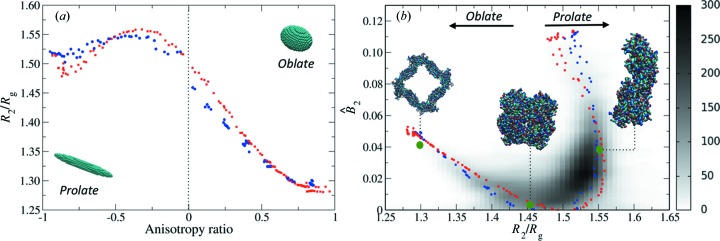
Figure 3.
(a) Example shape descriptors for l = 2. The ratio R
2/R
g is plotted against the anisotropic ratio for ellipsoids (black dots) or cylinders (red squares), allowing the identification of prolate or oblate features. (b) Including the use of 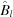 as a shape classifier, normalized against
as a shape classifier, normalized against 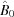 , provides further discriminative power between shapes. Small values of
, provides further discriminative power between shapes. Small values of 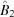 represent approximately spherical particles, while large values represent either prolate or oblate particles. The density in part (b) represents the empirical distribution of
represent approximately spherical particles, while large values represent either prolate or oblate particles. The density in part (b) represents the empirical distribution of 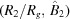 pairs, as obtained from known PDB structures (see Appendix A for details).
pairs, as obtained from known PDB structures (see Appendix A for details).