The title compounds were synthesized via an Arbuzov reaction between an α-bromoketone and isopropoxydiphenylphosphane. In the crystals of both compounds, molecules are linked via bifurcated C—H⋯(O,O) hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [100] and along [010].
Keywords: crystal structure, carbamoylmethylphosphane oxide (CMPO), α-bromoketone, isopropoxydiphenylphosphane, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
The title compounds, C20H16ClO2P, (I), and C18H21O2P, (II), were synthesized via an Arbuzov reaction between an α-bromoketone and isopropoxydiphenylphosphane. In the crystals of both compounds, molecules are linked via bifurcated C—H⋯(O,O) hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [100] for (I) and along [010] for (II). The chains are linked via C—H⋯π interactions, leading to the formation of sheets lying parallel to (010) for (I) and (001) for (II). The absolute structure of compound (II) was determined by resonant scattering [Flack parameter = 0.088 (14)].
Chemical context
The luminescent properties of lanthanide metals continue to gain attention from researchers interested in the coordination chemistry of f-block elements. Direct excitation of lanthanides is difficult due to the parity forbidden f–f transitions required and relatively low molar absorptivities, but fortunately this excitation can be sensitized with an appropriate organic ligand. The ligand acts as an antenna by harvesting the excitation energy and transferring this energy to the metal emitting state (Weissman, 1942 ▸). The resulting emission bands have peak widths less than 10 nm, with a color characteristic of each lanthanide ion. As such, lanthanide metals have found uses in both material and biological applications (de Bettencourt-Dias, 2007 ▸; Thibon & Pierre, 2009 ▸; Eliseeva & Bünzli, 2010 ▸).
Recently, the carbamoylmethylphosphane oxide (CMPO) group has been shown to be an effective ligand for the sensitization of lanthanide luminescence (Sharova et al., 2012 ▸; Rosario-Amorin et al., 2013 ▸; Sartain et al., 2015 ▸). We undertook this work to investigate the role of the aryl carbonyl group on the ability of the CMPO moiety to act as an antenna in this process. Tuning the structure of these organic ligands may be tantamount to potential improvements in the absorption, transfer, and emission of energy by the resultant lanthanide–ligand complex. We report herein on the synthesis and crystal structure of two new CMPO ligands.
Structural commentary
The molecular structures of compounds (I) and (II) are shown in Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸, respectively. While compound (I) crystallized in the orthorhombic centrosymmetric space group Pbca, compound (II) crystallized in the chiral monoclinic space group P21. In compound (I), the two phenyl rings (C9–C14 and C15–C20) are inclined to one another by 75.53 (8)°, and to the chlorobenzene ring (C3–C8) by 47.98 (8) and 62.16 (8)°, respectively. Atom P1 has a distorted tetrahedral geometry with the C—P=O bond angles varying from 112.02 (7) to 114.35 (7)°, while the C—P—C angles vary from 105.04 (7) to 106.60 (7)°. The carbonyl group (C1=O1) and the phosphoryl group (P1=O2) are anti to one another, most probably to minimize unfavourable dipole–dipole interactions. In compound (II), the two phenyl rings (C7–C12 and C13–C18) are inclined to one another by 86.4 (2)°. Atom P1 also has a distorted tetrahedral geometry with the C—P=O bond angles varying from 111.47 (16) to 115.06 (16)°, while the C—P—C bond angles vary from 101.84 (15) to 109.21 (16)°. Here the carbonyl group (C1=O1) and the phosphoryl group (P1=O2) are syn to one another.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of compound (I), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Figure 2.
A view of the molecular structure of compound (II), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Supramolecular features
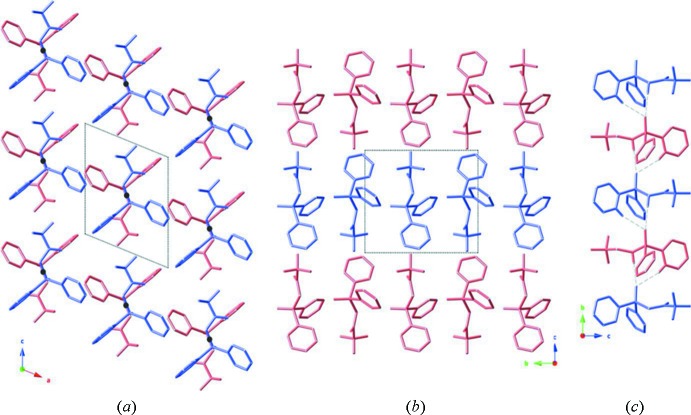
In the crystal of (I), the phosphoryl groups are aligned with the a axis, and as the individual molecules stack in this direction they appear to rotate around the chlorine atom that lies close to the twofold screw axis, creating a pinwheel arrangement of molecules (Fig. 3 ▸). The molecules are linked via bifurcated C—H⋯(O,O) hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [100]; see Fig. 3 ▸ and Table 1 ▸. The chains are linked via C—H⋯π interactions (Table 1 ▸), forming sheets lying parallel to (010).
