Abstract
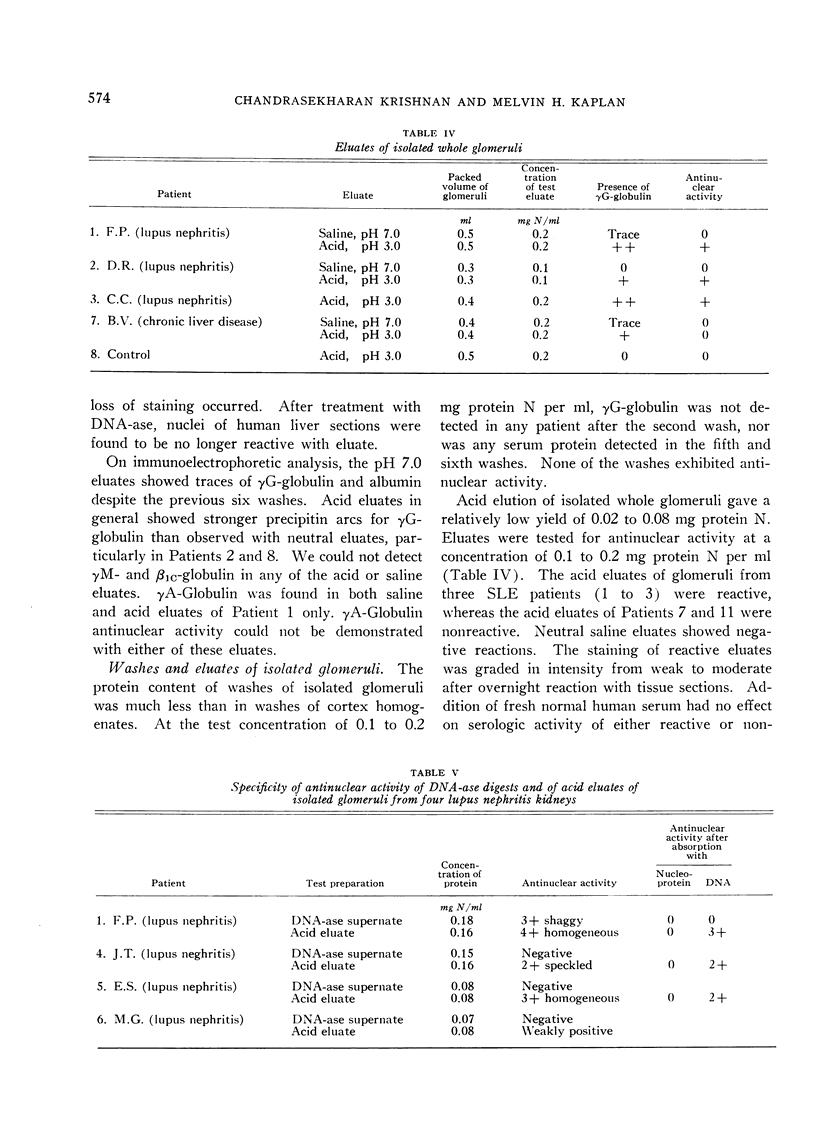
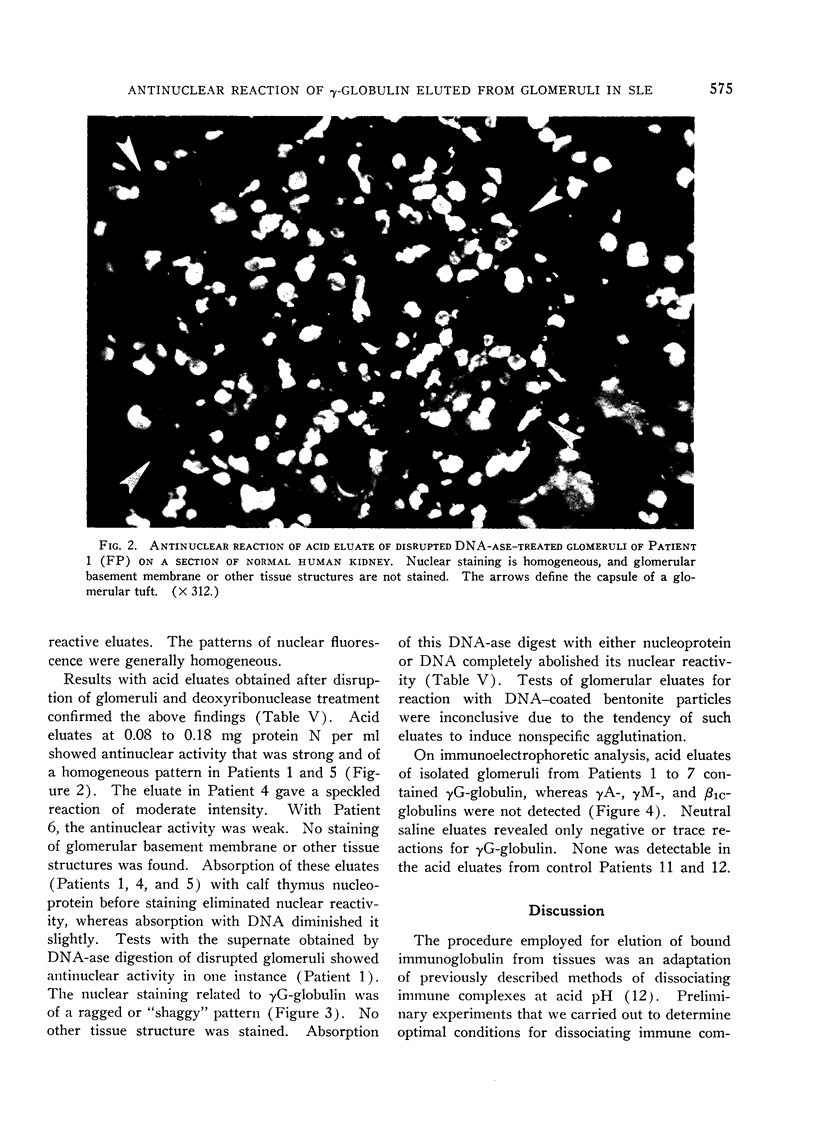
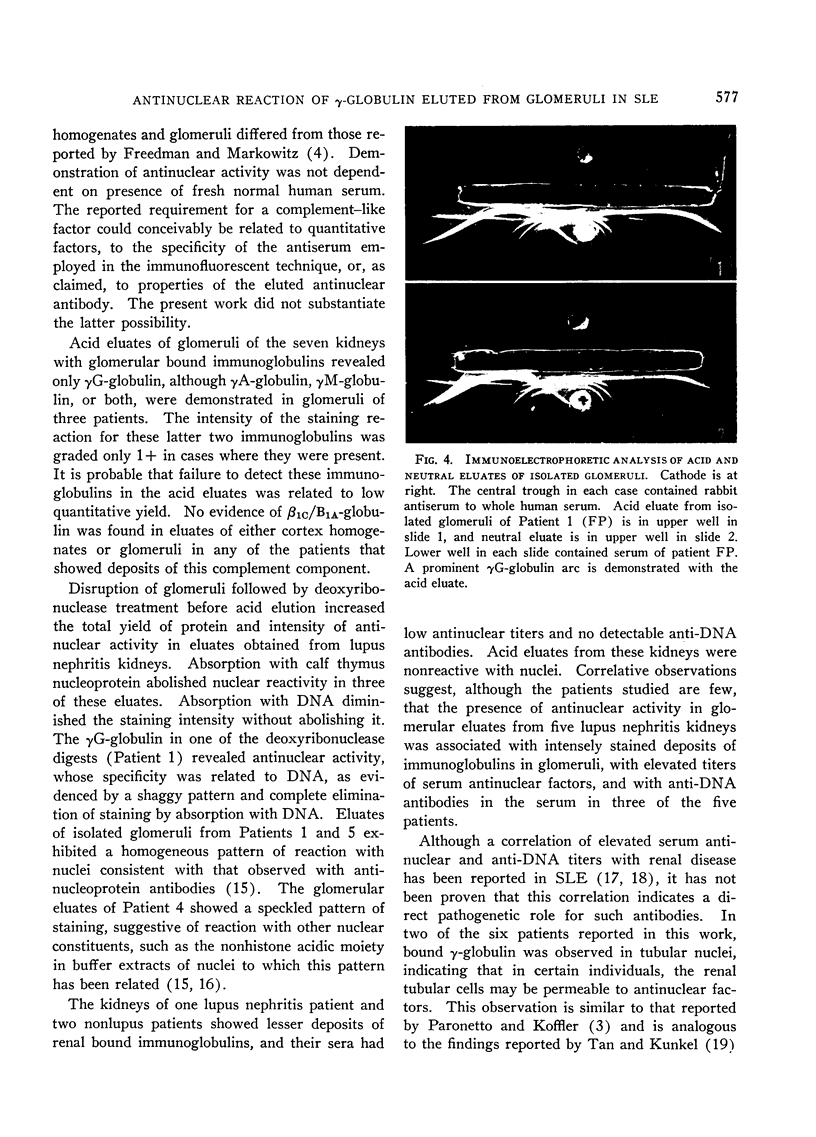
The γG-globulin eluted at acid pH from kidney cortex homogenates and isolated glomeruli of five of six patients with lupus nephritis was found to exhibit antinuclear activity, which was not dependent on presence of fresh human serum. Specificity, as demonstrated by absorption of antinuclear activity, was related to nucleoprotein in three glomerular acid eluates and to DNA in two acid eluates as well as in a deoxyribonuclease digest of disrupted glomeruli in one patient. Antinuclear activity was not found in acid eluates of kidneys from two patients with chronic liver disease and chronic discoid lupus, respectively, and one with lupus nephritis. These patients had a low titer of serum antinuclear factor and lesser amounts of kidney bound immunoglobulins. The presence of antinuclear activity in eluates of kidneys appeared to correlate with the amount of glomerular bound immunoglobulin and the level of antinuclear antibodies in serum. These findings suggest that in lupus nephritis, part of the glomerular bound immunoglobulin is derived from serum antinuclear factors possibly deposited as immune complexes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK J. S. Variations in the morphological patterns of "autoimmune" nuclear fluorescence. Lancet. 1961 Jun 3;1(7188):1203–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91944-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOZICEVICH J., NASOU J. P., KAYHOE D. E. Desoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-bentonite flocculation test for lupus erythematosus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWNE J. T., HUTT M. P., REGER J. F., SMITH S. W. LOCALIZATION OF "FIBRINOID" DEPOSIT IN LUPUS NEPHRITIS: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC DEMONSTRATION OF GLOMERULAR ENDOTHELIAL CELL PHAGOCYTOSIS. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Oct;6:599–614. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER I. A., FIRKIN B. G. DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIZING CELLS IN THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF PATIENTS WITH "AUTO-IMMUNE" DISORDERS. Australas Ann Med. 1965 May;14:142–145. doi: 10.1111/imj.1965.14.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN P., MARKOWITZ A. S. Isolation of antibody-like gamma-globulin from lupus glomeruli. Br Med J. 1962 Apr 28;1(5286):1175–1178. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5286.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN P., PETERS J. H., KARK R. M. Localization of gamma-globulin in the diseased kidney. Arch Intern Med. 1960 Apr;105:524–535. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1960.00270160022005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENSPON S. A., KRAKOWER C. A. Direct evidence for the antigenicity of the glomeruli in the production of nephrotoxic serums. AMA Arch Pathol. 1950 Mar;49(3):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUEFT B., LAUFER A. Further cytochemical studies in systemic lupus erythematosus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 Mar;57(3):201–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON L. A., TAN E. M. CHARACTERIZATION OF ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN URINE. J Clin Invest. 1965 May;44:703–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI105183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN H. R., DEICHER H. R., KUNKEL H. G. The L. E. cell and the L. E. serum factors. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1959 Jul;35(7):409–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TISELIUS A. Electrophoresis of proteins on filter paper. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Sep;35(1):89–118. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACHMANN P. J., KUNKEL H. G. Correlation of antinuclear antibodies and nuclear staining patterns. Lancet. 1961 Aug 19;2(7199):436–437. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLUSKEY R. T., BENACERRAF B., POTTER J. L., MILLER F. The pathologic effects of intravenously administered soluble antigen-antibody complexes. I. Passive serum sickness in mice. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:181–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Koffler D. Immunofluorescent localization of immunoglobulins, complement, and fibrinogen in human diseases. I. Systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1657–1664. doi: 10.1172/JCI105272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGMANN M. DNA ANTIBODIES. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Aug;6:SUPPL–557. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENS M. B., KNOWLES B. Significance of urinary gamma globulin in lupus nephritis. I. Electrophoretic analysis. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 6;267:1159–1166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212062672301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEC K. H., KAPLAN M. H. A variant L.E. cell factor reactive only with "altered" nuclear material. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Feb;6:11–22. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svec K. H., Blair J. D., Kaplan M. H. Immunopathologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). I. Tissue-bound immunoglobulins in relation to serum antinuclear immunoglobulins in systemic lupus and in chronic liver disease with LE cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):558–568. doi: 10.1172/JCI105557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWNES A. S., STEWART C. R., Jr, OSLER A. G. Immunologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Variations of nucleoprotein-reactive gamma globulin and hemolytic serum complement levels with disease activity. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1963 Apr;112:202–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. An immunofluorescent study of the skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Feb;9(1):37–46. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Steroids, lyosomes and systemic lupus erythematosus. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1962 Dec;38:779–787. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]