Abstract
The title compound, C13H14ClNO3, crystallizes with Z′ = 2 in the space group Pca21, but a search for possible additional crystallographic symmetry found none. However, the crystal structure exhibits pseudosymmetry as the two independent molecules are related by an approximate but non-crystallographic inversion located close to (0.38, 0.26, 1/2) in the selected asymmetric unit, and the structure exhibits partial inversion twinning. The approximate inversion relationship between the two molecules in the selected asymmetric unit is clearly shown by comparison of the relevant torsion angle in the two molecules; the corresponding torsion angles have similar, although not identical magnitudes but with opposite signs. The mean planes of the quinoline rings in the two independent molecules are almost parallel, with a dihedral angle of only 0.16 (3)° between them, and the mutual orientation of these rings permits significant π–π stacking interactions between them [centroid–centroid distances = 3.7579 (15) and 3.7923 (15) Å]. In addition, the bimolecular aggregates which are related by translation along [010] are linked by a further π–π stacking interaction [centroid–centroid distance = 3.7898 (15) Å], so forming a π-stacked chain running parallel to [010]. However, there are no C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds in the structure nor, despite the number of independent aromatic rings, are there any C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds; hence there are no direction-specific interactions between adjacent π-stacked chains.
Keywords: crystal structure, quinolone, pseudosymmetry, twinning, π–π stacking interactions
Related literature
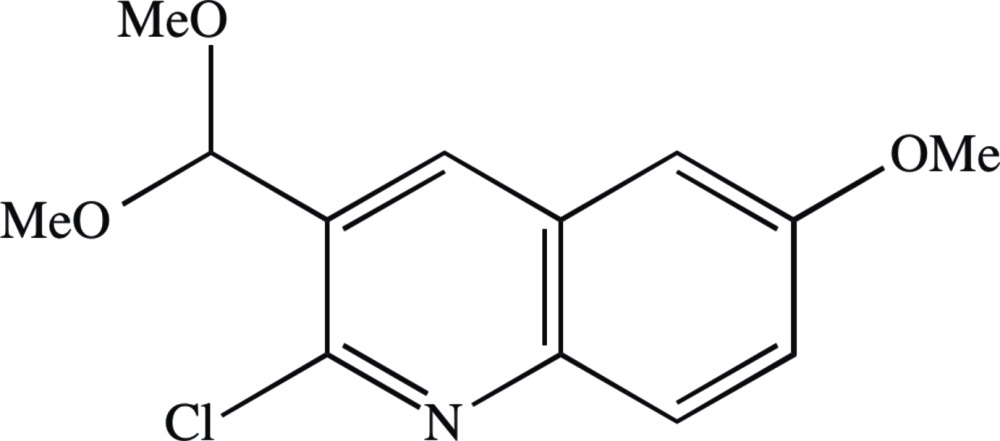
For structures of substituted 2-chloroquinolines, see Insuasty et al. (2006 ▸); Hathwar et al. (2010 ▸); Anuradha et al. (2013a
▸,b
▸).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H14ClNO3
M r = 267.70
Orthorhombic,

a = 27.1156 (9) Å
b = 7.1401 (3) Å
c = 13.0804 (5) Å
V = 2532.47 (17) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.30 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.48 × 0.32 × 0.22 mm
Data collection
Agilent Eos Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012 ▸) T min = 0.808, T max = 0.936
29727 measured reflections
5975 independent reflections
5204 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.037
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.097
S = 1.08
5975 reflections
331 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▸) x determined using 1610 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.43 (3)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▸); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Agilent, 2012 ▸); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL2014 and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig1.tif
The two independent molecules in the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 30% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig2.tif
The two molecules in the selected asymmetric unit, viewed normal to the planes of the quinolone units, showing the ring overlap which leads to a π..π sktacking interaction. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig3.tif
A stereoview of part of the crystal structure of the title compound showing the formation of a π-stacked chain parallel to [010]. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
CCDC reference: 1061227
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected torsion angles ().