Figure 3.
The crystal packing diagram of compound (I) (drawn as blue and orange sticks) viewed along: (a) the a axis (the Cl atoms are shown as dark grey dots); (b) the c axis; (c) along the b axis, with the bifurcated hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details). H atoms have been omitted for clarity in parts (a) and (b) and only those involved in hydrogen bonding are shown in part (c).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg1 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings C3–C8 and C15–C20, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C14—H14⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.30 | 3.1899 (19) | 156 |
| C20—H20⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4487 (19) | 176 |
| C5—H5⋯Cg3ii | 0.95 | 3.00 | 3.8873 (17) | 156 |
| C13—H13⋯Cg1i | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.5373 (19) | 126 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Compound (II) packs in a similar arrangement to (I) in the solid state, although subtle differences result in the formation of a chiral crystal from an achiral compound (Fig. 4 ▸). For compound (II), the phosphoryl groups are again aligned in one direction (along the b axis), but in this case, the P1—C2 bond in the center of the molecule lies about a twofold screw axis and acts as the pivot point for the pinwheel arrangement rather than the terminal chlorine atom as seen in the crystal of compound (I). The absence of an inversion center or mirror plane results in a chiral twist to the packing within this crystal. Here, molecules are also linked via bifurcated C—H⋯(O,O) hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along [010] (see Table 2 ▸ and Fig. 4 ▸) and the chains are linked via C—H⋯π interactions (Table 2 ▸), forming sheets parallel to (001).
Figure 4.
The crystal packing diagram of compound (II) (drawn as purple and pink sticks) viewed along: (a) the b axis (the center of the P1—C1 bond that coincides with the twofold screw axis is denoted with a grey dot); (b) the a axis; (c) along the b axis with the bifurcated hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines (see Table 2 ▸ for details). H atoms have been omitted for clarity in parts (a) and (b) and only those involved in hydrogen bonding are shown in (c).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
Cg1 is the centroid of ring C7–C12.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2B⋯O2i | 0.99 | 2.19 | 3.176 (5) | 176 |
| C12—H12⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.373 (5) | 148 |
| C17—H17⋯Cg1ii | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.721 (5) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Database Survey
The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.36, November 2014; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) contains 11 structures with a β-ketodiphenylphosphoryl moiety. Three of these structures are related to the title compounds, but have either an alkyl group bonded to the keto function or branching at the α-carbon, viz. E-(5SR,6SR)-3,6-dimethyl-5-diphenylphosphinoyl-7-triphenylmethoxyhept-2-en-4-one acetone solvate (SUGWOG; Doyle et al., 1993 ▸), anti-(2S,4S)-2-(N,N-dibenzylamino)-4-diphenylphosphinoyl-1-phenylpentan-3-one monohydrate (RIZCEI; O’Brien et al., 1997 ▸) and (4R,5R)-4,5-dihydroxy-1,5-diphenyl-2-(diphenylphosphinoyl)pentan-1-one) (FODBUW: Boesen et al., 2005 ▸). The last compound (FODBUW) crystallizes in a chiral space group (P212121), as does compound (II). The phenyl rings of the diphenylphosphinoyl group in each of these three compounds are inclined to one another by ca 67.97, 73.25 and 68.24°, respectively, similar to the arrangement in compound (I).
