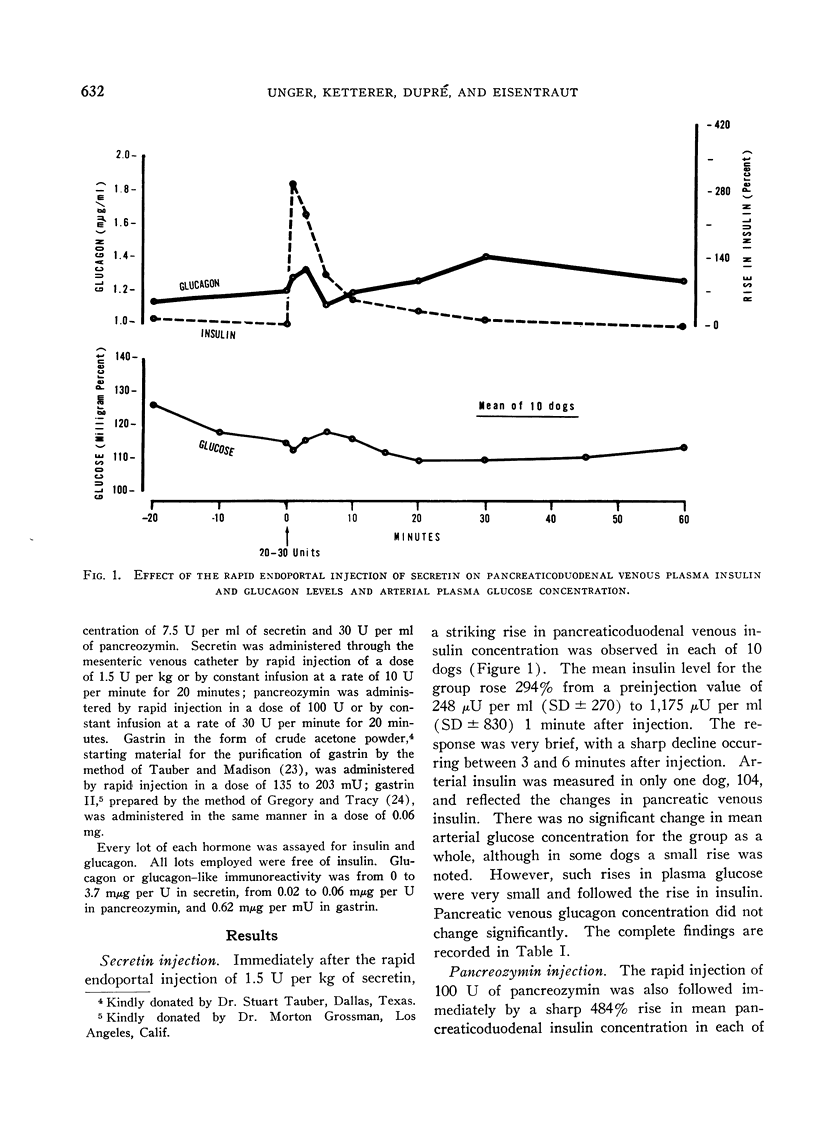
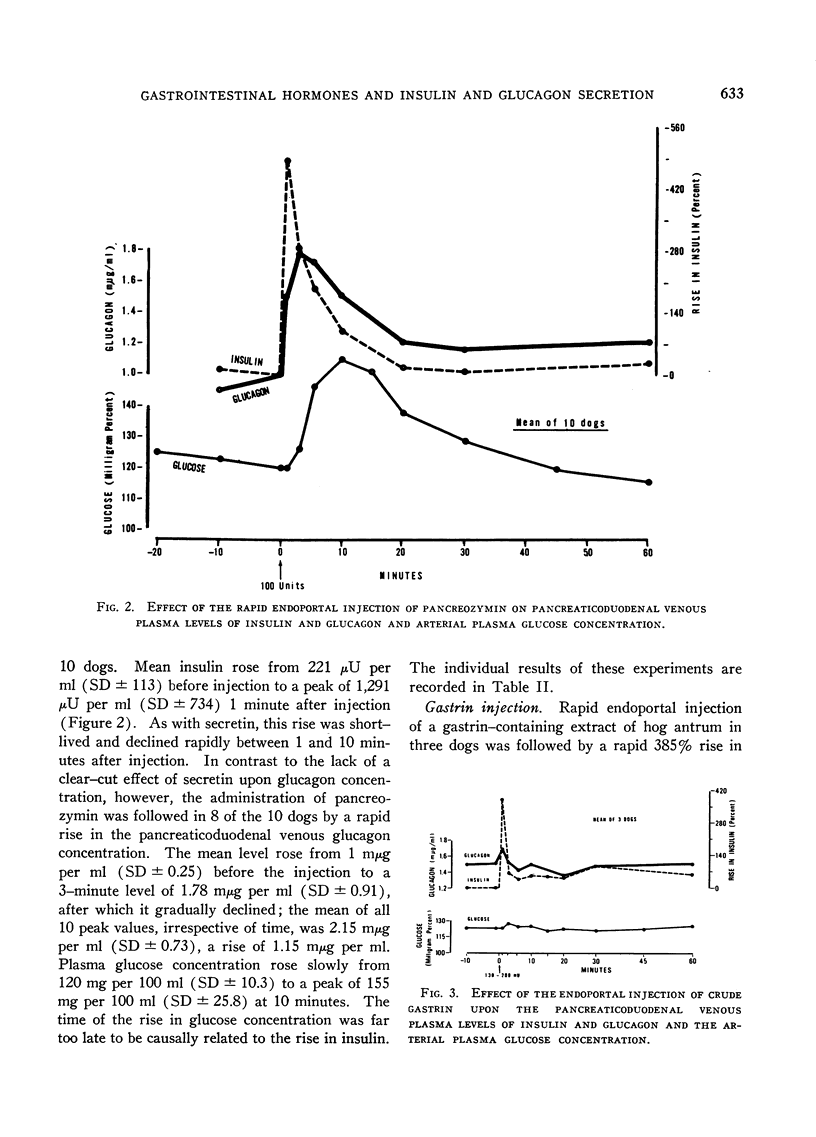
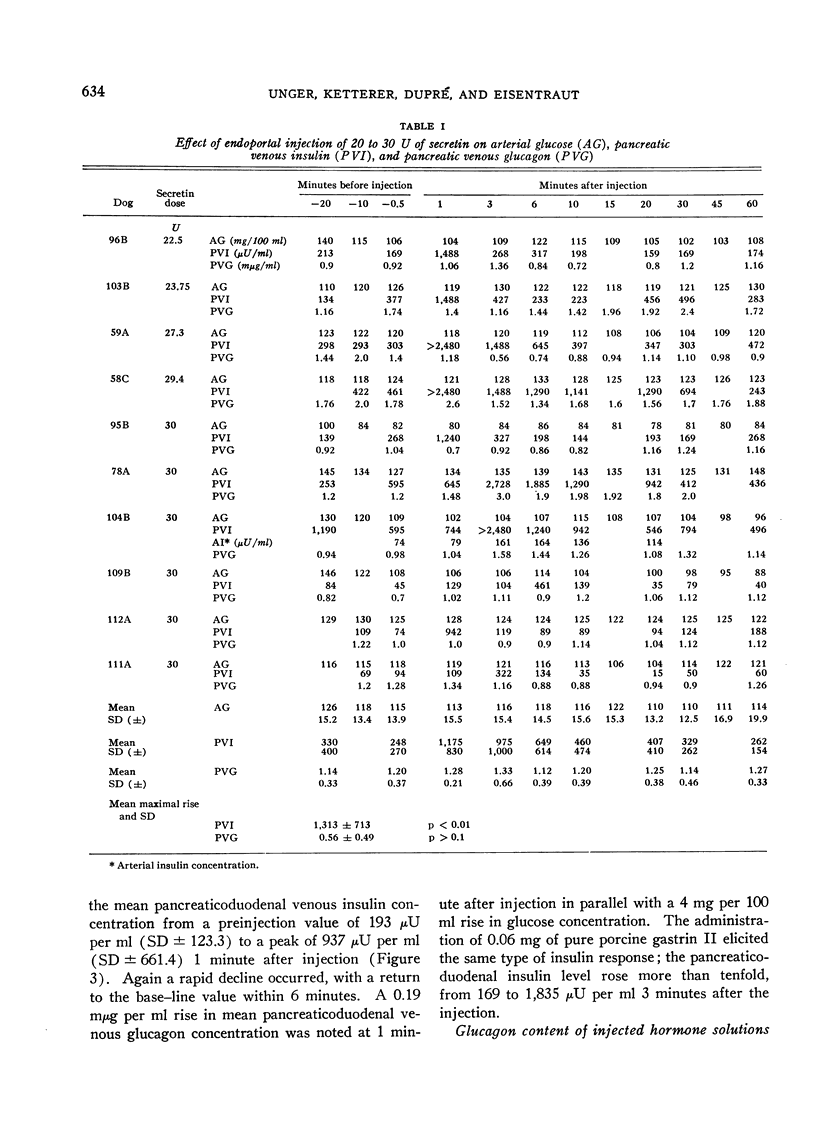
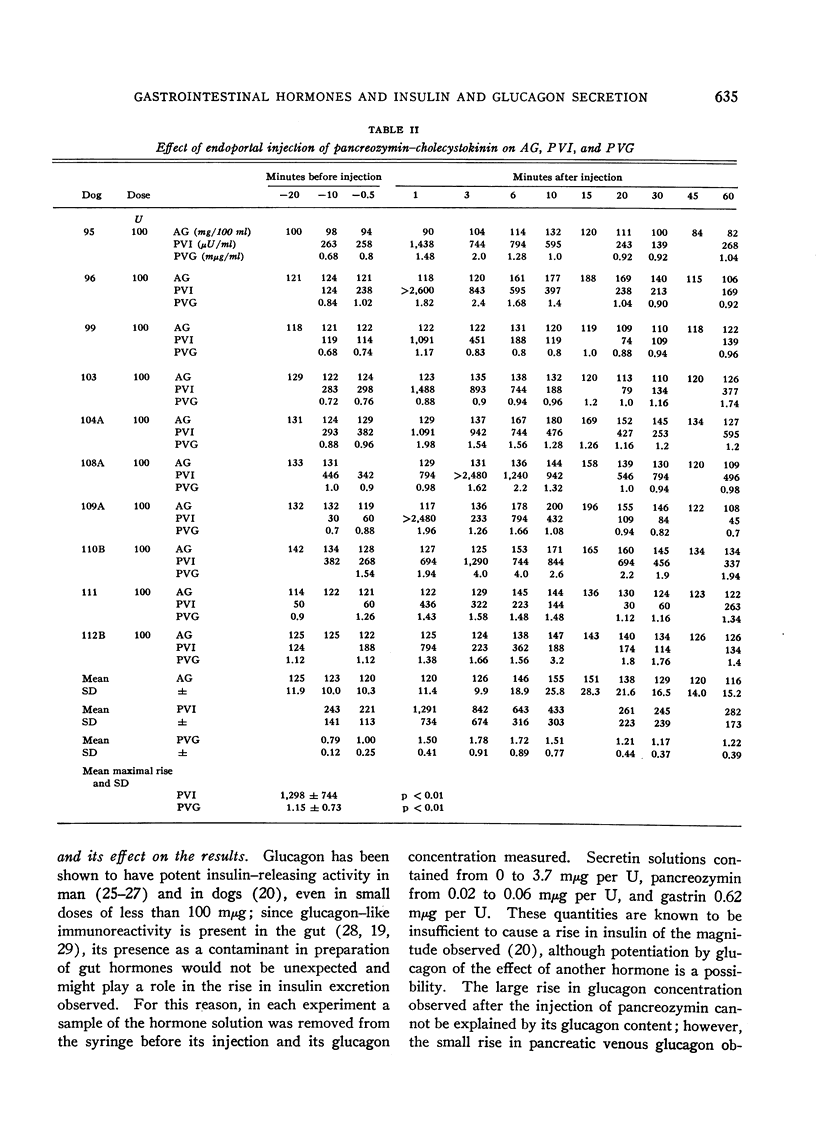
Abstract
The effects upon islet hormone secretion of highly purified preparations of secretin and of pancreozymin-cholecystokinin and of a crude gastrin-containing extract of hog antrum have been studied in acutely operated dogs. All three preparations were shown to cause a striking increase in insulin concentration in the pancreaticoduodenal venous plasma after their rapid endoportal injection in anesthetized dogs. With each hormone preparation, the peak in insulin secretion occurred 1 minute after injection, and a rapid decline was observed immediately thereafter. Whereas secretin and gastrin failed to alter significantly the pancreaticoduodenal venous glucagon or arterial glucose concentration, pancreozymin caused a dramatic rise in pancreaticoduodenal venous glucagon concentration, which reached a peak 3 minutes after injection, and hyperglycemia was noted to occur soon thereafter. Endoportal infusion of secretin and pancreozymin for 20 minutes caused responses that were sustained but qualitatively identical to the responses noted after rapid injection of the hormones. The beta-cytotropic effect of secretin was abolished by the infusion of epinephrine.