| C12C13C13AO131 | 69.4(3) |
| C12C13C13AO132 | 165.7(2) |
| C13C13AO131C131 | 57.4(3) |
| C13C13AO132C132 | 170.6(2) |
| C22C23C23AO231 | 73.3(3) |
| C22C23C23AO232 | 162.3(2) |
| C23C23AO231C231 | 58.2(3) |
| C23C23AO232C232 | 170.3(2) |
Acknowledgments
NC thanks Jain University for research facilities and JPJ acknowledges the NSF–MRI program (grant No. 1039027) for funds to purchase the X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Structural commentary
It is convenient to refer to the molecules containing atoms N11 and N21 as molecules of types 1 and 2 respectively. Within the selected asymmetric unit (Fig. 1), the mean planes of the heterocyclic ring of the type 1 molecule and the carbocyclic ring of the type 2 molecule make a dihedral angle of 2.84 (12) °; the ring centroid separation is 3.7579 (15) Å, and the shortest perpendicular distance for the centroid of one ring to the plane of the other is 3.3998 (10) Å, with a ring-centroid offset of ca 1.60 Å (Fig. 2). For contact between the carbocylic ring in the type 1 molecule and the heterocyclic ring of the type 2 molecule, the corresponding values are 2.63 (12)°, 3.7923 (15) Å, 3.3993 (11) Å and ca 1.68 Å (Fig. 2). In addition, the mean planes of the carbocyclic ring in the type 1 molecule at (x, y, z) and the type 2 molecule at (x, -1 + y, z) make a dihedral angle of only 0.12 (12)°: the ring-centroid separation is 3.7898 (15) Å, the interplanar spacing is 3.5924 (10) Å, and the ring-centroid offset is ca 1.207 Å, leading to the formation of a π-stacked chain of alternating type 1 and type 2 molecules running parallel to the [010] direction (Fig. 3).
S2. Synthesis and crystallization
Sodium cyanotrohydridoborate (963.9 mg, 15.1 mmol was added in a single portion to a solution of (E)-1-((2-chloro-6-methoxyquinolin-3-yl)methylene)-2- (3-fluorophenyl)hydrazine (500 mg, 1.5 mmol) in methanol (20 cm3) and the mixture was then stirred for 30 min. The solution was cooled to 273 K and hydrogen chloride solution (16 mol dm-3, 4 cm 3) was added dropwise during 10 min. Crushed ice was then added followed by the addition of ice-cold water, and the aqueous mixture was exhaustively extracted with ethyl acetate; the combined extracts were dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the organic solvent was removed under educed pressure. The resulting crude product was purified by chromatography on silica gel using a mixture of hexane and ethyl acetate (19:1, v/v). Crystals of the title compound suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation, at ambient temperature and in the presence of air, of a solution in hexane-ethyl acetate (1:1, v/v).
S3. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. All H atoms were located in difference maps and then treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions with C—H distances 0.95 Å (aryl and heteroaryl) 0.98 Å (methyl) or 1.00 Å (aliphatic CH), and with Uiso(H) = kUeq(C), where k = 1.5 for the methyl groups, which were permitted to rotate but not to tilt and 1.2 for all other H atoms. The value of the Flack x parameter (Flack, 1983) calculated using 1610 quotients of type [(I+)-(I–)]/[(I+)+(I–)] (Parsons et al., 2013), x = 0.0.43 (3), indicated partial inversion twinning: the conventional calculation using the TWIN and BASF commands in SHELXL gave a less precise value x = 0.49 (8).
Figures
Fig. 1.

The two independent molecules in the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.

The two molecules in the selected asymmetric unit, viewed normal to the planes of the quinolone units, showing the ring overlap which leads to a π..π sktacking interaction. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
Fig. 3.

