Abstract
The metabolism of human fibrinogen labeled with radioactive iodine was studied in 50 patients with documented cirrhosis of the liver and in 35 healthy control subjects. Results in cirrhotic subjects were the following: plasma volume 47 ± 10 ml/kg; plasma fibrinogen concentration 250 ± 102 mg/100 ml; total plasma fibrinogen pool 118 ± 59 mg/kg, representing 0.73 ± 0.10 of the total body pool; fibrinogen half-life 2.99 ± 0.59 days; fractional catabolic rate 0.34 ± 0.09 of the plasma pool per day; absolute catabolic rate 39 ± 20 mg/kg per day; fractional transcapillary efflux rate 0.82 ± 0.30 of the plasma pool per day. Results in the control subjects were the following: plasma volume 42 ± 7 ml/kg; plasma fibrinogen concentration 284 ± 71 mg/100 ml; total plasma fibrinogen pool 119 ± 40 mg/kg, representing 0.72 ± 0.07 of the total body pool; fibrinogen half-life 4.14 ± 0.56 days; fractional catabolic rate 0.24 ± 0.04 of the plasma pool per day; absolute catabolic rate 28 ± 9 mg/kg per day; fractional transcapillary efflux rate 0.60 ± 0.26 of the plasma pool per day.
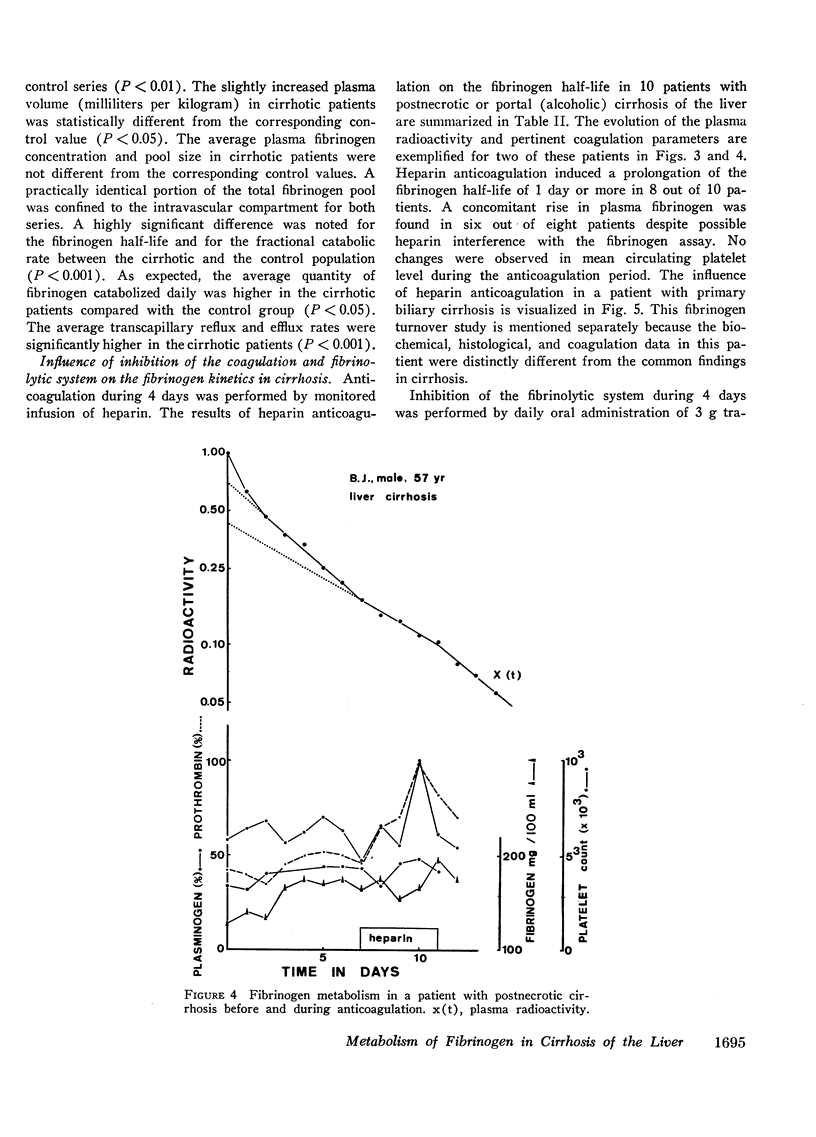
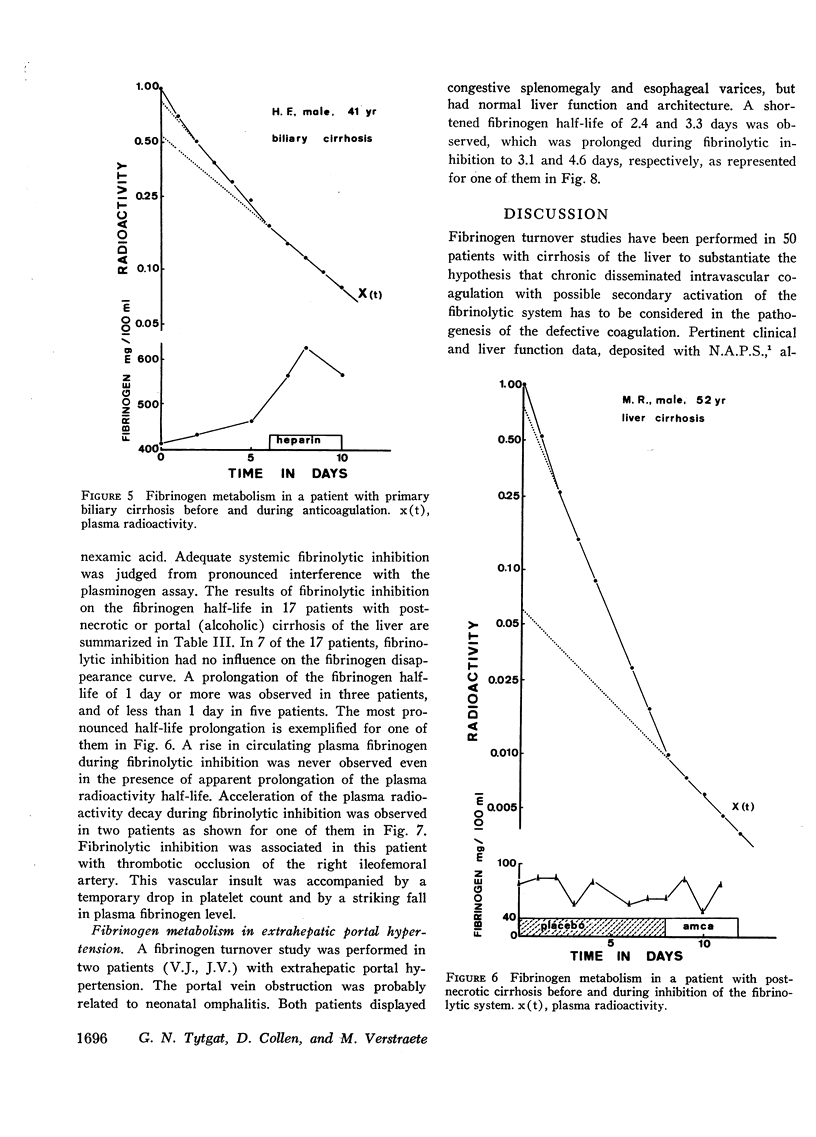
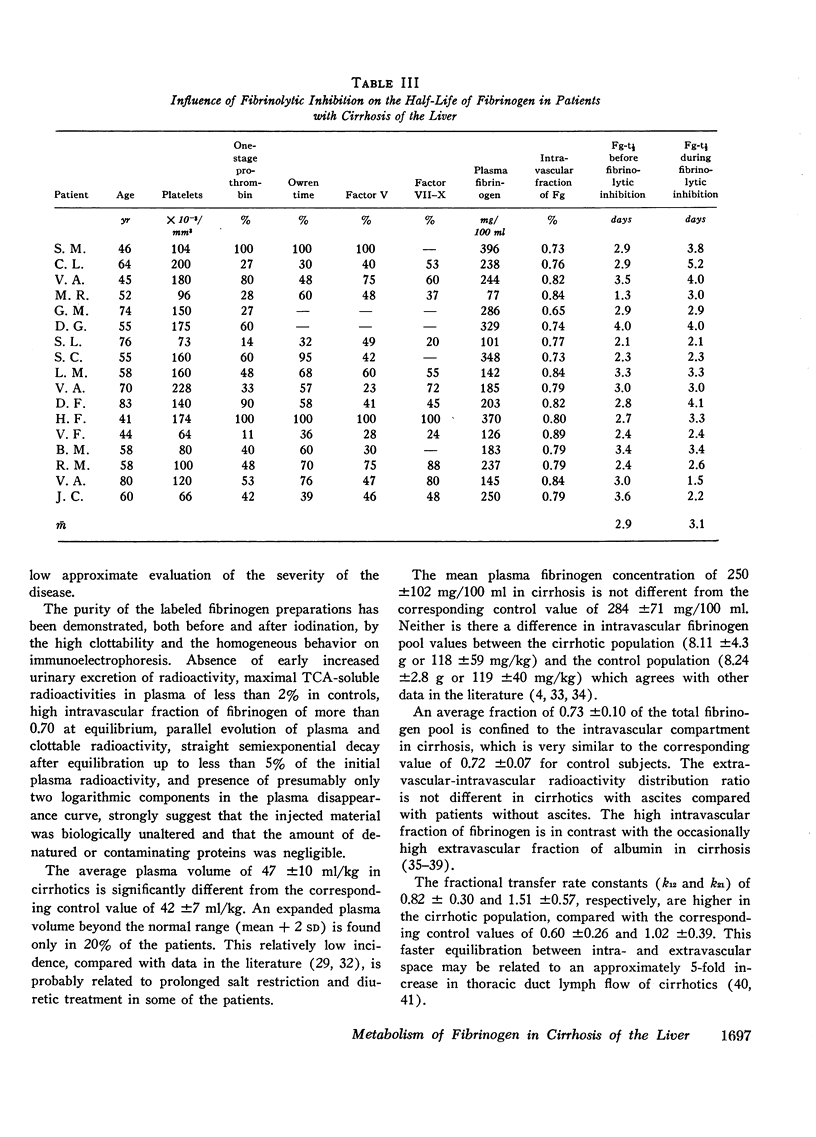
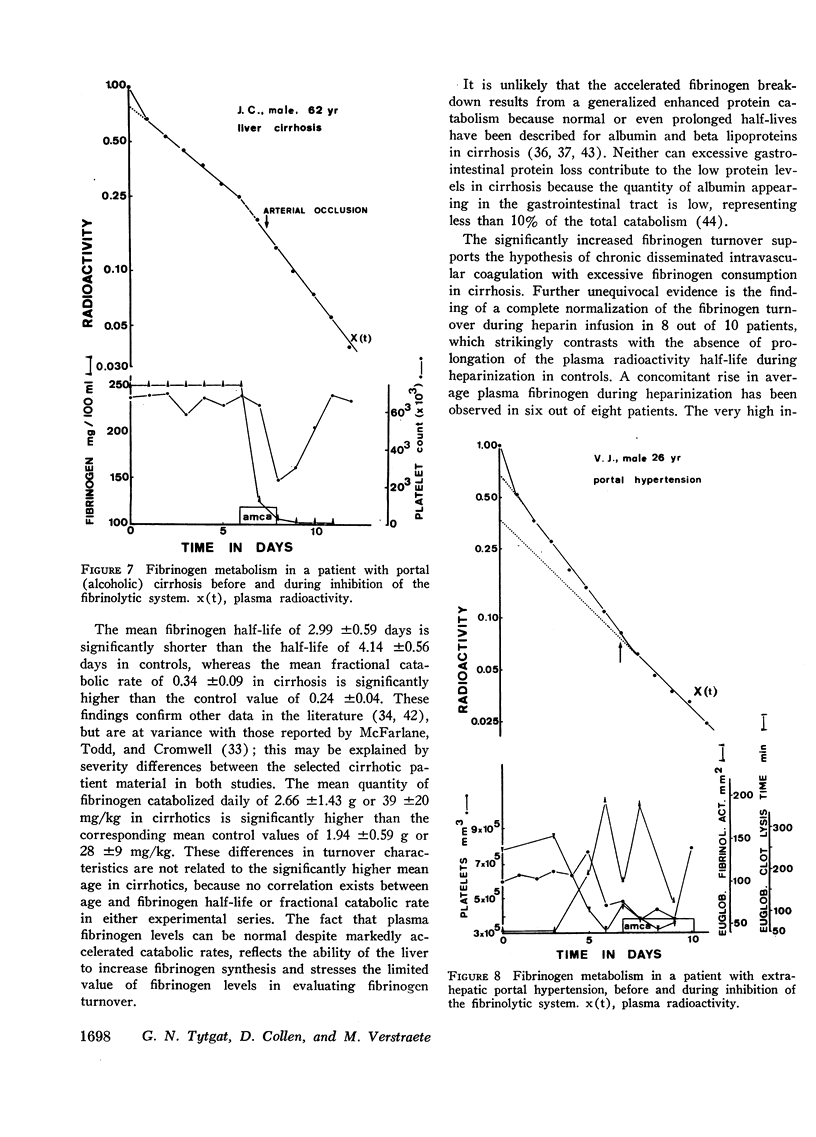
A significant difference between cirrhotics and controls was observed for plasma volume, fibrinogen half-life, fractional and total catabolic rates, and transcapillary efflux rate. During heparinization of 10 cirrhotic patients the fibrinogen half-life was prolonged from 3.15 ± 0.69 to 4.59 ± 0.79 days. This was associated with a rise in plasma fibrinogen in six out of eight patients. Heparinization did not influence the fibrinogen half-life in five control subjects. Inhibition of the fibrinolytic system in 17 patients resulted in prolongation of the plasma radioactivity half-life of more than 1 day in only three patients, an incidence comparable with that in five control subjects.