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compounds, (I) and (II), were prepared following slightly modified literature procedures (Arnaud-Neu et al., 1996 ▸; Schuster et al., 2009 ▸) by the Arbuzov reaction of isopropoxydiphenylphosphane (Shintou et al., 2003 ▸) with 2-bromo-4′-chloroacetophenone for (I) and 1-bromopinacolone for (II). For both compounds, crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were grown by slow evaporation of a solution of the compound in CDCl3.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. The hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms: C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å with U iso(H)= 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C20H16ClO2P | C18H21O2P |
| M r | 354.75 | 300.32 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P b c a | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 11.7380 (2), 14.4453 (3), 19.9515 (3) | 8.3416 (2), 10.5161 (2), 10.2790 (2) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 112.212 (1), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 3382.95 (10) | 834.77 (3) |
| Z | 8 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.97 | 1.47 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.36 × 0.17 × 0.13 | 0.43 × 0.14 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker SMART APEX CCD area detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.599, 0.754 | 0.631, 0.754 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 17900, 3297, 2880 | 7043, 3006, 2774 |
| R int | 0.033 | 0.042 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.617 | 0.617 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.032, 0.089, 1.04 | 0.042, 0.118, 1.13 |
| No. of reflections | 3297 | 3006 |
| No. of parameters | 217 | 193 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.32, −0.39 | 0.49, −0.38 |
| Absolute structure | – | Flack x determined using 1090 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | – | 0.088 (14) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Grand Valley State University (Weldon Fund, OURS, CSCE) for financial support of this work. We are grateful to the NSF for financial support (REU-1062944) and NMR instrumentation (300 MHz Jeol, CCLI-0087655), as well as Pfizer, Inc. for the generous donation of a Varian Inova 400 FT NMR. The CCD-based X-ray diffractometers at Michigan State University were upgraded and/or replaced by departmental funds. We also thank Professor James Krikke and Professor William Winchester (GVSU) for help with instrumentation.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Crystal data
| C20H16ClO2P | Dx = 1.393 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 354.75 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 9053 reflections |
| a = 11.7380 (2) Å | θ = 4.4–72.0° |
| b = 14.4453 (3) Å | µ = 2.97 mm−1 |
| c = 19.9515 (3) Å | T = 173 K |
| V = 3382.95 (10) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.36 × 0.17 × 0.13 mm |
| F(000) = 1472 |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2880 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.033 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 72.2°, θmin = 4.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.599, Tmax = 0.754 | k = −17→17 |
| 17900 measured reflections | l = −24→23 |
| 3297 independent reflections |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.089 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0502P)2 + 1.0258P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3297 reflections | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.80844 (4) | 0.25495 (3) | 0.98830 (2) | 0.04355 (14) | |
| P1 | 0.47545 (3) | 0.53879 (3) | 0.75031 (2) | 0.02092 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.33462 (10) | 0.47690 (9) | 0.89963 (6) | 0.0366 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.60062 (9) | 0.52376 (8) | 0.75506 (6) | 0.0292 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.40409 (13) | 0.43971 (11) | 0.86325 (8) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.38970 (12) | 0.44712 (10) | 0.78795 (7) | 0.0243 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.3084 | 0.4587 | 0.7777 | 0.029* | |
| H2B | 0.4109 | 0.3873 | 0.7673 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.50328 (13) | 0.38850 (10) | 0.89190 (7) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.51562 (14) | 0.38806 (11) | 0.96164 (8) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.4594 | 0.4170 | 0.9887 | 0.035* | |
| C5 | 0.60803 (15) | 0.34632 (12) | 0.99183 (8) | 0.0328 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.6163 | 0.3468 | 1.0392 | 0.039* | |
| C6 | 0.68856 (14) | 0.30356 (11) | 0.95145 (9) | 0.0314 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.67686 (14) | 0.30005 (12) | 0.88247 (9) | 0.0324 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.7316 | 0.2685 | 0.8559 | 0.039* | |
| C8 | 0.58415 (14) | 0.34315 (11) | 0.85264 (8) | 0.0289 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.5758 | 0.3417 | 0.8053 | 0.035* | |
| C9 | 0.42652 (13) | 0.54676 (10) | 0.66510 (7) | 0.0236 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.50496 (14) | 0.57592 (12) | 0.61691 (8) | 0.0319 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.5815 | 0.5886 | 0.6293 | 0.038* | |