A stereoview of part of the crystal structure of the title compound showing the formation of a π-stacked chain parallel to [010]. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C13H14ClNO3 | Dx = 1.404 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 267.70 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Cell parameters from 7046 reflections |
| a = 27.1156 (9) Å | θ = 3.0–32.9° |
| b = 7.1401 (3) Å | µ = 0.30 mm−1 |
| c = 13.0804 (5) Å | T = 173 K |
| V = 2532.47 (17) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.48 × 0.32 × 0.22 mm |
| F(000) = 1120 |
Data collection
| Agilent Eos Gemini diffractometer | 5204 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | Rint = 0.037 |
| ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 3.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) | h = −38→38 |
| Tmin = 0.808, Tmax = 0.936 | k = −10→10 |
| 29727 measured reflections | l = −18→11 |
| 5975 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.040P)2 + 0.6971P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.08 | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 5975 reflections | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 331 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack (1983) x determined using 1610 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.43 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N11 | 0.39039 (8) | 0.0376 (3) | 0.29016 (19) | 0.0292 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.43758 (10) | 0.0736 (4) | 0.2853 (2) | 0.0288 (6) | |
| Cl12 | 0.46105 (3) | 0.09675 (13) | 0.16196 (6) | 0.0454 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.46977 (9) | 0.0934 (3) | 0.3699 (2) | 0.0251 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.44942 (9) | 0.0669 (3) | 0.4645 (2) | 0.0231 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.4696 | 0.0759 | 0.5237 | 0.028* | |
| C14A | 0.39862 (9) | 0.0263 (3) | 0.4750 (2) | 0.0219 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.37608 (9) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.5722 (2) | 0.0233 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.3953 | 0.0050 | 0.6330 | 0.028* | |
| C16 | 0.32597 (9) | −0.0257 (4) | 0.5764 (2) | 0.0258 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.29751 (9) | −0.0318 (4) | 0.4865 (3) | 0.0319 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.2629 | −0.0496 | 0.4913 | 0.038* | |
| C18 | 0.31884 (10) | −0.0127 (4) | 0.3927 (3) | 0.0305 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.2992 | −0.0191 | 0.3326 | 0.037* | |
| C18A | 0.37043 (9) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.3853 (2) | 0.0249 (5) | |
| C13A | 0.52323 (9) | 0.1523 (4) | 0.3548 (2) | 0.0281 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.5234 | 0.2665 | 0.3106 | 0.034* | |
| O131 | 0.55262 (7) | 0.0153 (3) | 0.30701 (18) | 0.0321 (5) | |
| C131 | 0.55388 (11) | −0.1605 (4) | 0.3590 (3) | 0.0429 (8) | |
| H13B | 0.5794 | −0.2402 | 0.3284 | 0.064* | |
| H13C | 0.5217 | −0.2221 | 0.3527 | 0.064* | |
| H13D | 0.5614 | −0.1400 | 0.4314 | 0.064* | |
| O132 | 0.54123 (7) | 0.2034 (3) | 0.45089 (17) | 0.0352 (5) | |