These results strongly support the concept of accelerated fibrinogen consumption by a process of disseminated intravascular coagulation in cirrhosis of the liver.
Full text
PDF
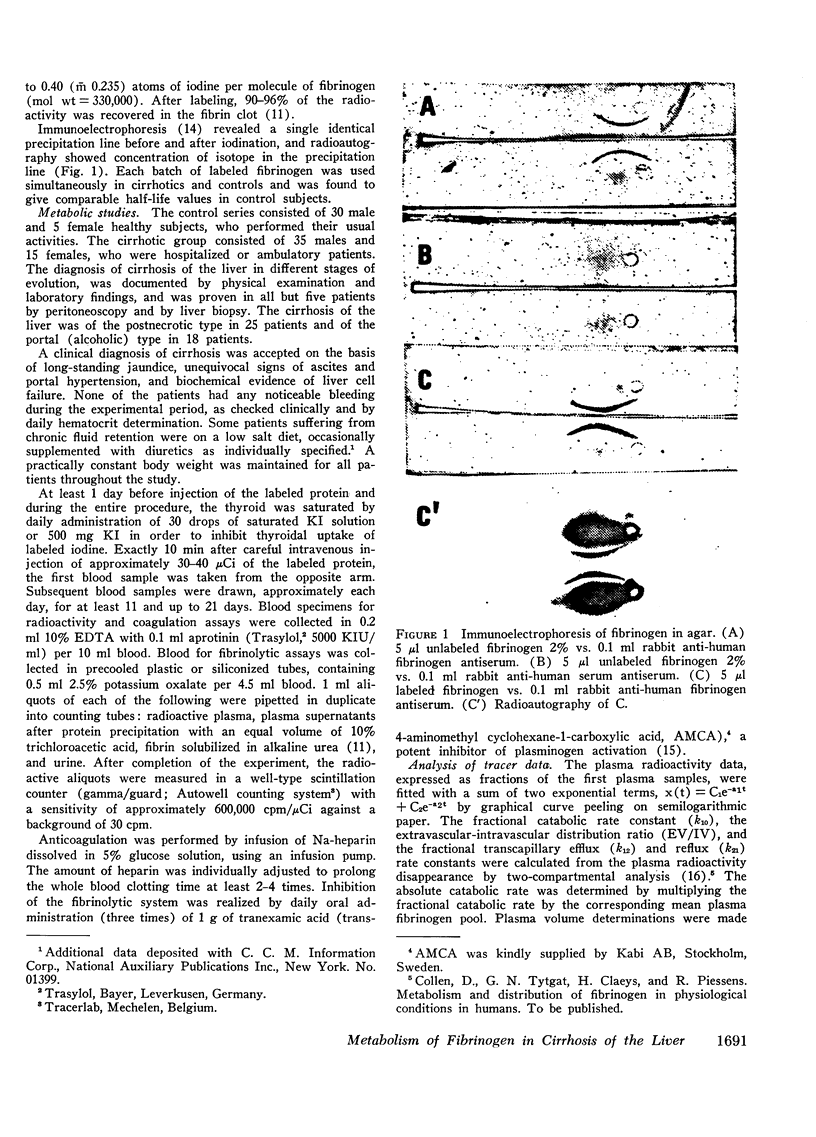
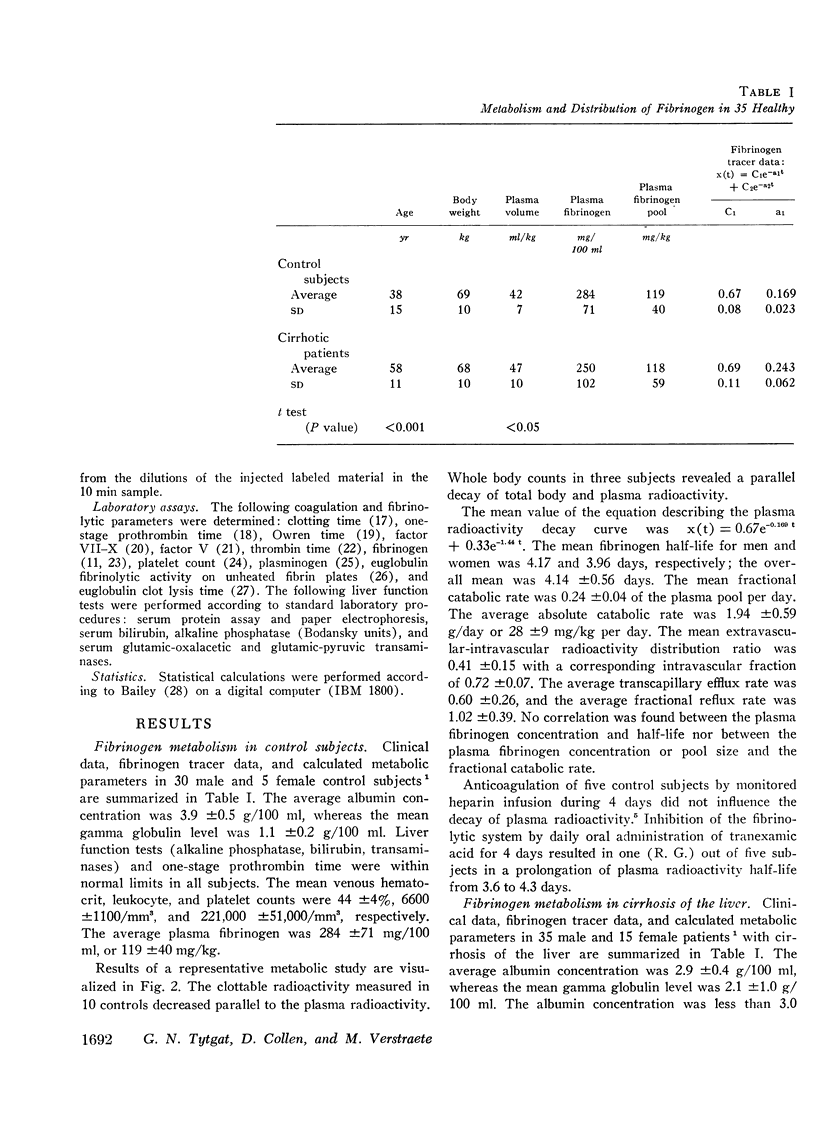
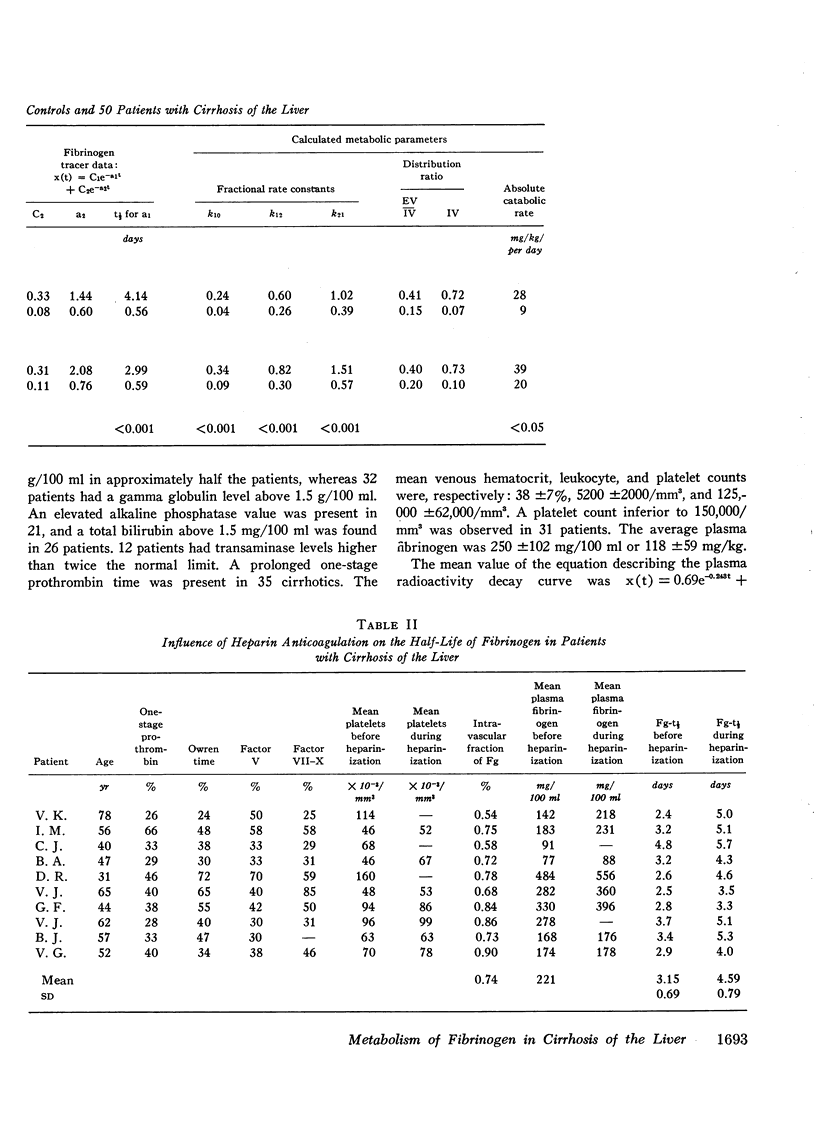
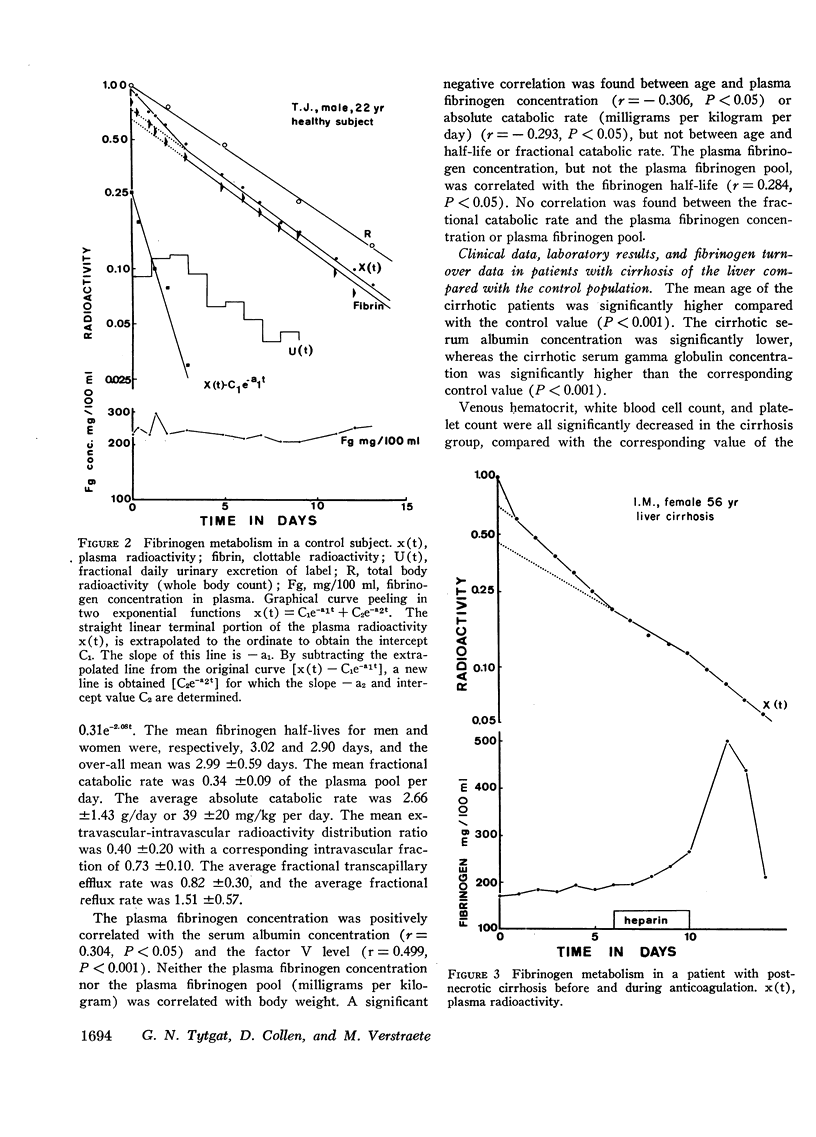



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN J. G., GLOTZER D. J. ACUTE DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION AND FIBRINOLYSIS. Arch Surg. 1964 Apr;88:694–698. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1964.01310220184028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMRIS A., AMRIS C. J. TURNOVER AND DISTRIBUTION OF 131-IODINE-LABELLED HUMAN FIBRINOGEN. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:404–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L., Nilsoon I. M., Colleen S., Granstrand B., Melander B. Role of urokinase and tissue activator in sustaining bleeding and the management thereof with EACA and AMCA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 28;146(2):642–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aster R. H. Pooling of platelets in the spleen: role in the pathogenesis of "hypersplenic" thrombocytopenia. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):645–657. doi: 10.1172/JCI105380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIX S. Studies on the fibrinolytic system in the euglobulin fraction of human plasma. A. Methodological study. B. Application of the methods. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1961;13 (Suppl 58):3–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOMBACK B., BLOMBACK M., STRUWE I. Studies on factor VIII. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962;7(Suppl):172–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECHER G., CRONKITE E. P. Morphology and enumeration of human blood platelets. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Dec;3(6):365–377. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.6.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Carlson L. A., Franzén S., Zetterqvist E. Turnover of 131-I-labelled fibrinogen in man. Studies in normal subjects, in congenital coagulation factor deficiency states, in liver cirrhosis, in polycythemia vera and in epidermolysis bullosa. Acta Med Scand. 1966 May;179(5):557–574. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb07973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Rubenberg M. L., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: mechanisms of red-cell fragmentation: in vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):643–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CACHERA R., DARNIS F., LEPERCQ G., DELORME M. L. Volume plasmatique, proteines totales circulantes et syndrome oedemateux des cirrhoses alcooliques. Presse Med. 1951 Dec 12;59(79):1660–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORTET P., KLEPPING C., DEVANT J., LEBEL J. P., JACQUOT B. LE FACTEUR PLAQUETTAIRE AU COURS DES CIRRHOSES ALCOOLIQUES. ETUDE DE L'ADH'ESIVIT'E IN VIVO PAR LE TEST DE BORCHGREVINK. Arch Mal Appar Dig Mal Nutr. 1964 Sep;53:1041–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D. The role of the liver in serum-induced hypercoagulability. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):256–263. doi: 10.1172/JCI105338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes P. W. The rates of distribution and catabolism of albumin in normal subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci. 1968 Feb;34(1):161–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., BIEDERMAN O., MOORE D., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. ABNORMAL PLASMINOGEN-PLASMIN SYSTEM ACTIVITY (FIBRINOLYSIS) IN PATIENTS WITH HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS: ITS CAUSE AND CONSEQUENCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:681–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI104953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. Cryptogenetic congestive severe coagulopathy in splenomegaly. JAMA. 1968 Jul 8;205(2):111–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILDER H., REDO S. F., BARR D., CHILD C. G., 3rd Water distribution in normal subjects and in patients with Laënnec's cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):555–564. doi: 10.1172/JCI102926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLLUB S., ULIN A. W. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Mar;59:430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gans H., Lowman J. T. The uptake of fibrin and fibrin-degradation products by the isolated perfused rat liver. Blood. 1967 Apr;29(4):526–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gans H., Stern R., Tan B. H. On the in vivo clearance of thrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Aug 31;22(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebell H., Bickel H., Bode C., Egbring R., Martini G. A. Veränderte Aktivitäten der Enzyme des Energiestoffwechsels in Thrombocyten von Patienten mit Lebercirrhose und Splenomegalie. Klin Wochenschr. 