| C11 | 0.47052 (16) | 0.58623 (13) | 0.55074 (9) | 0.0391 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.5234 | 0.6071 | 0.5180 | 0.047* | |
| C12 | 0.35988 (17) | 0.56633 (13) | 0.53235 (8) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.3372 | 0.5726 | 0.4869 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | 0.28230 (15) | 0.53745 (12) | 0.57968 (9) | 0.0347 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.2063 | 0.5238 | 0.5667 | 0.042* | |
| C14 | 0.31441 (13) | 0.52817 (11) | 0.64629 (8) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.2603 | 0.5092 | 0.6789 | 0.034* | |
| C15 | 0.43163 (12) | 0.64440 (10) | 0.79158 (7) | 0.0230 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.51476 (14) | 0.70315 (11) | 0.81674 (8) | 0.0290 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.5927 | 0.6859 | 0.8143 | 0.035* | |
| C17 | 0.48423 (15) | 0.78728 (12) | 0.84549 (8) | 0.0338 (4) | |
| H17 | 0.5413 | 0.8276 | 0.8624 | 0.041* | |
| C18 | 0.37069 (16) | 0.81216 (12) | 0.84948 (8) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.3498 | 0.8701 | 0.8683 | 0.041* | |
| C19 | 0.28765 (15) | 0.75256 (12) | 0.82598 (9) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.2097 | 0.7692 | 0.8299 | 0.041* | |
| C20 | 0.31663 (13) | 0.66892 (11) | 0.79674 (8) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| H20 | 0.2591 | 0.6286 | 0.7803 | 0.034* |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0357 (2) | 0.0428 (3) | 0.0521 (3) | 0.00128 (18) | −0.01410 (19) | 0.00816 (19) |
| P1 | 0.0163 (2) | 0.0199 (2) | 0.0265 (2) | −0.00157 (13) | −0.00033 (13) | −0.00008 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0337 (6) | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0080 (5) | 0.0075 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0386 (6) | −0.0002 (5) | −0.0015 (4) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0311 (8) | −0.0041 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0307 (8) | −0.0029 (6) | −0.0001 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0289 (7) | −0.0046 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0292 (8) | −0.0031 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0416 (9) | 0.0299 (9) | 0.0269 (8) | −0.0052 (7) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0036 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0395 (9) | −0.0037 (7) | −0.0057 (7) | 0.0052 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0303 (8) | 0.0305 (9) | 0.0365 (9) | 0.0029 (7) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0314 (8) | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0269 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0011 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0281 (8) | 0.0333 (9) | 0.0342 (8) | −0.0055 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | −0.0028 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0454 (10) | 0.0409 (10) | 0.0310 (8) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0106 (7) | 0.0015 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0508 (11) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0020 (8) | −0.0037 (7) | 0.0012 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0328 (9) | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0357 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | −0.0088 (7) | −0.0015 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0007 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0315 (8) | −0.0037 (6) | −0.0027 (6) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0440 (9) | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0307 (8) | −0.0075 (7) | −0.0060 (7) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0511 (10) | 0.0234 (8) | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0021 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0341 (9) | 0.0302 (9) | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0088 (7) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0002 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0345 (8) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C6 | 1.7360 (16) | C9—C14 | 1.395 (2) |
| P1—O2 | 1.4882 (11) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| P1—C2 | 1.8251 (15) | C10—C11 | 1.389 (2) |
| P1—C9 | 1.7982 (15) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| P1—C15 | 1.8083 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.380 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.2168 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.515 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.377 (3) |
| C1—C3 | 1.493 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C13—C14 | 1.388 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.399 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.387 (2) |
| C3—C8 | 1.394 (2) | C15—C20 | 1.399 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.391 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.387 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.383 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.384 (2) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C18—C19 | 1.382 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.388 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C19—C20 | 1.384 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.396 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| O2—P1—C2 | 114.35 (7) | C14—C9—C10 | 119.68 (14) |
