Abstract
The title molecule, C16H9BrO3, deviates slightly from planarity. The benzene ring makes a dihedral angle of 1.02 (9)° with the plane defined by the five-membered ring of the indandione moiety. The latter exhibits a minute twist indicated by the dihedral angle of 0.47 (9)° between the planes of the five- and six-membered rings. An intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond between the attached benzene ring with one of the indandione carbonyl O atoms stabilizes the molecular conformation. In the crystal, the molecules form dimers across centres of inversion via pairwise O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The dimers form stacks running parallel to [010] and interact through π–π interactions between the five-membered ring of one molecule and the six-membered rings of the indandione moiety of an adjacent molecule [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.5454 (10) Å].
Keywords: crystal structure; 3-substituted indan-1,3-diones; hydrogen bonding; π–π interactions
Related literature
Indan-1,3-dione and its analogues are synthons for building highly interesting compounds with a wide range of applications in both pharmaceutical and industrial chemistry (Kuhn & Rae, 1971 ▸; Junek & Sterk, 1968 ▸; Kunz & Polansky, 1969 ▸; Aldersley et al., 1983 ▸). For chemical reactions and bio-activities of 3-substituted indan-1,3-diones, see: Hochrainer & Wessely (1966 ▸); Zargar & Khan (2015 ▸).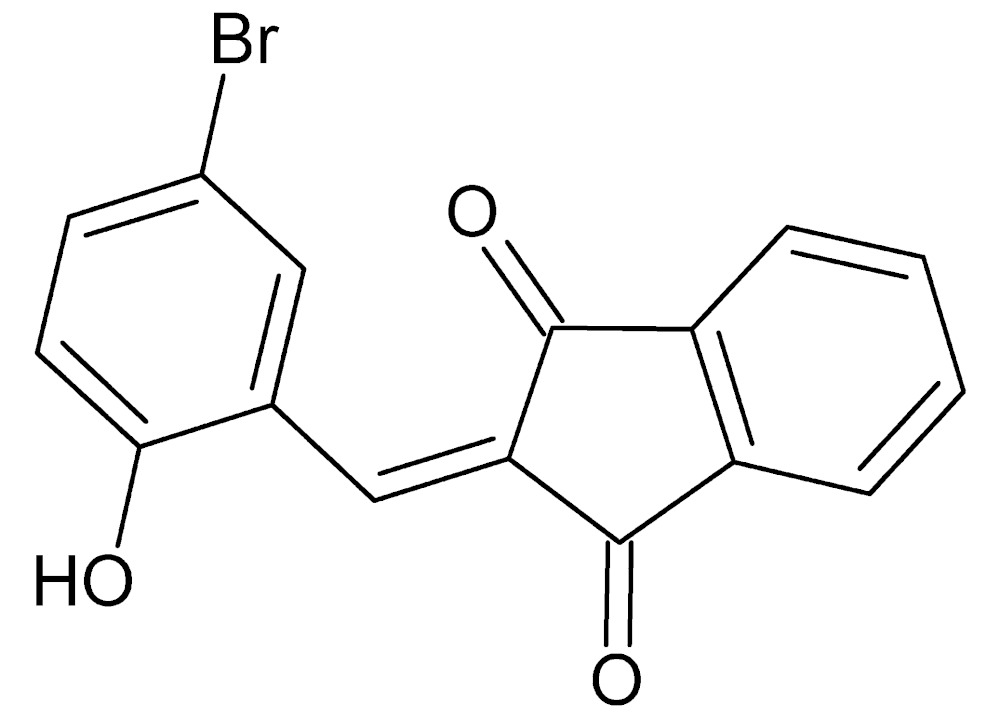
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H9BrO3
M r = 329.14
Monoclinic,

a = 13.8820 (4) Å
b = 3.8695 (1) Å
c = 24.0068 (5) Å
β = 102.483 (1)°
V = 1259.07 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 4.50 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.22 × 0.07 × 0.04 mm
Data collection
Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer
Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) T min = 0.67, T max = 0.84
8943 measured reflections
2510 independent reflections
2386 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.020
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.021
wR(F 2) = 0.056
S = 1.09
2510 reflections
181 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2014 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2014 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXT (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2012 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145fig1.tif
The title molecule with labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H⋯O interaction is shown as a dotted line.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed down [010]. Intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
CCDC reference: 1059869
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H6O3 | 0.95 | 2.15 | 2.994(2) | 148 |
| O1H1O2i | 0.84 | 1.83 | 2.6641(16) | 173 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The support of NSF–MRI grant No. 1228232 for the purchase of the diffractometer and Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory are gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Experimental
A mixture of 1 mmol (146 mg) of 1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione and 1 mmol (201 mg) of 5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde in 30 ml ethanol was refluxed for 30 min. The resulting solid product was collected under vacuum and re-crystallized from ethanol to afford yellow needles suitable for X-ray diffraction in 83% yield.