| C132 | 0.58878 (11) | 0.2904 (6) | 0.4464 (3) | 0.0505 (9) | |
| H13E | 0.5886 | 0.3884 | 0.3939 | 0.076* | |
| H13F | 0.6137 | 0.1963 | 0.4292 | 0.076* | |
| H13G | 0.5966 | 0.3462 | 0.5129 | 0.076* | |
| O161 | 0.29952 (6) | −0.0473 (3) | 0.66505 (19) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| C161 | 0.32646 (11) | −0.0603 (4) | 0.7579 (2) | 0.0359 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.3514 | −0.1591 | 0.7520 | 0.054* | |
| H16B | 0.3039 | −0.0902 | 0.8140 | 0.054* | |
| H16C | 0.3427 | 0.0596 | 0.7718 | 0.054* | |
| N21 | 0.36627 (8) | 0.4764 (3) | 0.7052 (2) | 0.0283 (5) | |
| C22 | 0.31896 (9) | 0.4430 (4) | 0.7132 (2) | 0.0266 (5) | |
| Cl22 | 0.29765 (3) | 0.42155 (12) | 0.83834 (6) | 0.04137 (18) | |
| C23 | 0.28587 (9) | 0.4207 (3) | 0.6311 (2) | 0.0244 (5) | |
| C24 | 0.30472 (9) | 0.4451 (4) | 0.5349 (2) | 0.0232 (5) | |
| H24 | 0.2836 | 0.4347 | 0.4772 | 0.028* | |
| C24A | 0.35540 (9) | 0.4858 (3) | 0.5202 (2) | 0.0210 (5) | |
| C25 | 0.37671 (9) | 0.5086 (3) | 0.4222 (2) | 0.0230 (5) | |
| H25 | 0.3567 | 0.5039 | 0.3626 | 0.028* | |
| C26 | 0.42667 (9) | 0.5376 (4) | 0.4143 (2) | 0.0248 (5) | |
| C27 | 0.45641 (9) | 0.5448 (4) | 0.5036 (3) | 0.0284 (6) | |
| H27 | 0.4910 | 0.5632 | 0.4970 | 0.034* | |
| C28 | 0.43643 (9) | 0.5259 (4) | 0.5976 (2) | 0.0293 (6) | |
| H28 | 0.4569 | 0.5329 | 0.6564 | 0.035* | |
| C28A | 0.38520 (9) | 0.4957 (3) | 0.6092 (2) | 0.0235 (5) | |
| C23A | 0.23260 (9) | 0.3619 (4) | 0.6500 (2) | 0.0272 (5) | |
| H23A | 0.2329 | 0.2542 | 0.6989 | 0.033* | |
| O231 | 0.20304 (7) | 0.5042 (3) | 0.6925 (2) | 0.0374 (5) | |
| C231 | 0.20056 (11) | 0.6697 (4) | 0.6326 (3) | 0.0458 (9) | |
| H23B | 0.1889 | 0.6385 | 0.5638 | 0.069* | |
| H23C | 0.2334 | 0.7264 | 0.6282 | 0.069* | |
| H23D | 0.1777 | 0.7584 | 0.6645 | 0.069* | |
| O232 | 0.21399 (6) | 0.2972 (3) | 0.55662 (16) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| C232 | 0.16713 (11) | 0.2090 (5) | 0.5660 (3) | 0.0424 (8) | |
| H23E | 0.1599 | 0.1387 | 0.5034 | 0.064* | |
| H23F | 0.1417 | 0.3044 | 0.5767 | 0.064* | |
| H23G | 0.1676 | 0.1231 | 0.6244 | 0.064* | |
| O261 | 0.45217 (6) | 0.5572 (3) | 0.32579 (18) | 0.0332 (4) | |
| C261 | 0.42426 (10) | 0.5695 (4) | 0.2333 (3) | 0.0359 (7) | |
| H26A | 0.4468 | 0.5846 | 0.1752 | 0.054* | |
| H26B | 0.4020 | 0.6775 | 0.2368 | 0.054* | |
| H26C | 0.4049 | 0.4548 | 0.2243 | 0.054* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N11 | 0.0278 (10) | 0.0365 (11) | 0.0233 (13) | 0.0061 (9) | −0.0032 (9) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0206 (14) | 0.0088 (10) | 0.0021 (11) | 0.0011 (11) |
| Cl12 | 0.0410 (4) | 0.0734 (5) | 0.0217 (3) | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0051 (3) | 0.0014 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0266 (12) | 0.0248 (13) | 0.0051 (9) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0012 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0211 (11) | 0.0261 (12) | 0.0221 (13) | 0.0026 (9) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C14A | 0.0218 (11) | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0248 (14) | 0.0031 (8) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0225 (10) | 0.0247 (12) | 0.0226 (14) | −0.0012 (9) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0029 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0256 (11) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0281 (15) | 0.0001 (9) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0358 (13) | 0.0387 (19) | −0.0008 (10) | −0.0035 (11) | 0.0006 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0251 (11) | 0.0368 (14) | 0.0295 (16) | 0.0033 (10) | −0.0060 (11) | −0.0002 (12) |
| C18A | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0254 (12) | 0.0255 (15) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0008 (10) |
| C13A | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0343 (12) | 0.0235 (14) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0065 (10) | 0.0029 (11) |
| O131 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0383 (11) | 0.0302 (13) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0101 (8) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C131 | 0.0310 (14) | 0.0372 (15) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0050 (12) | 0.0101 (14) | 0.0021 (15) |
| O132 | 0.0266 (9) | 0.0515 (12) | 0.0276 (11) | −0.0055 (8) | 0.0059 (8) | −0.0048 (9) |
| C132 | 0.0339 (15) | 0.072 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0184 (15) | 0.0083 (14) | −0.0148 (18) |
| O161 | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0496 (11) | 0.0318 (13) | −0.0054 (8) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0062 (11) |
| C161 | 0.0329 (14) | 0.0461 (16) | 0.0286 (16) | −0.0009 (12) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0056 (13) |
| N21 | 0.0260 (10) | 0.0350 (12) | 0.0237 (12) | 0.0051 (9) | −0.0022 (9) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C22 | 0.0287 (12) | 0.0329 (13) | 0.0181 (13) | 0.0054 (10) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0005 (10) |
| Cl22 | 0.0379 (3) | 0.0660 (5) | 0.0201 (3) | 0.0034 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0248 (11) | 0.0255 (11) | 0.0227 (13) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0008 (10) | −0.0002 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0216 (10) | 0.0261 (11) | 0.0219 (13) | 0.0007 (9) | −0.0029 (10) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C24A | 0.0224 (10) | 0.0175 (10) | 0.0231 (13) | 0.0016 (8) | −0.0003 (10) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C25 | 0.0227 (11) | 0.0233 (12) | 0.0230 (14) | −0.0014 (8) | −0.0013 (10) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C26 | 0.0236 (11) | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0277 (15) | −0.0008 (9) | 0.0007 (10) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C27 | 0.0204 (10) | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0337 (16) | −0.0019 (9) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0015 (12) |
| C28 | 0.0220 (11) | 0.0349 (13) | 0.0310 (16) | −0.0011 (10) | −0.0059 (11) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C28A | 0.0238 (11) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0231 (14) | 0.0037 (9) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0030 (10) |