These results could not be attributed to the small degree of contamination of the enteric hormone preparations with insulin or glucagon, and it would appear that secretin, pancreozymin, and probably gastrin have insulin-releasing activity and that pancreozymin has, in addition, glucagon-releasing activity.
The demonstration that these three hormones possess insulin-releasing activity suggests that there is in the gastrointestinal tract a chain of betacytotropic hormones from antrum to ileum that is capable of augmenting insulin secretion as required for disposal of substrate loads. It is suggested that the existence of this “entero-insular axis” prevents high substrate concentrations that would otherwise follow ingestion of large meals were the insular response entirely a function of arterial substrate concentration.
Full text
PDF

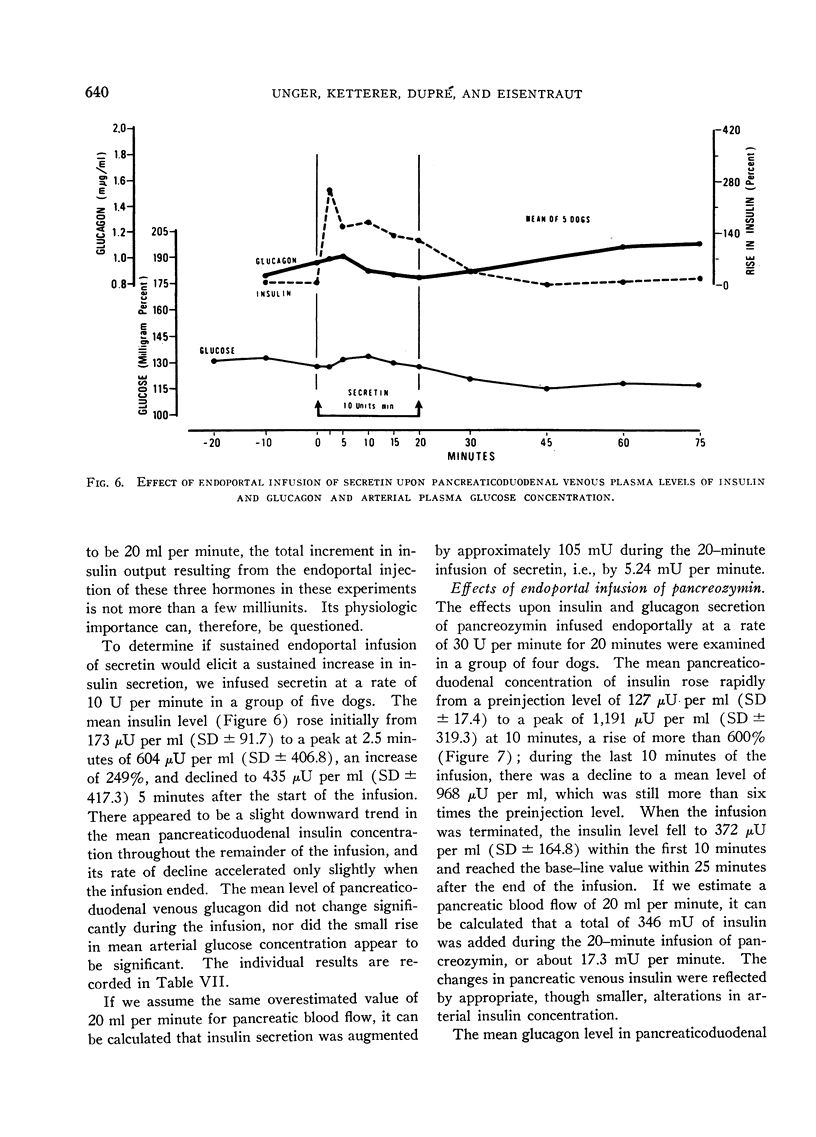
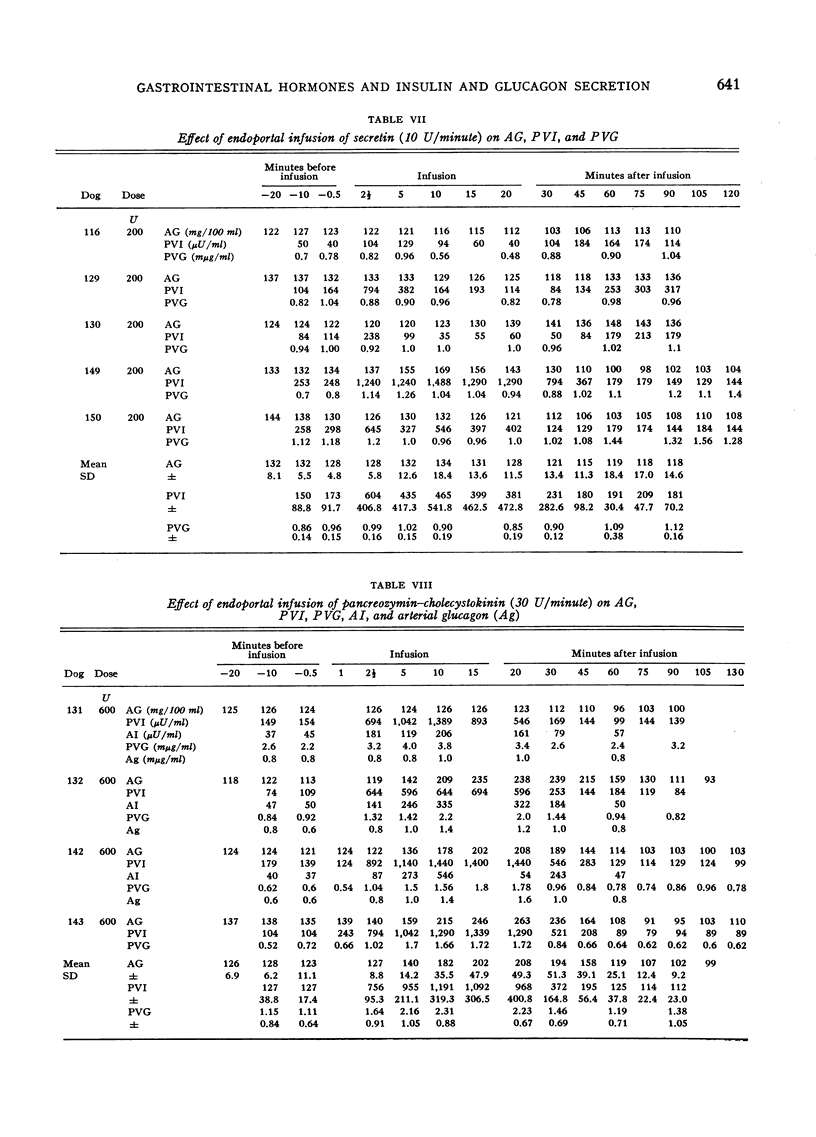
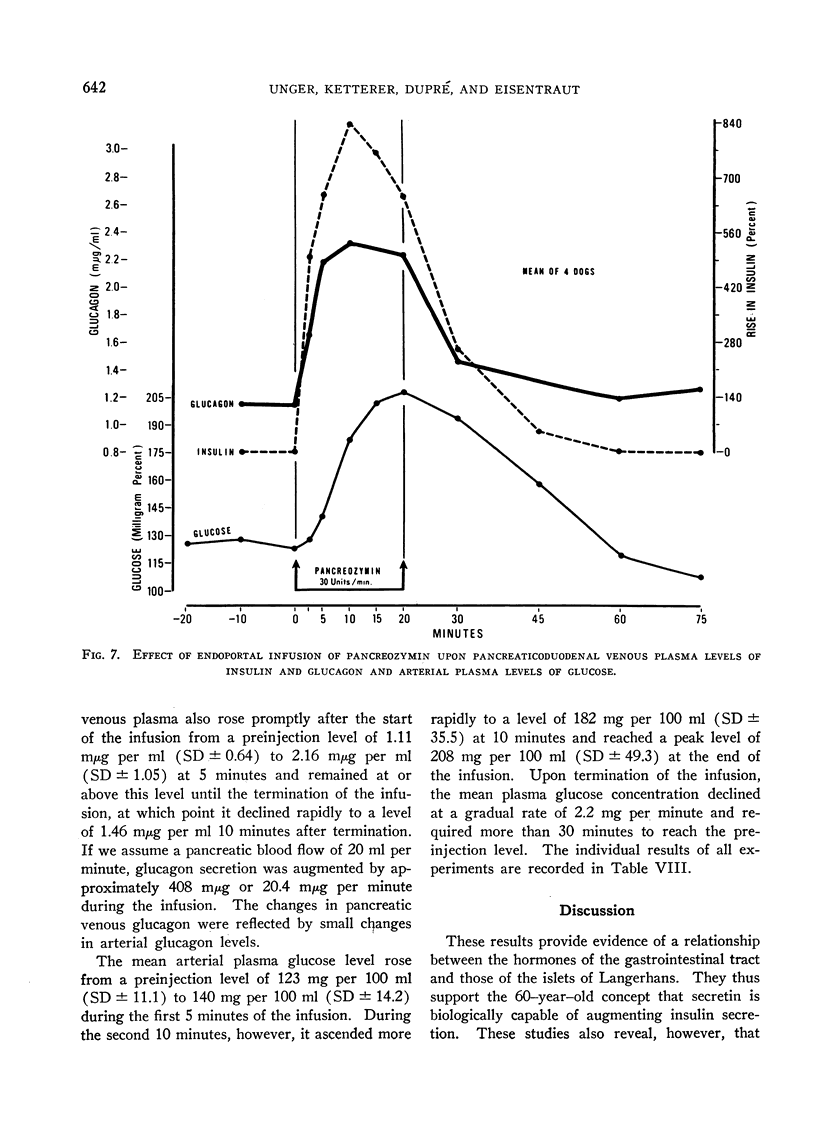



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyns D. R., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Intestinal hormones and plasma-insulin. Lancet. 1966 Feb 19;1(7434):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK J., HARPER A. A., RAPER H. S. On the preparation of secretin and pancreozymin. J Physiol. 1949 Dec;110(3-4):367–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockford P. M., Porte D., Jr, Wood F. C., Jr, Williams R. H. Effect of glucagon on serum insulin, plasma glucose and free fatty acids in man. Metabolism. 1966 Feb;15(2):114–122. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUPRE J. AN INTESTINAL HORMONE AFFECTING GLUCOSE DISPOSAL IN MAN. Lancet. 1964 Sep 26;2(7361):672–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupré J., Beck J. C. Stimulation of release of insulin by an extract of intestinal mucosa. Diabetes. 1966 Aug;15(8):555–559. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.8.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupré J., Rojas L., White J. J., Unger R. H., Beck J. C. Effects of secretin on insulin and glucagon in portal and peripheral blood in man. Lancet. 1966 Jul 2;2(7453):26–27. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91750-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY R. A., TRACY H. J. THE CONSTITUTION AND PROPERTIES OF TWO GASTRINS EXTRACTED FROM HOG ANTRAL MUCOSA. Gut. 1964 Apr;5:103–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKMAN M. H., SUTHERLAND E. W., Jr USE OF LIVER ADENYL CYCLASE FOR ASSAY OF GLUCAGON IN HUMAN GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT AND PANCREAS. Endocrinology. 1964 Jul;75:127–134. doi: 10.1210/endo-75-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. On the treatment of Diabetus mellitus by acid extract of Duodenal Mucous Membrane. Biochem J. 1906;1(1):28–38. doi: 10.1042/bj0010028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Graber A. L., Kuzuya T., Williams R. H. The effect of epinephrine on immunoreactive insulin levels in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI105335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMOLS E., MARRI G., MARKS V. PROMOTION OF INSULIN SECRETION BY GLUCAGON. Lancet. 1965 Aug 28;2(7409):415–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Tyler J., Megyesi C., Marks V. Immunochemical glucagon in human pancreas, gut, and plasma. Lancet. 1966 Oct 1;2(7466):727–729. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92982-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBER S., MADISON L. L. THE ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PORCINE GASTRIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:645–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGER R. H., EISENTRAUT A. M., McCALL M. S., MADISON L. L. Glucagon antibodies and an immunoassay for glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1280–1289. doi: 10.1172/JCI104357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ketterer H., Eisentraut A. M. Distribution of immunoassayable glucagon in gastrointestinal tissues. Metabolism. 1966 Oct;15(10):865–867. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ketterer H., Eisentraut A., Dupré J. Effect of secretin on insulin secretion. Lancet. 1966 Jul 2;2(7453):24–26. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91749-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. C., GROSSMAN M. I. Physiological determination of release of secretin and pancreozymin from intestine of dogs with transplanted pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):527–545. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