S2. Refinement
H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 Å) while that attached to oxygen was placed in a location derived from a difference map and its coordinates adjusted to give a distance O—H = 0.84 Å. All H atoms were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 times those of the attached atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.

The title molecule with labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H···O interaction is shown as a dotted line.
Fig. 2.

Crystal packing of the title compound viewed down [010]. Intermolecular O—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Crystal data
| C16H9BrO3 | F(000) = 656 |
| Mr = 329.14 | Dx = 1.736 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 13.8820 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 7789 reflections |
| b = 3.8695 (1) Å | θ = 3.3–74.5° |
| c = 24.0068 (5) Å | µ = 4.50 mm−1 |
| β = 102.483 (1)° | T = 150 K |
| V = 1259.07 (6) Å3 | Needle, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.22 × 0.07 × 0.04 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer | 2510 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: INCOATEC IµS micro–focus source | 2386 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4167 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 74.5°, θmin = 3.3° |
| ω scans | h = −16→17 |
| Absorption correction: numerical (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | k = −4→4 |
| Tmin = 0.67, Tmax = 0.84 | l = −29→29 |
| 8943 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.021 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0301P)2 + 0.6412P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2510 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 181 parameters | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 Å) while that attached to oxygen was placed in a location derived from a difference map and its coordinates adjusted to give O—H = 0.84 Å. All were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 times those of the attached atoms. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.74761 (2) | 0.32460 (5) | 0.72665 (2) | 0.02597 (8) | |
| O1 | 1.00458 (9) | −0.0525 (4) | 0.56417 (5) | 0.0324 (3) | |
| H1 | 1.0561 | −0.1618 | 0.5789 | 0.039* | |
| O2 | 0.82877 (9) | 0.4018 (4) | 0.39794 (5) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.63542 (9) | 0.6391 (4) | 0.53435 (5) | 0.0331 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.85867 (12) | 0.2074 (4) | 0.57969 (6) | 0.0188 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.94845 (11) | 0.0308 (4) | 0.60120 (6) | 0.0216 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.97616 (11) | −0.0550 (4) | 0.65901 (6) | 0.0227 (3) | |
| H3 | 1.0370 | −0.1702 | 0.6731 | 0.027* | |
| C4 | 0.91553 (12) | 0.0270 (4) | 0.69553 (6) | 0.0215 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.9339 | −0.0334 | 0.7348 | 0.026* | |
| C5 | 0.82703 (12) | 0.1991 (4) | 0.67450 (6) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.79773 (12) | 0.2902 (4) | 0.61786 (6) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.7370 | 0.4079 | 0.6046 | 0.023* | |
| C7 | 0.83772 (12) | 0.2944 (4) | 0.51956 (6) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.8883 | 0.2221 | 0.5011 | 0.024* | |
| C8 | 0.76223 (11) | 0.4559 (4) | 0.48379 (6) | 0.0193 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.76467 (11) | 0.4982 (4) | 0.42218 (6) | 0.0195 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.67288 (11) | 0.6780 (4) | 0.39402 (7) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.64124 (13) | 0.7720 (4) | 0.33723 (7) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.6801 | 0.7253 | 0.3100 | 0.028* | |
| C12 | 0.55046 (13) | 0.9372 (4) | 0.32177 (7) | 0.0262 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.5268 | 1.0061 | 0.2833 | 0.031* | |
| C13 | 0.49331 (12) | 1.0039 (5) | 0.36193 (7) | 0.0269 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.4315 | 1.1172 | 0.3502 | 0.032* | |
| C14 | 0.52519 (12) | 0.9075 (5) | 0.41869 (7) | 0.0243 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.4862 | 0.9515 | 0.4459 | 0.029* | |
| C15 | 0.61626 (12) | 0.7441 (4) | 0.43405 (7) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.66754 (12) | 0.6133 (4) | 0.49114 (7) | 0.0216 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.03096 (11) | 0.02856 (12) | 0.02164 (10) | 0.00308 (7) | 0.01281 (7) | −0.00170 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0525 (8) | 0.0217 (5) | 0.0200 (6) | 0.0089 (4) | 0.0075 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0239 (6) | 0.0394 (7) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0084 (4) | 0.0042 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0278 (6) | 0.0513 (8) | 0.0223 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0053 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0208 (8) | 0.0175 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0037 (7) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0236 (7) | 0.0225 (8) | 0.0172 (6) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0203 (8) | 0.0193 (7) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0079 (6) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0217 (8) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0062 (6) | −0.0013 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0190 (7) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0049 (5) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0190 (7) | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0215 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0262 (8) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0039 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0022 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0317 (8) | 0.0043 (7) | −0.0032 (6) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0191 (7) | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0031 (6) | −0.0019 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0196 (7) | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C5 | 1.9014 (15) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C2 | 1.3418 (19) | C8—C16 | 1.493 (2) |
