Excellence, Vijnana Bhavana, University of Mysore, Mysuru, for providing the single-crystal X-ray diffraction facility.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound (scheme 1) was synthesized by the reaction of 2-chloroacetyl chloride with 3-fluoroaniline at room temperature. The reaction mixture was poured into crushed ice and the resulting solid was washed thoroughly with water, dilute hydrochloric acid and filtered.
A small portion of the resulting compound was taken in a 10.0 ml beaker and dissolved in a 1:1 ratio of a mixture of EtOH/H2O to obtain colourless prisms by a slow evaporation method at ~24°C.
S2. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. The H atoms of the NH groups were located in a difference map and later restrained to N—H = 0.86 (4) Å. The other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å. All H atoms were refined with isotropic displacement parameters (set to 1.2 times of the Ueq of the parent atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.

A view of the molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

Crystal packing of (I). N—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Crystal data
| C8H7ClFNO | Prism |
| Mr = 187.60 | Dx = 1.551 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 385 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 5.0441 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 1297 reflections |
| b = 18.2374 (7) Å | θ = 5.6–64.3° |
| c = 8.8653 (3) Å | µ = 3.95 mm−1 |
| β = 99.843 (1)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 803.53 (5) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.31 × 0.24 × 0.19 mm |
| F(000) = 384 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 1297 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.041 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 64.3°, θmin = 5.6° |
| phi and φ scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.368, Tmax = 0.472 | l = −9→10 |
| 6045 measured reflections | 1 standard reflections every 1 reflections |
| 1304 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.15 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0565P)2 + 0.4965P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1304 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 123 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Melting point was determined by using open capillary. FT—IR Spectrum was recorded on Jasco FT—IR Spectrometer. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on Jeol-400 MHz NMR instrument using DMSO-d6 as solvent. Chemical shift values were expressed in δ (p.p.m.) relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal reference standard. Mass spectrum of the compound was recorded on Shimadzu LC-2010EV with ESI probe. The analysis of various spectra are as follows.IR wavenumbers (cm-1): C=O 1674.9, C—N 1348–1060, N—H 3510–3120, C—N—C 515–409, C—Cl 850–550, C—Cl 650–515. 1H-NMR (399.6 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 10.49 (s, 1H, NH), 7.57–7,55 (dd, 1H, Ar—H), 7.34–7.27 (m, 2H, Ar—H), 6.88–6.83 (m, 1H, Ar—H), 2.47 (s, 2H, –CH2-). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ: 165.41, 163.76, 140.67, 130.89, 115.54, 110.80, 106.77, 43.92. MS: Predicted Mass: 187.07; Obtained Mass 188.07 (M+1). |
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| H1 | −0.643 (5) | 0.2133 (14) | 0.515 (3) | 0.032 (7)* | |
| Cl1 | −0.02090 (10) | 0.34713 (3) | 0.71994 (6) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| O1 | −0.3206 (3) | 0.22817 (8) | 0.83631 (16) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| N1 | −0.5907 (3) | 0.19920 (9) | 0.61148 (19) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| C1 | −0.7435 (4) | 0.14033 (11) | 0.6567 (2) | 0.0193 (4) | |
| C7 | −0.3994 (4) | 0.23849 (10) | 0.7000 (2) | 0.0200 (4) | |
| C6 | −0.9766 (4) | 0.12164 (11) | 0.5553 (2) | 0.0222 (5) | |
| H6 | −1.0266 | 0.1475 | 0.4645 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | −0.6672 (4) | 0.10139 (11) | 0.7913 (2) | 0.0220 (5) | |
| H2 | −0.5110 | 0.1133 | 0.8589 | 0.026* | |
| C4 | −1.0643 (4) | 0.02475 (12) | 0.7255 (3) | 0.0286 (5) | |
| H4 | −1.1717 | −0.0135 | 0.7496 | 0.034* | |
| C8 | −0.2919 (4) | 0.29966 (12) | 0.6089 (2) | 0.0271 (5) | |
| H8A | −0.4359 | 0.3340 | 0.5733 | 0.032* | |
| H8B | −0.2326 | 0.2787 | 0.5198 | 0.032* | |
| C5 | −1.1321 (4) | 0.06407 (12) | 0.5923 (3) | 0.0271 (5) | |
| H5 | −1.2875 | 0.0516 | 0.5247 | 0.033* | 0.574 (4) |
| F1A | −1.3441 (5) | 0.04244 (15) | 0.5018 (3) | 0.0275 (9) | 0.426 (4) |
| C3 | −0.8308 (5) | 0.04424 (12) | 0.8222 (3) | 0.0273 (5) | |
| H3 | −0.7808 | 0.0178 | 0.9122 | 0.033* | 0.426 (4) |
| F1 | −0.7655 (5) | 0.00473 (14) | 0.9442 (3) | 0.0394 (8) | 0.574 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0277 (3) | 0.0285 (4) | 0.0258 (4) | −0.00754 (18) | −0.0003 (2) | −0.00248 (19) |