| C23A | 0.0261 (11) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0214 (13) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0021 (10) | 0.0036 (11) |
| O231 | 0.0294 (9) | 0.0439 (12) | 0.0387 (14) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0089 (9) | −0.0039 (10) |
| C231 | 0.0265 (13) | 0.0388 (15) | 0.072 (3) | 0.0013 (11) | 0.0056 (15) | 0.0013 (16) |
| O232 | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0260 (11) | −0.0084 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0010 (8) |
| C232 | 0.0353 (15) | 0.0542 (18) | 0.0378 (18) | −0.0194 (13) | 0.0039 (13) | −0.0012 (14) |
| O261 | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0288 (12) | −0.0042 (8) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0046 (10) |
| C261 | 0.0320 (14) | 0.0484 (17) | 0.0275 (16) | 0.0008 (12) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0028 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N11—C12 | 1.307 (3) | N21—C22 | 1.309 (3) |
| N11—C18A | 1.365 (4) | N21—C28A | 1.363 (4) |
| C12—C13 | 1.417 (4) | C22—C23 | 1.408 (4) |
| C12—Cl12 | 1.742 (3) | C22—Cl22 | 1.743 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.368 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.370 (4) |
| C13—C13A | 1.522 (3) | C23—C23A | 1.524 (3) |
| C14—C14A | 1.414 (3) | C24—C24A | 1.417 (3) |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| C14A—C18A | 1.402 (4) | C24A—C25 | 1.416 (4) |
| C14A—C15 | 1.422 (4) | C24A—C28A | 1.419 (4) |
| C15—C16 | 1.374 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.374 (3) |
| C15—H15 | 0.9500 | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C16—O161 | 1.372 (4) | C26—O261 | 1.355 (3) |
| C16—C17 | 1.407 (4) | C26—C27 | 1.420 (4) |
| C17—C18 | 1.364 (5) | C27—C28 | 1.351 (4) |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| C18—C18A | 1.418 (3) | C28—C28A | 1.414 (3) |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C28—H28 | 0.9500 |
| C13A—O132 | 1.396 (3) | C23A—O232 | 1.400 (3) |
| C13A—O131 | 1.408 (3) | C23A—O231 | 1.408 (3) |
| C13A—H13A | 1.0000 | C23A—H23A | 1.0000 |
| O131—C131 | 1.428 (4) | O231—C231 | 1.419 (4) |
| C131—H13B | 0.9800 | C231—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C131—H13C | 0.9800 | C231—H23C | 0.9800 |
| C131—H13D | 0.9800 | C231—H23D | 0.9800 |
| O132—C132 | 1.433 (3) | O232—C232 | 1.424 (3) |
| C132—H13E | 0.9800 | C232—H23E | 0.9800 |
| C132—H13F | 0.9800 | C232—H23F | 0.9800 |
| C132—H13G | 0.9800 | C232—H23G | 0.9800 |
| O161—C161 | 1.420 (4) | O261—C261 | 1.430 (4) |
| C161—H16A | 0.9800 | C261—H26A | 0.9800 |
| C161—H16B | 0.9800 | C261—H26B | 0.9800 |
| C161—H16C | 0.9800 | C261—H26C | 0.9800 |
| C12—N11—C18A | 117.0 (2) | C22—N21—C28A | 117.4 (2) |
| N11—C12—C13 | 125.8 (3) | N21—C22—C23 | 125.7 (3) |
| N11—C12—Cl12 | 114.9 (2) | N21—C22—Cl22 | 114.6 (2) |
| C13—C12—Cl12 | 119.3 (2) | C23—C22—Cl22 | 119.7 (2) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 116.4 (2) | C24—C23—C22 | 116.6 (2) |
| C14—C13—C13A | 122.7 (2) | C24—C23—C23A | 122.5 (2) |
| C12—C13—C13A | 120.9 (3) | C22—C23—C23A | 120.7 (2) |
