Abstract
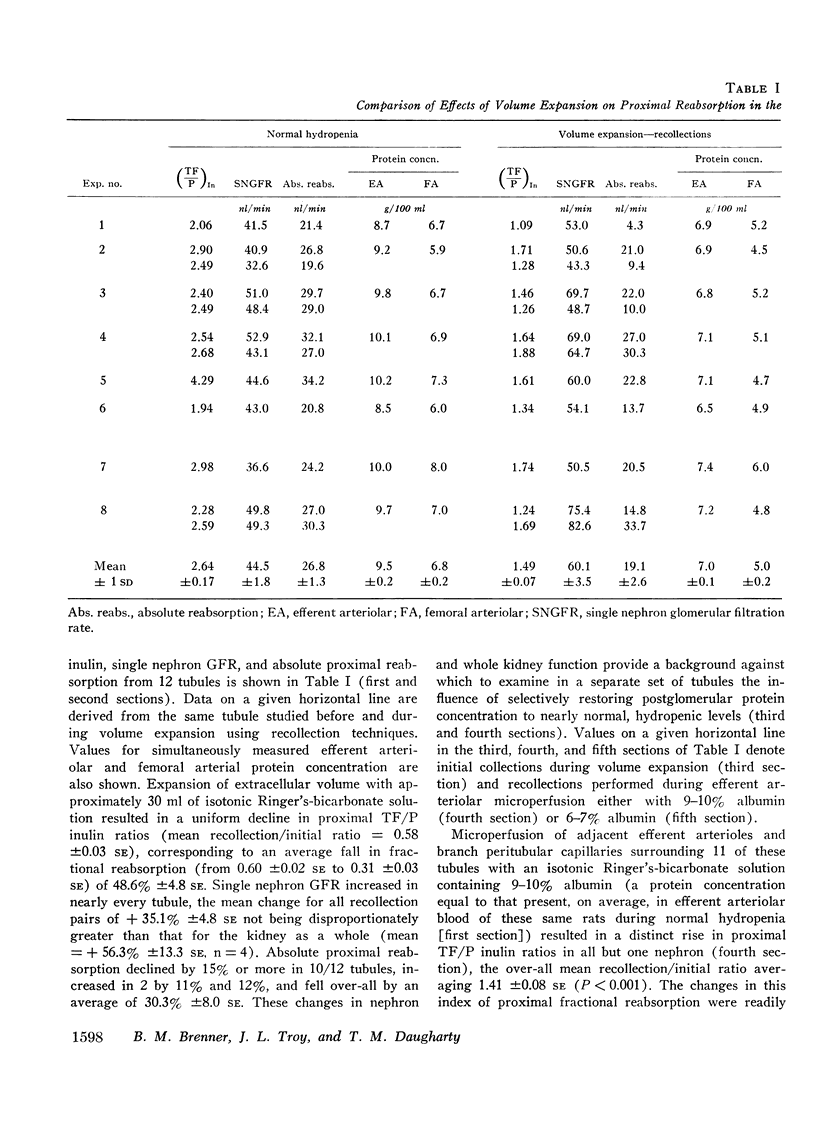
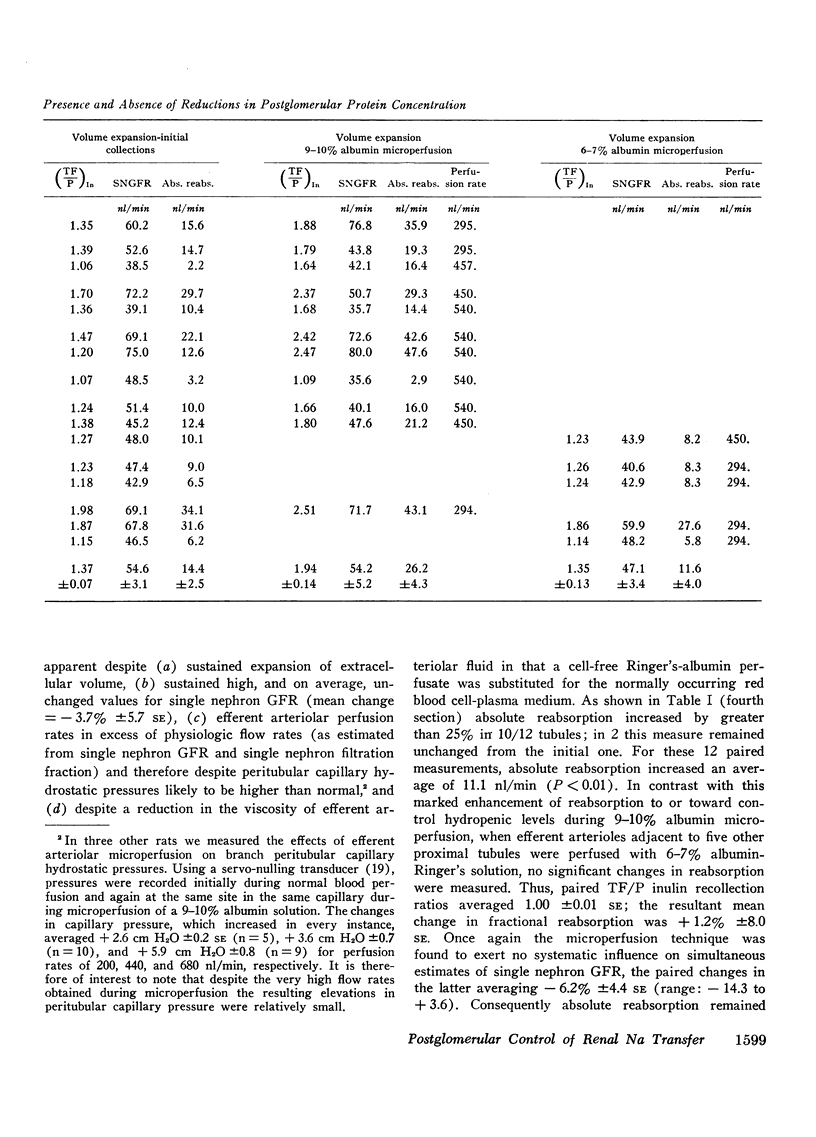
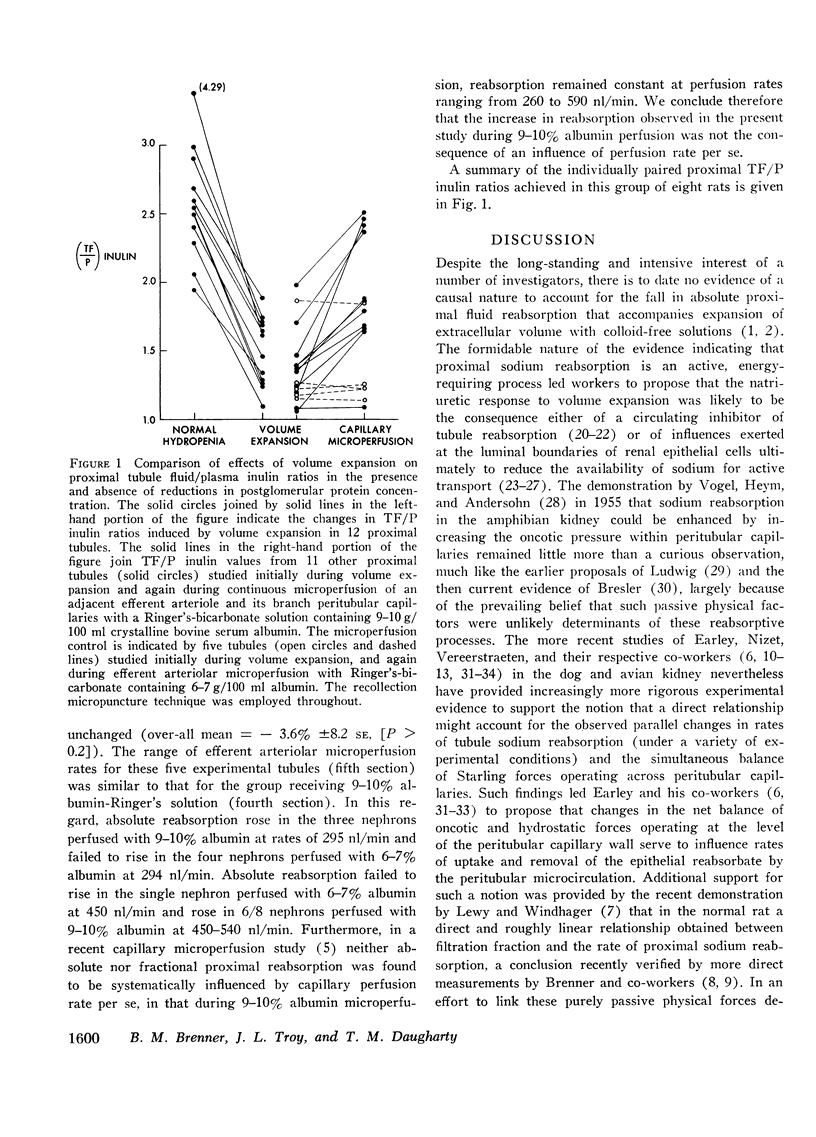
We undertook to determine the extent to which the inhibition in absolute proximal fluid reabsorption in response to expansion of extracellular volume with noncolloid-containing solutions is the result of concomitant reductions in postglomerular (efferent arteriolar) protein concentration. Selective elevation of efferent arteriolar oncotic pressure in volume-expanded rats (Ringer's 10% body weight) to levels slightly in excess of normal by microperfusion with 9-10% albumin-Ringer's solution nearly completely reversed the inhibition in absolute and fractional reabsorption in adjacent proximal tubules. In contrast, during similar microperfusion with a 6-7% albumin solution, no increase in proximal reabsorption was measured. We interpret these findings to indicate that the bulk of the inhibition in absolute proximal reabsorption in response to volume expansion with colloid-free solutions is causally mediated by the accompanying parallel decline in postglomerular vascular protein concentration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRESLER E. H. The problem of the volume component of body fluid homeostasis. Am J Med Sci. 1956 Jul;232(1):93–104. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195607000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Bennett C. M., Berliner R. W. The relationship between glomerular filtration rate and sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1358–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI105828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Daugharty T. M., Ueki I. F., Troy J. L. Quantitative assessment of proximal tubule function in single nephrons of the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):2058–2067. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.2058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Falchuk K. H., Keimowitz R. I., Berliner R. W. The relationship between peritubular capillary protein concentration and fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1519–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI106118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Galla J. H. Influence of postglomerular hematocrit and protein concentration on rat nephron fluid transfer. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):148–161. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L. Postglomerular vascular protein concentration: evidence for a causal role in governing fluid reabsorption and glomerulotublar balance by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):336–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI106501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner F. P., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance. II. Regulation of proximal tubular reabsorption by tubular volume, as studied by stopped-flow microperfusion. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):603–611. doi: 10.1172/JCI105374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., MACINTOSH J. R. A model system for biological water transport. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:347–348. doi: 10.1038/193347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WARDENER H. E., MILLS I. H., CLAPHAM W. F., HAYTER C. J. Studies on the efferent mechanism of the sodium diuresis which follows the administration of intravenous saline in the dog. Clin Sci. 1961 Oct;21:249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty T. M., Belleau L. J., Martino J. A., Earley L. E. Interrelationship of physical factors affecting sodium reabsorption in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Dec;215(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.6.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Bossert W. H. Standing-gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2061–2083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Daugharty T. M. Sodium metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 10;281(2):72–86. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907102810205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Friedler R. M. The effects of combined renal vasodilatation and pressor agents on renal hemodynamics and the tubular reabsorption of sodium. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):542–551. doi: 10.1172/JCI105368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Martino J. A., Friedler R. M. Factors affecting sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule as determined during blockade of distal sodium reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1668–1684. doi: 10.1172/JCI105474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. H., Brenner B. M., Tadokoro M., Berliner R. W. Oncotic and hydrostatic pressures in peritubular capillaries and fluid reabsorption by proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1427–1433. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertz K. H., Mangos J. A., Braun G., Pagel H. D. On the glomerular tubular balance in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Sep 15;285(4):360–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00363236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. I., Davis J. O., Howards S. S., Wright F. S. Cross-circulation experiments on the mechanism of the natriuresis during saline loading in the dog. Circ Res. 1967 Jan;20(1):1–10. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELMAN R. B. A theoretical note on exponential flow in the proximal part of the mammalian nephron. Bull Math Biophys. 