Abstract
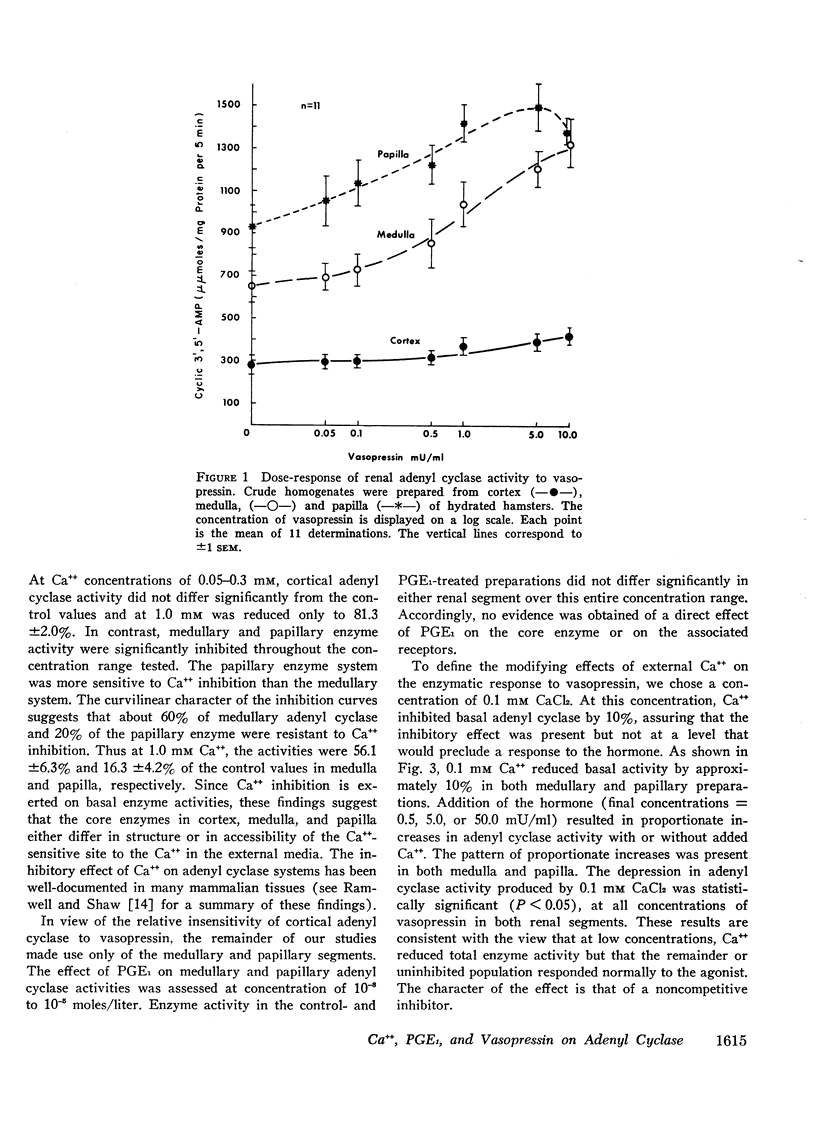
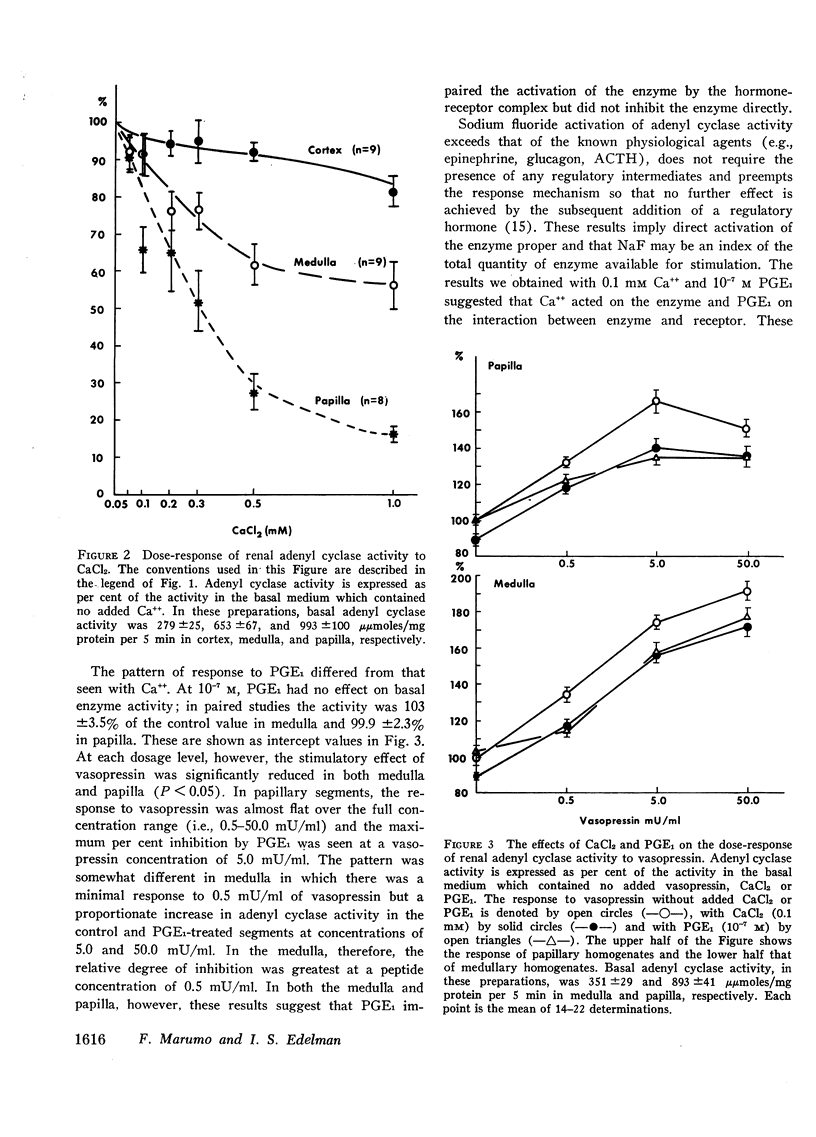
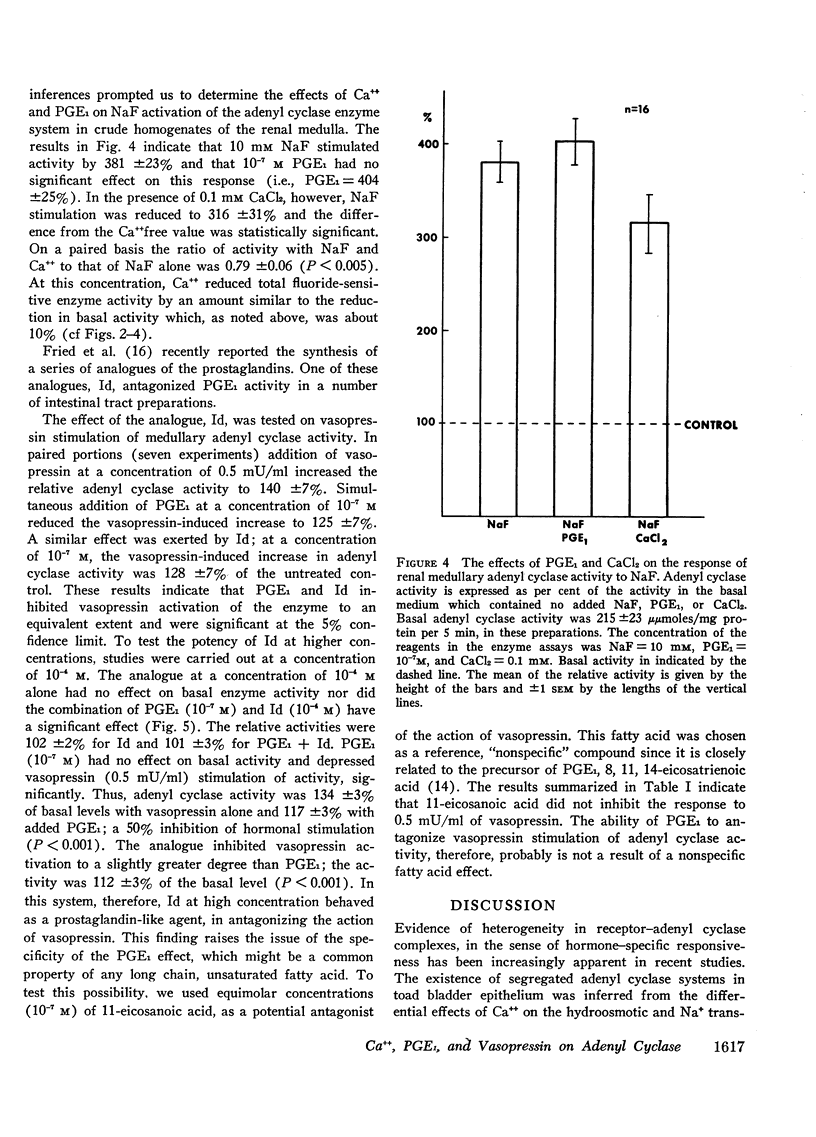
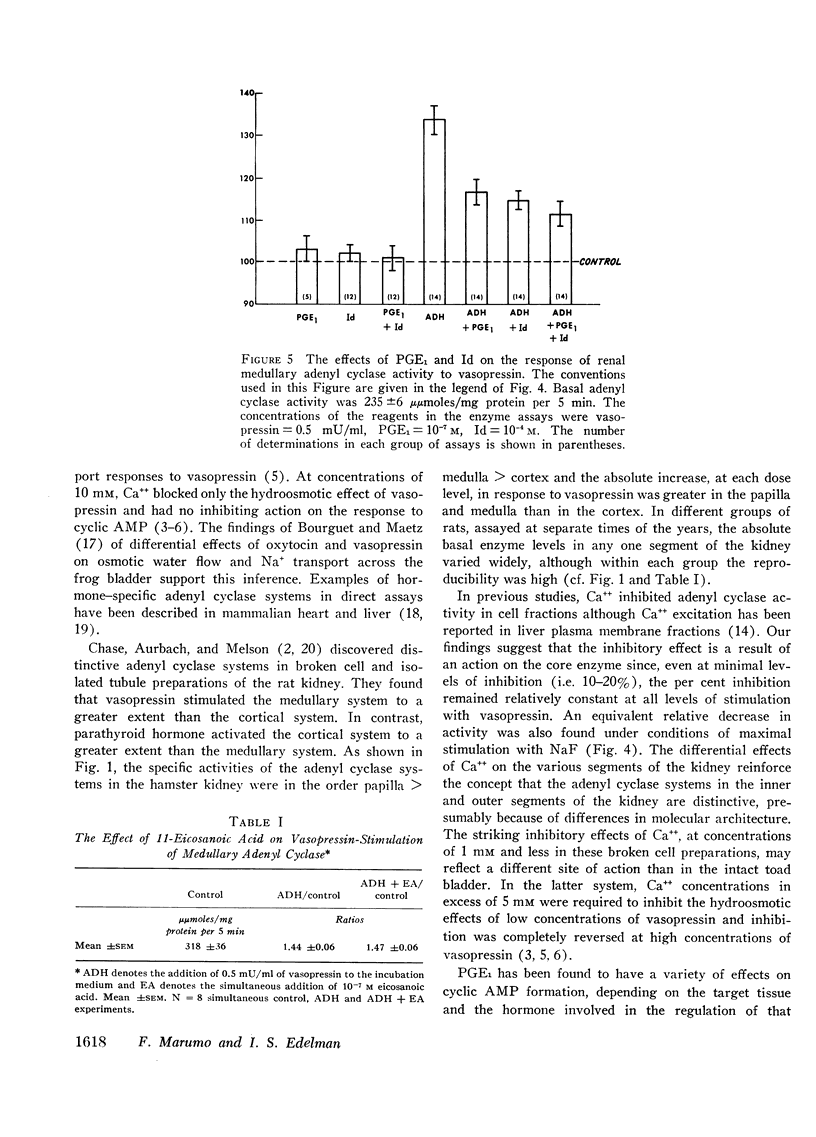
Adenyl cyclase activity was assayed in crude homogenates of the renal cortex, medulla, and papilla of the golden hamster. The specific activity (moles C-AMP/unit of time per mg protein of tissue) of the enzyme under basal conditions, was greatest in papilla, somewhat lower in medulla, and least in cortex. On an absolute scale, the sensitivity to vasopressin was greater in the medullary and papillary than in the cortical homogenates. In addition, at concentrations of 0.1-1.0 mm, CaCl2 inhibited the enzyme in the order papilla > medulla > cortex. These results imply the existence of distinct differences in the composition of the adenyl cyclase-receptor complex in various parts of the kidney. We proposed that Ca++ inhibits the core enzyme directly since at the minimally inhibitory concentration (0.1 mm), CaCl2 reduced to an equivalent extent (a) basal activity, (b) the response to graded doses of vasopressin (0.5 to 50.0 mU/ml) and (c) the response to maximal stimulatory concentrations of NaF (10 mm). Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1 = 10−7m) had no effect on either basal adenyl-cyclase activity or the response to 10 mm NaF in medullary and papillary homogenates. 