| C13—C14—C14A | 120.6 (2) | C23—C24—C24A | 120.8 (2) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.7 | C23—C24—H24 | 119.6 |
| C14A—C14—H14 | 119.7 | C24A—C24—H24 | 119.6 |
| C18A—C14A—C14 | 117.4 (3) | C25—C24A—C24 | 122.8 (2) |
| C18A—C14A—C15 | 120.5 (2) | C25—C24A—C28A | 120.3 (2) |
| C14—C14A—C15 | 122.0 (2) | C24—C24A—C28A | 116.8 (3) |
| C16—C15—C14A | 118.6 (3) | C26—C25—C24A | 119.2 (3) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 120.7 | C26—C25—H25 | 120.4 |
| C14A—C15—H15 | 120.7 | C24A—C25—H25 | 120.4 |
| O161—C16—C15 | 124.5 (3) | O261—C26—C25 | 125.6 (3) |
| O161—C16—C17 | 114.6 (2) | O261—C26—C27 | 114.1 (2) |
| C15—C16—C17 | 120.9 (3) | C25—C26—C27 | 120.2 (3) |
| C18—C17—C16 | 121.1 (2) | C28—C27—C26 | 121.2 (2) |
| C18—C17—H17 | 119.5 | C28—C27—H27 | 119.4 |
| C16—C17—H17 | 119.5 | C26—C27—H27 | 119.4 |
| C17—C18—C18A | 119.7 (3) | C27—C28—C28A | 120.4 (3) |
| C17—C18—H18 | 120.2 | C27—C28—H28 | 119.8 |
| C18A—C18—H18 | 120.2 | C28A—C28—H28 | 119.8 |
| N11—C18A—C14A | 122.8 (2) | N21—C28A—C28 | 118.9 (2) |
| N11—C18A—C18 | 118.0 (3) | N21—C28A—C24A | 122.4 (2) |
| C14A—C18A—C18 | 119.2 (3) | C28—C28A—C24A | 118.6 (3) |
| O132—C13A—O131 | 112.5 (2) | O232—C23A—O231 | 112.2 (2) |
| O132—C13A—C13 | 106.8 (2) | O232—C23A—C23 | 106.9 (2) |
| O131—C13A—C13 | 113.9 (2) | O231—C23A—C23 | 113.9 (2) |
| O132—C13A—H13A | 107.8 | O232—C23A—H23A | 107.9 |
| O131—C13A—H13A | 107.8 | O231—C23A—H23A | 107.9 |
| C13—C13A—H13A | 107.8 | C23—C23A—H23A | 107.9 |
| C13A—O131—C131 | 114.4 (2) | C23A—O231—C231 | 114.2 (3) |
| O131—C131—H13B | 109.5 | O231—C231—H23B | 109.5 |
| O131—C131—H13C | 109.5 | O231—C231—H23C | 109.5 |
| H13B—C131—H13C | 109.5 | H23B—C231—H23C | 109.5 |
| O131—C131—H13D | 109.5 | O231—C231—H23D | 109.5 |
| H13B—C131—H13D | 109.5 | H23B—C231—H23D | 109.5 |
| H13C—C131—H13D | 109.5 | H23C—C231—H23D | 109.5 |
| C13A—O132—C132 | 113.0 (2) | C23A—O232—C232 | 113.1 (2) |
| O132—C132—H13E | 109.5 | O232—C232—H23E | 109.5 |
| O132—C132—H13F | 109.5 | O232—C232—H23F | 109.5 |
| H13E—C132—H13F | 109.5 | H23E—C232—H23F | 109.5 |
| O132—C132—H13G | 109.5 | O232—C232—H23G | 109.5 |
| H13E—C132—H13G | 109.5 | H23E—C232—H23G | 109.5 |
| H13F—C132—H13G | 109.5 | H23F—C232—H23G | 109.5 |
| C16—O161—C161 | 117.47 (19) | C26—O261—C261 | 117.32 (19) |
| O161—C161—H16A | 109.5 | O261—C261—H26A | 109.5 |
| O161—C161—H16B | 109.5 | O261—C261—H26B | 109.5 |
| H16A—C161—H16B | 109.5 | H26A—C261—H26B | 109.5 |
| O161—C161—H16C | 109.5 | O261—C261—H26C | 109.5 |
| H16A—C161—H16C | 109.5 | H26A—C261—H26C | 109.5 |
| H16B—C161—H16C | 109.5 | H26B—C261—H26C | 109.5 |
| C18A—N11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (4) | C28A—N21—C22—C23 | 1.6 (4) |
| C18A—N11—C12—Cl12 | 179.47 (19) | C28A—N21—C22—Cl22 | −179.65 (19) |
| N11—C12—C13—C14 | 2.0 (4) | N21—C22—C23—C24 | −3.3 (4) |
| Cl12—C12—C13—C14 | −177.72 (19) | Cl22—C22—C23—C24 | 178.01 (19) |
| N11—C12—C13—C13A | −174.6 (3) | N21—C22—C23—C23A | 173.5 (3) |
| Cl12—C12—C13—C13A | 5.7 (3) | Cl22—C22—C23—C23A | −5.2 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—C14A | −1.4 (3) | C22—C23—C24—C24A | 1.6 (4) |
| C13A—C13—C14—C14A | 175.1 (2) | C23A—C23—C24—C24A | −175.1 (2) |