| O2—P1—C9 | 112.64 (7) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| O2—P1—C15 | 112.02 (7) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.67 (16) |
| C9—P1—C2 | 105.04 (7) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C9—P1—C15 | 106.60 (7) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C15—P1—C2 | 105.54 (7) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.30 (16) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 119.05 (14) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| O1—C1—C3 | 120.86 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C3—C1—C2 | 120.09 (13) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.22 (16) |
| P1—C2—H2A | 108.9 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| P1—C2—H2B | 108.9 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—P1 | 113.43 (10) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.44 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.9 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 108.9 | C9—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.7 | C13—C14—C9 | 119.69 (15) |
| C4—C3—C1 | 117.63 (14) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.2 |
| C8—C3—C1 | 123.27 (14) | C16—C15—P1 | 118.74 (12) |
| C8—C3—C4 | 119.09 (15) | C16—C15—C20 | 119.81 (15) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C20—C15—P1 | 121.42 (12) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.18 (15) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.17 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.8 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.47 (15) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.8 | C18—C17—C16 | 119.95 (15) |
| C5—C6—Cl1 | 119.11 (13) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.0 |
| C7—C6—Cl1 | 119.12 (13) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.1 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.75 (15) | C19—C18—C17 | 119.88 (16) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C19—C18—H18 | 120.1 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.20 (15) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.6 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C18—C19—C20 | 120.89 (16) |
| C3—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C20—C19—H19 | 119.6 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 120.25 (15) | C15—C20—H20 | 120.4 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 | C19—C20—C15 | 119.27 (15) |
| C10—C9—P1 | 117.37 (12) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.4 |
| C14—C9—P1 | 122.92 (12) | ||
| Cl1—C6—C7—C8 | −176.61 (13) | C4—C5—C6—Cl1 | 177.30 (13) |
| P1—C9—C10—C11 | −177.86 (13) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.5 (3) |
| P1—C9—C14—C13 | 178.80 (13) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 2.2 (3) |
| P1—C15—C16—C17 | 176.49 (12) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | −0.7 (3) |
| P1—C15—C20—C19 | −176.96 (12) | C8—C3—C4—C5 | 2.2 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—P1 | 97.28 (15) | C9—P1—C2—C1 | −170.57 (11) |
| O1—C1—C3—C4 | −2.5 (2) | C9—P1—C15—C16 | −117.67 (13) |
| O1—C1—C3—C8 | 178.73 (16) | C9—P1—C15—C20 | 60.42 (14) |
| O2—P1—C2—C1 | 65.44 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.1 (3) |
| O2—P1—C9—C10 | −25.46 (15) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.0 (2) |
| O2—P1—C9—C14 | 156.68 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.0 (3) |
| O2—P1—C15—C16 | 5.96 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (3) |
| O2—P1—C15—C20 | −175.96 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −1.1 (3) |
| C1—C3—C4—C5 | −176.70 (15) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (2) |
| C1—C3—C8—C7 | 177.34 (15) | C15—P1—C2—C1 | −58.14 (12) |
| C2—P1—C9—C10 | −150.53 (13) | C15—P1—C9—C10 | 97.79 (13) |
| C2—P1—C9—C14 | 31.61 (15) | C15—P1—C9—C14 | −80.08 (14) |
| C2—P1—C15—C16 | 130.99 (12) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.5 (2) |
| C2—P1—C15—C20 | −50.92 (14) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 1.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C3—C4 | 176.67 (14) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C3—C8 | −2.1 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −1.7 (3) |
| C3—C1—C2—P1 | −81.86 (15) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | 0.6 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.7 (2) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −1.6 (2) |
| C4—C3—C8—C7 | −1.4 (2) |
(I) 1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2-(diphenylphosphoryl)ethan-1-one. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings C3–C8 and C15–C20, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C14—H14···O2i | 0.95 | 2.30 | 3.1899 (19) | 156 |
| C20—H20···O2i | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4487 (19) | 176 |
| C5—H5···Cg3ii | 0.95 | 3.00 | 3.8873 (17) | 156 |
| C13—H13···Cg1i | 0.95 | 2.90 | 3.5373 (19) | 126 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, y, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+2.