1968 May 15;46(10):526–533. doi: 10.1007/BF01747771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahn E. P., Dietz A. A., Stefani S. S., Donnelly W. J. Burr cells, hemolytic anemia and cirrhosis. Am J Med. 1968 Jul;45(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasch E., Jarnum S., Tygstrup N. Albumin synthesis rate as a measure of liver function in patient with cirrhosis. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Jul;182(1):83–92. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb11502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörder M. H. Consumption coagulopathy in liver cirrhosis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1969;36:313–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izak G., Galewsky K. Studies on experimentally induced hypercoagulable state in rabbits. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jul 31;16(1):228–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHANSSON S. A. STUDIES ON BLOOD COAGULATION FACTORS IN A CASE OF LIVER CIRRHOSIS. REMISSION OF THE HEMORRHAGIC TENDENCY ON TREATMENT WITH HEPARIN. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Feb;175:177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMBER C., DELLER D. J., IBBOTSON R. N., LANDER H. THE MECHANISM OF ANAEMIA IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE. Q J Med. 1965 Jan;34:33–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr R. M., Du Bois J. J., Holt P. R. Use of 125-I- and 51-Cr-labeled albumin for the measurement of gastrointestinal and total albumin catabolism. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2064–2082. doi: 10.1172/JCI105694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL E. E., LAZERSON J. Thrombasthenia in liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1961 Jul 13;265:56–61. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196107132650202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S., TODD D., CROMWELL S. FIBRINOGEN CATABOLISM IN HUMANS. Clin Sci. 1964 Jun;26:415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY J. F., DAWSON A. M., SHERLOCK S. Circulatory changes in chronic liver disease. Am J Med. 1958 Mar;24(3):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90322-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margaretten W., Csavossy I., McKay D. G. An electron microscopic study of thrombin-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood. 1967 Feb;29(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Johnson A. J., Kleiner G. J., Wohl H. The defibrination syndrome: clinical features and laboratory diagnosis. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):528–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natelson E. A., Lynch E. C., Alfrey C. P., Jr, Gross J. B. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. An unexpected response to treatment of consumption coagulopathy. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Dec;71(6):1121–1125. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-6-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWREN P. A., AAS K. The control of dicumarol therapy and the quantitative determination of prothrombin and proconvertin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3(3):201–208. doi: 10.3109/00365515109060600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(2):239–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUICK A. J. Influence of erythrocytes on the coagulation of blood. Am J Med Sci. 1960 Jan;239:51–60. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196001000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowsell H. C., Glynn M. F., Mustard J. F., Murphy E. A. Effect of heparin on platelet economy in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):915–922. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenberg M. L., Regoeczi E., Bull B. S., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the experimental production of haemolysis and red-cell fragmentation by defibrination in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jun;14(6):627–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. A., LONERGAN E. T., STERLING K. SPUR-CELL ANEMIA: HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH RED CELLS RESEMBLING ACANTHOCYTES IN ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Aug 20;271:396–398. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196408202710804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H. Studies on the in vivo behavior of blood coagulation product I in rats. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Nov 15;8:276–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K. The turnover rate of serum albumin in man as measured by I131-tagged albumin. J Clin Invest. 1951 Nov;30(11):1228–1237. doi: 10.1172/JCI102542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORMORKEN H. The preparation of proaccelerin deficient (parahemophilia) plasma for the assay of proaccelerin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1957;9(3):273–276. doi: 10.3109/00365515709079970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber R., Amorosi E., Lhowe J., Kayden H. J. Spur-shaped erythrocytes in Laennec's cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Sep 22;275(12):639–643. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196609222751204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. P., Ream V. J., Stuart R. K. Platelet aggregation in patients with Laennec's cirrhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jun 15;276(24):1344–1348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196706152762403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G., Collen D., De Vreker R., Verstraete M. Investigations on the fibrinolytic system in liver cirrhosis. Acta Haematol. 1968;40(5):265–274. doi: 10.1159/000208914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMYLEN C., DE VREKER R. A., VERSTRAETE M. A rapid enzymatic method for assay of fibrinogen fibrin polymerization time (FPT test). Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:418–424. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERMYLEN C., VERSTRAETE M. Antithrombin V: Critical evaluation of its assessment and properties. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:267–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERSTRAETE M., VERMYLEN C., VERMYLEN J., VANDENBROUCKE J. EXCESSIVE CONSUMPTION OF BLOOD COAGULATION COMPONENTS AS CAUSE OF HEMORRHAGIC DIATHESIS. Am J Med. 1965 Jun;38:899–908. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLWILER W., GOLDSWORTHY P. D., MACMARTIN M. P., WOOD P. A., MACKAY I. R., FREMONT-SMITH K. Biosynthetic determination with radioactive sulfur of turn-over rates of various plasma proteins in normal and cirrhotic man. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):1126–1146. doi: 10.1172/JCI103162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON P., MENDENHALL C. L. SERUM ALBUMIN TURNOVER IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS MEASURED BY 131I-LABELLED HUMAN ALBUMIN. Clin Sci. 1963 Oct;25:281–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte M. H., Cole W. R., Burton D. F., Alvarez L., Dumont A. E. Thoracic duct cannulation and differential diagnosis of obstructive jaundice. JAMA. 1968 Apr 29;204(5):366–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZETTERQVIST E., von FRANCKEN Coagluation disturbances with manifest bleeding in extrahepatic portal hypertension and in liver cirrhosis. Preliminary results of heparin treatment. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Jun;173:753–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vreker R. A. A technique for routine evaluation of plasminogen in humans during streptokinase therapy. Acta Haematol. 1965 Nov;34(5):305–320. doi: 10.1159/000209454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