| O1—H1 | 0.8400 | C8—C9 | 1.4956 (19) |
| O2—C9 | 1.2221 (19) | C9—C10 | 1.481 (2) |
| O3—C16 | 1.218 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.387 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.412 (2) | C10—C15 | 1.390 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.417 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.390 (2) |
| C1—C7 | 1.449 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.398 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.399 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.377 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—C14 | 1.390 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.393 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.390 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.378 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C15—C16 | 1.490 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.355 (2) | ||
| C2—O1—H1 | 113.9 | O2—C9—C10 | 124.70 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.43 (14) | O2—C9—C8 | 127.73 (14) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 125.05 (14) | C10—C9—C8 | 107.57 (13) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 116.51 (14) | C11—C10—C15 | 121.66 (15) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 121.74 (14) | C11—C10—C9 | 129.07 (15) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 117.73 (13) | C15—C10—C9 | 109.27 (13) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.53 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 117.32 (15) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.16 (14) | C10—C11—H11 | 121.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C12—C11—H11 | 121.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C11—C12—C13 | 121.16 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.47 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.3 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.3 | C14—C13—C12 | 121.23 (15) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.94 (14) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C6—C5—Br1 | 119.65 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.4 |
| C4—C5—Br1 | 118.37 (11) | C13—C14—C15 | 117.44 (15) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.46 (14) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 | C15—C14—H14 | 121.3 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 | C14—C15—C10 | 121.19 (15) |
| C8—C7—C1 | 134.39 (15) | C14—C15—C16 | 128.67 (15) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 112.8 | C10—C15—C16 | 110.15 (14) |
| C1—C7—H7 | 112.8 | O3—C16—C15 | 124.43 (15) |
| C7—C8—C16 | 133.85 (14) | O3—C16—C8 | 128.87 (14) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.83 (14) | C15—C16—C8 | 106.70 (13) |
| C16—C8—C9 | 106.32 (13) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 178.65 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.35 (16) |
| C7—C1—C2—O1 | −2.4 (2) | O2—C9—C10—C15 | 179.00 (16) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | −0.22 (18) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 178.19 (15) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.3 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.38 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 179.34 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.0 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.7 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—Br1 | −177.54 (13) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −179.70 (17) |
| Br1—C5—C6—C1 | 177.74 (12) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (2) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −179.15 (15) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −178.61 (15) | C11—C10—C15—C16 | 179.48 (15) |
| C6—C1—C7—C8 | −1.5 (3) | C9—C10—C15—C16 | 0.27 (19) |
| C2—C1—C7—C8 | 179.65 (18) | C14—C15—C16—O3 | −1.4 (3) |
| C1—C7—C8—C16 | −0.2 (3) | C10—C15—C16—O3 | 179.24 (17) |
| C1—C7—C8—C9 | −179.21 (17) | C14—C15—C16—C8 | 179.14 (17) |
| C7—C8—C9—O2 | 0.1 (3) | C10—C15—C16—C8 | −0.22 (19) |
| C16—C8—C9—O2 | −179.12 (17) | C7—C8—C16—O3 | 1.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.33 (15) | C9—C8—C16—O3 | −179.35 (18) |
| C16—C8—C9—C10 | 0.08 (17) | C7—C8—C16—C15 | −179.02 (18) |
| O2—C9—C10—C11 | −0.1 (3) | C9—C8—C16—C15 | 0.08 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···O3 | 0.95 | 2.15 | 2.994 (2) | 148 |
| O1—H1···O2i | 0.84 | 1.83 | 2.6641 (16) | 173 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WM5145).
References
- Aldersley, F. M., Dean, F. M. & Nayyir-Mazhir, R. (1983). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 1753–1757.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Hochrainer, A. & Wessely, F. (1966). Monatsh. Chem. 97, 1–9.
- Junek, H. & Sterk, H. (1968). Tetrahedron Lett. 9, 4309–4310.
- Kuhn, S. J. & Rae, I. D. (1971). Can. J. Chem. 49, 157–160.
- Kunz, F. J. & Polansky, O. (1969). Monatsh. Chem. 100, 95–105.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Zargar, N. U. D. & Khan, K. Z. (2015). J. Chem. Sci. Photon, 109, 274–278.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145fig1.tif
The title molecule with labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H⋯O interaction is shown as a dotted line.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015007434/wm5145fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed down [010]. Intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
CCDC reference: 1059869
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