| C13—C14—C14A—C18A | −0.7 (3) | C23—C24—C24A—C25 | 178.7 (2) |
| C13—C14—C14A—C15 | −178.6 (2) | C23—C24—C24A—C28A | 1.3 (4) |
| C18A—C14A—C15—C16 | −1.8 (4) | C24—C24A—C25—C26 | −176.4 (2) |
| C14—C14A—C15—C16 | 176.1 (2) | C28A—C24A—C25—C26 | 1.0 (3) |
| C14A—C15—C16—O161 | −178.7 (2) | C24A—C25—C26—O261 | 178.4 (2) |
| C14A—C15—C16—C17 | 0.6 (4) | C24A—C25—C26—C27 | −0.1 (4) |
| O161—C16—C17—C18 | −179.9 (3) | O261—C26—C27—C28 | −179.5 (3) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.8 (4) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | −0.8 (4) |
| C16—C17—C18—C18A | −1.0 (4) | C26—C27—C28—C28A | 0.9 (4) |
| C12—N11—C18A—C14A | −2.1 (4) | C22—N21—C28A—C28 | −178.0 (2) |
| C12—N11—C18A—C18 | 176.8 (2) | C22—N21—C28A—C24A | 1.7 (4) |
| C14—C14A—C18A—N11 | 2.6 (4) | C27—C28—C28A—N21 | 179.7 (3) |
| C15—C14A—C18A—N11 | −179.5 (2) | C27—C28—C28A—C24A | 0.0 (4) |
| C14—C14A—C18A—C18 | −176.3 (2) | C25—C24A—C28A—N21 | 179.4 (2) |
| C15—C14A—C18A—C18 | 1.6 (4) | C24—C24A—C28A—N21 | −3.1 (3) |
| C17—C18—C18A—N11 | −179.2 (3) | C25—C24A—C28A—C28 | −0.9 (3) |
| C17—C18—C18A—C14A | −0.2 (4) | C24—C24A—C28A—C28 | 176.6 (2) |
| C14—C13—C13A—O132 | −10.6 (3) | C24—C23—C23A—O232 | 14.3 (3) |
| C12—C13—C13A—O131 | −69.4 (3) | C22—C23—C23A—O231 | 73.3 (3) |
| C12—C13—C13A—O132 | 165.7 (2) | C22—C23—C23A—O232 | −162.3 (2) |
| C14—C13—C13A—O131 | 114.2 (3) | C24—C23—C23A—O231 | −110.1 (3) |
| O132—C13A—O131—C131 | 64.3 (3) | O232—C23A—O231—C231 | −63.4 (3) |
| C13—C13A—O131—C131 | −57.4 (3) | C23—C23A—O231—C231 | 58.2 (3) |
| O131—C13A—O132—C132 | 63.7 (3) | O231—C23A—O232—C232 | −64.2 (3) |
| C13—C13A—O132—C132 | −170.6 (2) | C23—C23A—O232—C232 | 170.3 (2) |
| C15—C16—O161—C161 | −6.5 (4) | C25—C26—O261—C261 | 7.3 (4) |
| C17—C16—O161—C161 | 174.2 (3) | C27—C26—O261—C261 | −174.2 (2) |
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG5440).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Anuradha, T., Srinivasan, J., Seshadri, P. R. & Bakthadoss, M. (2013a). Acta Cryst. E69, o779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Anuradha, T., Srinivasan, J., Seshadri, P. R. & Bakthadoss, M. (2013b). Acta Cryst. E69, o990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hathwar, V. R., Roopan, S. M., Subashini, R., Khan, F. N. & Guru Row, T. N. (2010). J. Chem. Sci. 122, 677–685.
- Insuasty, B., Torres, H., Cobo, J., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, o39–o41. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig1.tif
The two independent molecules in the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 30% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig2.tif
The two molecules in the selected asymmetric unit, viewed normal to the planes of the quinolone units, showing the ring overlap which leads to a π..π sktacking interaction. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901500804X/hg5440fig3.tif
A stereoview of part of the crystal structure of the title compound showing the formation of a π-stacked chain parallel to [010]. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms have been omitted.
CCDC reference: 1061227
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