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Crystal data
| C18H21O2P | F(000) = 320 |
| Mr = 300.32 | Dx = 1.195 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 8.3416 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 5567 reflections |
| b = 10.5161 (2) Å | θ = 4.7–72.0° |
| c = 10.2790 (2) Å | µ = 1.47 mm−1 |
| β = 112.212 (1)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 834.77 (3) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.43 × 0.14 × 0.08 mm |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3006 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 2774 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.042 |
| Detector resolution: 8 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 72.0°, θmin = 4.7° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −9→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.631, Tmax = 0.754 | l = −12→12 |
| 7043 measured reflections |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0722P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.118 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.13 | Δρmax = 0.49 e Å−3 |
| 3006 reflections | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 193 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1090 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.088 (14) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| P1 | 0.46337 (9) | 0.13395 (7) | 0.54974 (7) | 0.0247 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.2783 (3) | 0.1230 (4) | 0.2325 (3) | 0.0450 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.4313 (3) | 0.2739 (3) | 0.5441 (3) | 0.0352 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.4309 (5) | 0.1015 (3) | 0.2672 (3) | 0.0328 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.5430 (4) | 0.0741 (4) | 0.4198 (3) | 0.0286 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.6592 | 0.1108 | 0.4399 | 0.034* | |
| H2B | 0.5572 | −0.0192 | 0.4317 | 0.034* | |
| C3 | 0.5199 (5) | 0.0970 (4) | 0.1613 (4) | 0.0403 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.3850 (8) | 0.0965 (11) | 0.0140 (5) | 0.105 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.3118 | 0.0210 | 0.0006 | 0.157* | |
| H4B | 0.4422 | 0.0952 | −0.0536 | 0.157* | |
| H4C | 0.3133 | 0.1731 | −0.0008 | 0.157* | |
| C5 | 0.6294 (11) | 0.2154 (7) | 0.1830 (7) | 0.090 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.5596 | 0.2900 | 0.1842 | 0.135* | |
| H5B | 0.6712 | 0.2237 | 0.1062 | 0.135* | |
| H5C | 0.7284 | 0.2094 | 0.2726 | 0.135* | |
| C6 | 0.6318 (9) | −0.0220 (7) | 0.1848 (6) | 0.0713 (17) | |
| H6A | 0.7288 | −0.0159 | 0.2757 | 0.107* | |
| H6B | 0.6765 | −0.0295 | 0.1096 | 0.107* | |
| H6C | 0.5619 | −0.0970 | 0.1842 | 0.107* | |
| C7 | 0.6358 (4) | 0.0881 (4) | 0.7129 (3) | 0.0280 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.7278 (5) | 0.1814 (4) | 0.8067 (4) | 0.0400 (9) | |
| H8 | 0.6982 | 0.2684 | 0.7865 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.8634 (5) | 0.1477 (6) | 0.9304 (4) | 0.0518 (12) | |
| H9 | 0.9264 | 0.2117 | 0.9946 | 0.062* | |
| C10 | 0.9069 (5) | 0.0207 (5) | 0.9603 (4) | 0.0485 (11) | |
| H10 | 0.9994 | −0.0023 | 1.0449 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 0.8157 (5) | −0.0721 (5) | 0.8669 (4) | 0.0459 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.8455 | −0.1590 | 0.8873 | 0.055* | |
| C12 | 0.6802 (4) | −0.0389 (4) | 0.7431 (4) | 0.0341 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.6178 | −0.1031 | 0.6790 | 0.041* | |
| C13 | 0.2784 (4) | 0.0408 (4) | 0.5431 (3) | 0.0270 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.2209 (5) | −0.0666 (4) | 0.4600 (4) | 0.0399 (9) | |
| H14 | 0.2786 | −0.0945 | 0.4012 | 0.048* | |
| C15 | 0.0789 (6) | −0.1332 (5) | 0.4632 (5) | 0.0486 (11) | |
| H15 | 0.0387 | −0.2059 | 0.4051 | 0.058* | |
| C16 | −0.0046 (5) | −0.0952 (5) | 0.5495 (5) | 0.0462 (10) | |
| H16 | −0.1014 | −0.1416 | 0.5513 | 0.055* | |
| C17 | 0.0532 (5) | 0.0105 (4) | 0.6328 (4) | 0.0422 (9) | |
| H17 | −0.0035 | 0.0366 | 0.6930 | 0.051* | |
| C18 | 0.1936 (5) | 0.0793 (4) | 0.6298 (4) | 0.0337 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.2320 | 0.1528 | 0.6870 | 0.040* |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| P1 | 0.0238 (4) | 0.0270 (4) | 0.0251 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | 0.0113 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0312 (12) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0044 (14) | 0.0085 (10) | 0.0033 (14) |
| O2 | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0428 (14) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0200 (11) | 0.0020 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0345 (17) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0268 (15) | −0.0019 (13) | 0.0119 (13) | −0.0008 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0276 (15) | 0.0364 (18) | 0.0257 (15) | 0.0004 (13) | 0.0143 (12) | −0.0003 (13) |