| O1 | 0.0374 (9) | 0.0285 (8) | 0.0142 (8) | −0.0067 (6) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0009 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0232 (9) | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0118 (9) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0193 (9) | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0045 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0214 (10) | 0.0148 (10) | 0.0020 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0231 (10) | 0.0247 (11) | 0.0187 (10) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0030 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0234 (10) | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0172 (10) | 0.0009 (8) | 0.0046 (8) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0306 (12) | 0.0244 (11) | 0.0348 (13) | −0.0028 (9) | 0.0166 (10) | −0.0036 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0321 (12) | 0.0276 (11) | 0.0193 (11) | −0.0079 (9) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0229 (11) | 0.0278 (11) | 0.0319 (12) | −0.0040 (8) | 0.0080 (9) | −0.0111 (9) |
| F1A | 0.0209 (15) | 0.0318 (17) | 0.0282 (17) | −0.0062 (11) | −0.0001 (11) | −0.0039 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0348 (12) | 0.0252 (11) | 0.0252 (11) | 0.0023 (9) | 0.0143 (9) | 0.0017 (9) |
| F1 | 0.0487 (16) | 0.0436 (15) | 0.0266 (13) | −0.0043 (11) | 0.0082 (10) | 0.0146 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C8 | 1.768 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C7 | 1.221 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.374 (3) |
| N1—C7 | 1.342 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.380 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.419 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.89 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.386 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.394 (3) | C5—F1A | 1.284 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.530 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C5 | 1.383 (3) | C3—F1 | 1.295 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (3) | ||
| C7—N1—C1 | 127.59 (17) | C3—C4—H4 | 121.3 |
| C7—N1—H1 | 118.2 (17) | C7—C8—Cl1 | 111.91 (14) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 113.9 (17) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.61 (19) | Cl1—C8—H8A | 109.2 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 123.14 (18) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 116.23 (18) | Cl1—C8—H8B | 109.2 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 125.18 (19) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107.9 |
| O1—C7—C8 | 123.40 (18) | F1A—C5—C4 | 115.8 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 111.42 (16) | F1A—C5—C6 | 122.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.9 (2) | C4—C5—C6 | 122.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.6 | C4—C5—H5 | 118.9 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.6 | C6—C5—H5 | 118.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.9 (2) | F1—C3—C4 | 116.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.0 | F1—C3—C2 | 120.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.0 | C4—C3—C2 | 123.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.4 (2) | C4—C3—H3 | 118.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.3 | C2—C3—H3 | 118.5 |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | −18.4 (3) | N1—C7—C8—Cl1 | −175.19 (14) |
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | 163.16 (19) | C3—C4—C5—F1A | 177.0 (2) |
| C1—N1—C7—O1 | 1.9 (3) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.8 (3) |
| C1—N1—C7—C8 | −177.30 (18) | C1—C6—C5—F1A | −177.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.7 (3) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | 0.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.19 (17) | C5—C4—C3—F1 | −177.5 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (3) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | 0.8 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.04 (18) | C1—C2—C3—F1 | 178.1 (2) |
| O1—C7—C8—Cl1 | 5.6 (3) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O1 | 0.93 | 2.33 | 2.885 (3) | 118 |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.89 (2) | 1.99 (3) | 2.843 (2) | 160 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7400).
References
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT-Plus. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Nayak, S. K., Reddy, M. K., Chopra, D. & Guru Row, T. N. (2012). CrystEngComm, 14, 200–210.
- Sanjeevarayappa, C., Iyengar, P., Manoj Kumar, K. E. & Suchetan, P. A. (2015). Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 607, 232–241.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007240/hb7400fig2.tif
Crystal packing of (I). N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
CCDC reference: 1049536
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


