Abstract
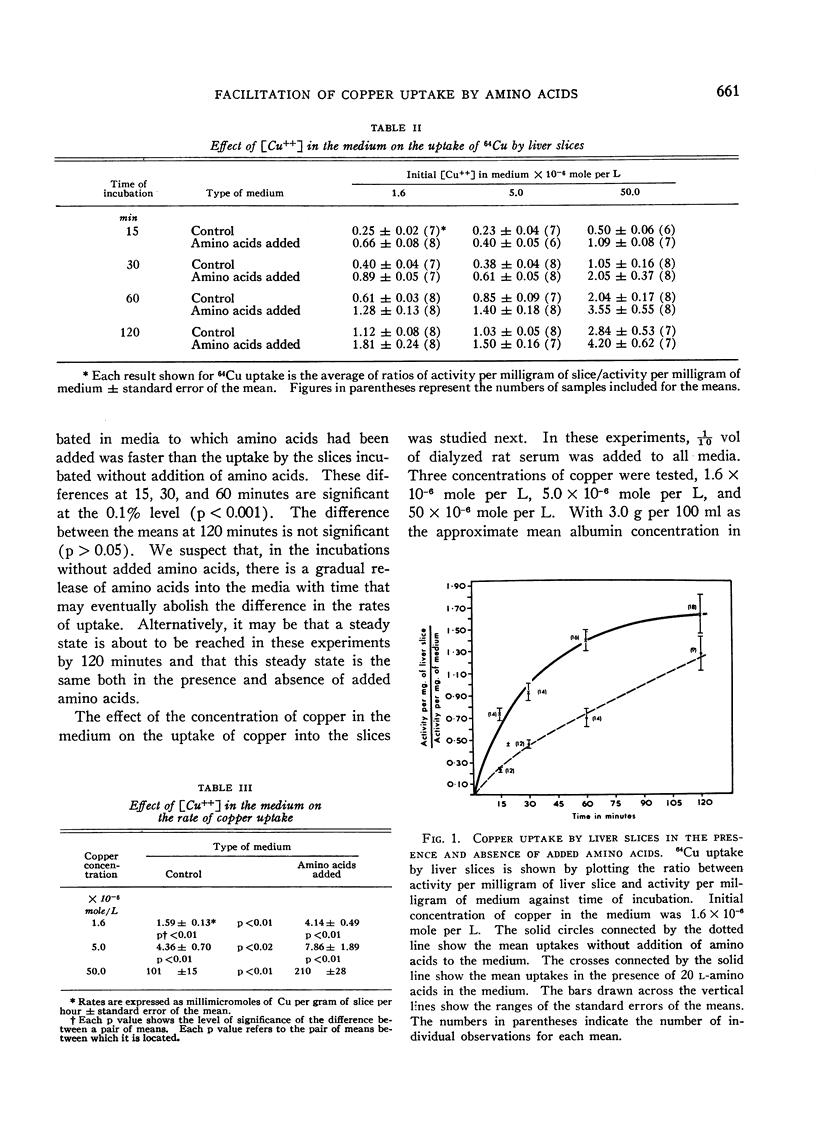
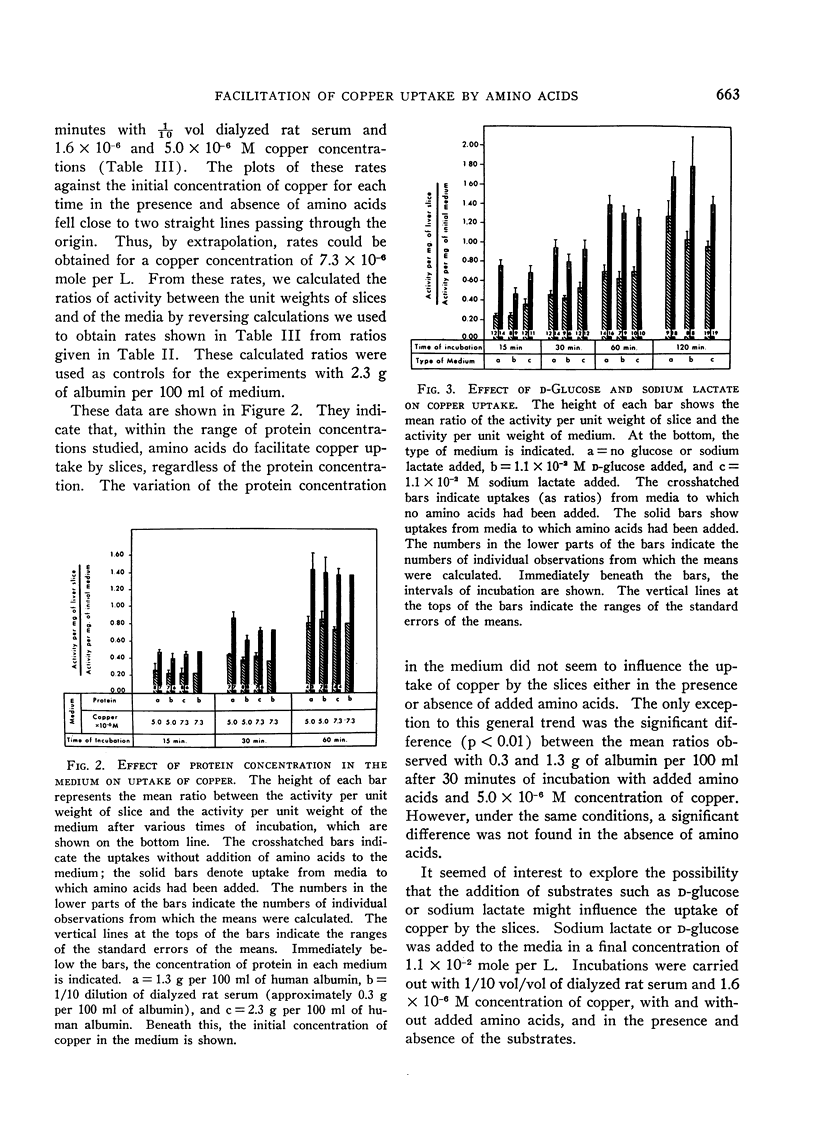
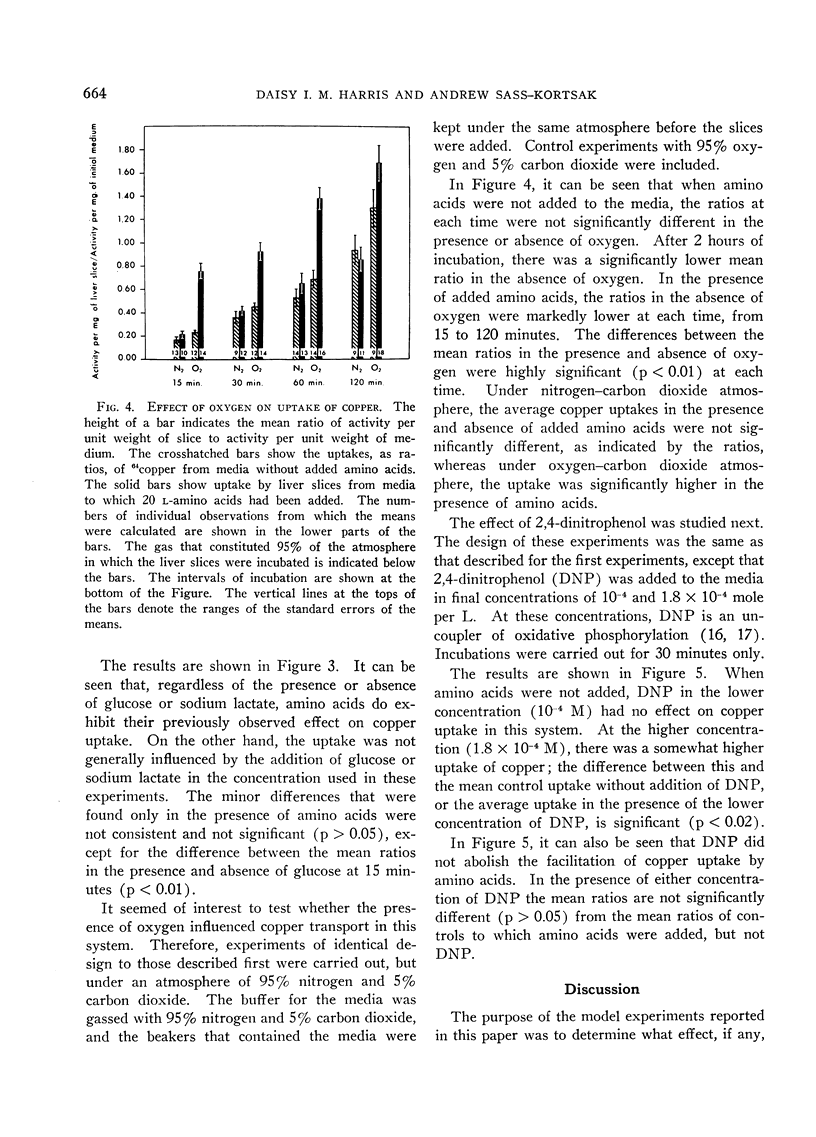
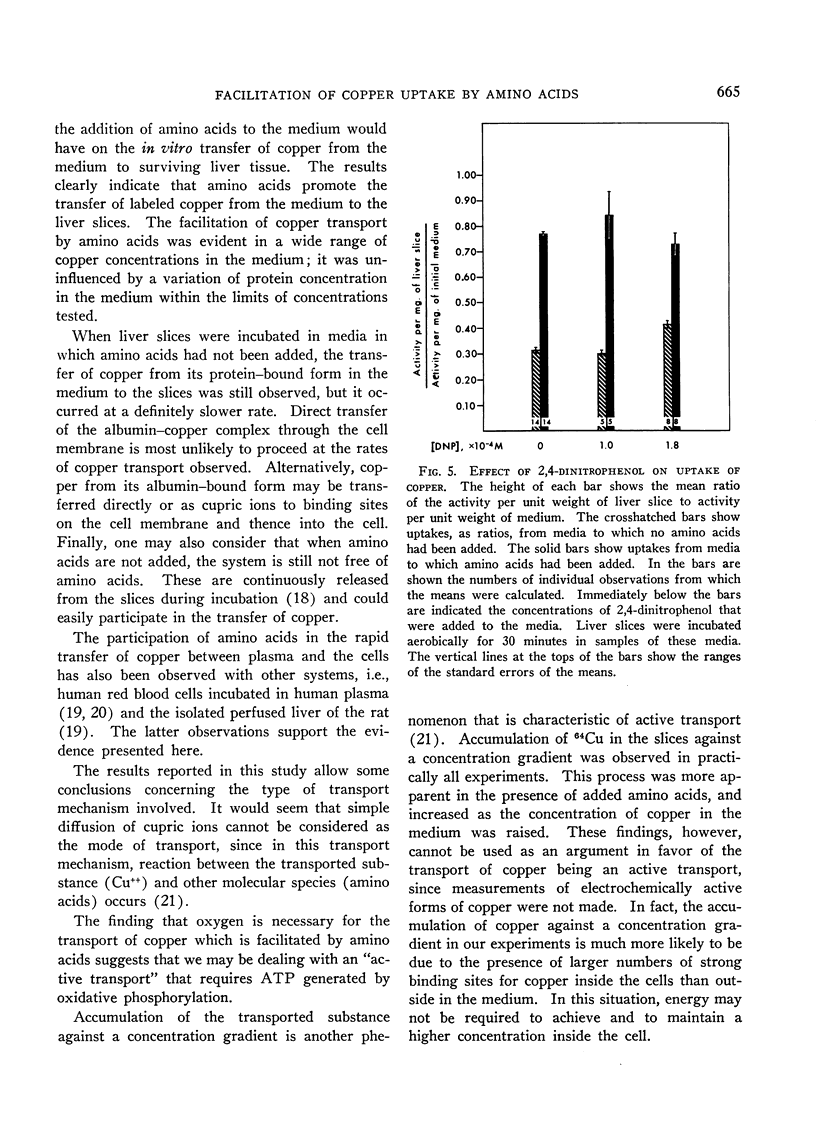
Addition of physiological concentrations of 20 l-amino acids to the incubation medium facilitates the uptake of copper by liver slices. This effect can be observed in a wide range of initial concentrations of copper in the medium, including the low physiological concentrations. The uptake of copper was not influenced by the addition of sodium lactate or d-glucose to the incubation media. The facilitation of copper uptake by amino acids is abolished under anaerobic conditions. It is not affected by the presence of 2,4-dinitrophenol. The type of transport and its exact mechanism have not been established, but this type of transport does not fulfill the criteria for classification as simple diffusion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUSH J. A., MAHONEY J. P., MARKOWITZ H., GUBLER C. J., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies on copper metabolism. XIV. Radioactive copper studies in normal subjects and in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration. J Clin Invest. 1955 Dec;34(12):1766–1778. doi: 10.1172/JCI103232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden A., Green H. H. Micro-determination of copper in biological material. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1202–1208. doi: 10.1042/bj0341202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUBLER C. J., LAHEY M. E., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies on copper metabolism. IX. The transportation of copper in blood. J Clin Invest. 1953 May;32(5):405–414. doi: 10.1172/JCI102752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. M., Salter J. M. Report of a component(s) in blood that accelerates urea synthesis by surviving liver slices from rats when L-amino acids are the sources of urea nitrogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann P. Z., Sass-Kortsak A. The state of copper in human serum: evidence for an amino acid-bound fraction. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):646–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI105566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann P. Z., Silverberg M. Active copper transport in mammalian tissues--a possible role in Wilson's disease. Nature. 1966 Apr 23;210(5034):414–416. doi: 10.1038/210414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN S. B., ROBERTS C. N., WALSHE J. M. Uptake of radiocopper by the liver. A study of patients with Wilson's disease and various control groups. Clin Sci. 1963 Feb;24:13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass-Kortsak A., Harris D. I. Copper transport in mammalian tissues. Nature. 1966 Aug 20;211(5051):852–853. doi: 10.1038/211852b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTROBE M. M., CARTWRIGHT G. E., GUBLER C. J. Studies on the function and metabolism of copper. J Nutr. 1953 Aug;50(4):395–419. doi: 10.1093/jn/50.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