| C3 | 0.043 (2) | 0.054 (3) | 0.0278 (16) | 0.0021 (17) | 0.0182 (16) | 0.0016 (15) |
| C4 | 0.068 (3) | 0.218 (12) | 0.027 (2) | 0.022 (5) | 0.018 (2) | −0.004 (4) |
| C5 | 0.138 (6) | 0.084 (5) | 0.094 (5) | −0.045 (5) | 0.096 (5) | −0.025 (4) |
| C6 | 0.092 (4) | 0.080 (4) | 0.067 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.011 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0222 (13) | 0.0427 (18) | 0.0212 (14) | −0.0043 (13) | 0.0106 (12) | −0.0009 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0411 (19) | 0.047 (2) | 0.0348 (19) | −0.0138 (17) | 0.0173 (16) | −0.0079 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0411 (19) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0333 (17) | −0.027 (2) | 0.0120 (15) | −0.016 (2) |
| C10 | 0.0291 (17) | 0.083 (3) | 0.0281 (17) | −0.006 (2) | 0.0045 (14) | 0.0044 (19) |
| C11 | 0.0315 (18) | 0.063 (3) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0070 (18) | 0.0082 (16) | 0.0108 (19) |
| C12 | 0.0267 (16) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0292 (17) | −0.0013 (14) | 0.0066 (14) | 0.0005 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0200 (13) | 0.0328 (16) | 0.0276 (15) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0083 (12) | 0.0047 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0336 (18) | 0.042 (2) | 0.047 (2) | −0.0061 (16) | 0.0181 (17) | −0.0107 (16) |
| C15 | 0.0392 (19) | 0.041 (3) | 0.065 (3) | −0.012 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.0121 (19) |
| C16 | 0.0262 (16) | 0.052 (2) | 0.062 (3) | −0.0053 (18) | 0.0184 (18) | 0.011 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0314 (17) | 0.057 (3) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0000 (17) | 0.0216 (16) | 0.0036 (18) |
| C18 | 0.0292 (16) | 0.0431 (19) | 0.0306 (16) | 0.0007 (15) | 0.0133 (14) | −0.0011 (14) |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| P1—O2 | 1.493 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.389 (6) |
| P1—C2 | 1.814 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| P1—C7 | 1.814 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.391 (6) |
| P1—C13 | 1.807 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C1 | 1.207 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.387 (8) |
| C1—C2 | 1.520 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C3 | 1.533 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.378 (7) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C11—C12 | 1.390 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.507 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C5 | 1.509 (7) | C13—C14 | 1.388 (6) |
| C3—C6 | 1.525 (7) | C13—C18 | 1.391 (5) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9800 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9800 | C14—C15 | 1.387 (6) |
| C4—H4C | 0.9800 | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9800 | C15—C16 | 1.378 (7) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9800 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5C | 0.9800 | C16—C17 | 1.375 (7) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9800 | C17—C18 | 1.387 (5) |
| C6—H6C | 0.9800 | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| C7—C8 | 1.387 (5) | ||
| O2—P1—C2 | 115.06 (16) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| O2—P1—C7 | 111.47 (16) | C8—C7—P1 | 119.5 (3) |
| O2—P1—C13 | 113.25 (15) | C8—C7—C12 | 119.6 (3) |
| C7—P1—C2 | 101.84 (15) | C12—C7—P1 | 120.9 (3) |
| C13—P1—C2 | 109.21 (16) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 |
| C13—P1—C7 | 104.98 (16) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.0 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 120.6 (3) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.0 |
| O1—C1—C3 | 122.4 (3) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—C3 | 117.0 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.1 (4) |
| P1—C2—H2A | 108.3 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| P1—C2—H2B | 108.3 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—P1 | 116.1 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.9 (4) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.3 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 108.3 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.4 | C10—C11—C12 | 120.2 (4) |
| C4—C3—C1 | 109.6 (4) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C5 | 109.4 (6) | C7—C12—C11 | 120.1 (4) |
| C4—C3—C6 | 109.7 (5) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C5—C3—C1 | 107.3 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C5—C3—C6 | 110.7 (5) | C14—C13—P1 | 123.8 (3) |
| C6—C3—C1 | 110.1 (4) | C14—C13—C18 | 119.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C18—C13—P1 | 116.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 119.7 (4) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.6 |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.8 (4) |
| C3—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.6 |