1962 Sep;24:303–317. doi: 10.1007/BF02477961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinsky N. G. Nonaldosterone influences on renal sodium transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewy J. E., Windhager E. E. Peritubular control of proximal tubular fluid reabsorption in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):943–954. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino J. A., Earley L. E. Demonstraton of a role of physical factors as determinants of the natriuretic response to volume expansion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1963–1978. doi: 10.1172/JCI105686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizet A. Influence of serumalbumin and dextran on sodium and water excretion by the isolated dog kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;301(1):7–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00412414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr, Brunner F. P., Seldin D. W. Mechanism of glomerulotubular balance. I. Effect of aortic constriction and elevated ureteropelvic pressure on glomerular filtration rate, fractional reabsorption, transit time, and tubular size in the proximal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):590–602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer A., Windhager E. E. Effect of peritubular oncotic pressure changes on proximal tubular fluid reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1188–1193. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL G., HEYM E., ANDERSSOHN K. Versuche zur Bedeutung kolloidosmotischer Druckdifferenzen für einen passiven Transportmechanismus in der Nierenkanälchen. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1955;126(5):485–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereerstraeten P., Toussaint C. Role of the peritubular oncotic pressure on sodium excretion by the avian kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):13–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00586779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereerstraeten P., Toussaint C. Réduction de la natriurèse par la perfusion d'albumine dans la veine porte rénale du coq. Nephron. 1965;2(6):355–366. doi: 10.1159/000179417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereerstraeten P., de Myttenaere M. Effect of raising the transtubular oncotic gradient on sodium excretion in the dog. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00586778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereerstraeten P., de Myttenaere M., Lambert P. P. Réduction de la natriurèse par la perfusion de protéines dans l'artère rénale du chien. Nephron. 1966;3(2):103–122. doi: 10.1159/000179451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wardener H. E. Control of sodium reabsorption. Br Med J. 1969 Sep 20;3(5672):676–683. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5672.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