7-Oxa-13-prostynoic acid (10−4m) similarly had no effect under basal conditions or on stimulation with NaF in medullary homogenates. Both fatty acids, however, inhibited the enzymic response to vasopressin, particularly at low concentrations of the peptide. The straight-chain fatty acid, 11-eicosanoic acid (10−7m), was inactive on basal activity or on the response to vasopressin. The possibility that PGE1 modifies the coupling mechanism between the core enzyme and the hormone-specific receptor is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argy W. P., Jr, Handler J. S., Orloff J. Ca++ and Mg++ effects on toad bladder response to cyclic AMP, theophylline, and ADH analogues. Am J Physiol. 1967 Sep;213(3):803–808. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.3.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURGUET J., MAETZ J. [Arguments in favor of the independence of the mechanisms of action of various neurohypophyseal hormones on the osmotic flux of water and on the active transport of sodium in the same receptor; studies on the bladder and the skin of Rana esculenta L]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 30;52:552–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär H. P., Hechter O., Schwartz I. L., Walter R. Neurohypophyseal hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase of toad urinary bladder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):7–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggena P., Schwartz I. L., Walter R. Threshold and receptor reserve in the action of neurohypophyseal peptides. A study of synergists and antagonists of the hydroosmotic response of the toad urinary bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):250–271. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried J., Santhanakrishnan T. S., Himizu J., Lin C. H., Ford S. H., Rubin B., Grigas E. O. Prostaglandin antagonists: synthesis and smooth muscle activity. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):208–210. doi: 10.1038/223208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Orloff J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on the permeability response of the isolated collecting tubule to vasopressin, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl F. A., Jr, Humes J. L., Tarnoff J., Cirillo V. J., Ham E. A. Prostaglandin receptor site: evidence for an essential role in the action of luteinizing hormone. Science. 1970 Aug 28;169(3948):883–886. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3948.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S., Epstein S. E. Myocardial adenyl cyclase: activation by thyroid hormones and evidence for two adenyl cyclase systems. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1663–1669. doi: 10.1172/JCI106131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melson G. L., Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase in isolated renal tubules. Endocrinology. 1970 Mar;86(3):511–518. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-3-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S., BERGSTROM S. EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN (PGE-1) ON THE PERMEABILITY RESPONSE OF TOAD BLADDER TO VASOPRESSIN, THEOPHYLLINE AND ADENOSINE 3',5'-MONOPHOSPHATE. Nature. 1965 Jan 23;205:397–398. doi: 10.1038/205397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S. THE CELLULAR MODE OF ACTION OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:686–697. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN M. J., EDELMAN I. S. CALCIUM INHIBITION OF THE ACTION OF VASOPRESSIN ON THE URINARY BLADDER OF THE TOAD. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:583–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI104943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Biological significance of the prostaglandins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:139–187. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L., Petzold G. L., Higgins J. A., Greengard P., Barrnett R. J. Hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase: cytochemical localization in rat liver. Science. 1970 Apr 17;168(3929):382–384. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3929.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Jones A. B., Chiappe de Cingolani G. E., Birnbaumer L. The actions of insulin and catabolic hormones on the plasma membrane of the fat cells. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:215–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTEMBURY G., SUGINO N., SOLOMON A. K. Effect of antidiuretic hormone and calcium on the equivalent pore radius of kidney slices from Necturus. Nature. 1960 Aug 20;187:699–701. doi: 10.1038/187699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