| C3—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| C3—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C17—C16—C15 | 119.5 (4) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.3 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.7 |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C16—C17—C18 | 120.6 (4) |
| C3—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.7 |
| C3—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C13—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| C3—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C17—C18—C13 | 120.0 (4) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.0 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | ||
| P1—C7—C8—C9 | −178.3 (3) | C3—C1—C2—P1 | 158.4 (3) |
| P1—C7—C12—C11 | 178.3 (3) | C7—P1—C2—C1 | −177.5 (3) |
| P1—C13—C14—C15 | 179.1 (3) | C7—P1—C13—C14 | −102.8 (3) |
| P1—C13—C18—C17 | −178.4 (3) | C7—P1—C13—C18 | 75.6 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—P1 | −23.1 (5) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.0 (6) |
| O1—C1—C3—C4 | −11.3 (7) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.3 (5) |
| O1—C1—C3—C5 | 107.4 (6) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (6) |
| O1—C1—C3—C6 | −132.0 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (6) |
| O2—P1—C2—C1 | −56.8 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.1 (6) |
| O2—P1—C7—C8 | −5.5 (3) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.2 (5) |
| O2—P1—C7—C12 | 176.4 (3) | C13—P1—C2—C1 | 71.8 (3) |
| O2—P1—C13—C14 | 135.4 (3) | C13—P1—C7—C8 | −128.5 (3) |
| O2—P1—C13—C18 | −46.2 (3) | C13—P1—C7—C12 | 53.5 (3) |
| C2—P1—C7—C8 | 117.7 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.0 (7) |
| C2—P1—C7—C12 | −60.4 (3) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | 0.0 (6) |
| C2—P1—C13—C14 | 5.8 (4) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.3 (7) |
| C2—P1—C13—C18 | −175.8 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.5 (7) |
| C2—C1—C3—C4 | 167.2 (5) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | −0.7 (6) |
| C2—C1—C3—C5 | −74.1 (5) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 0.8 (6) |
| C2—C1—C3—C6 | 46.5 (5) |
(II) 1-(Diphenylphosphoryl)-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of ring C7–C12.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2B···O2i | 0.99 | 2.19 | 3.176 (5) | 176 |
| C12—H12···O2i | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.373 (5) | 148 |
| C17—H17···Cg1ii | 0.95 | 2.80 | 3.721 (5) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1; (ii) x−1, y, z.
References
- Arnaud-Neu, F., Böhmer, V., Dozol, J.-F., Grüttner, C., Jakobi, R. A., Kraft, D., Mauprivez, O., Rouquette, H., Schwing-Weill, M.-J., Simon, N. & Vogt, W. (1996). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 1175–1182.
- Bettencourt-Dias, A. de (2007). Curr. Org. Chem 11, 1460–1480.
- Boesen, T., Fox, D. J., Galloway, W., Pedersen, D. S., Tyzack, C. R. & Warren, S. (2005). Org. Biomol. Chem. 3, 630–637. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bourhis, L. J., Dolomanov, O. V., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2015). Acta Cryst. A71, 59–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Doyle, M. J., Hall, D., Raithby, P. R., Skelton, N. & Warren, S. (1993). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 517–523.
- Eliseeva, S. V. & Bünzli, J. G. (2010). Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 189–227. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P., Powell, H. R., Raithby, P. R. & Warren, S. (1997). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 1031–1040.
- Palmer, D. (2007). CrystalMaker. CrystalMaker Software, Bicester, England.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rosario-Amorin, D., Ouizem, S., Dickie, D. A., Wen, Y., Paine, R. T., Gao, J., Grey, J. K., de Bettencourt-Dias, A., Hay, B. P. & Delmau, L. H. (2013). Inorg. Chem. 52, 3063–3083. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sartain, H. T., McGraw, S. N., Lawrence, C. L., Werner, E. J. & Biros, S. M. (2015). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 426, 126–135.
- Schuster, E. M., Nisnevich, G., Botoshansky, M. & Gandelman, M. (2009). Organometallics, 28, 5025–5031.
- Sharova, E. V., Artyushin, O. I., Turanov, A. N., Karandashev, V. K., Meshkova, S. B., Topilova, Z. M. & Odinets, I. L. (2012). Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 10, 146–156.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shintou, T., Kikuchi, W. & Mukaiyama, T. (2003). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 76, 1645–1667.
- Thibon, A. & Pierre, V. C. (2009). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 394, 107–120. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Weissman, S. I. (1942). J. Chem. Phys. 10, 214–217.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015006994/su5111IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report